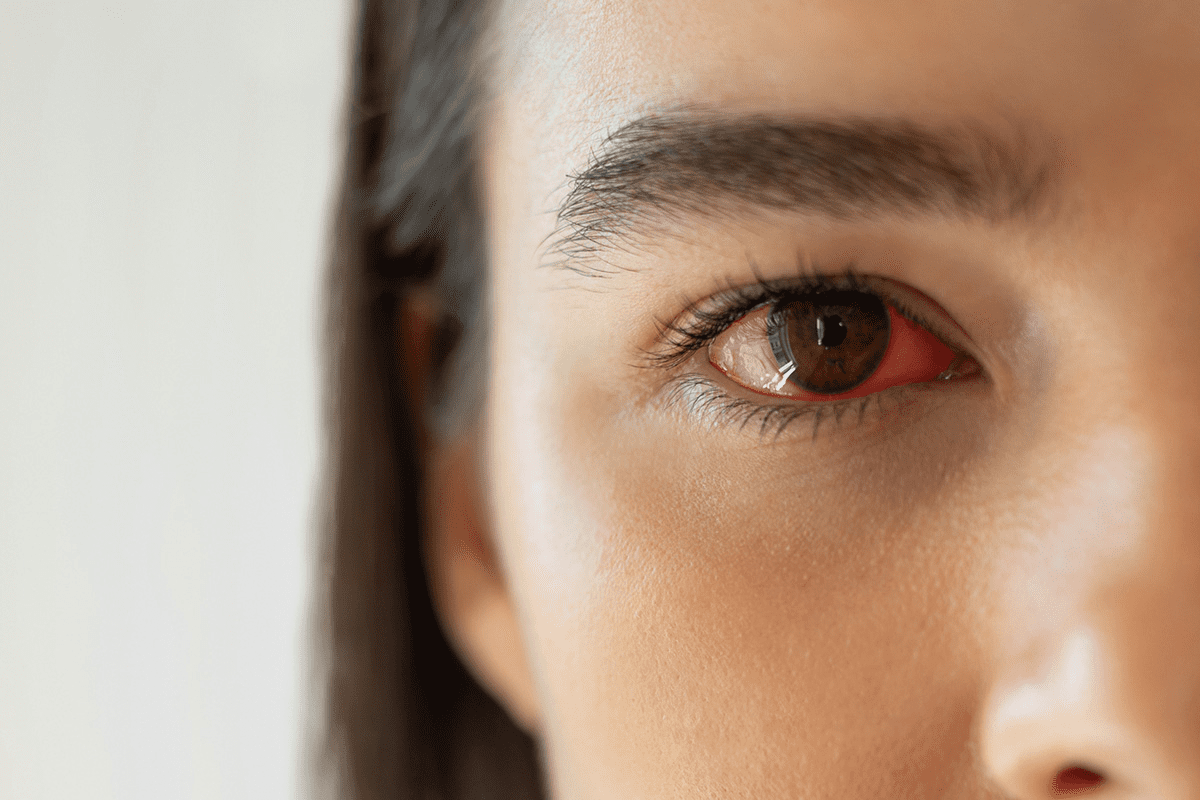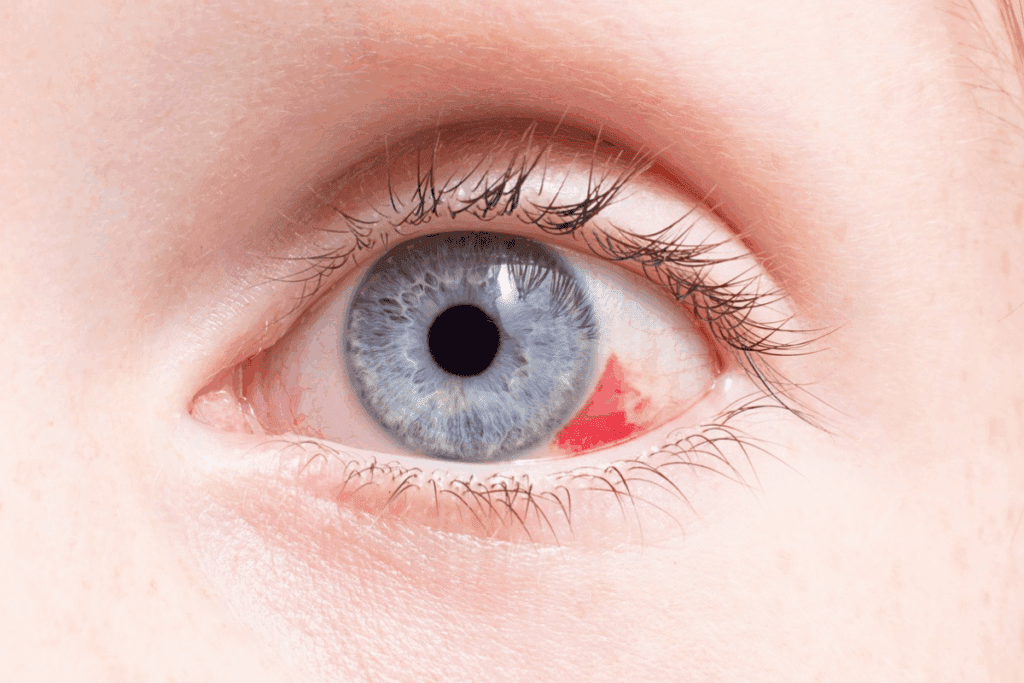
Seeing the white of your eye stay red can be scary. The white part of the eye, called the sclera, looks red when its blood vessels get bigger. This can happen for many reasons, like irritation, allergies, infections, or other health issues chronic eye redness.
At Liv Hospital, we know how important it is to find out why your eye is red. We use the latest tools and our top-notch eye care team to figure out what’s going on. This way, we can give you the best care possible.
Key Takeaways
- Redness in the white of the eye can be caused by various factors, including irritation, allergies, and infections.
- The condition can be a symptom of an underlying medical issue that needs attention.
- Liv Hospital’s advanced diagnostic capabilities help identify the cause of persistent redness.
- A patient-centered approach ensures comprehensive care for international patients.
- Understanding the cause is key to finding the right treatment.
Understanding Eye Anatomy and Redness
Eye redness can be alarming, but to comprehend its causes, we must first dive into the eye’s anatomy. The eye is a complex organ, with many parts working together to give us vision. Knowing these parts is key to figuring out why the white part of the eye might turn red.
The Structure of the White Part of the Eye
The white part of the eye is called the sclera. It protects and gives structure to the eye. A thin membrane called the conjunctiva covers the sclera and also lines the eyelids. This membrane has tiny blood vessels that are usually not seen.
The conjunctiva plays a significant role in eye redness. When these blood vessels get inflamed or irritated, the eye can look red or bloodshot. This can happen due to many reasons, like environmental irritants, allergies, or infections.
