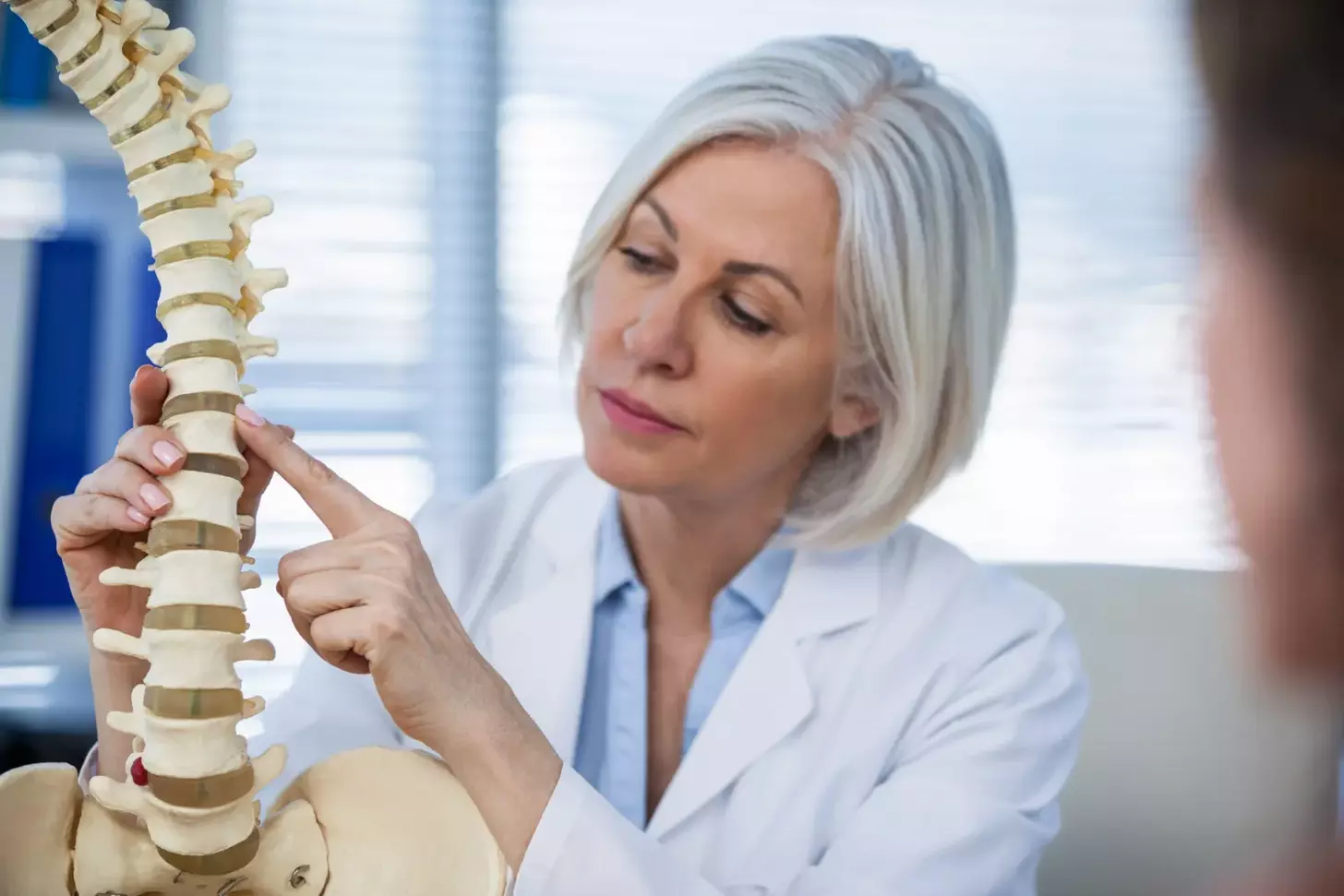
We understand that degenerative cervical spine disease can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) is a widely used surgical intervention for this condition, making up approximately 62% of all cervical spine surgeries.
