Knowing the early signs and symptoms of clotting disorders can save lives. At Liv Hospital, quality healthcare is built on trust and patient-centered values. Understanding these warning signals is vital for prevention and treatment.Learn clotting disorder symptoms and understand the warning signs every patient should know for early detection.
Clotting disorders can show up in different ways, depending on where and how severe the clot is. Common signs include pain, swelling, redness, or warmth in the arms or legs. Early detection is key for managing these conditions well.
Liv Hospital is known worldwide for its medical excellence, including treating clotting disorders. Knowing the signs and symptoms is the first step to getting timely medical help.
Key Takeaways
- Clotting disorders can have varied symptoms based on the location and severity.
- Common signs include unexplained pain, swelling, redness, or warmth in the limbs.
- Early detection is critical for effective management.
- Liv Hospital is renowned for its expertise in treating clotting disorders.
- Understanding the signs and symptoms is key to timely medical intervention.
Understanding Blood Clotting Disorders: An Overview
Blood clotting disorders happen when the blood clotting process goes wrong. This can cause health problems. These issues can show up as too much bleeding or clots forming where they shouldn’t.
What Are Blood Clotting Disorders?
Blood clotting disorders, or coagulopathies, affect how the body makes blood clots. Normal blood clotting is key to stop bleeding when a blood vessel gets hurt. But, people with clotting disorders have trouble with this, leading to too much or too little clotting.
How Normal Blood Clotting Works
Normal blood clotting is a complex process. It involves platelets and clotting factors. When a blood vessel gets damaged, platelets stick to it. Then, a series of chemical reactions happens, forming a fibrin clot. This clot stops the bleeding by sealing the damaged vessel.
The process has several key stages:
- Platelet activation and aggregation
- Coagulation cascade initiation
- Fibrin clot formation
- Clot stabilization
Types of Clotting Disorders
Clotting disorders fall into two main types: bleeding disorders and thrombotic disorders. Bleeding disorders, like hemophilia, make it hard to stop bleeding because of missing clotting factors. Thrombotic disorders, on the other hand, cause blood clots that can block blood vessels. This can lead to serious problems like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE).
Some common clotting disorders include:
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
- Factor V Leiden thrombophilia
- Antiphospholipid syndrome
It’s important to understand these disorders to spot their signs of blood clotting disorder and get medical help. Recognizing blood clotting disease symptoms early can help prevent serious problems.
Common Clotting Disorder Symptoms and Warning Signs
Knowing the signs of blood clotting problems is key to early treatment. Clotting disorders show up in different ways. It’s important to watch for warning signs.
The Spectrum of Symptom Severity
Symptoms of blood clotting disorders can vary. Some people might not show any signs until a serious problem happens. The severity of symptoms depends on the clot’s size and where it is.
Mild symptoms could be a bit of pain or swelling. Severe symptoms might include a lot of pain, big swelling, or even life-threatening issues like pulmonary embolism.
Why Symptoms Vary by Location
The place of a blood clot affects the symptoms. For example, a leg clot might cause pain and swelling. But a lung clot could lead to shortness of breath and chest pain.
- Clots in the extremities can cause pain, swelling, and redness.
- Clots in vital organs like the brain or lungs can result in more severe and potentially life-threatening symptoms.
Importance of Early Recognition
Spotting clotting disorder symptoms early is vital. It helps manage the condition better and prevents serious problems. Quick medical help can greatly improve outcomes for those with clotting disorders.
| Symptom | Possible Clot Location | Severity |
| Pain and Swelling | Leg or Arm | Mild to Severe |
| Shortness of Breath | Lungs | Severe |
| Headaches and Vision Changes | Brain | Mild to Severe |
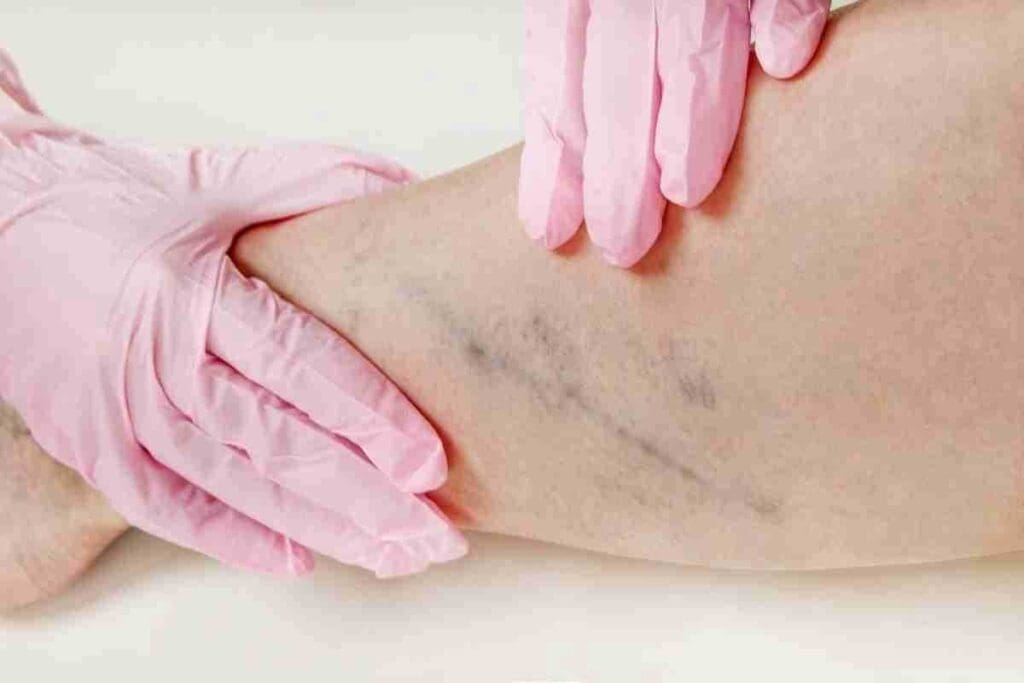
Sign #1: Extremity Issues – Pain, Swelling, and Redness
Issues with your extremities, like pain, swelling, and redness, are warning signs of clotting disorders. These symptoms often show up in your legs but can also appear in other parts of your body.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Indicators
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is when a blood clot forms in the deep veins, usually in your legs. The signs of DVT include:
- Pain or tenderness in the leg, which may occur while standing or walking
- Swelling in the affected leg
- Redness or discoloration of the skin
- Warmth or tenderness to the touch
Spotting these symptoms early is key to avoiding serious problems like pulmonary embolism.
