A cleft lip and/or palate is a major birth defect that affects millions of newborns every year. The CDC says cleft lip with or without cleft palate happens in about 1 in 1,032 births in the US. This means over 3,500 babies in the US are affected each year.
We are dedicated to giving full care to those with congenital malformations. This condition changes how a baby looks and can make eating, speaking, and growing harder. By looking closely at cleft lip and/or palate, we hope to spread the word and help people understand more about it and other birth defects.Discover a Classic Congenital Anomaly Example and understand its implications. Learn about the features and medical considerations of this condition.
Key Takeaways
- A cleft lip and/or palate is a common congenital anomaly worldwide.
- The condition affects over 3,500 babies annually in the US.
- A cleft lip and/or palate has implications for feeding, speech, and overall development.
- Comprehensive care is key for those with this condition.
- It’s important to raise awareness to help people understand and support.
Understanding Congenital Anomalies: Definition and Overview
It’s key to understand congenital anomalies to help those affected. These are birth defects that happen during fetal development. They can greatly affect a person’s life, so knowing about them is vital.
What Are Congenital Anomalies?

Congenital anomalies are changes in the body structure at birth. They can be big or small and affect a person’s life differently. Big anomalies need medical help, while small ones might not, but can affect looks or function.
Global Prevalence and Statistics
Worldwide, about 6% of babies are born with congenital anomalies. This leads to around 300,000 baby deaths each year. It shows we need better healthcare for these families.
Classification of Structural Birth Defects
Birth defects are sorted by how severe they are and what part of the body they affect. This helps doctors know how to treat them. Defects are often grouped as single or multiple, and then by cause or affected area.
Understanding congenital anomalies is critical for proper care. Knowing about them helps healthcare teams improve the lives of those affected.
Cleft Lip and Palate: Classic Congenital Anomaly Example
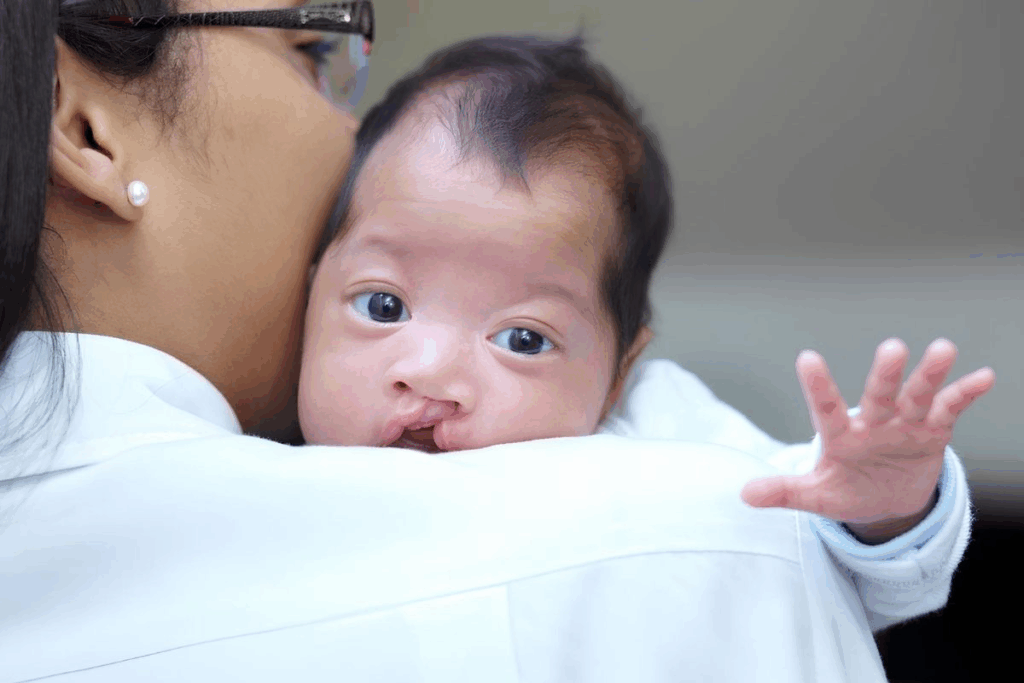
Cleft lip and palate a common birth defects. It affects the upper lip and the roof of the mouth. We help those with this condition, understanding its effects on their lives.
Anatomy and Formation of Cleft Lip/Palate
Cleft lip and palate happen when the lip or palate doesn’t form properly in the womb. This can cause a gap in the lip or roof of the mouth. The size and location of the gap can vary a lot.
Prevalence in the United States
In the US, cleft lip and palate happen in about 1 in 1,032 births. This means over 3,500 babies are affected each year. It shows how important it is to know about and care for this condition.
Impact on Feeding, Speech, and Development
A cleft lip and/or palate can make eating and speaking hard. Babies might have trouble feeding because of the shape of their mouths. As they get older, they might need speech therapy to help with speaking.
Getting help from a team of experts is key to overcoming these challenges.
Social and Psychological Considerations
Cleft lip and palate can also affect a person’s feelings and how they see themselves. The visible nature of the condition can cause social and emotional issues, mainly in kids and teens. We offer not just medical help but also emotional support to face these challenges.
5 Other Common Congenital Anomalies
There are many congenital anomalies aside from cleft lip and palate. These conditions can greatly affect a person’s health and quality. They often require medical care.
