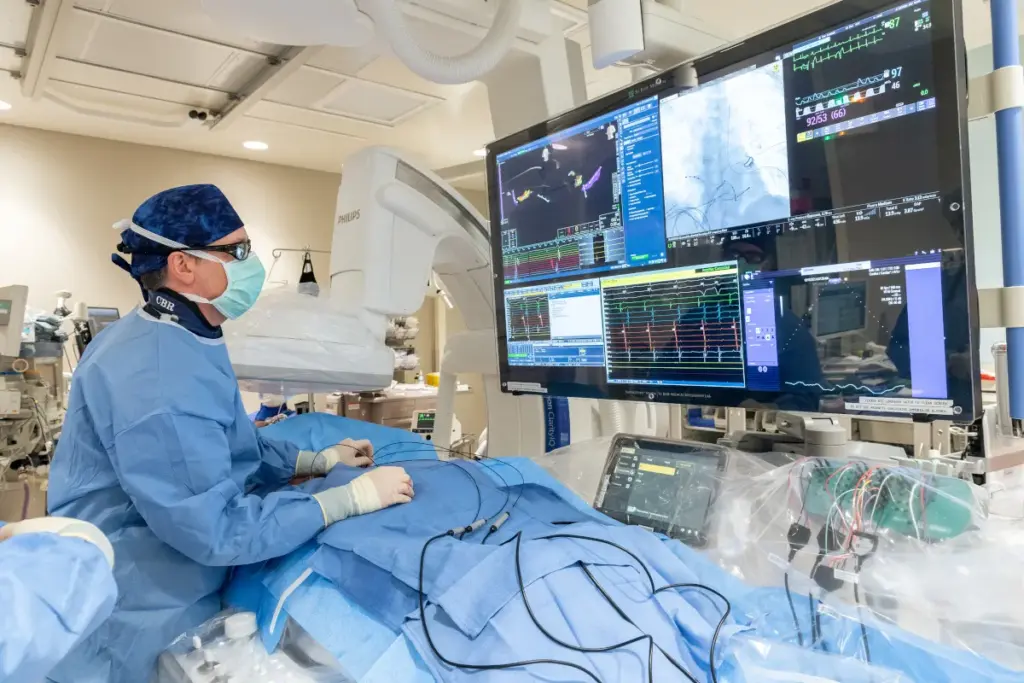
Heart disease is the top killer worldwide. Thanks to new tech, cardiac catheterization is key in finding and fixing heart problems.
This method lets us see inside the heart. We can spot blockages or oddities. This helps us figure out the best treatment for heart disease patients.
Key Takeaways
- Cardiac catheterization is a vital diagnostic tool for heart conditions.
- The procedure involves inserting a catheter into the heart’s chambers and blood vessels.
- It helps us identify blockages or abnormalities in the heart.
- Advanced medical technology has improved the accuracy and safety of the procedure.
- Cardiac catheterization plays a critical role in finding the best treatment for heart disease patients.
What is Cardiac Catheterization?

Cardiac catheterization is a way to look at the heart’s structure and function. It helps diagnose and sometimes treat heart conditions. This method gives us important insights into heart health.
Definition and Purpose
Cardiac catheterization involves inserting a thin, flexible tube into an artery or vein. This tube, called a catheter, is guided to the heart. The main goal is to diagnose heart conditions by seeing the heart’s chambers, valves, and blood vessels.
During the procedure, we can measure heart pressure, take blood samples, or do other interventions. This info is key for diagnosing heart diseases like coronary artery disease. It helps us plan the right treatment.
How It Works
The process starts with local anesthesia to numb the area. A small incision is made, and the catheter is inserted into the blood vessel. Imaging technology, like X-ray, guides the catheter to the heart.
Once in place, we can do tests like angiography to see the coronary arteries. We can also take biopsies of heart tissue. This info helps us understand the heart’s condition and choose the best treatment.
A study in a medical journal showed cardiac catheterization’s effectiveness in diagnosing coronary artery disease. A leading cardiologist said, “Cardiac catheterization is key in diagnosing and treating heart disease. It gives a detailed view of the heart’s anatomy and function.”