Distinguishing DVT from Other Conditions
DVT symptoms can be unique, but they can also look like other conditions. For example, muscle strain or cellulitis can cause similar signs. A detailed medical check-up, including tests like ultrasound, is needed to confirm DVT.
| Condition | Common Symptoms | Distinguishing Features |
| Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) | Pain, swelling, redness, warmth | Symptoms often unilateral, clot formation in deep veins |
| Cellulitis | Redness, swelling, warmth, pain | Infection of the skin and subcutaneous tissues, often with fever |
| Muscle Strain | Pain, swelling | Typically related to physical activity, no redness or warmth |
If you notice symptoms of extremity issues, seeing a blood clotting doctor is vital. They can give you the right diagnosis and treatment plan. Early action can greatly improve your chances of recovery from clotting disorders.
Sign #2: Respiratory Distress – Chest Pain and Shortness of Breath
Chest pain and shortness of breath are serious signs. They might mean you have a clotting disorder like pulmonary embolism. This is a condition that needs quick medical help.
Pulmonary Embolism Warning Signs
Pulmonary embolism happens when a blood clot goes to the lungs. It blocks blood flow. This can be very dangerous and even deadly. Look out for these signs:
- Sudden onset of shortness of breath
- Chest pain that worsens with deep breathing or coughing
- Rapid heart rate
- Coughing up blood
- Lightheadedness or fainting
Emergency Indicators Requiring Immediate Attention
If you or someone else has symptoms of pulmonary embolism, get help right away. Waiting too long can lead to serious problems, even death.
| Symptom | Description | Action |
| Severe Chest Pain | Pain that worsens with deep breaths or movement | Call emergency services |
| Shortness of Breath | Sudden difficulty breathing | Seek immediate medical help |
| Rapid Heart Rate | Heart beats faster than normal | Monitor and seek medical attention |
Knowing the signs of pulmonary embolism and when to get help can save lives. If you’re showing these symptoms, call emergency services without delay.
Sign #3: Neurological Symptoms – Headaches, Vision Changes, and Speech Problems
The third key sign of clotting disorders is neurological symptoms. These include severe headaches, vision changes, and speech problems. These signs can point to cerebral venous thrombosis, a rare brain condition.
Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Symptoms
Cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT) is a rare stroke caused by a blood clot in the brain’s sinuses. Symptoms can vary but often include:
- Headaches: These can be severe and get worse over time. They may also cause confusion and changes in consciousness.
- Vision Changes: People might see things blurry, have double vision, or lose vision in one or both eyes.
- Speech Problems: It can be hard to speak or understand speech, similar to other strokes.
Stroke-Like Symptoms and Their Significance
CVT symptoms can look like other strokes, making it hard to diagnose. But, if you notice these symptoms, you should see a doctor right away. Stroke-like symptoms include:
- Weakness or numbness in parts of the body
- Difficulty with coordination and balance
- Seizures, in some cases
It’s important to know the signs of CVT to get help quickly. The table below shows the main symptoms and what they might mean.
| Symptom | Potential Implication |
| Severe Headaches | Increased intracranial pressure |
| Vision Changes | Impaired cranial nerve function |
| Speech Problems | Brain area affected by clot |
Spotting these symptoms early can help manage CVT better. Quick medical care is key to avoiding lasting damage.
Sign #4: Unusual Bleeding Tendencies
Unusual bleeding can be a sign of clotting disorders, even though they’re often seen as clot-forming issues. Some people with these conditions might bleed more than usual. This is because their condition affects blood clotting in complex ways.
