The term “ablation” might sound scary, but it’s not as bad as it seems, even when it’s about heart issues. Cardiac ablation is a small procedure. It’s used to fix heart rhythm problems by getting rid of bad electrical paths in the heart.
Ablation surgery is different from big surgeries. It uses a catheter that goes in through veins or arteries. This makes it safer and cuts down on recovery time.
Most AF ablations are done without needing to stay in the hospital. This shows how minor and safe this treatment is. We use the latest methods to make sure it works well and is safe for everyone.
Key Takeaways
- Cardiac ablation is a minimally invasive procedure.
- It is used to treat arrhythmias by correcting abnormal heart rhythms.
- The procedure involves the use of a catheter to reach the heart.
- Over 88% of AF ablations are outpatient procedures.
- Ablation surgery has a high success rate and low risk.
What Is Cardiac Ablation?
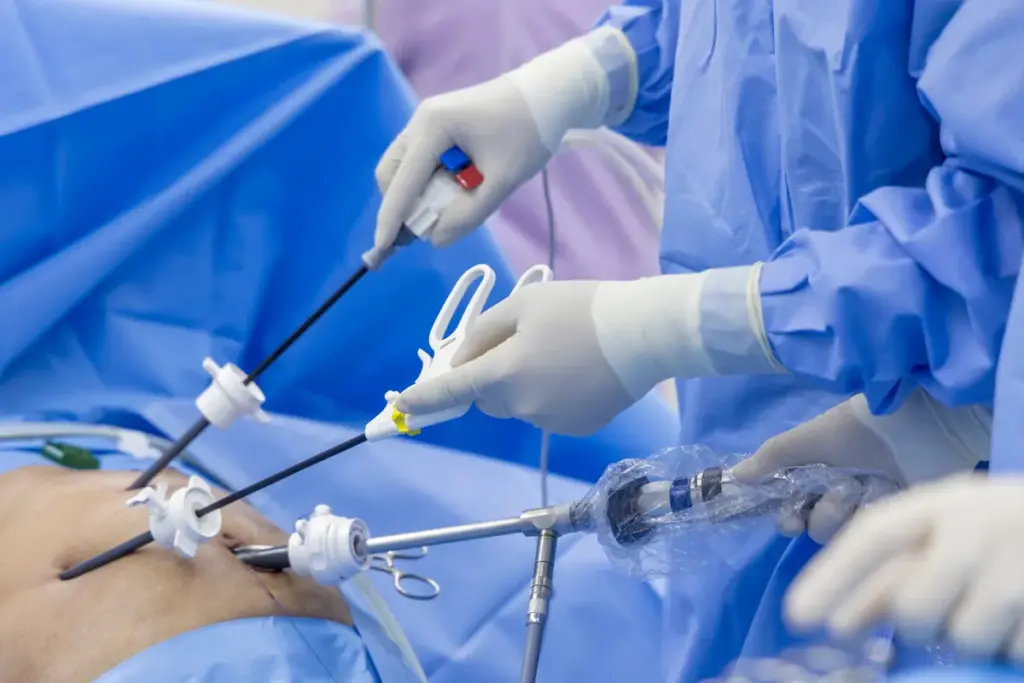
Cardiac ablation is a method to fix irregular heartbeats by finding and fixing the problem. It uses energy, like heat or cold, to make small scars in the heart. These scars stop the bad electrical signals that cause arrhythmias, helping the heart beat normally again.
Definition and Purpose of Ablation Procedures
Cardiac ablation is a medical process that uses energy to destroy a small part of the heart tissue causing bad heart rhythms. Its main goal is to treat arrhythmias, which are irregular heartbeats. By removing the faulty electrical pathways, it aims to make the heart rhythm normal again, bettering the patient’s life.
According to medical experts,
“Cardiac ablation has become an essential tool in the management of arrhythmias, providing a highly effective treatment option for patients who don’t respond to medication or other therapies.”
Common Heart Conditions Treated with Ablation
Cardiac ablation is often used to treat different heart rhythm disorders, including:
- Atrial fibrillation (AF): a condition with an irregular and often rapid heart rhythm.
- Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT): a condition that makes the heart beat too quickly.
- Ventricular tachycardia (VT): a condition that starts in the heart’s ventricles, leading to a rapid heartbeat.
- Atrial flutter: a condition that causes the heart to beat too quickly due to a short circuit in the heart’s atria.
Understanding cardiac ablation helps patients see its benefits in treating heart rhythm disorders. As we learn more about cardiac ablation, it’s key to see how it can improve lives worldwide.
The Minimally Invasive Nature of Modern Ablation
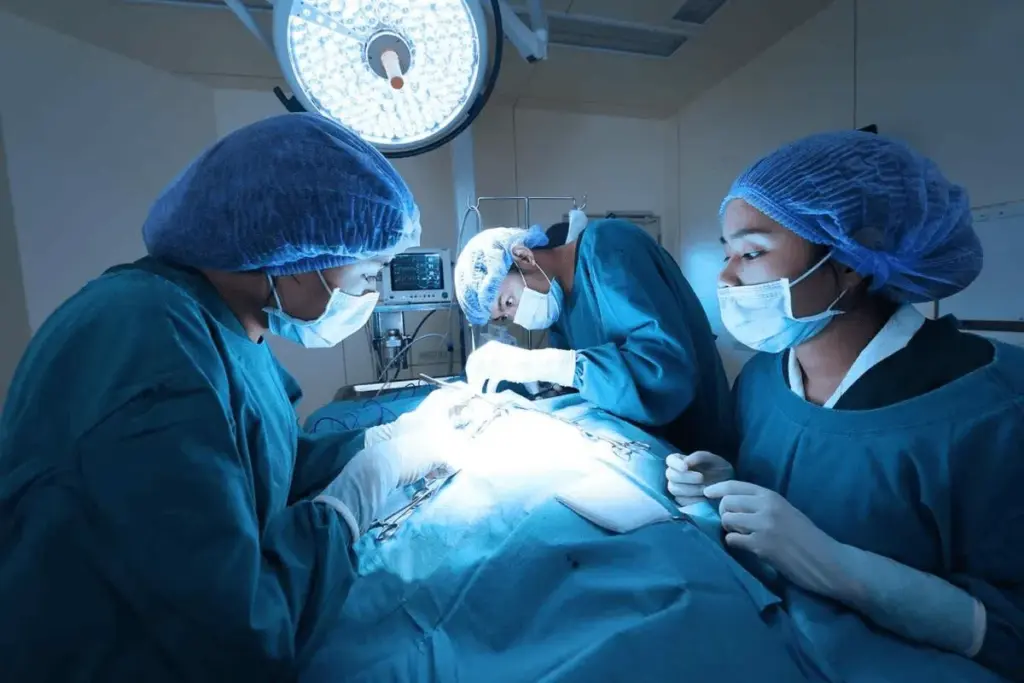
Modern ablation techniques have changed how we treat heart conditions. They moved from big surgeries to small procedures. This change helps patients recover faster and reduces risks.
Evolution from Open Surgery to Minimally Invasive Techniques
Catheters and advanced mapping tools have been key in this change. Catheter ablation is now a main way to treat heart rhythm problems. It goes through blood vessels, avoiding big surgeries and lowering risks.
This new approach has many benefits. Patients feel less pain, stay in the hospital less, and get back to life sooner. The chance of infections and other problems also goes down.
|
Feature |
Open Surgery |
Minimally Invasive Ablation |
|---|---|---|
|
Incision Size |
Large incision |
Small puncture sites |
|
Recovery Time |
Several weeks to months |
A few days to a week |
|
Pain and Discomfort |
Significant pain |
Minimal discomfort |
|
Risk of Complications |
Higher risk |
Lower risk |
Why Ablation Is Not Considered “Big Surgery”
Ablation is often seen as a big deal because it treats serious heart issues. But, modern ablation, like catheter ablation, is much less invasive than old surgeries.
“Big surgery” means big cuts, a lot of damage, and long recovery times. Ablation is different. It’s small, quick, and lets patients get back to life fast.