How Blood Vessels Affect Eye Appearance
Blood vessels in the conjunctiva can greatly affect the eye’s look. Normally, these vessels are not very visible. But when they get dilated or damaged, they can make the eye look red.
A subconjunctival hemorrhage happens when a blood vessel in the conjunctiva bursts. This leads to blood leaking under the conjunctiva, making a big part of the white eye turn bright red. Even though it looks scary, this condition is usually harmless and goes away on its own.
“The presence of redness in the eye often indicates an underlying issue that needs attention. Understanding the role of blood vessels in the conjunctiva can help in diagnosing the cause of eye redness.”
The table below summarizes the key points related to eye anatomy and redness:
Component | Function | Relation to Redness |
Sclera | Provides protection and structure | Visible redness due to underlying conditions |
Conjunctiva | Covers the sclera and lines the eyelids | Contains blood vessels that can cause redness when inflamed |
Blood Vessels | Supply oxygen and nutrients | Can become dilated or damaged, leading to redness |
By understanding the eye’s anatomy and how its parts can affect its look, we can better find out why the white part of the eye turns red. This helps us seek the right treatment.
Common Causes of Chronic Eye Redness
Chronic eye redness can really disrupt our daily lives. It’s important to know what causes it to find a solution. This issue can stem from environmental irritants, our lifestyle, or underlying health problems.
Environmental Irritants
Things around us can cause eye redness. Dry air, too much sun, and pollution are big culprits.
Dry air dries out our eyes, causing irritation. Not wearing eye protection in the sun can also strain our eyes and make them red.
