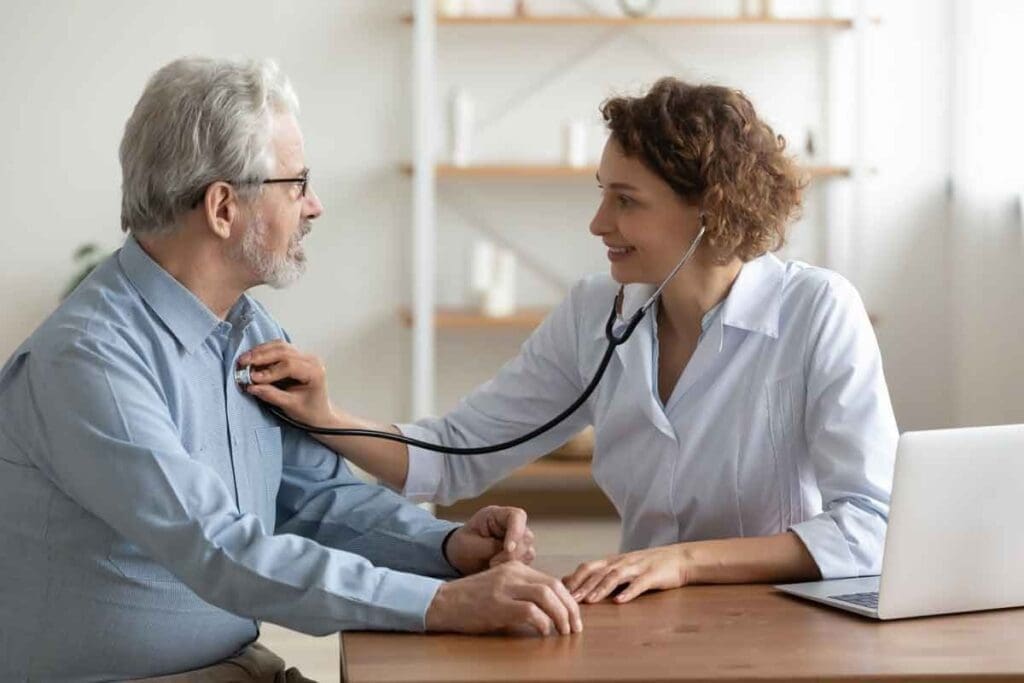
Catheter ablation is a medical procedure. It treats irregular heartbeats by destroying the small area of heart tissue causing the arrhythmia.
For those with abnormal heart rhythms, knowing about this treatment can be very empowering. Liv Hospital’s cardiology department offers advanced solutions for heart arrhythmias. They use internationally trusted care.
The procedure uses radiofrequency energy to target and eliminate the source of irregular heartbeats. It offers a potentially life-changing solution for those affected.
Key Takeaways
- Catheter ablation treats irregular heartbeats by targeting the source.
- Liv Hospital offers advanced cardiology care.
- The procedure uses radiofrequency energy.
- It’s a solution for those with abnormal heart rhythms.
- Understanding catheter ablation can empower patients.
The Fundamentals of Heart Rhythm Disorders
To understand how catheter ablation helps with heart arrhythmias, we need to know the basics. The heart’s electrical system is complex. It controls the heartbeat, making sure blood flows well throughout the body.
Normal Heart Electrical System
The heart’s electrical system starts with the sinus node in the right atrium. This small group of cells acts as the heart’s natural pacemaker. It sends out electrical impulses that make the heart beat.
These impulses go through the AV node and down the bundle of His. They reach the ventricles, making them contract. This process leads to a coordinated heartbeat, usually between 60 to 100 beats per minute when we’re resting.
What Causes Cardiac Arrhythmias
Cardiac arrhythmias happen when the heart’s electrical system gets disrupted. Several things can cause these disruptions, including:
- Abnormal electrical pathways: Extra or abnormal electrical connections in the heart can cause arrhythmias.
- Damage to the heart tissue: Heart attacks, infections, or other conditions can damage the heart’s electrical system.
- Imbalances in electrolytes: Electrolytes like potassium and sodium play a key role in the heart’s electrical activity.
- Certain medications: Some medications can affect the heart’s rhythm.
- Underlying medical conditions: Conditions such as hyperthyroidism or sleep apnea can contribute to arrhythmias.