Key advantages of ablation include:
- Minimally invasive with small incisions or puncture sites
- Reduced risk of complications
- Shorter hospital stays
- Faster recovery times
- Less pain and discomfort
Understanding modern ablation helps patients choose better treatments. It shows ablation is not a big surgery but a precise way to treat heart issues.
Types of Cardiac Ablation Procedures
Ablation therapy for heart conditions has many options. Each method is designed for different heart issues and patient needs.
Radiofrequency Ablation
Radiofrequency ablation is a common heart treatment. It uses high-frequency energy to make scar tissue in the heart. This stops abnormal heart rhythms.
A catheter guides the energy to the heart through blood vessels. The catheter heats the tissue, making lesions that stop bad electrical signals.
Cryoablation
Cryoablation, or cryotherapy, treats heart rhythm disorders with cold. It creates scar tissue by freezing the area.
A cryoablation catheter freezes the targeted area. This method is good for treating some arrhythmias, like AV nodal reentrant tachycardia.
Laser and Microwave Ablation
Laser and microwave ablation are used in some cases. Laser ablation uses a laser to make precise lesions. Microwave ablation heats the tissue with microwave energy.
These methods are not as common but might be used for specific conditions or when other options don’t work.
The right ablation technique depends on many factors. These include the arrhythmia type, the patient’s health, and the doctor’s opinion.
The Role of Catheter Technology in Modern Ablation
Modern catheter technology is key to the success of cardiac ablation. We use advanced catheters to navigate the heart’s complex paths. This ensures the treatment is both effective and safe.
How Catheters Function During Ablation Procedures
Catheters are thin, flexible tubes inserted through a leg vein and guided to the heart. They deliver energy to the heart tissue causing arrhythmias. The precision of catheter placement is vital for the procedure’s success.
Key functions of catheters during ablation include:
- Mapping the heart’s electrical activity
- Delivering ablative energy (such as radiofrequency or cryoablation)
- Monitoring the heart’s response to the treatment
Advanced Mapping and Navigation Systems
Advanced mapping and navigation systems have greatly improved catheter-based ablation. These systems create detailed 3D models of the heart. This allows for more accurate navigation and treatment delivery.
Some of the benefits of these advanced systems include:
- Improved accuracy in targeting arrhythmogenic areas
- Reduced procedure times
- Enhanced safety through better visualization
Latest Innovations in Catheter Design
Recent innovations in catheter design have focused on improving flexibility and maneuverability. These advancements have expanded the range of treatable conditions. They have also improved patient outcomes.
As catheter technology evolves, we can expect better safety and effectiveness in cardiac ablation. The ongoing development of more sophisticated catheters and mapping systems will shape the future of cardiac care.
Atrial Fibrillation Ablation: The Most Common Application
Atrial fibrillation (AF) affects millions worldwide. It causes an irregular and often rapid heart rhythm. This can lead to stroke, heart failure, and other heart problems.
Understanding AF and Its Impact on Quality of Life
Atrial fibrillation significantly impacts patients’ quality of life. Symptoms include palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue. These symptoms can make daily activities hard and affect overall well-being.
We see AF as more than just a heart issue. It affects the whole person. So, treatments like ablation are chosen to improve symptoms and quality of life.
Pulmonary Vein Isolation Procedure
Pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) is a key procedure in AF ablation. It uses ablation to create lesions around the pulmonary veins. These veins are the main source of errant electrical signals causing AF.
Pulmonary Vein Isolation (PVI) Procedure Details:
|
Procedure Aspect |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Objective |
Isolate pulmonary veins to prevent errant electrical signals |
|
Method |
Ablation creating lesions around pulmonary veins |
|
Outcome |
Restoration of normal heart rhythm |
Success Rates for AF Ablation
AF ablation success rates vary, from 60% to nearly 80% after multiple procedures. Success depends on several factors. These include the patient’s overall health, the duration of AF, and other heart conditions.
Patients often see big improvements in symptoms and quality of life after AF ablation. Success is measured by fewer or no AF episodes and better overall well-being.