“The use of cardiac catheterization has revolutionized cardiology. It allows for precise diagnoses and targeted treatments, improving patient outcomes.”
|
Procedure |
Description |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Cardiac Catheterization |
A procedure where a catheter is guided to the heart to diagnose or treat heart conditions. |
Provides detailed images of the heart’s structure, allows for pressure measurements, and enables interventions. |
|
Angiography |
A diagnostic test performed during cardiac catheterization to visualize the coronary arteries. |
Helps identify blockages or abnormalities in the coronary arteries. |
|
Cardiac Biopsy |
A procedure where a sample of heart tissue is taken for examination. |
Assists in diagnosing heart muscle diseases or other conditions affecting the heart. |
Cardiac catheterization is a powerful tool for diagnosing heart health. But, it’s not the only way to monitor the heart. Other tests, like heart monitors or Holter monitors, can also provide valuable insights over time.
Indications for Cardiac Catheterization

Deciding to have cardiac catheterization depends on heart health factors. It’s a key tool for checking the heart’s condition. We use it to find and check different heart diseases.
Diagnosing Heart Conditions
Cardiac catheterization is great for finding coronary artery disease (CAD). It shows if the arteries are blocked or narrowed. We can see the arteries and find any problems.
Before the test, some patients wear a portable Holter heart monitor. This lets us watch the heart’s rhythm over time. It helps find patterns that a regular ECG might miss.
Evaluating Heart Function
Cardiac catheterization also checks how well the heart pumps and the valves work. It tells us about heart pressure and oxygen levels. This helps diagnose other heart issues.
Knowing how to use heart monitors, like how to put a heart monitor on a patient, is important. It helps before and after the test.
The table below shows why we use cardiac catheterization:
|
Indication |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) |
Diagnosis of CAD through visualization of coronary arteries |
|
Heart Valve Disease |
Assessment of heart valve condition and function |
|
Heart Failure |
Evaluation of heart pumping function and pressure |
|
Congenital Heart Defects |
Diagnosis and assessment of congenital heart abnormalities |
Understanding when to use cardiac catheterization helps doctors choose the right tests and treatments for patients.
Types of Cardiac Catheterization Procedures
Cardiac catheterization comes in many forms, each serving different needs. It’s not a single procedure but a variety of techniques. These are tailored to meet the unique needs of each patient.
Coronary Angiography
Coronary angiography is a common cardiac catheterization type. It uses dye to see blockages in the coronary arteries on an X-ray. This helps diagnose coronary artery disease and plan treatments like angioplasty or stenting.
Some key aspects of coronary angiography include:
- Minimally invasive, reducing recovery time
- Provides detailed images of the coronary arteries
- Helps in assessing the need for interventions like angioplasty
Cardiac Biopsy
A cardiac biopsy takes a small heart tissue sample for examination. It’s used to diagnose conditions like myocarditis or cardiomyopathy. The procedure involves inserting a bioptome through a vein in the neck or groin.
Key aspects of cardiac biopsy include:
- Diagnosing heart muscle diseases
- Monitoring heart transplant rejection
- Guiding treatment decisions based on tissue analysis
When discussing cardiac catheterization, it’s key to know about related tools. For example, learning how to put on a heart monitor is important. Also, knowing what to avoid while wearing a Holter monitor improves both accuracy and comfort.
The Cardiac Catheterization Process
Understanding the cardiac catheterization process is essential. It includes the steps before and during the procedure. Knowing this can help reduce anxiety and prepare patients better.
Pre-Procedure Preparations
Before starting, several steps are needed.
- Patients usually need to fast beforehand.
- They must tell their doctor about any medicines they take.
- Tests like blood work and a Holter monitor test might be done.
Steps Involved in the Procedure
- Preparation in the Cath Lab:Patients lie down on a table in the cath lab.
- The area for the catheter is cleaned and numbed.
- Insertion of the Catheter:A small cut is made to put in the catheter.
- The catheter is then guided to the heart using images.