Lifestyle Contributors
Our daily habits can also lead to eye redness. Too much screen time, smoking, and not getting enough sleep are big factors.
Looking at screens for too long can make our eyes dry and red. Smoking harms our eyes by exposing them to harmful chemicals and reducing tear quality.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Some health issues can also cause eye redness. Allergies, infections, and autoimmune diseases are examples.
Allergies can make our eyes red, itchy, and watery. Infections like conjunctivitis can also cause redness, along with discharge and discomfort.
Cause | Description | Examples |
Environmental Irritants | Factors in the environment that irritate the eyes | Dry air, pollution, UV radiation |
Lifestyle Contributors | Habits and choices that affect eye health | Prolonged screen time, smoking, inadequate sleep |
Underlying Medical Conditions | Health issues that cause or worsen eye redness | Allergies, infections, autoimmune disorders |
Distinguishing Between Temporary and Persistent Redness
It’s important to know the difference between temporary and persistent eye redness. This helps decide when to see a doctor. Eye redness can come from many things, from small irritants to serious health issues.
Normal Duration of Eye Redness
Eye redness from minor irritants or allergies usually goes away in a day or two. For example, redness from dust or pollen goes away when the irritant is gone or with eye drops.
Factors Influencing Eye Redness Duration:
- Exposure to irritants
- Allergic reactions
- Dry eye syndrome
- Infections
When Redness Becomes a Concern
If eye redness lasts more than one to two days, it’s time to see a doctor. This is true if you also have pain, vision changes, or discharge. Long-lasting redness might mean there’s a problem that needs fixing.
Symptom | Possible Cause | Action |
Redness with pain or vision changes | Possible infection or inflammation | Seek medical attention |
Redness with discharge | Possible infection | Consult a doctor |
Redness without other symptoms | Minor irritant or allergy | Monitor, consider over-the-counter relief |
As an expert once said,
“The eyes are the windows to the soul, and redness can be a sign of what’s going on inside.”
This quote isn’t about medical diagnosis. But it shows how important eye health is.
In summary, while temporary eye redness is common, long-lasting redness might be serious. Knowing how long it lasts and what else happens can help decide when to get medical help.
Dry Eye Syndrome and Its Impact on Scleral Redness
It’s important to know about dry eye syndrome to tackle chronic scleral redness. This redness can mess with your vision and make your eyes uncomfortable. Dry eye happens when your eyes don’t make enough tears or when the tears are not good.
Symptoms and Characteristics
Dry eye syndrome shows up in many ways, like persistent dryness, grittiness, and redness in the eyes. You might also see blurred vision, light sensitivity, and eye tiredness.
People can experience different symptoms. But common ones include:
- Dryness or grittiness in the eyes
- Redness or inflammation
- Blurred vision
- Sensitivity to light or wind
- Eye fatigue or heaviness
Risk Factors for Dry Eye
There are several things that can make you more likely to get dry eye syndrome. These include:
Risk Factor | Description |
Age | Dry eye is more common in older people because they make fewer tears. |
Environmental Conditions | Being in dry, windy, or dusty places can make dry eye worse. |
Contact Lens Use | Wearing contact lenses can lower tear production and raise dry eye risk. |
Eye Surgery | Some eye surgeries, like LASIK, can lead to dry eye. |
Connection to Chronic Redness
Dry eye syndrome is closely tied to chronic scleral redness. Not having enough tears can cause inflammation and irritation. This makes the eyes look red. It’s key to manage dry eye to reduce chronic redness and improve eye health.
By understanding dry eye syndrome, we can tackle chronic scleral redness better. This helps us find effective ways to manage it.
Episcleritis: A Leading Cause of Scleral Redness
The episclera is a thin layer on the sclera’s surface. When it gets inflamed, it leads to episcleritis. This condition is a big reason for scleral redness and can be quite uncomfortable.
Symptoms and Appearance
Episcleritis shows up as redness and inflammation of the episclera. Symptoms can be mild or severe and may include discomfort or irritation. Pain is usually not as bad as in other conditions like scleritis.
The look of episcleritis can vary. Some cases have a diffuse redness, while others show nodules.