Success Rate Factors:
- Patient’s overall health
- Duration of atrial fibrillation
- Presence of other heart conditions
Preparing for an Ablation Procedure
To make sure the ablation procedure goes well, patients must follow a certain pre-procedure plan. This plan is key for the treatment’s success and the patient’s safety.
Pre-Procedure Testing and Evaluation
We do several tests before the procedure to check the heart’s health. These tests include electrocardiograms (ECGs), echocardiograms, and blood tests. We might also do a cardiac MRI or CT scan to see the heart clearly.
We look at the patient’s medical history too. This includes any heart problems, surgeries, or allergies. This helps us make the procedure fit the patient’s needs perfectly.
Medication Adjustments Before Ablation
Changing medications is a big part of getting ready for the procedure. We might tell patients to stop or adjust certain medications before the ablation. This is important for medications that affect blood clotting or interact with anesthesia.
Patients on anticoagulant therapy might need to change their dosage or stop it. This is to lower the risk of bleeding during the procedure. We give specific instructions based on the patient’s situation and the type of ablation.
By preparing well for the ablation procedure, we can reduce risks and improve the chances of success. Our team will help patients through every step, making sure they know what to expect and feel comfortable.
What Happens During the Ablation Procedure
Our medical team follows a detailed plan for the ablation procedure. This ensures the best results. We plan carefully, execute precisely, and monitor closely to treat heart issues well.
Anesthesia Options and Sedation
We offer different anesthesia options for comfort during the procedure. Choices include conscious sedation and local anesthesia, based on the patient’s needs and the ablation type.
Conscious sedation makes patients relaxed and comfortable. Local anesthesia numbs the area where the catheter goes. Our anesthesiologists and cardiologists choose the best anesthesia for each patient together.
Step-by-Step Procedure Overview
The ablation procedure has several important steps:
- Inserting a catheter through a vein in the leg or arm.
- Using advanced imaging to guide the catheter to the heart.
- Making a detailed map of the heart’s electrical pathways.
- Finding and targeting areas causing arrhythmia.
- Using energy (like radiofrequency or cryoablation) to stop abnormal signals.
Our team watches the patient’s heart activity closely. This ensures the treatment is accurate and effective.
Duration and Intraoperative Monitoring
The ablation procedure usually lasts 2 to 4 hours. This depends on the case’s complexity. Our team keeps a close eye on the patient’s vital signs and heart activity in real-time.
This monitoring lets us adjust the treatment as needed. It ensures the best outcome. Patients are also watched for any complications, though serious side effects are rare.
After the procedure, patients often feel relieved. They know their heart condition is being treated. This is the start of their journey to better heart health and overall well-being.
Outpatient vs. Inpatient Ablation Statistics
A big change in heart care is the move to outpatient ablation. It helps patients recover faster and saves money. Now, over 88% of atrial fibrillation (AF) ablations are done outside the hospital.
The Trend Toward Same-Day Discharge
The shift to same-day discharge comes from better catheter tech and methods. It cuts costs and lowers infection risks. Patients get to heal at home.
What makes outpatient ablation work well includes:
- Improved catheter designs and navigation systems
- Enhanced patient selection criteria
- Advanced anesthesia and sedation techniques
- Streamlined procedural protocols
When Overnight Hospitalization May Be Required
Even with most procedures done outside the hospital, some need inpatient care. This includes:
- Patients with serious health issues, like heart failure or COPD
- Those needing complex or multiple procedures
- Patients facing complications, like cardiac tamponade or bleeding
Studies show age, health, and procedure complexity decide if a patient stays overnight.
As cardiac electrophysiology improves, more procedures will be done outside the hospital. This means safer, more affordable care for patients.
Recovery Timeline After Ablation
Recovering from cardiac ablation takes several stages. These include immediate care after the procedure and long-term follow-ups. Knowing these stages helps manage expectations and ensures a smooth recovery.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
Right after the procedure, patients stay in a recovery area for a few hours. Medical staff watch their vital signs and look for any immediate problems. It’s key to follow the post-procedure instructions from your healthcare team to avoid risks.