ACDF surgery is a prevalent procedure for treating various cervical spine conditions, including radiculopathy and myelopathy. At Liv Hospital, we deliver gold-standard, patient-centered care, addressing conditions across multiple spinal levels with rigorous medical standards and internationally recognized surgical expertise.
Key Takeaways
- ACDF surgery is a common treatment for degenerative cervical spine disease.
- Liv Hospital provides patient-centered care for cervical spine conditions.
- ACDF surgery can address conditions across multiple spinal levels.
- Our medical team adheres to rigorous standards and international best practices.
- Advanced ACDF surgery techniques enhance patient outcomes.
The Significance of Cervical Disc Fusion in Spine Surgery
The importance of cervical disc fusion in modern spine surgery cannot be overstated. As a common solution for neck pain, this procedure has become vital in orthopedic surgery. We will explore its significance by understanding the cervical spine anatomy and the prevalence of ACDF in cervical spine surgeries.
Understanding Cervical Spine Anatomy
The cervical spine is a complex structure consisting of seven vertebrae, labeled C1 to C7. Understanding its anatomy is crucial for diagnosing and treating various spinal conditions. The cervical spine supports the head, allows for a wide range of motion, and protects the spinal cord.
Why ACDF Comprises 62% of All Cervical Spine Surgeries
Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) is a preferred surgical method for treating cervical spine disorders. It involves removing a degenerative or herniated disc and fusing the adjacent vertebrae. ACDF is widely used due to its effectiveness in relieving pain and stabilizing the spine.
According to a study published in the Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine, ACDF accounts for approximately 62% of all cervical spine surgeries due to its high success rate and minimal complications.
| Surgical Procedure | Success Rate | Complication Rate |
|---|---|---|
| ACDF | 85-90% | 5-10% |
| Posterior Cervical Fusion | 80-85% | 10-15% |
| Cervical Disc Replacement | 90-95% | 5% |
“ACDF has revolutionized the treatment of cervical spine disorders, offering patients a reliable solution for neck pain and improved quality of life.”
Common levels treated with ACDF include C5-6, C6-7, and C4-C7. Understanding the specific level of disc herniation or degeneration is crucial for determining the most appropriate surgical approach.
Key Fact #1: What is ACDF Surgery and How it Works

The anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) procedure has become a cornerstone in treating various cervical spine conditions. ACDF surgery involves removing the degenerative disc and fusing the vertebrae to stabilize the spine and alleviate pain.
The Anterior Approach Explained
The anterior approach in ACDF surgery refers to accessing the cervical spine through the front of the neck. This method allows surgeons to directly reach the affected disc without disturbing the spinal cord or nerve roots. The benefits of the anterior approach include reduced risk of nerve damage and less post-operative pain, making it a preferred method for many surgeons.
Surgical Techniques and Materials Used
In ACDF surgery, various techniques and materials are employed to ensure successful fusion and optimal outcomes. The surgical technique typically involves:
- Removing the degenerative disc material
- Preparing the disc space for fusion
- Inserting a bone graft or spacer to facilitate fusion
- Using plates and screws to stabilize the vertebrae
The choice of materials for ACDF surgery has evolved, with options including:
| Material | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Autograft | Patient’s own bone used for grafting | High fusion rates, no risk of rejection |
| Allograft | Donated bone used for grafting | Availability, reduced morbidity |
| Synthetic | Artificial materials used for spacing and fusion | Customizable, no risk of disease transmission |
ACDF at levels such as C3-C4 fusion, C5-6 ACDF, C6-7 ACDF, and C5-7 ACDF demonstrates consistently improved clinical scores postoperatively. The versatility of ACDF surgery in addressing different cervical levels makes it a valuable treatment option for a wide range of cervical spine disorders.
Key Fact #2: Most Common Cervical Levels Treated with ACDF
When it comes to Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) surgery, understanding the specific cervical levels treated is crucial for effective treatment. The choice of cervical level for ACDF depends on the patient’s condition, and certain levels are more commonly treated than others.