Knowing these causes is key to diagnosing and treating cardiac arrhythmias. Catheter ablation targets the heart areas causing the arrhythmia. It aims to restore a normal heart rhythm.
What Is Catheter Ablation?
Catheter ablation is a key treatment for heart arrhythmias. It’s a less invasive method compared to surgery. This technique has changed cardiology, giving patients a new option.
Definition and Basic Principles
Catheter ablation destroys abnormal heart tissue causing arrhythmia. It uses thin, flexible tubes called catheters. Radiofrequency ablation cardiology is common, using energy to create scars.
The goal is to find and fix the heart area causing arrhythmia. By making small scars, it aims to get the heart back to normal.
Historical Development of the Procedure
Catheter ablation started in the 1980s for some arrhythmias. Over time, technology and techniques have improved a lot. Better mapping and new energy sources have made it more effective.
Today, catheter ablation is more precise. This has led to better results and more conditions treated.
Is Catheter Ablation Surgery? Clarifying Common Misconceptions
Many wonder, “Is catheter ablation surgery?” It’s a serious procedure but not traditional surgery. It doesn’t need a big cut or open-heart surgery.
The procedure is done in a special lab. It uses local anesthesia and sedation. Because it’s less invasive, recovery time is shorter than with surgery.
In summary, catheter ablation is a great option for heart arrhythmias. It’s effective and minimally invasive. As technology gets better, it will help more people.
Types of Arrhythmias Treated with Catheter Ablation
Several types of arrhythmias can be treated with catheter ablation. This offers patients many options for their heart rhythm disorders.
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
Atrial fibrillation is a common heart rhythm disorder. It causes the heart to beat too fast and irregularly. Catheter ablation for AFib creates lesions in the heart to stop the arrhythmia, usually in the pulmonary veins.
This procedure can help the heart beat normally again. It reduces symptoms like palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue. It’s a good option for those who can’t take antiarrhythmic medications.
Atrial Flutter
Atrial flutter is another arrhythmia treated with catheter ablation. It causes a fast, regular heart rhythm. The procedure targets the cavo-tricuspid isthmus in the right atrium.
By creating a block in this area, it stops the arrhythmia. This restores a normal heart rhythm and relieves symptoms.
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
Supraventricular tachycardia is a group of arrhythmias that start above the ventricles. SVT causes rapid heart rates that start and stop suddenly. Catheter ablation is very effective for SVT, targeting the specific electrical pathway.
Many patients see a complete end to their symptoms after SVT ablation.
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT)
Ventricular tachycardia is a serious arrhythmia that starts in the ventricles. It’s often treated with catheter ablation for those at risk of sudden cardiac death. The procedure aims to find and ablate the VT source.
This helps prevent future episodes and lowers the risk of complications.
| Arrhythmia Type | Characteristics | Catheter Ablation Targets | Success Rate |
| Atrial Fibrillation | Rapid, irregular heart rhythm | Pulmonary veins | 60-80% |
| Atrial Flutter | Rapid, regular heart rhythm | Cavo-tricuspid isthmus | 90% |
| Supraventricular Tachycardia | Rapid heart rate episodes | Specific electrical pathways | 90-95% |
| Ventricular Tachycardia | Life-threatening arrhythmia | Source of VT | 50-90% |
Catheter Ablation Techniques and Technology
Catheter ablation has grown a lot, using new tech to fix heart rhythm problems. It uses different methods to find and fix the heart’s bad electrical paths.
Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation
Radiofrequency catheter ablation is a top choice. It heats bad heart tissue with electrical energy. It’s great for fixing many heart rhythm issues, like atrial fibrillation and supraventricular tachycardia.
- Works well for many heart rhythm problems
- Is a small procedure
- Patients recover quickly
Cryoablation Technology
Cryoablation freezes bad heart paths. It’s good for tricky spots in the heart because it’s more precise than heat.
Cryoablation’s perks are:
- It’s safer for the heart around it
- Works well for some heart rhythm issues
- Safe for areas where heat might be too risky
Emerging Ablation Technologies
New tech in catheter ablation is exciting. Emerging ablation technologies likepulsed-field ablation use electrical pulses to make lesions. These new methods aim to make ablation safer and more effective.
With ongoing research, we’ll see even more progress in treating heart rhythm problems.
