Understanding Carotid Artery Occlusion and Its Risks
Carotid artery occlusion is a serious vascular condition that can lead to life-threatening complications such as stroke or paralysis. The carotid arteries are large blood vessels located on both sides of the neck that supply oxygen-rich blood to the brain. When these arteries become narrowed or blocked, the brain may not receive enough oxygen, leading to symptoms that can range from mild dizziness to severe neurological damage.
Symptoms such as loss of sensation, muscle weakness, temporary or permanent vision loss, and fainting should never be ignored. While these symptoms can be caused by several health issues, a blockage in the carotid artery remains one of the most critical causes to consider. Recognizing the warning signs early and seeking immediate medical attention can significantly reduce the risk of stroke or permanent disability.
According to Liv Hospital Vascular Surgery Specialist Professor Dr. Ahmet Ozkara, early diagnosis and treatment of carotid artery disease are vital to preventing severe complications. With timely medical intervention and lifestyle management, the risk of stroke and other related outcomes can be dramatically lowered.
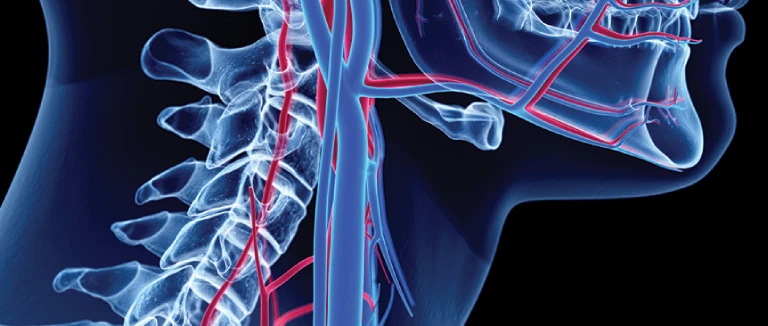
How Carotid Artery Disease Develops
Carotid artery disease occurs when the arteries responsible for supplying blood to the brain become narrowed due to plaque buildup. This process, known as atherosclerosis, involves the accumulation of fatty deposits composed of cholesterol, calcium, and other substances in the blood. Over time, this buildup hardens and narrows the arteries, restricting blood flow.
When atherosclerosis advances, it may lead to the formation of blood clots. If one of these clots breaks loose and travels to the brain, it can completely block blood circulation, resulting in an ischemic stroke. The severity of the condition depends on how much the artery has narrowed and how long the brain has been deprived of oxygen.
Several factors contribute to the development of carotid artery disease, including high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, and genetic predisposition. Understanding these risk factors is key to early prevention and effective treatment.
Main Causes of Carotid Artery Disease
Tobacco use is one of the most significant contributors to carotid artery blockage. Chemicals in tobacco damage the lining of the blood vessels, encouraging plaque buildup.
High cholesterol and high levels of fat in the blood accelerate the formation of atherosclerotic plaque, which reduces blood flow to the brain.
High blood pressure exerts excessive strain on artery walls, making them more susceptible to injury and plaque formation.
Diabetes and insulin resistance increase inflammation and damage blood vessels, contributing to narrowing of the arteries.
Genetic factors can also play a role, meaning individuals with a family history of heart or vascular disease may be at higher risk.
By understanding these causes and adopting preventive measures, individuals can significantly slow the progression of carotid artery disease and lower their risk of serious complications.
Symptoms of Carotid Artery Disease
Carotid artery disease often develops silently, showing no symptoms until a major event like a stroke occurs. However, there are several warning signs that should prompt immediate medical attention.
Early symptoms can include dizziness, numbness or weakness in the arms or legs, difficulty speaking, short-term vision loss, or brief episodes of fainting. These symptoms may last only a few minutes and are known as transient ischemic attacks, often referred to as mini strokes. They are early indicators that the blood flow to the brain is compromised and that a more serious stroke may occur if the condition is not treated.
In more advanced cases, when the arteries are severely narrowed or completely blocked, symptoms may become more intense. These can include prolonged paralysis, memory problems, confusion, difficulty walking, or even sudden loss of consciousness. If a blood clot forms and travels from the carotid artery to the brain, it can cause irreversible damage or sudden death.
Treatment Options for Carotid Artery Disease
Treatment for carotid artery disease depends on the degree of blockage and the patient’s overall health. The primary goal of treatment is to restore blood flow to the brain, prevent stroke, and manage underlying risk factors.