Key symptoms include:
- Redness of the sclera
- Mild irritation or discomfort
- Possible presence of nodules
Diagnosis and Prevalence
To diagnose episcleritis, we do a detailed eye exam. We look for inflammation on the episclera and rule out other conditions. Episcleritis is relatively common among inflammatory eye conditions.
Diagnosis involves:
- A thorough medical history
- Slit-lamp examination to see the episclera
- Other tests to check for systemic conditions
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for episcleritis aims to reduce inflammation and ease symptoms. We might suggest lubricating eye drops for comfort. Sometimes, we use topical corticosteroids or NSAIDs to fight inflammation.
Common treatments include:
- Lubricating eye drops
- Topical corticosteroids
- NSAIDs
Scleritis: When Deeper Eye Tissues Become Inflamed
When the deeper parts of the eye get inflamed, it’s called scleritis. This serious eye disease affects the sclera, the white outer layer. It can also be linked to other health issues. Scleritis is a serious condition that needs quick medical help.
Recognizing Scleritis Symptoms
Scleritis can cause severe eye pain, redness, and tenderness. The pain feels deep and boring, sometimes spreading to the forehead or jaw. Other signs include light sensitivity, blurry vision, and tearing. It can also make vision worse.
Common symptoms of scleritis include:
- Severe eye pain
- Redness and tenderness
- Sensitivity to light
- Blurred vision
- Tearing
- Decreased visual acuity
Associated Systemic Conditions
Scleritis often links to conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or granulomatosis with polyangiitis. These diseases can cause inflammation in the eyes. Treating these conditions is key to managing scleritis.
Systemic Condition | Association with Scleritis |
Rheumatoid Arthritis | Commonly associated with scleritis, mainly in severe cases. |
Lupus | Can cause scleritis as part of its symptoms. |
Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis | May cause scleritis due to its vasculitic nature. |
Potential Complications
If scleritis isn’t treated, it can cause vision loss, glaucoma, and cataracts. The inflammation can also change the eye’s structure, leading to permanent damage.
Quick medical care is key to avoid these problems and keep vision safe.
We know how important early diagnosis and treatment are for scleritis. Recognizing symptoms and understanding related conditions help us care for patients effectively. This approach helps prevent long-term damage and keeps vision safe.
Types of Conjunctivitis Causing Persistent Redness
Redness that doesn’t go away can be a sign of conjunctivitis. This is an inflammation or infection of the conjunctiva. The conjunctiva is the clear membrane covering the white part of the eye and the inside of the eyelids. We will look at the different types of conjunctivitis that can cause persistent redness.
Bacterial Conjunctivitis
Bacterial conjunctivitis is caused by bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pneumoniae. It has a purulent discharge, redness, and swelling of the conjunctiva. This type is contagious and spreads through direct contact with the discharge.
Symptoms: Redness, discharge, itching, and irritation.
Viral Conjunctivitis
Viral conjunctivitis is caused by viruses such as adenovirus or herpes simplex virus. It has watery discharge, redness, and sometimes pre-auricular lymphadenopathy. This type is highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets or direct contact.
Symptoms: Watery discharge, redness, sensitivity to light.
Allergic Conjunctivitis
Allergic conjunctivitis happens when the conjunctiva reacts to an allergen like pollen, dust, or pet dander. Symptoms include itching, redness, and swelling. This type is not contagious.
Symptoms: Itching, redness, swelling, watery discharge.
Giant Papillary Conjunctivitis
Giant papillary conjunctivitis (GPC) is linked to contact lens use, mainly rigid lenses. It causes large papillae on the underside of the upper eyelid, leading to irritation and redness.
Symptoms: Irritation, redness, blurred vision, discomfort.
Type of Conjunctivitis | Cause | Symptoms |
Bacterial | Bacteria (e.g., Staphylococcus aureus) | Redness, purulent discharge, itching |
Viral | Viruses (e.g., adenovirus) | Watery discharge, redness, sensitivity to light |
Allergic | Allergens (e.g., pollen, dust) | Itching, redness, swelling, watery discharge |
Giant Papillary | Contact lens use | Irritation, redness, blurred vision, discomfort |
When One Eye Is Affected: Unilateral Redness Concerns
It’s puzzling when one eye turns red and the other stays clear. Unilateral eye redness can stem from infections, injuries, or foreign objects in the eye.