The Catheter Ablation Procedure: Step by Step
The catheter ablation procedure is a detailed process with several steps. It starts with preparation and ends with post-procedure care. Knowing each step helps patients understand what to expect and how to prepare.
Pre-Procedure Evaluation and Preparation
Before the procedure, patients go through a detailed evaluation. This checks if they’re a good candidate for the treatment. They review their medical history, current medications, and test results like echocardiograms and electrocardiograms. Patients need to tell their doctor about any medications they’re taking, like blood thinners.
Preparation also means discussing the procedure’s risks and benefits. Patients often need to fast beforehand and adjust their medications.
During the Procedure
During the procedure, patients are given sedation to relax. Catheters are inserted through a vein in the groin or arm and guided to the heart. Advanced imaging helps place the catheters accurately. The catheter then delivers energy to the heart, creating lesions that stop the arrhythmia.
How Long Does a Catheter Ablation Take?
The procedure’s length varies based on the arrhythmia and case complexity. It usually takes 2 to 4 hours. Some procedures might be shorter or longer, and the team will give a more precise estimate.
Immediate Post-Procedure Monitoring
After the procedure, patients are closely monitored for several hours. They watch for bleeding, check heart rhythm, and manage pain. Patients must stay as motionless as possible to avoid bleeding from the catheter site.
Once stable, patients are usually sent home the same day or the next. Following post-procedure instructions is key toa smooth recovery.
Benefits and Risks of Catheter Ablation Therapy
It’s important to know the benefits and risks of catheter ablation before deciding. This procedure is used to treat heart rhythm disorders. It can cure some arrhythmias.
Potential Benefits and Success Rates
Catheter ablation can greatly reduce or stop arrhythmia episodes. says it’s effective for some arrhythmias. Success rates depend on the condition being treated.
Technology and technique have improved catheter ablation. Radiofrequency catheter ablation and cryoablation are common methods. Cryoablation is often chosen for precise lesions without harming nearby tissue.
Possible Complications and Risks
Catheter ablation is generally safe but carries risks. These include bleeding, infection, and damage to the heart or blood vessels. Rarely, serious issues like stroke or cardiac tamponade can happen.
It’s key to talk to your doctor about these risks. They can explain the specific risks for your situation.
Who Is an Ideal Candidate?
Catheter ablation is for those who haven’t improved with medication. It’s for people with arrhythmias that really affect their life.
Choosing catheter ablation means your doctor will evaluate your condition. They’ll look at your arrhythmia, health, and what you prefer. They can decide if this treatment is right for you.
Recovery and Life After Catheter Ablation
Recovering from catheter ablation is a detailed process. It needs careful watching and follow-up care. Even though it’s a minimally invasive procedure, you’ll need time to rest and recover well.
Hospital Discharge and Early Recovery
Most people can go home the same day as the procedure. But it’s important to have someone with you for the first night. Right after the procedure, you’ll need to watch for any problems and manage any pain or discomfort.
Here’s what to do in the early days of recovery:
- Avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities for a few days
- Follow a normal diet, unless your doctor tells you not to
- Watch the insertion site for signs of infection or bleeding
Long-Term Follow-Up Care
Follow-up care is key to checking if the procedure worked and to address any issues. Usually, you’ll see your cardiologist or electrophysiologist a few weeks after.
At these visits, your doctor might:
- Check your heart rhythm and overall heart health
- Change your medications if needed
- Talk about lifestyle changes or extra treatments
Lifestyle Modifications and Medication Changes
After the procedure, you might need to make some lifestyle changes. This could include:
- Eating a heart-healthy diet with lots of fruits, veggies, and whole grains
- Doing regular, moderate exercise
- Managing stress with meditation or yoga
You might also need to change your medications. Some people can stop taking certain drugs, while others might need to start or continue new ones.
When to Contact Your Doctor
It’s important to know when to call your doctor after catheter ablation. Call them if you have:
- Severe chest pain or trouble breathing
- Signs of infection at the catheter site, like redness, swelling, or fever
- Arrhythmia symptoms coming back
Knowing about the recovery process and what to watch for can help you have a smooth recovery after catheter ablation.
| Recovery Aspect | Guidelines |
| Hospital Discharge | Same-day discharge; have someone accompany you |
| Early Recovery | Avoid heavy lifting; monitor for complications |
| Follow-Up Care | Schedule follow-up appointments within a few weeks |
| Lifestyle Changes | Adopt a heart-healthy diet and regular exercise |
Alternative Treatments for Heart Arrhythmias
Managing heart arrhythmias can involve many treatment options. This includes medications and device therapies. Catheter ablation is a common choice, but other treatments are also effective.