Patients might feel some soreness at the catheter site, but this usually goes away in a few days. It’s best to have someone drive you home and stay with you for the first 24 hours.
First Week After Ablation
In the first week, balance rest with slowly getting back to activities. Most people can get back to their usual routines in 3 to 7 days. But, avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting for at least a week.
- Watch the catheter site for signs of infection.
- Take your medications as directed.
- Go to your follow-up appointments as scheduled.
Long-Term Recovery and Follow-Up Protocol
The long-term recovery includes watching your heart rhythm and adjusting medications as needed. We usually schedule follow-ups at 1, 3, and 6 months to check how well the ablation worked and watch for any issues.
|
Follow-Up Timeline |
Assessment Focus |
|---|---|
|
1 Month |
Initial recovery, medication adjustment |
|
3 Months |
Heart rhythm assessment, symptom review |
|
6 Months |
Long-term outcome evaluation, further adjustments |
One patient said, “The follow-up care after my ablation procedure was thorough and reassuring. My healthcare team was always available to answer my questions and address any concerns.”
“The care I received after my cardiac ablation was exceptional. The follow-up appointments were key in making sure my recovery was on track.”
A patient after cardiac ablation
Success Rates and Outcomes of Ablation Procedures
Knowing how well ablation works is key for both patients and doctors. This procedure treats heart rhythm problems and has mixed results. The success depends on the type of arrhythmia, the patient’s health, and the technique used.
First-Time Procedure Success Rates
Research shows that the first-time success rate for ablation is about 60%. This means 60% of patients see big improvements or no symptoms after one try. But, success can change based on the condition and the patient’s situation.
Multiple Procedure Success Rates
Not all patients get better with just one procedure. Studies say that after more tries, success jumps to almost 80%. This shows that even if the first try fails, more attempts can lead to better results.
Factors Affecting Ablation Outcomes
Many things can affect how well an ablation works. These include:
- The type and length of the arrhythmia
- The patient’s age and health
- Any heart disease they might have
- The doctor’s skill and experience
- The ablation method used (like radiofrequency or cryoablation)
It’s important to know these factors to set realistic hopes and improve treatment success. Doctors can make better choices by looking at each patient’s unique case.
Potential Risks and Complications of Ablation
It’s important for patients to know about the risks of ablation. This treatment is usually safe, but there are some dangers. Understanding these risks helps patients make informed choices.
Minor Complications and Their Frequency
Some patients might face minor issues after ablation. These can be discomfort at the catheter site, minor bleeding, or brief heart rhythm problems. Most of these problems get better on their own without needing much help.
These minor issues don’t happen often, affecting less than 5% of people. Knowing about them helps patients report and manage them quickly.
Serious Complications
Though rare, serious problems can be serious. These include cardiac tamponade, stroke, or pulmonary vein stenosis. Our data show serious complications happen in about 3.1% of cases.
Doctors must carefully check patients before the procedure to lower these risks. Using advanced tools and precise technology helps a lot.
Mortality Rates Associated with Ablation
Mortality rates for ablation are a key concern. Our data show a mortality rate of about 0.4%. This shows ablation is generally safe when done by skilled doctors.
While risks exist, ablation is safer than many surgeries. Patients should talk to their doctors about their risks to make the best choice.
Comparing Ablation to Other Treatment Options
When looking at ablation against other treatments like medication and surgery, it’s key for both patients and doctors to understand the options. This helps in making the best choice.
There are many ways to manage arrhythmias, each with its own good and bad points. Ablation is a less invasive method that’s become popular for treating some arrhythmias.
Medication Management vs. Ablation Therapy
Medications are often the first step in treating arrhythmias. But, ablation therapy is a more lasting solution for some. Medications can manage symptoms, but ablation can fix the problem at its source.
|
Treatment Option |
Benefits |
Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
|
Medication Management |
Non-invasive, easily accessible |
May have side effects, requires long-term commitment |
|
Ablation Therapy |
Potential cure, minimally invasive |
Requires a procedure, possible risks and complications |
Surgical Alternatives to Catheter-Based Ablation
For some, surgical options might be needed or preferred over catheter-based ablation. This includes surgical maze procedures or open-heart surgeries.