Potential Causes of Single Eye Redness
Redness in one eye can be due to several reasons. These include:
- Infections such as conjunctivitis or keratitis
- Foreign bodies or irritants in the eye
- Injuries or trauma to the eye
- Subconjunctival hemorrhage
- Inflammatory conditions like episcleritis or scleritis
Knowing the cause is key to treating it and easing symptoms.
Evaluating Severity of Unilateral Symptoms
The severity of unilateral eye redness can differ greatly. When assessing severity, consider:
Symptom | Mild | Moderate | Severe |
Redness | Minimal redness | Noticeable redness | Intense redness |
Pain | No pain | Mild discomfort | Significant pain |
Vision | Normal vision | Blurred vision | Significantly impaired vision |
These factors help gauge the condition’s severity and if medical help is needed.
When the Corner or Side of the Eye Is Red
Redness at the corner or side of the eye is alarming. It might be linked to:
- Conjunctivitis
- Inflammation of the lacrimal gland
- Blockage of the tear ducts
If you notice redness in the corner or side of your eye, seeing an eye care professional is vital. They can find the cause and treat it.
Diagnostic Procedures for Chronic Eye Redness
A thorough eye check is key to finding why your eyes stay red. At the eye doctor, you’ll get a detailed check to find what’s causing your symptoms.
What to Expect at the Eye Doctor
The eye doctor will start by asking about your health history. They’ll want to know about your symptoms, daily life, and any past eye issues. This helps them guess what might be causing your red eyes.
A detailed eye exam will follow. This might include tests to see how well you can see and a look at your eye’s outside and inside parts.
Common Tests and Examinations
Several tests can help figure out why your eyes are red. These include:
- Slit-lamp examination to inspect the anterior segment of the eye
- Conjunctival or corneal scraping for cytology or culture
- Tear film assessment to check for dry eye syndrome
- Intraocular pressure measurement
Here’s a quick look at common tests in a table:
Test | Purpose |
Slit-lamp examination | Inspect anterior segment |
Conjunctival or corneal scraping | Cytology or culture for infection |
Tear film assessment | Diagnose dry eye syndrome |
Specialized Testing for Persistent Cases
If your eye redness doesn’t go away after the first checks, specialized testing might be needed. This could include imaging or lab tests to check for other health issues.
Warning Signs That Require Immediate Medical Attention
It’s important to know the warning signs that mean you need to see a doctor right away. Eye health is critical, and knowing when to act fast can help a lot.
Pain and Vision Changes
Pain or vision changes can mean something serious is going on. If you see things blurry, double, or if your vision goes away, get help fast. Don’t ignore pain that’s bad, lasts a long time, or comes with redness or discharge.
Discharge and Other Concerning Symptoms
Discharge with redness, swelling, or light sensitivity might mean an infection. Also, watch for floaters, eye tiredness, or changes in how your eyes look.
Symptom | Possible Cause | Action Required |
Pain and Redness | Inflammation or Infection | Seek immediate medical attention |
Vision Changes | Various conditions including retinal detachment | Urgent medical evaluation |
Discharge | Infection (bacterial or viral) | Consult a healthcare professional promptly |
Emergency Situations
For acute eye injuries, chemical exposure, or sudden vision loss, get emergency care fast. These can cause permanent damage if not treated quickly.
Knowing these signs and acting fast can greatly help your eye health. If you notice any of these symptoms, get medical help right away.
Treatment Options for Persistent Eye Redness
Dealing with persistent eye redness requires knowing your treatment options. The right approach depends on finding the cause. This could be from environmental irritants or medical conditions.
Over-the-Counter Solutions
For mild eye redness, over-the-counter (OTC) products can help. These include:
- Artificial tears to lubricate the eyes
- Antihistamine eye drops for allergic reactions
- Decongestant eye drops to reduce redness
It’s important to use these products wisely. Using decongestants too long can cause more redness.
Prescription Medications
If OTC solutions don’t work, you might need prescription drugs. These include:
- Antibiotic eye drops for bacterial infections
- Anti-inflammatory eye drops for conditions like episcleritis
- Immunosuppressive drugs for severe inflammatory conditions
Always use prescription medications as directed by an eye doctor.