C5-6 ACDF: Indications and Outcomes
The C5-6 level is one of the most frequently treated levels in ACDF surgery. This is because the C5-6 disc is more prone to degeneration due to its location and the amount of stress it bears. Radiculopathyand myelopathy are common indications for C5-6 ACDF. Studies have shown that patients undergoing C5-6 ACDF experience significant improvements in symptoms and quality of life.
C6-7 ACDF Surgery: When It’s Necessary
C6-7 ACDF is another common procedure, often performed to address disc herniation or degeneration at this level. The decision to undergo C6-7 ACDF surgery is typically made when conservative treatments fail to alleviate symptoms such as pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs. Outcomes for C6-7 ACDF are generally favorable, with most patients experiencing relief from their symptoms.
C3-C4 Fusion: Less Common but Critical Cases
While less common than C5-6 or C6-7 ACDF, C3-C4 fusion is performed in cases where the upper cervical spine is affected. This might be due to trauma, severe degeneration, or other conditions affecting the C3-C4 disc. Although less frequent, C3-C4 fusion is a critical procedure that requires precise surgical technique to ensure successful outcomes.
Multilevel procedures, including C4-C7 ACDF and C4-C6 anterior cervical discectomy and fusion, are effective but carry higher rates of complications. The decision to perform a multilevel ACDF is made on a case-by-case basis, taking into account the patient’s overall condition and the extent of their spinal pathology.
Key Fact #3: Single-Level vs. Multilevel ACDF Procedures
ACDF surgery can be performed at one or multiple levels, and understanding the differences is key to successful outcomes. We often encounter patients who require treatment at more than one cervical level, making the choice between single-level and multilevel ACDF procedures critical.
C4-C7 ACDF and Other Multilevel Approaches
Multilevel ACDF procedures, such as C4-C7 ACDF, are effective for treating multiple levels of degenerative disc disease. These complex surgeries involve fusion at three or more adjacent levels, offering comprehensive relief for patients with widespread cervical spine issues.
C4-C6 Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Considerations
C4-C6 ACDF is another common multilevel approach, addressing disc degeneration or herniation at two levels. When considering this procedure, we weigh factors such as the extent of disc damage, spinal alignment, and the patient’s overall health to determine the best course of treatment.
C5-7 ACDF: Challenges and Solutions
C5-7 ACDF, while less extensive than C4-C7, still presents unique challenges. We have found that careful preoperative planning, precise surgical technique, and appropriate postoperative care are crucial in achieving successful outcomes for these patients.
In conclusion, both single-level and multilevel ACDF procedures have their place in treating cervical spine disorders. By understanding the specific needs of each patient and the nuances of different surgical approaches, we can provide personalized care that leads to optimal results.
Key Fact #4: Clinical Outcomes Based on Cervical Levels
Clinical outcomes following Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) surgery vary significantly based on the cervical levels treated. We have observed that the success of ACDF procedures is closely linked to the specific cervical levels being fused, with different levels presenting unique challenges and outcomes.
Success Rates for Different Levels (C5-6, C6-7, C4-5)
Studies have demonstrated that ACDF can lead to significant improvements in patient outcomes, particularly for certain cervical levels. For instance, C5-6 ACDF has shown a high success rate due to the relatively straightforward surgical approach and the critical need to address radiculopathy at this level.
Success rates for common ACDF levels:
| Cervical Level | Success Rate (%) | Common Indications |
|---|---|---|
| C5-6 | 85-90 | Radiculopathy, disc herniation |
| C6-7 | 80-85 | Radiculopathy, spondylosis |
| C4-5 | 75-80 | Myelopathy, disc degeneration |
The 33% Fusion Success Rate for Three-Level ACDF
Multilevel ACDF procedures, such as three-level fusions, present additional challenges. Research indicates that three-level ACDF achieves a fusion success rate of approximately 33%, highlighting the complexity and increased risk associated with these procedures.
The use of advanced surgical techniques and materials has shown promise in improving outcomes for multilevel ACDF.
Reduction in Complications with Posterior Fixation
The incorporation of posterior fixation in ACDF surgery has been shown to reduce complications, particularly in multilevel procedures. By providing additional stability, posterior fixation can enhance fusion rates and minimize the risk of construct failure.