Surgical alternatives are more invasive and riskier than catheter-based ablation. Yet, they might be the only choice for complex arrhythmias or when other treatments fail.
Cost-Effectiveness and Quality of Life Improvements
Ablation surgery is changing how we treat heart conditions. It’s less invasive and saves money. This procedure improves patient life and is a smart choice for healthcare.
Insurance Coverage for Ablation Procedures
Insurance coverage is key for patients to get ablation. Most plans, including Medicare, cover it for heart issues like atrial fibrillation. But, what’s covered can differ a lot.
Key factors influencing insurance coverage include:
- The specific heart condition being treated
- The type of ablation procedure performed
- The patient’s overall health status
- Previous treatments or failed therapies
Long-Term Economic Benefits
Ablation surgery saves money in the long run. It cuts down on medication costs and hospital stays. This leads to big savings for both patients and healthcare systems.
|
Economic Benefits |
Short-Term |
Long-Term |
|---|---|---|
|
Reduced medication costs |
Minimal |
Significant |
|
Hospitalization reduction |
Moderate |
Substantial |
|
Improved productivity |
Limited |
High |
Quality-Adjusted Life Years (QALYs) Gained
QALYs measure how well medical treatments work. Ablation surgery boosts QALYs for heart patients. This makes it a great choice for both health and wallet.
A study found patients with atrial fibrillation gained 0.42 QALYs after ablation. This means better health and happiness for them.
Looking at ablation’s cost-effectiveness, insurance, and long-term gains helps us see its value. As medical tech advances, ablation will likely play a bigger role in healthcare.
Patient Selection: Who Should Consider Ablation
It’s important to know who will benefit most from cardiac ablation. The procedure works well for some heart rhythm problems. But, choosing the right patients is key.
Ideal Candidates for Ablation Procedures
People with heart rhythm issues who can’t take medicine might be good for ablation. They often see big improvements in their life quality after the treatment.
Characteristics of Ideal Candidates:
- Symptomatic arrhythmias unresponsive to medication
- Intolerance to anti-arrhythmic medications
- Specific types of arrhythmias known to respond well to ablation (e.g., AVNRT, typical atrial flutter)
- Presence of structural heart disease in some cases, depending on the arrhythmia type
A top electrophysiologist says, “Choosing the right patients is the heart of successful ablation therapy.”
“The key to success lies in identifying patients who are most likely to benefit from the procedure while minimizing risks.”
When Ablation May Not Be Recommended
Cardiac ablation is a good option for many, but not all. It’s not right for those with serious health issues, anatomical problems, or high risk of complications.
|
Contraindication |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Severe Comorbidities |
Patients with severe heart failure, advanced kidney disease, or other serious health conditions may be at too high a risk for complications. |
|
Anatomical Challenges |
Certain anatomical variations or previous surgical interventions can make the procedure technically challenging or risky. |
|
Reversible Causes |
If the arrhythmia is caused by a reversible condition (e.g., thyroid disorder, medication side effect), treating the underlying cause may be more appropriate. |
In conclusion, picking the right patients for cardiac ablation is complex. It depends on the arrhythmia type, symptoms, past treatments, and overall health. By carefully looking at these factors, doctors can find the best candidates and improve treatment results.
Advances in Hospital Protocols for Ablation
Hospital care for ablation is changing, focusing on teamwork and best practices. This shift is key to improving medical care. Refined hospital protocols are essential for this progress.
Multidisciplinary Care Approaches
One big change is the use of teams for ablation care. These teams include experts from cardiology, electrophysiology, and cardiac surgery. They work together to help patients during and after ablation.
- Comprehensive Pre-Procedural Evaluation: Teams make sure patients get full checks before ablation, leading to better results.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: With many experts, hospitals can create plans that fit each patient’s needs.
- Enhanced Post-Procedural Care: Teams also help with recovery, lowering the chance of problems.
A study in a found benefits. Hospitals using teams see fewer complications from ablation.