- Diagnostic or Interventional Procedure:Contrast dye is injected to see the heart’s structures.
- An interventional procedure like angioplasty might be done based on findings.
|
Procedure Step |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Pre-procedure Checks |
Includes blood tests, possibly wearing a Holter monitor for 24-48 hours |
|
Preparation in Cath Lab |
Positioning on the exam table, cleaning, and numbing the insertion site |
|
Catheter Insertion |
Making a small incision to insert the catheter into an artery or vein |
|
Diagnostic Procedure |
Using contrast dye to visualize heart structures |
|
Possible Intervention |
Performing procedures like angioplasty based on diagnostic findings |
Risks and Complications of Cardiac Catheterization
Cardiac catheterization is a valuable tool for diagnosing heart issues. But, it also carries risks and complications. Most patients do well without major problems. Yet, knowing about these risks helps in making informed health choices.
Common Risks Associated with Cardiac Catheterization
Most people face little to no side effects from this procedure. Yet, some common risks include:
- Bleeding or bruising at the catheter site
- Allergic reactions to the contrast dye used during the procedure
- Temporary discomfort or pain at the catheter insertion site
Patients are watched closely on a heart monitor during and after the procedure. This helps catch any issues quickly.
Serious Complications
Though rare, serious complications can happen. These include:
- Heart attack or stroke
- Infection or severe bleeding
- Damage to the blood vessels or heart
Knowing about cardiac catheterization risks helps both patients and doctors prepare.
To grasp the risks better, let’s look at the frequency and severity of complications:
|
Complication |
Frequency |
Severity |
|---|---|---|
|
Bleeding or bruising |
Common |
Mild to Moderate |
|
Allergic reactions |
Uncommon |
Moderate to Severe |
|
Heart attack or stroke |
Rare |
Severe |
It’s key for patients to talk about their risks with their doctor. Knowing the risks helps prepare for the procedure and recovery. We focus on patient care and safety at every step of cardiac catheterization, aiming for the best outcomes.
Recovery After Cardiac Catheterization
Recovering from cardiac catheterization involves both immediate care and long-term follow-up. Knowing what to expect can help patients heal better. We support our patients every step of the way, ensuring they get the care they need.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
Right after the procedure, patients are watched in a recovery area for a few hours. It’s key to listen to the healthcare team about rest, medication, and follow-up visits. Some soreness or bruising at the catheter site is normal and can be managed with pain meds and pressure.
- Rest for the rest of the day and avoid hard activities.
- Keep the catheter site clean and dry.
- Take your medication as your doctor says.
Long-Term Recovery
Long-term recovery means slowly getting back to normal and going to follow-up visits. It’s important to stick to lifestyle changes like diet, exercise, and quitting smoking if needed. Knowing the signs of complications and when to get medical help is also key.
|
Activity |
Guideline |
|---|---|
|
Exercise |
Start slowly with physical activity as your doctor advises. |
|
Diet |
Eat a heart-healthy diet with lots of fruits, veggies, and whole grains. |
|
Follow-Up |
Go to all your scheduled check-ups to keep an eye on your health. |
By following the care instructions and tips for recovery, patients can lower the risk of problems. Our team is dedicated to giving full support during the recovery journey.
Comparing Cardiac Catheterization to Major Surgery
Cardiac catheterization is seen as a less invasive procedure. But how does it stack up against major surgery? It’s key to grasp the meanings and impacts of both.
Definition of Major Surgery
Major surgery means operations with big risks and complex steps. They often need a long time to recover. These surgeries can save lives or greatly improve a patient’s life quality. Examples include CABG, heart transplants, and other complex heart surgeries.
How Cardiac Catheterization Fits In
Cardiac catheterization is a big medical step but is different from major surgery. It’s minimally invasive, using a small incision, usually in the groin or arm. It’s used for checking the heart, like with coronary angiography, or for fixing problems, like with angioplasty.