We continue to refine our approach to ACDF surgery, leveraging the latest advancements to optimize clinical outcomes for our patients. By understanding the nuances of different cervical levels and employing tailored strategies, we aim to achieve the best possible results.
Cervical Disc Fusion Recovery Timeline and Expectations
The journey to recovery after ACDF surgery involves several stages, from immediate post-operative care to long-term rehabilitation milestones. Understanding these stages is crucial for managing expectations and ensuring a smooth recovery process.
Immediate Post-Operative Care
Immediately after ACDF surgery, patients are closely monitored in the recovery room for any potential complications. We emphasize the importance of following post-operative instructions to minimize risks and promote healing. Some key aspects of immediate post-operative care include:
- Rest and Relaxation: Patients are advised to rest and avoid strenuous activities.
- Pain Management: Effective pain management strategies are implemented to ensure patient comfort.
- Neck Support: A cervical collar may be recommended to support the neck during the initial healing phase.
Long-term Recovery Milestones
As patients progress through their recovery, several long-term milestones are typically achieved. These include:
- Return to Light Activities: Most patients can resume light activities within a few weeks post-surgery.
- Physical Therapy: A structured physical therapy program is often recommended to restore strength and flexibility.
- Full Recovery: Complete recovery, including the return to more strenuous activities, may take several months.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy plays a vital role in the rehabilitation process after ACDF surgery. A well-structured physical therapy program helps in:
- Improving Neck Mobility: Gentle exercises are introduced to enhance range of motion.
- Strengthening Surrounding Muscles: Targeted exercises help strengthen the muscles supporting the cervical spine.
- Enhancing Overall Functionality: Patients are guided through activities that promote overall functional recovery.
By understanding the recovery timeline and expectations, patients can better prepare themselves for the journey ahead, ensuring a successful outcome from their ACDF surgery.
Key Fact #5: Conditions Treated with ACDF at Various Levels
Cervical disc fusion is used to address multiple spinal issues, including radiculopathy and myelopathy. The choice of treatment depends on the underlying condition and its severity. We will discuss the conditions treated with ACDF, including radiculopathy and myelopathy, and how the choice of treatment depends on the level and severity of the condition.
Radiculopathy: Symptoms and Treatment
Radiculopathy refers to the compression or irritation of nerve roots as they exit the spinal canal. This condition can cause significant pain, numbness, or weakness in the neck and arms. Symptoms of radiculopathy include sharp pain, tingling sensations, and muscle weakness. ACDF surgery is often recommended when conservative treatments fail to alleviate radiculopathy symptoms.
As noted by a spine specialist,
“Radiculopathy can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life, making surgical intervention a viable option for those who do not respond to conservative treatments.”
Myelopathy: When ACDF is Necessary
Myelopathy is a more severe condition resulting from compression of the spinal cord itself. It can lead to significant neurological deficits, including difficulty walking, loss of hand dexterity, and bladder dysfunction. ACDF is considered when myelopathy is caused by anterior spinal cord compression. The decision to proceed with ACDF depends on the severity of myelopathy and the presence of significant spinal cord compression.
Degenerative Disc Disease Patterns by Level
Degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a condition where the intervertebral discs lose their height and integrity over time. The pattern of DDD varies by cervical level, with some levels being more prone to degeneration than others. C5-6 and C6-7 are common levels affected by DDD, often leading to radiculopathy or myelopathy. Understanding the level-specific patterns of DDD is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment.
In conclusion, ACDF is a versatile surgical technique used to treat various cervical spine conditions, including radiculopathy, myelopathy, and degenerative disc disease. The choice of treatment and the decision to undergo ACDF depend on the specific condition, its severity, and the level of the spine affected.
Key Fact #6: Potential Complications and Risks of ACDF Surgery
ACDF surgery, like any other surgical procedure, comes with its own set of potential complications and risks. While generally considered safe, understanding these risks is crucial for patients to make informed decisions about their treatment.
Common Complications by Cervical Level
The cervical level treated can influence the type and frequency of complications. For instance, surgeries at the C5-6 level are common and generally have a lower risk of complications compared to higher or multilevel procedures.