“The integration of multidisciplinary teams in the care of patients undergoing ablation has been a game-changer, significantly improving patient outcomes and reducing hospital stay.”
An Electrophysiologist
Academic Protocols and Best Practices
Following academic guidelines is also key for better ablation care. Hospitals are using evidence-based guidelines to standardize care. This helps improve results.
|
Protocol Component |
Description |
Benefit |
|---|---|---|
|
Pre-Procedural Testing |
Comprehensive testing to assess patient suitability for ablation |
Reduces risk of procedural complications |
|
Intraprocedural Monitoring |
Advanced monitoring techniques during ablation |
Enhances procedural safety and efficacy |
|
Post-Procedural Care |
Standardized care protocols for patient recovery |
Improves patient outcomes and reduces hospital stay |
By adopting these advanced protocols, hospitals can greatly improve care for ablation patients.
Looking ahead, the evolution of ablation protocols is vital for cardiac care’s future. By focusing on teamwork and best practices, we can give patients the best care.
Conclusion
Catheter ablation has changed how we treat heart problems. It’s a less invasive option compared to old surgeries. This method uses advanced technology to cut down on recovery time and risks. This procedure’s success in treating conditions like atrial fibrillation has changed our view of “big surgery.” It has smaller cuts, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery times. As technology gets better, we’ll see even more advanced treatments and better results for patients. Overall, catheter ablation has made cardiac care safer and more effective. It shows that “big surgery” is evolving to focus more on patient health and better outcomes. As we go on, we’ll keep seeing new ways to make treatments better and safer.
FAQ
What is cardiac ablation?
Cardiac ablation is a medical procedure. It treats arrhythmias by destroying abnormal electrical pathways in the heart.
Is cardiac ablation considered a major surgery?
No, it’s not. Cardiac ablation is a minimally invasive procedure. It uses catheters inserted through veins or arteries to reach the heart. This reduces recovery time and risks.
What conditions are treated with cardiac ablation?
It’s used to treat conditions like atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia, and ventricular tachycardia.
What are the different techniques used in cardiac ablation?
Techniques include radiofrequency ablation, cryoablation, and less common methods like laser and microwave ablation.
How does catheter technology contribute to modern ablation?
Catheter technology is key in modern ablation. It enables precise mapping and navigation. This enhances procedure outcomes.
What is the success rate of atrial fibrillation ablation?
The success rate varies. But it’s generally seen as an effective treatment for atrial fibrillation.
How should I prepare for an ablation procedure?
Patients undergo pre-procedure testing and evaluation. They may need to adjust their medications.
What happens during an ablation procedure?
Patients are given anesthesia options and sedation. The procedure is closely monitored for safety.
Can I go home the same day after an ablation procedure?
Yes, many patients can go home the same day. But some may need overnight hospitalization.
What is the recovery process like after ablation?
Recovery involves immediate post-procedure care and a period of rest. Follow-up appointments are needed to monitor progress.
What are the possible risks and complications of ablation?
Risks include minor complications like bruising and serious complications like cardiac tamponade.
How does ablation compare to other treatment options?
Ablation is often compared to medication management and surgical alternatives. It’s considered effective for certain conditions.
Is ablation cost-effective?
Yes, it’s generally cost-effective. It can improve quality of life and reduce the need for ongoing medication.
Who is a good candidate for ablation?
Ideal candidates have certain heart conditions, like atrial fibrillation, that haven’t responded to other treatments.
What advancements have been made in hospital protocols for ablation?
Advances include adopting multidisciplinary care approaches and academic protocols. These enhance patient outcomes.
What is ambulation after ablation?
Ambulation, or walking, is encouraged after ablation. It helps prevent complications and promotes recovery.
What is the role of libation in the context of medical treatment?
Libation is not directly related to medical treatment. It refers to pouring a liquid as an offer. In medicine, it’s not commonly used.
What is the difference between ablation and cauterize?
Ablation and cauterize both destroy tissue. But they use different techniques and are used in different contexts.
What is epilation in relation to ablation?
Epilation refers to hair removal. It’s not directly related to cardiac ablation.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from





