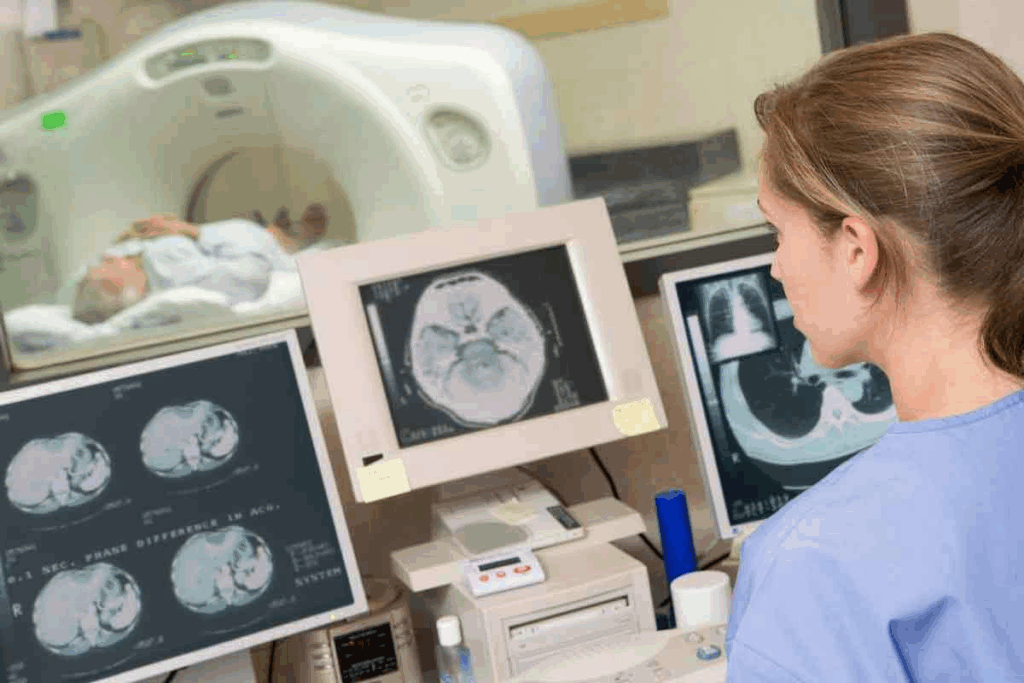
At LivHospital, we use chest computed tomography scans to help patients. These scans are noninvasive and show detailed images of the lungs, heart, and blood vessels. They help us find the right treatment for you.
CT scans use X-rays to take pictures from different angles. Then, a computer makes detailed images. This is key for spotting lung cancer, infections, and other issues. It also helps us understand strange symptoms.
Key Takeaways
- CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images of the body’s internal structures.
- They are key for diagnosing lung cancer, infections, and other conditions.
- A CT scan is a noninvasive imaging technique.
- It uses X-rays to capture images from multiple angles.
- CT scans help in evaluating unexplained chest pain or shortness of breath.
What Is a Chest Computed Tomography Scan: Definition and Technology

A chest computed tomography (CT) scan is a high-tech medical tool. It gives detailed pictures of the chest area. This has changed how doctors diagnose diseases, letting them see inside the chest clearly.
Cross-Sectional Imaging of Chest Structures
Chest CT scans take pictures of the chest in thin slices. They look at the lungs, heart, blood vessels, and more. This cross-sectional imaging is key for spotting many diseases, like lung nodules and heart problems.
CT scans show the chest’s details better than regular X-rays. They help doctors find issues like interstitial lung disease. This is because they can see small changes in lung tissue.
How CT Technology Creates Detailed Thoracic Images
CT scans use X-rays and computers to make body images. When you get a chest CT, you lie on a table that moves into a big machine. The machine takes X-ray pictures from all sides.
Then, a computer turns these pictures into detailed chest images. You can see these images one by one or as 3D models. This helps doctors see the chest’s anatomy well. It’s great for finding and tracking diseases like lung cancer and pulmonary embolism.
A CT chest scan without contrast is good for finding lung nodules and lung diseases. CT tech has gotten better, making pictures clearer and using less radiation. This makes it safer for patients.