Some common complications include:
- Dysphagia (swallowing difficulties)
- Hoarseness due to recurrent laryngeal nerve injury
- Infection
- Nerve damage
- Pseudoarthrosis (failure of fusion)
We will examine these complications in more detail and discuss how they vary by cervical level.
Higher Complication Rates in Multilevel Procedures
Multilevel ACDF procedures, such as C4-C7 ACDF, involve treating multiple levels of the cervical spine. While necessary for some patients, these procedures are associated with higher complication rates compared to single-level surgeries.
| Procedure Type | Complication Rate | Common Complications |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Level ACDF | Lower | Dysphagia, Infection |
| Multilevel ACDF | Higher | Nerve damage, Pseudoarthrosis |
Risk Factors for Poor Outcomes
Certain patient factors can increase the risk of complications following ACDF surgery. These include:
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Previous neck surgery
- Poor bone quality
Understanding these risk factors helps us tailor our approach to minimize complications and optimize outcomes for each patient.
By being aware of the potential complications and taking steps to mitigate them, we can improve the safety and efficacy of ACDF surgery for our patients.
Key Fact #7: Cervical Disc Replacement vs. Fusion
We explore the differences between cervical disc replacement and fusion to help patients make informed decisions about their treatment options.
Cervical disc replacement has emerged as a significant alternative to traditional fusion surgery, particularly for younger patients or those with specific cervical spine conditions. While both procedures aim to alleviate pain and restore function, they approach the problem from different angles.
Advantages for Younger Patients
Cervical disc replacement offers several advantages, especially for younger patients. By preserving motion at the operated level, disc replacement can potentially reduce the risk of adjacent segment disease, a common complication of fusion surgery. This is particularly important for younger patients who are more likely to require long-term spinal health.
Studies have shown that cervical disc replacement can maintain cervical spine mobility, which is crucial for reducing stress on adjacent discs and facet joints. This mobility preservation is a key factor in the decision-making process for patients who are active or have a high level of physical demand.
Comparative Outcome Improvements
Comparative studies between cervical disc replacement and fusion have shown varying results, but there is evidence to suggest that disc replacement can lead to improved outcomes in certain patient populations. For instance, some studies indicate that patients undergoing disc replacement may experience faster recovery times and reduced neck pain compared to those undergoing fusion.
However, the success of either procedure heavily depends on patient selection, surgical technique, and post-operative care. We emphasize the importance of a comprehensive evaluation to determine the most appropriate treatment for each individual.
Selection Criteria for Each Approach
The choice between cervical disc replacement and fusion is not straightforward and depends on several factors, including the patient’s age, the specific condition being treated, and the presence of any degenerative changes. For example, patients with significant degenerative disc disease or those requiring multilevel surgery may be more suited to fusion.
In contrast, patients with single-level disc disease and minimal degenerative changes may benefit more from disc replacement. Ultimately, the decision should be made on a case-by-case basis, taking into account the patient’s overall health, lifestyle, and personal preferences.
By carefully evaluating these factors and discussing the potential benefits and risks of each approach, we can help patients make informed decisions about their care.
Latest Advances in ACDF Surgical Techniques
The field of ACDF surgery has witnessed significant innovations in recent years, improving patient outcomes and reducing recovery times. We are now seeing a shift towards more sophisticated and less invasive procedures.
Minimally Invasive Approaches
Minimally invasive ACDF techniques have gained popularity due to their potential to reduce tissue damage, minimize scarring, and accelerate patient recovery. These approaches often involve the use of specialized retractors and microscopes to perform the surgery through smaller incisions.