Lifestyle and nutrition changes are the first step in managing carotid artery disease. A healthy diet low in saturated fats, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and keeping blood pressure and cholesterol levels within normal ranges are essential steps in preventing further plaque buildup. Regular physical activity and proper stress management also contribute to vascular health.
Medical treatment focuses on managing related conditions and reducing the risk of clot formation. Physicians often prescribe medications such as blood thinners to prevent clots and vasodilators to improve blood flow. Patients with high cholesterol may be prescribed statins to help lower lipid levels.
Interventional treatment may be considered when the artery is narrowed but not completely blocked. Minimally invasive techniques can help improve blood circulation and stabilize plaque deposits. However, for arteries that are fully blocked, surgical treatment is often the most effective solution.
Surgical treatment, known as carotid endarterectomy, involves removing plaque from the artery to restore normal blood flow. This procedure is performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the patient’s condition. The artery is opened, the plaque is carefully removed, and the vessel is repaired using a patch to widen the passage. This method has shown excellent long-term results in preventing stroke recurrence.
Interventional radiology may also be an option for some patients who are not suitable candidates for surgery. In such cases, a stent can be placed within the artery to keep it open and allow blood to flow more freely. However, stenting is typically reserved for patients who cannot undergo surgery due to other health concerns.
Even after surgical or interventional procedures, adopting a healthy lifestyle remains essential to prevent the disease from returning. Regular follow-up appointments with ultrasound and imaging tests allow doctors to monitor the condition and ensure that the arteries remain clear.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Prevention
Carotid artery disease is one of the leading causes of stroke worldwide, alongside heart disease and brain hemorrhage. Because it can progress silently, early diagnosis is crucial. Regular checkups and vascular screenings are particularly important for people over the age of 50 and those with known risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, or smoking.
Ultrasound examinations are a simple and noninvasive way to detect narrowing in the carotid arteries before symptoms appear. Early detection allows for timely medical intervention, which can prevent irreversible damage to the brain.
Preventive measures can be highly effective. Avoiding tobacco use, eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and maintaining an active lifestyle all help improve vascular health. Managing blood sugar and blood pressure levels also reduces the likelihood of developing atherosclerosis.
Comprehensive Care at Liv Hospital
Liv Hospital provides advanced diagnosis and treatment for carotid artery disease with a team of experienced vascular surgeons and interventional radiologists. Each patient receives a personalized treatment plan designed to restore blood flow, prevent complications, and enhance quality of life.
The hospital integrates advanced imaging technologies, minimally invasive procedures, and evidence-based surgical techniques to ensure the best outcomes. Continuous monitoring and patient education are key components of care, ensuring that patients remain informed and empowered to take control of their health.
Professor Dr. Ahmet Ozkara and the vascular surgery team at Liv Hospital emphasize the importance of early detection, prevention, and comprehensive care in managing carotid artery disease. Through timely intervention, advanced medical techniques, and a commitment to long-term patient wellness, Liv Hospital continues to shape the future of vascular healthcare in Türkiye.
* Liv Hospital Editorial Board has contributed to the publication of this content .
* Contents of this page is for informational purposes only. Please consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment. The content of this page does not include information on medicinal health care at Liv Hospital .
For more information about our academic and training initiatives, visit Liv Hospital Academy
Frequently Asked Questions
What is carotid artery occlusion?
Carotid artery occlusion occurs when the main arteries in the neck become narrowed or blocked, reducing blood flow to the brain and increasing stroke risk.
What causes carotid artery disease?
It is primarily caused by atherosclerosis, a buildup of cholesterol and fatty deposits in the arteries, often linked to smoking, high cholesterol, and hypertension.
What are the warning symptoms?
Sudden weakness, numbness, vision loss, dizziness, or trouble speaking may indicate reduced blood flow to the brain and require urgent care.
How is carotid artery disease diagnosed?
Doctors use imaging methods such as Doppler ultrasound, CT angiography, or MRI to detect narrowing or blockage in the carotid arteries.
What treatments are available?
Treatment may include medication, lifestyle changes, or surgical options like carotid endarterectomy or stent placement to restore blood flow.
Can carotid artery blockage be prevented?
Yes. Avoiding smoking, eating a balanced diet, managing blood pressure and cholesterol, and exercising regularly help reduce risk.
Why choose Liv Hospital for treatment?
Liv Hospital in Türkiye offers advanced imaging, minimally invasive surgery, and expert vascular specialists for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Who is at higher risk for carotid artery disease?
People over 50, smokers, and those with high blood pressure, diabetes, or high cholesterol are more likely to develop carotid artery blockage.