Antiarrhythmic Medications
Antiarrhythmic medications are often the first treatment for heart arrhythmias. These drugs help control the heart’s rhythm. They can prevent or treat arrhythmia episodes.
Types of Antiarrhythmic Medications:
- Beta-blockers: Slow the heart rate and reduce the force of the heart’s contractions.
- Calcium channel blockers: Affect the amount of calcium entering the heart cells, slowing the heart rate.
- Potassium channel blockers: Prolong the repolarization phase, helping to maintain a normal heart rhythm.
- Sodium channel blockers: Slow the conduction of electrical impulses through the heart.
The American Heart Association says these medications can improve life for arrhythmia patients. They can manage symptoms and enhance quality of life.
“The choice of antiarrhythmic medication depends on the type of arrhythmia, the patient’s underlying health, and other factors.”
— American Heart Association
Surgical Options for Arrhythmia Treatment
Surgical interventions may be needed for some arrhythmias. The Maze procedure is one option. It creates scar tissue in the heart to block abnormal signals.
| Surgical Option | Description | Indications |
| Maze Procedure | Creates scar tissue to block abnormal electrical signals | Atrial fibrillation |
| Surgical Ablation | Destroys abnormal electrical pathways | Various arrhythmias |
Device Therapies: Pacemakers and ICDs
Device therapies, like pacemakers and ICDs, are key for managing arrhythmias. These devices regulate the heart’s rhythm. They prevent life-threatening arrhythmias.
Comparing Treatment Options
When choosing a treatment for heart arrhythmias, compare your options. Consider the arrhythmia type, your health, and the risks and benefits of each treatment.
Treatment Comparison:
| Treatment | Benefits | Risks |
| Antiarrhythmic Medications | Effective for symptom management, non-invasive | Side effects, may not prevent arrhythmia |
| Surgical Options | Can be curative for certain arrhythmias | Invasive, risks associated with surgery |
| Device Therapies | Can prevent life-threatening arrhythmias | Battery replacement, device malfunction |
The best treatment plan varies by patient. It should be decided with a healthcare provider’s help.
Conclusion: Making an Informed Decision About Catheter Ablation
Catheter ablation is a treatment for some heart arrhythmias. It’s important to know its benefits and risks before deciding.
We’ve looked at heart rhythm disorders, the catheter ablation process, and its good and bad sides. Knowing this helps you decide if catheter ablation is right for you.
Patients can think about the benefits and risks to make a choice that fits their health needs. This way, they can decide what’s best for them.
Catheter ablation can greatly improve life for those with arrhythmias. It’s key to talk to a doctor to see if it’s the best option for you.
FAQ
What is catheter ablation?
Catheter ablation is a procedure that fixes heart rhythm problems. It uses energy to destroy bad heart paths.
Is catheter ablation considered surgery?
No, it’s not surgery. It’s a small procedure where doctors use catheters through a leg vein to reach the heart.
What types of arrhythmias can be treated with catheter ablation?
It treats many heart rhythm issues. This includes atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and more.
How long does a catheter ablation procedure take?
It usually takes a few hours to finish.
What is radiofrequency catheter ablation?
It’s a method that uses electrical energy to heat and destroy bad heart paths.
What are the benefits of catheter ablation?
It can reduce or stop arrhythmia symptoms. It also improves life quality and may cut down medication needs.
What are the risks and complications of catheter ablation?
Risks include bleeding, infection, and heart or blood vessel damage. There’s also a chance of arrhythmia coming back.
Who is an ideal candidate for catheter ablation?
It’s best for those with arrhythmia symptoms that don’t respond to meds or other treatments.
What is the recovery time after catheter ablation?
Recovery time varies, but most can get back to normal in a few days to a week.
Are there alternative treatments for heart arrhythmias?
Yes, other options include medications, surgery, and devices like pacemakers and ICDs.
References
National Health Service. (2023). Catheter ablation. nhs.uk.https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/catheter-ablation/



