Clinical Applications: When and Why Doctors Order a CT Thorax

Doctors use CT thorax scans for many important reasons. These scans help check the chest and the area around it. They give key information about the lungs, heart, and other parts.
Diagnosing Lung Cancer, Infections, and Pulmonary Embolism
Doctors often order a CT thorax scan to check for lung cancer. The scan can spot tumors and see how big they are. It also shows if the cancer has spread.
A CT scan is key in figuring out how serious lung cancer is. This helps doctors plan the best treatment.
CT thorax scans also help find infections and inflammation in the chest. They can spot problems like consolidation or abscesses in the lungs. This helps doctors choose the right treatment.
They are also used to find blood clots in the lungs. This is called a pulmonary embolism. Whether to use contrast or not depends on what the doctor needs to know.
Evaluating Unexplained Chest Pain and Shortness of Breath
When people have unexplained chest pain or trouble breathing, doctors might order a CT thorax scan. These scans can find the cause of these symptoms. It could be something in the heart, lungs, or other parts of the chest.
- They help see how bad lung diseases like emphysema or COPD are.
- They check for injuries to the chest, like broken ribs or lung damage, after an accident.
- They help guide minimally invasive procedures like biopsies or drainages.
Whether to use a ct thorax wo contrast or a scan with contrast depends on the situation. It’s up to the doctor to decide what’s best.
CT Chest Without Contrast: Indications and Benefits
A non-contrast CT scan of the chest is often the first choice for diagnosing chest issues. We use CT chest without contrast to see inside the chest. This helps us find different problems.
This type of scan is great for spotting lung nodules and interstitial lung disease. Non-contrast CT scans show the lung’s details well. They help find small nodules and changes in the lung tissue.
Detecting Lung Nodules and Interstitial Lung Disease
Lung nodules are growths in the lungs that can be harmless or cancerous. CT chest without contrast is good at finding these nodules, even the tiny ones. For example, it can spot nodules as small as 3 mm.
- Finding lung nodules early can lead to better treatment and outcomes.
- Non-contrast CT scans are great for tracking lung nodules over time.
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a group of conditions that cause lung inflammation and scarring. CT chest without contrast helps see how much and how severe ILD is. It shows the lung’s involvement patterns.
When CT Chest W/O Contrast Is Preferred
There are times when a CT chest w/o contrast is better than one with contrast. For instance, people with allergies to contrast or kidney problems might prefer non-contrast scans.
- Those with a history of allergic reactions to iodinated contrast.
- People with severe kidney issues.
- When the main concern is lung disease.
Using premedication to prevent allergic reactions to contrast is debated. So, avoiding contrast with a CT chest without contrast is safer for some patients.
CT Chest With IV Contrast: Enhanced Diagnostic Capabilities
Using IV contrast in a CT chest scan boosts its ability to diagnose. This is key for spotting and treating chest problems.
What Does Chest CT Scan With Contrast Show
A chest CT scan with contrast reveals the blood vessels, organs, and more. The contrast agent makes these parts stand out, helping spot issues.
IV contrast is great for:
- Seeing blood vessels clearly
- Telling tumors apart from other growths
- Finding problems like aneurysms
Differentiating Tumors and Enhancing Vascular Structures
IV contrast makes tumors and normal tissue easier to tell apart. Tumors show up differently on scans, making them easier to spot.
The contrast is given at a rate of 5 to 7 mL/s. A common method is 80 mL of contrast at 5 mL/s, then 40 mL of saline at the same rate. This method enhances vascular and lesion details.
Key benefits of using IV contrast in CT chest scans include:
- Spotting small tumors and lesions better
- Seeing vascular anatomy and problems clearly
- Understanding what lesions and tumors are
Preparation for CT Scan of Chest: Patient Guidelines
Getting ready for a CT scan of the chest is key to getting good results and a smooth process. We know it can feel scary to go through a medical test. So, we’re here to help you get ready.
Fasting Requirements and Medication Considerations
For some CT scans, you might need to fast for a few hours before. Fasting requirements mean not eating or drinking for 2-4 hours before the scan. It’s important to follow these rules to get the best scan results.
Talk to your doctor about any medicines you’re taking. Some medicines might need to be changed or stopped before the scan. Always check with your doctor before changing your medicine.
