Understanding Cellulitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
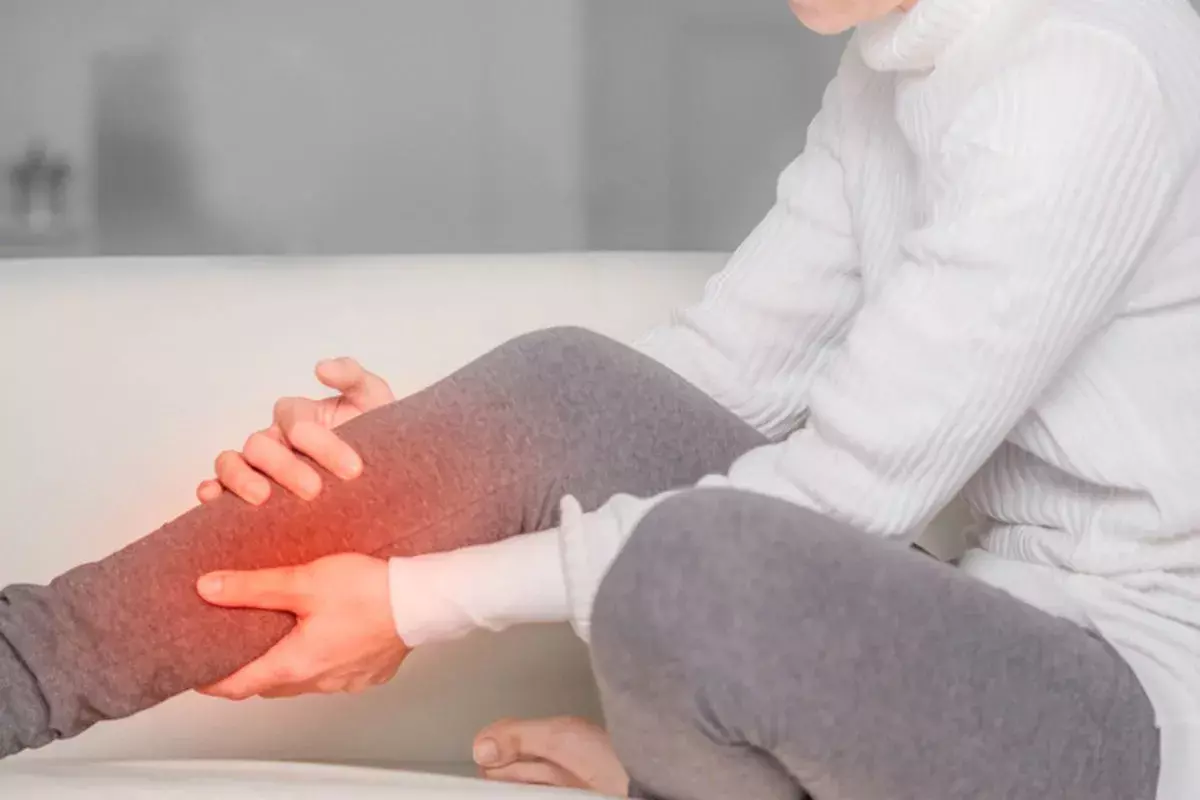
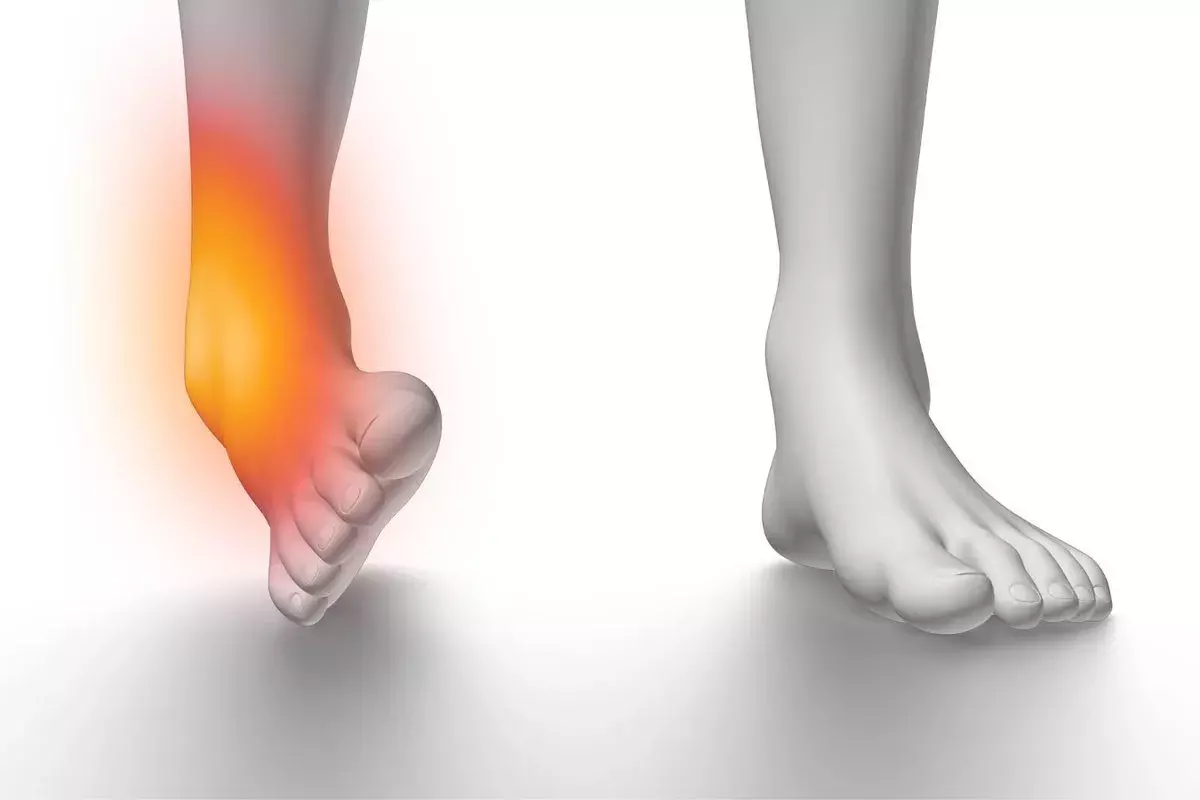
Cellulitis is a common but potentially serious bacterial skin infection that affects the deeper layers of the skin and the tissues beneath it. It typically occurs when bacteria enter the body through small breaks, cuts, or cracks in the skin, leading to redness, swelling, warmth, and pain in the affected area. Although cellulitis can develop anywhere on the body, it most frequently affects the lower legs.
This condition requires prompt medical evaluation and treatment, as the infection can spread rapidly to other parts of the body if left untreated. While most cases respond well to antibiotics, delayed treatment can result in serious complications, including bloodstream infections or abscess formation.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what cellulitis is, examine its underlying causes and risk factors, review its common symptoms, and discuss the most effective treatment and prevention strategies. Understanding cellulitis and recognizing its early warning signs are key to ensuring quick recovery and preventing recurrence.
What is Cellulitis?
Cellulitis is an infection that usually affects the skin on the lower legs, but it can occur anywhere on the body. It is most commonly caused by bacteria, typically Streptococcus or Staphylococcus species, entering through a break in the skin such as a cut, scrape, insect bite, or cracked, dry skin. The bacteria then multiply, leading to infection. This results in the characteristic redness, swelling, and warmth associated with cellulitis.
What Causes Cellulitis?
Cellulitis typically occurs when bacteria enter the body through small openings or injuries in the skin. Once inside, the bacteria can spread rapidly, leading to redness, swelling, and pain. Several factors can increase the risk of developing cellulitis:
1. Skin Breaks
Even minor cuts, scrapes, surgical wounds, or insect bites can allow bacteria to penetrate the skin and cause infection.
2. Skin Conditions
Conditions such as eczema, athlete’s foot, or fungal infections can weaken the skin’s natural barrier, making it easier for bacteria to enter.
3. Intravenous Drug Use
Using unclean or shared needles introduces bacteria directly into the bloodstream, significantly increasing the risk of cellulitis.