Congenital Heart Defects
Congenital heart defects are common in newborns worldwide. They affect the heart’s structure and function. Examples include atrial septal defects, ventricular septal defects, and tetralogy of Fallot.
Thanks to better prenatal screening and surgery, many children now live healthier lives.
Neural Tube Defects
Neural tube defects, like spina bifida, happen when the neural tube doesn’t close properly. Spina bifida can cause mobility and cognitive problems. Preventing these with folic acid before and during pregnancy is key.
Knowing the causes and how to prevent them is vital.
Down Syndrome and Other Chromosomal Conditions
Down syndrome is caused by an extra chromosome 21. It leads to developmental and intellectual disabilities. Other conditions include Turner and Klinefelter syndromes. Early diagnosis and help can greatly improve life quality.
Support for families is very important.
Limb Reduction Defects
Limb reduction defects mean one or more limbs are missing or underdeveloped. These can vary a lot in severity. Better prosthetics and rehab have helped many.
Understanding what causes these defects is key to prevention.
These anomalies show how complex and varied birth defects are. Knowing their causes and treatments helps improve lives. Awareness and support are essential for those affected.
Causes and Risk Factors for Developmental Abnormalities
It’s important to know what causes developmental abnormalities. This knowledge helps us prevent and treat these issues. Congenital anomalies come from genetics, environment, and social factors.
Genetic Factors and Inheritance Patterns
Genetics is key to congenital anomalies. Chromosomal abnormalities and single-gene disorders can cause them. Knowing how genes are passed down is vital for family planning.
- Autosomal dominant inheritance
- Autosomal recessive inheritance
- X-linked inheritance
Environmental Exposures During Pregnancy
What a mother is exposed to in pregnancy affects the baby. Maternal exposure to teratogens, like some chemicals, can harm the fetus. Keeping the prenatal environment safe is critical.
- Avoiding alcohol and tobacco
- Minimizing exposure to pollutants
- Managing chronic conditions
Maternal Health Considerations
Maternal health is vital for the baby’s development. Conditions like diabetes and infections in pregnancy can raise the risk of anomalies. Good prenatal care and managing health are key.
Socioeconomic and Demographic Influences
Socioeconomic and demographic factors also play a role. Socioeconomic status affects healthcare access, nutrition, and environmental exposure. Tackling these disparities is essential to lowering anomaly rates.
- Access to prenatal care
- Nutritional status
- Exposure to environmental hazards
Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support Systems
Managing congenital anomalies starts with early detection and action. We’ve made big steps in prenatal screening and diagnosis. This has helped us better handle these conditions.
Prenatal Screening and Diagnostic Methods
Prenatal screening is key in today’s prenatal care. It helps spot congenital anomalies early. Ultrasound technology and maternal serum screening are used for this. Sometimes, tests like amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS) are needed for a clear diagnosis.
Surgical and Medical Interventions
After finding a congenital anomaly, a team creates a treatment plan. Surgical interventions are often needed to fix structural issues. New surgical methods have led to better results for many conditions. Medical management also helps with related health problems.
Long-Term Care and Follow-up
Congenital anomalies need ongoing care after treatment. We stress the need for long-term follow-up. This ensures development is tracked and any new problems are caught early. A team of healthcare experts, including pediatricians and surgeons, is involved.
Family Support Resources
Dealing with a congenital anomaly is tough for families. We offer support resources like counseling and support groups. These help families cope with the challenges of caring for a child with a congenital anomaly. They also provide emotional support during hard times.
With early detection, effective treatment, and strong support, we can greatly improve life for those with congenital anomalies and their families.
Conclusion
Congenital anomalies are a big problem worldwide. They cause a lot of sickness and death. For example, congenital heart disease affects many children.
Other common issues include CNS hydrocephalus and malformations in the gut and bones. These are all types of birth defects.
It’s key to raise awareness about these issues. This helps people understand and support those with birth defects. Knowing the causes helps us give better care and support.
We need to be aware, understand, and support those with congenital malformations. Together, we can help them live healthy lives. They deserve the care and support to thrive.
FAQ’s:
What are congenital anomalies?
Congenital anomalies are conditions present at birth. They can affect health and development.
What is a classic example of a congenital anomaly?
Cleft lip and/or palate is a classic example. It occurs in about 1 in 1,032 births in the US.
What are the implications of a cleft lip and/or palate?
It can affect feeding, speech, and development. It also has emotional and psychological impacts.
What are some other common congenital anomalies?
Other common ones include heart defects, neural tube defects, and chromosomal conditions like Down syndrome.
What causes congenital anomalies?
They result from genetic, environmental, and socioeconomic factors.
How are congenital anomalies diagnosed?
They are diagnosed through prenatal screening and tests like ultrasound and genetic testing.
What are the treatment options for congenital anomalies?
Treatment includes surgical and medical interventions. It also includes long-term care and follow-up.
What support systems are available for families affected by congenital anomalies?
Families can find support through counselling and support groups. These help with emotional and psychological challenges.
Can congenital anomalies be prevented?
Some can’t be prevented, but strategies like folic acid and avoiding exposures during pregnancy can help.
Why is early diagnosis and intervention important for congenital anomalies?
Early diagnosis and intervention are key. They help manage anomalies effectively and improve outcomes.
References:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2025). About congenital heart defects. https://www.cdc.gov/heart-defects/about/index.html
- World Health Organization. (2023). Congenital anomalies: Key facts. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/con