Kidney Function Testing Before Contrast Administration
If your scan uses contrast dye, we might ask for a kidney function test. This is because contrast dye can be hard on the kidneys, if they’re not working well.
“Patients with a history of prior allergic-type reaction to iodinated contrast are at risk for a recurrent reaction upon future contrast administration.” This shows why it’s important to know your medical history before getting a scan with contrast.
| Kidney Function Test | Purpose | Implication for CT Scan |
|---|---|---|
| Serum Creatinine Test | Measures kidney function by assessing waste product levels in the blood. | If kidney function is impaired, alternative imaging methods or precautions may be considered. |
| eGFR (estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate) | Estimates the rate at which kidneys filter waste from the blood. | A lower eGFR may indicate kidney disease, necessitating adjustments in contrast dosage or choice of imaging modality. |
Day-of-Scan Instructions and What to Bring
On the day of your CT scan, arrive at least 30 minutes early. Wear comfy, loose clothes and avoid metal jewelry or clothes.
- Bring any relevant medical records, including previous imaging studies.
- Have a list of your current medications and dosages.
- If you have a history of allergies or reactions to contrast dye, inform the staff.
By following these steps, you’ll be ready for your CT scan of the chest. This will make your experience successful and stress-free. If you have any questions or concerns, talk to your healthcare provider.
The Chest Computed Tomography Scan Procedure: Step by Step
A CT scan of the chest is a detailed imaging method. It needs careful preparation and execution. Knowing the steps can ease worries and make the experience smoother for patients.
Before Entering the Scanner: Positioning and Contrast Administration
A radiographer will guide you before the scan starts. “The radiographer is a trained medical imaging professional who will carry out your scan and support you during the procedure,” ensuring you’re comfortable and informed.
The radiographer will place you on the CT scanner table, usually on your back. They might use straps or pillows to keep you in the right spot. If contrast is needed, it’s given through an IV line in your arm or hand. This agent makes certain chest areas, like blood vessels or tumors, stand out on the CT images.
During the Scan: Breathing Instructions and Scan Duration
Once you’re set and the contrast is given (if needed), the CT scanner table will move into the scanner. You’ll be asked to hold your breath for short periods, usually 10-15 seconds. This ensures clear images are captured. The scanning itself is quick, taking just a few minutes.
During scanning, the scanner rotates around you, taking detailed images of your chest. You might hear a clicking or whirring noise. But you can talk to the radiographer through an intercom system.
Immediate Post-Scan Care and Follow-up
After the scan, the radiographer will help you off the table and check if you’re okay. If you got contrast, you’ll be watched for any bad reactions.
Your CT scan images will then be reviewed by a radiologist, who will interpret the results and give a report to your doctor. You might get your results quickly, within hours, or a bit later, in a few days.
“The detailed images from a CT scan of the chest can provide critical information for diagnosing and treating a range of conditions, from lung cancer to cardiovascular disease.”
We know a CT scan can make patients anxious. But knowing the steps can help you feel more ready and at ease during the procedure.
Interpreting Thoracic CT Scan Results: From Images to Diagnosis
Understanding thoracic CT scans is key. We need radiologists to analyze images and help with patient care.
Normal Anatomy on Computed Tomography Thorax
Knowing normal thoracic anatomy is vital. On a CT scan, we see the lungs, heart, and more. The lungs are dark because they’re filled with air. The heart and blood vessels show up because they’re denser.
Key structures visible on a CT thorax include:
- The trachea and bronchi
- Pulmonary arteries and veins
- The heart and its chambers
- Mediastinal lymph nodes
Common Pathological Findings and Their Clinical Significance
CT scans can show many conditions. We often see lung nodules, masses, and pleural effusions. Where and how big these are matters a lot.
For example: A lung nodule might be harmless or cancer. Its look on the scan tells us what to do next. Consolidations could mean pneumonia or other issues.
The Radiologist’s Role in Analysis and Reporting
Radiologists are vital in reading CT scans. They look at images, match them with patient info, and write detailed reports. These reports help doctors plan treatments and check on patients.
A radiologist said, “Getting imaging right is key for patient care. We aim to give reports that help doctors make the best choices.”
Safety Considerations: Radiation Exposure and Contrast Risks
When we use CT technology for chest imaging, we must think about safety. Chest CT scans expose us to radiation and contrast agents. Both have risks.