4. Compromised Immune System
People with weakened immune systems such as those with diabetes, cancer, or immune disorders—are more vulnerable to infections and slower to heal.
5. Previous Cellulitis
A history of cellulitis can damage the skin’s structure, leaving it more prone to recurring infections in the same or nearby areas.

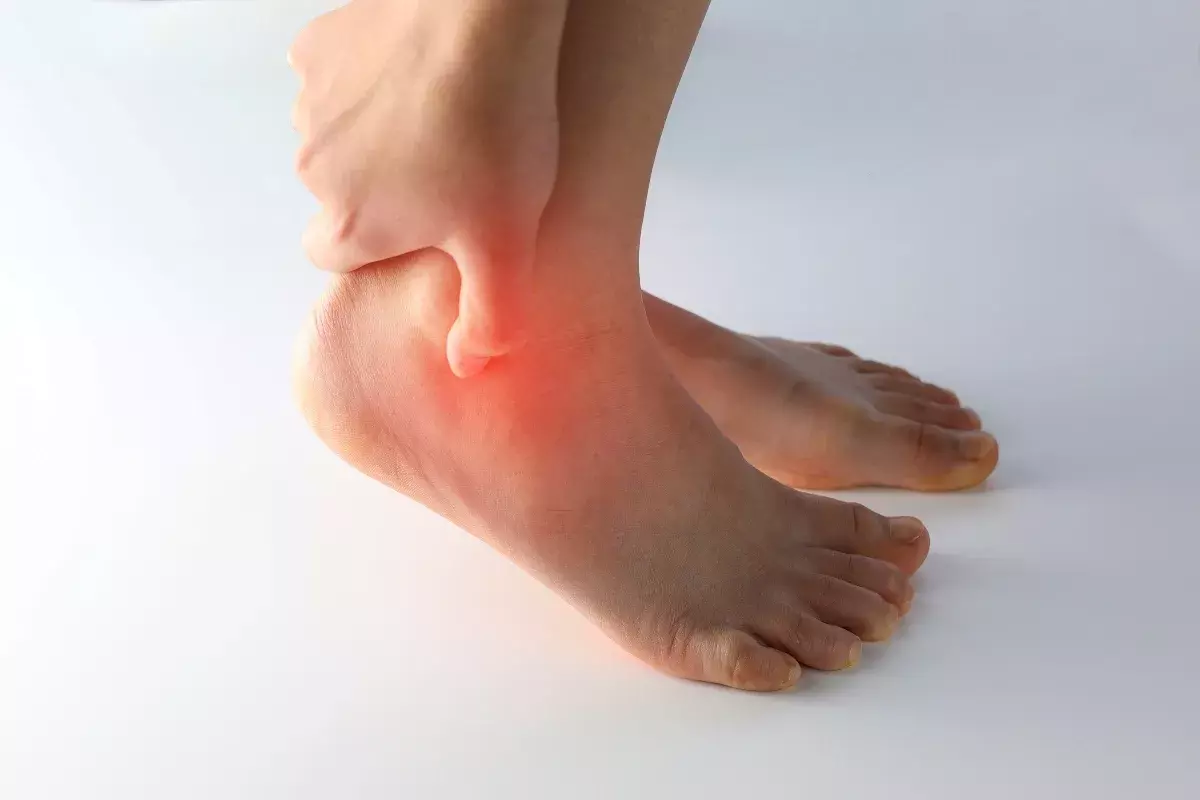
Cellulitis Symptoms
Cellulitis symptoms can vary in severity from person to person but generally develop rapidly in the affected area. Common signs and symptoms include:
1. Redness
The infected skin area appears red, inflamed, and may spread quickly if untreated.
2. Swelling
The skin often becomes swollen, tender, and warm to the touch, indicating inflammation beneath the surface.
3. Pain
Cellulitis can cause increasing pain or discomfort, which may worsen as the infection progresses.
4. Fever
In some cases, individuals may develop a fever as the body responds to the infection.
5. Blisters
Fluid-filled blisters may form on the skin in more severe cases of cellulitis.
Recognizing these symptoms early and seeking prompt medical attention is crucial, as untreated cellulitis can lead to serious complications and systemic infection.
How to Treat Cellulitis
Cellulitis treatment focuses on eliminating the bacterial infection, reducing inflammation, and preventing complications. The specific approach depends on the severity of the infection and the patient’s overall health condition.
1. Oral Antibiotics
For mild to moderate cases, healthcare providers typically prescribe oral antibiotics. These medications effectively target the bacteria causing the infection and usually begin to improve symptoms within a few days.
2. Intravenous (IV) Antibiotics
In more severe casesespecially when the infection spreads rapidly or affects individuals with weakened immune systems hospitalization and intravenous (IV) antibiotics may be necessary to ensure faster and stronger results.
3. Elevation and Rest
Keeping the affected limb elevated helps reduce swelling, promote circulation, and relieve discomfort. Adequate rest is also important to support the body’s healing process.
4. Pain and Symptom Relief
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, may be used to manage pain, fever, and inflammation during recovery.