Benefits of Minimally Invasive ACDF:
- Less muscle disruption and trauma
- Reduced risk of complications
- Smaller scars and improved cosmesis
- Faster return to normal activities
New Fusion Materials and Technologies
Advances in fusion materials and technologies have significantly improved the outcomes of ACDF surgery. New materials such as bioactive glasses and ceramics are being used to enhance fusion rates and reduce the need for autografts.
| Fusion Material | Characteristics | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Bioactive Glasses | Osteoconductive and osteoinductive properties | Enhanced fusion rates, reduced autograft need |
| Ceramic Materials | High compressive strength, biocompatible | Improved structural support, reduced subsidence risk |
| PEEK Cages | Radiolucent, elastic modulus similar to bone | Improved fusion assessment, reduced stress shielding |
Adjunct Posterior Fixation Benefits
The use of adjunct posterior fixation in ACDF surgery has been shown to enhance stability and improve fusion rates, particularly in multilevel procedures. This technique involves supplementing the anterior fusion with posterior instrumentation to provide additional support.
We are committed to staying at the forefront of these advancements, ensuring that our patients receive the most effective and safest treatments available. By combining the latest technologies with our clinical expertise, we can provide personalized care that meets the unique needs of each patient.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About Cervical Fusion
Understanding the benefits and risks of ACDF surgery is crucial for making informed decisions about cervical fusion. We have explored the key facts and considerations that patients should be aware of when evaluating their treatment options.
Patients should be empowered to make informed decisions about their care. By considering the potential outcomes and complications associated with cervical fusion, individuals can better navigate their treatment journey.
Cervical fusion outcomes can vary depending on the levels treated and the specific surgical techniques used. Being aware of the potential risks, such as cervical fusion complications, can help patients prepare for the possibilities and make more informed choices.
We encourage patients to discuss their individual needs and concerns with their healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment. By doing so, individuals can make informed decisions about their ACDF surgery and subsequent care.
What is Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) surgery?
ACDF is a surgical procedure used to treat degenerative cervical spine disease by removing a damaged disc and fusing the surrounding vertebrae to stabilize the spine and alleviate symptoms such as pain, numbness, and weakness.
Why is ACDF a preferred surgical method for treating cervical spine conditions?
ACDF is a preferred method because it is effective in treating conditions such as radiculopathy and myelopathy, and it constitutes about 62% of all cervical spine surgeries due to its high success rate and ability to provide long-term relief.
What are the most common cervical levels treated with ACDF?
The most common levels treated with ACDF are C5-6 and C6-7, as these levels are more prone to degenerative changes and disc herniation, leading to radiculopathy and myelopathy.
What is the difference between single-level and multilevel ACDF procedures?
Single-level ACDF involves treating one level of the spine, whereas multilevel ACDF involves treating multiple levels. Multilevel procedures, such as C4-C7 ACDF, can be more complex and may have a higher risk of complications.
What are the benefits of posterior fixation in ACDF surgery?
Posterior fixation can help reduce complications and improve outcomes by providing additional stability to the spine, especially in multilevel procedures.
What is the recovery process like after ACDF surgery?
The recovery process typically involves immediate post-operative care, followed by a period of rest and rehabilitation, and eventually, physical therapy to help restore strength and mobility to the neck and spine.
What conditions are treated with ACDF at various levels?
ACDF is used to treat conditions such as radiculopathy, myelopathy, and degenerative disc disease, with the choice of treatment depending on the level and severity of the condition.
What are the potential complications and risks associated with ACDF surgery?
Potential complications include those specific to certain cervical levels, as well as increased risks with multilevel procedures, such as higher complication rates and risk factors for poor outcomes.
How does cervical disc replacement compare to fusion?
Cervical disc replacement is an alternative to fusion, especially for younger patients, offering advantages such as preserving motion and reducing the risk of adjacent segment disease.
What are the latest advances in ACDF surgical techniques?
The latest advances include minimally invasive approaches, new fusion materials and technologies, and the use of adjunct posterior fixation, which can improve outcomes and reduce complications.
What are the advantages of minimally invasive ACDF surgery?
Minimally invasive ACDF surgery offers benefits such as smaller incisions, less tissue damage, and reduced recovery time, making it an attractive option for patients.
How is the success rate of ACDF surgery determined?
The success rate of ACDF surgery is determined by factors such as the level treated, the number of levels treated, and the patient’s overall health, with success rates varying depending on these factors.



