Understanding Radiation Dose in Standard vs. Low-Dose CT Chest Scan
CT scans carry a risk of radiation exposure. New CT tech has led to low-dose CT chest scans. These scans use less radiation but keep image quality high.
A standard chest CT scan gives about 7 millisieverts (mSv) of radiation. But a low-dose scan cuts this to around 1.5 mSv. This is similar to a chest X-ray.
Low-dose scans are great for patients needing many scans. This is true for those with ongoing conditions or watching lung nodules. Choosing low-dose scans helps lower total radiation exposure.
Potential Contrast Reactions and Contraindications
Contrast agents are another safety concern. While mostly safe, iodinated contrast can cause problems in some. Past allergic reactions to these agents increase the risk of future ones.
Patients with past reactions might get corticosteroids and antihistamines before a scan. For those at high risk, other imaging options or non-contrast scans might be better.
Balancing Diagnostic Benefits Against Risks
Healthcare providers must think about risks and benefits when ordering a CT scan. They consider the patient’s history and the question being asked. They also look at if other scans could work just as well.
Often, the benefits of a CT scan are worth the risks. This is true when the scan will change how the patient is treated. By knowing the risks and taking steps to reduce them, we use CT scans wisely.
Conclusion: Advancing Chest Diagnosis Through CT Technology
CT technology is making big strides, and chest diagnosis is getting better. New cardiac imaging tools, like CT scans, help us see heart problems more clearly. This is a big win for heart health.
Cardiac imaging is key in heart medicine. It gives doctors tools to check on heart health. CT scans have changed how we treat chest problems, helping us catch issues early.
As CT tech gets better, we’ll see even clearer chest images. This means better diagnosis and treatment for chest issues. CT scans will keep being a big part of heart medicine’s future.
Chest CT scans are a game-changer for diagnosing chest problems. As we keep improving, CT scans will lead the way in medical imaging. This will help us care for patients better and get better results.
FAQ
What is a chest CT scan?
A chest CT scan is a test that uses X-rays and computer tech to show detailed images of the chest. It looks at the lungs, heart, and blood vessels.
What is the difference between a CT chest with contrast and without contrast?
A CT chest with contrast uses a special dye to highlight certain areas. This dye is given through a vein. Without contrast, the scan looks for lung nodules or lung disease.
Why is contrast used in a CT chest scan?
Contrast makes certain structures or problems more visible. This helps doctors spot tumors, blood clots, or other issues. It’s key for diagnosing lung cancer or blood clots in the lungs.
How do I prepare for a CT scan of the chest?
To prepare, you might need to fast for a few hours. Remove any metal items and tell your doctor about your medications. If contrast is used, your kidney function might be checked first.
What happens during a CT chest scan?
During the scan, you lie on a table that moves into a CT scanner. You might get breathing instructions. The scan takes just a few minutes. If contrast is used, it’s given through a vein beforehand.
Are there any risks associated with CT scans?
Yes, there are risks like radiation and reactions to the dye. But, the benefits usually outweigh these risks. Low-dose scans are used when possible to reduce risks.
How are CT scan results interpreted?
A radiologist looks at the images to find any problems. They report the findings to your doctor. Your doctor will then talk to you about what the results mean and what to do next.
What is a low-dose CT chest scan?
A low-dose CT scan uses less radiation. It’s safer for people at high risk for lung cancer.
Can I undergo a CT scan if I have kidney problems?
If you have kidney issues, you might need special care before a CT scan with dye. The dye could harm your kidneys. Your doctor will weigh the risks and might suggest other tests.
How long does it take to get the results of a CT chest scan?
The time to get results varies. It depends on the facility and how urgent the scan is. Sometimes, results are ready in hours, but it can take a day or more.
What are the benefits of a CT chest scan?
CT chest scans give detailed images. They help diagnose many conditions, like lung cancer, blood clots, and infections. This leads to timely and effective treatment.
Can a CT chest scan detect lung cancer?
Yes, a CT chest scan can find lung cancer, mainly in those at high risk. Low-dose CT scans are often used for early detection.
References
- NHS. (2023). CT scan. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/ct-scan/



