5. Complete the Full Course of Treatment
It is essential to finish the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms begin to improve before the medication is completed. Stopping treatment too early can allow the infection to return or become resistant to antibiotics.
With early diagnosis and appropriate medical care, cellulitis can usually be treated successfully. However, if symptoms worsen or do not improve within a few days, it’s crucial to contact your healthcare provider for further evaluation.
* Liv Hospital Editorial Board has contributed to the publication of this content .
* Contents of this page is for informational purposes only. Please consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment. The content of this page does not include information on medicinal health care at Liv Hospital .
For more information about our academic and training initiatives, visit Liv Hospital Academy
Frequently Asked Questions
What is cellulitis?
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that causes redness, swelling, warmth, and pain in the affected area.
What causes cellulitis?
It occurs when bacteria enter through cuts, cracks, insect bites, or other breaks in the skin.
What are the early symptoms of cellulitis?
Common symptoms include redness, swelling, pain, warmth, and sometimes fever.
Is cellulitis contagious?
No, cellulitis itself is not contagious, but the bacteria causing it can spread through shared items or direct contact with wounds.
How is cellulitis diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose it through physical examination and, if needed, blood tests or cultures.
How is cellulitis treated?
Most cases are treated with oral antibiotics, rest, elevation, and pain relievers.
When is hospitalization needed?
Hospitalization may be required if symptoms are severe, rapidly spreading, or if the patient has a weakened immune system.
Can cellulitis come back?
Yes, previous cellulitis increases the risk of recurrence, especially if skin issues persist.
How long does cellulitis take to heal?
Symptoms typically improve within a few days of starting antibiotics, but full healing may take one to two weeks.
How can cellulitis be prevented?
Good skin care, treating wounds promptly, managing chronic conditions, and preventing fungal infections all reduce risk.