Addressing Underlying Conditions
Eye redness can be a sign of a deeper issue. This might involve:
- Treatment for dry eye syndrome
- Management of allergies
- Control of systemic diseases like rheumatoid arthritis
Fixing the underlying problem can help reduce eye redness.
When Eye Redness Is Painful to Touch
If eye redness hurts when touched, it could be serious. This might mean you have scleritis. You need to see a doctor right away. Treatment might include:
Condition | Treatment Approach |
Scleritis | Oral NSAIDs or corticosteroids |
Episcleritis | Topical NSAIDs or corticosteroids |
Finding out why your eyes are red is the first step to treatment. Always talk to an eye doctor to find the best solution.
Conclusion
Chronic eye redness can be a lasting concern, often pointing to a deeper issue that needs a doctor’s check-up. We’ve looked into many reasons for this, like environmental factors, lifestyle habits, and serious health issues like dry eye, episcleritis, and scleritis.
Knowing why your eyes stay red is key to figuring out what to do next. We talked about how to tell if the redness is just temporary or if it’s a sign of something more serious. We also covered how doctors find out what’s causing the redness.
In short, don’t ignore eye redness that lasts. We stress the need to see a doctor if your eyes stay red for a long time. Getting help early can ease your symptoms and fix any health problems. By understanding the reasons and getting the right care, you can feel better and keep your eyes healthy.
FAQ
Why is the white of my eye red and not going away?
The white of your eye, or sclera, can turn red for many reasons. This includes things like environmental irritants, lifestyle choices, and health issues. If the redness doesn’t go away, you should see a doctor to find out why and get the right treatment.
What are the common causes of chronic eye redness?
Chronic eye redness can come from many sources. This includes things like dry eye syndrome, episcleritis, scleritis, and different kinds of conjunctivitis.
How can I distinguish between temporary and persistent eye redness?
Temporary eye redness usually goes away on its own. But if the redness lasts a long time or comes with other symptoms, you should see an eye doctor.
What is dry eye syndrome, and how does it contribute to chronic redness?
Dry eye syndrome means your eyes don’t make enough tears or the tears aren’t good quality. This can make your eyes red and irritated. It’s a common reason for red eyes.
What is episcleritis, and how is it treated?
Episcleritis is an inflammation of the thin layer on top of the sclera. It causes redness, irritation, and sometimes pain. Treatment includes eye drops and, in some cases, anti-inflammatory medicines.
What is scleritis, and what are its symptoms?
Scleritis is a serious inflammation of the sclera. It causes severe pain, redness, and sensitivity to light. It can be linked to other health issues and needs quick medical attention.
Can conjunctivitis cause persistent eye redness?
Yes, conjunctivitis, including bacterial, viral, allergic, and giant papillary conjunctivitis, can cause long-lasting eye redness. The treatment depends on the type and cause of conjunctivitis.
Why is only one eye red, and what are the possible causes?
One eye being red can be due to many things, like infection, injury, or a condition affecting just one eye. Seeing an eye doctor is important to find the cause and get the right treatment.
What can I expect during a visit to an eye doctor for chronic eye redness?
At an eye doctor’s visit, you’ll get a full check-up. This includes looking at your medical history, a visual exam, and possibly some tests. The doctor will try to find out why your eyes are red.
What are the warning signs that require immediate medical attention?
Signs that mean you need to see a doctor right away include severe pain, vision changes, discharge, and other concerning symptoms. If you have any of these, get help fast.
What are the treatment options for persistent eye redness?
Treatment for long-lasting eye redness depends on the cause. It might include over-the-counter or prescription medicines, or treating any underlying health issues. Sometimes, special treatments are needed.
Why is my eye red but not itchy?
If your eye is red but not itchy, it could be due to several reasons. This includes dry eye syndrome, episcleritis, or scleritis. It’s important to see an eye doctor to find out why and get the right treatment.
Why is the corner or side of my eye red?
Redness in the corner or side of your eye can be caused by many things. This includes dry eye syndrome, infection, or irritation. If the redness doesn’t go away or comes with other symptoms, you should see an eye doctor.
Can eye redness be painful to touch?
Yes, eye redness can hurt when touched, like in cases of scleritis or other inflammatory conditions. If touching your eye hurts, you should get medical help.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Red Sclera: Causes, Irritation, Allergies, and Infections. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24150470/