To see the differences, let’s look at a comparison table:
|
Characteristics |
Major Surgery |
Cardiac Catheterization |
|---|---|---|
|
Invasiveness |
Highly invasive, involving large incisions |
Minimally invasive, involving small incisions |
|
Recovery Time |
Often requires several weeks to months for recovery |
Typically requires a few days or less for recovery |
|
Risks and Complications |
Higher risk of complications, including infection and bleeding |
Lower risk of complications, but can include bleeding or vascular damage |
|
Purpose |
Often used for complex repairs or replacements |
Used for diagnostic purposes or interventions like angioplasty |
In conclusion, cardiac catheterization is a big deal but is different from major surgery. It’s less invasive and has a shorter recovery time. Knowing these differences is important for patients and doctors when choosing treatments.
Alternatives to Cardiac Catheterization
There are many ways to check for heart disease, not just cardiac catheterization. Some people might not be good candidates for it. Or they might want to try other ways to find out what’s going on with their heart.
Non-Invasive Diagnostic Tests
Non-invasive tests are great alternatives to cardiac catheterization. They let doctors check the heart without using catheters. Here are some examples:
- Echocardiography: Uses sound waves to see the heart’s structure and how it works.
- Stress Tests: Checks how well the heart works when it’s stressed, usually through exercise or medicine.
- Cardiac MRI: Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to get detailed heart images.
- Coronary CT Angiography: Uses X-rays to create detailed pictures of the heart and its blood vessels.
These tests are often the first step in diagnosing heart problems. They help doctors understand how the heart is doing.
Other Invasive Procedures
For some, other invasive tests might be better than cardiac catheterization. These include:
|
Procedure |
Description |
Use |
|---|---|---|
|
Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE) |
Uses an ultrasound probe down the esophagus for closer heart images. |
Great for looking at heart structures, like valves, and finding blood clots. |
|
Electrophysiology Studies (EPS) |
Checks the heart’s electrical system by inserting catheters through veins. |
Helps diagnose and treat irregular heart rhythms by studying electrical pathways. |
Even though they’re not cardiac catheterization, these tests are very useful. They give doctors important information to help manage heart disease.
Conclusion: Understanding the Role of Cardiac Catheterization
Cardiac catheterization is key in managing heart health. It helps diagnose and treat heart issues. Knowing its role and process helps patients make informed choices.
Key Takeaways
This procedure is vital for diagnosing and treating heart conditions. It lets doctors check heart function and find problems early. This way, they can act quickly to help.
Patient Care Considerations
Good patient care is essential for cardiac catheterization. We stress the need for proper preparation before and after the procedure. This includes recovery plans to ensure the best results.
By focusing on patient care, doctors can make cardiac catheterization more successful. It’s a big part of managing heart health, and care makes it even better.
FAQ
What is a Holter monitor used for?
A Holter monitor is a portable device. It records the heart’s electrical activity for 24 to 48 hours. It helps find heart problems like arrhythmias.
How to wear a Holter monitor?
To wear a Holter monitor, attach it to your chest with electrodes. Then, connect it to a recorder. Wear comfy clothes that let you move easily.
How long do I have to wear a Holter monitor?
You’ll wear a Holter monitor for 24 to 48 hours. Sometimes, it’s worn longer, depending on your doctor’s advice.
Can I sleep with a Holter monitor?
Yes, you can sleep with it. It’s made to be worn all the time, even when you sleep. This way, it captures all your heart activity.
What are the limitations of wearing a Holter monitor?
Avoid getting the monitor wet, like taking a bath or swimming. Also, some activities might be off-limits to protect the device.
What is a Holter shirt?
A Holter shirt is a special garment. It keeps the monitor and electrodes in place, making it more comfy to wear.
Are there any alternatives to a Holter monitor?
Yes, there are other options like event monitors or echocardiograms. Your doctor can tell you the best one for your situation.
Can I exercise while wearing a Holter monitor?
Usually, you can keep exercising as normal. But, always check with your doctor first.
How do I care for my Holter monitor?
Keep it away from water, extreme temperatures, and stress. Follow the care tips from your doctor or the maker of the device.
Reference
New England Journal of Medicine. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMra1711228



