Bleeding Disorders vs. Clotting Disorders
Bleeding and clotting disorders are different blood conditions. Bleeding disorders, like hemophilia, make it hard for blood to clot, leading to long bleeding. Clotting disorders, on the other hand, cause harmful clots that block blood flow. But, the difference between them can be tricky because of how blood clots.
| Condition | Primary Symptom | Underlying Cause |
| Bleeding Disorders | Prolonged Bleeding | Inability to form clots |
| Clotting Disorders | Formation of harmful clots | Abnormal clot formation |
Paradoxical Symptoms in Some Clotting Conditions
Some clotting disorders can show strange symptoms, like unusual bleeding. For example, Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) can cause both clots and bleeding. This makes it hard to diagnose and needs a deep understanding of the condition.
In summary, unusual bleeding can be a key sign of clotting disorders. It shows how complex these conditions are. Knowing the difference between bleeding and clotting disorders, and spotting paradoxical symptoms, is key for right diagnosis and treatment.
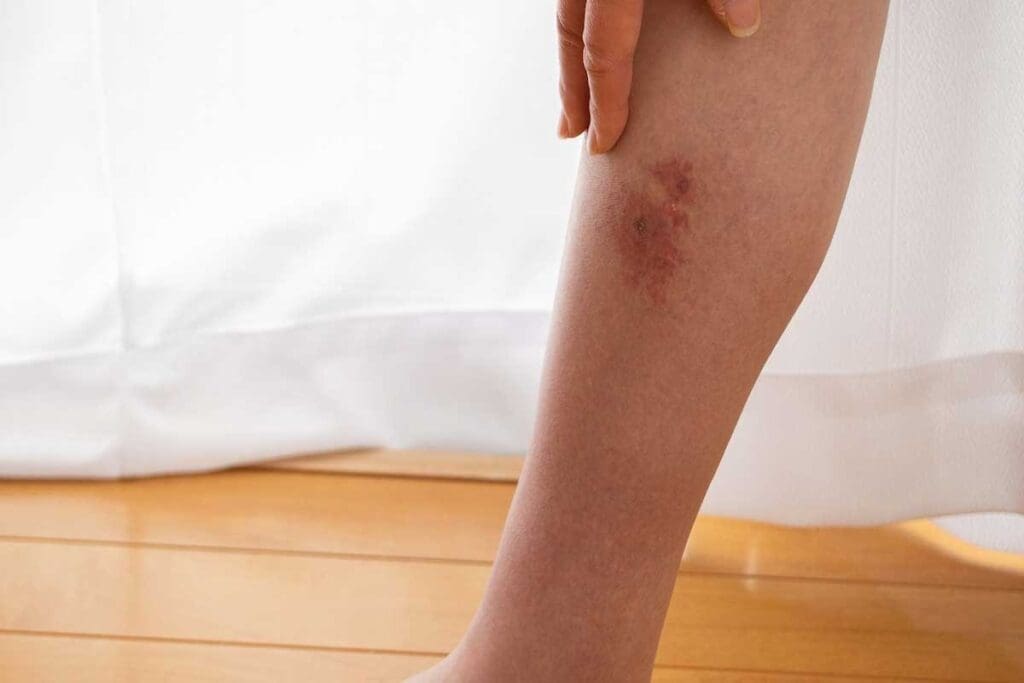
Sign #5: Skin Manifestations and Discoloration
Discoloration and other skin changes can signal a clotting disorder. These signs show up because of blood coagulation problems. It’s key to spot them early.
Visible Signs on the Skin Surface
Skin signs of clotting disorders vary. You might see redness, swelling, or color changes. Sometimes, the skin looks pale or blue because of bad circulation or oxygen.
Notable skin changes include:
- Redness and warmth around the affected area
- Swelling or inflammation
- Discoloration, such as purplish or bluish tint
- Pain or tenderness to the touch
Patterns of Discoloration and Their Meaning
The type and pattern of discoloration can hint at the clotting disorder. For example, pulmonary embolism might not show skin changes. But, related issues like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can cause skin color changes.
“The presence of skin manifestations can be a critical indicator of an underlying clotting disorder, necessitating prompt medical evaluation.”
Knowing these signs is vital for early treatment. If you see unusual skin changes, see a doctor right away.
Sign #6: Gastrointestinal and Abdominal Symptoms
People with clotting disorders might have stomach problems that need doctor’s help. These signs can show there’s something serious going on that needs quick action.
Abdominal Pain and Internal Clotting
Stomach pain is a big warning sign of internal clotting. A clot in the veins or arteries of the belly can cause a lot of pain. This is called mesenteric thrombosis.
This problem can cut off blood to the intestines. If not treated fast, it can cause serious damage or even death.
The pain from internal clotting in the belly can be different for everyone. It might also cause nausea, vomiting, or changes in how you go to the bathroom. If you have bad or lasting belly pain, you should see a doctor right away.
Digestive System Complications
Clotting disorders can also mess with the digestive system. For example, portal vein thrombosis happens when a clot blocks the vein that carries blood from the intestines to the liver. This can cause high pressure in the vein, leading to problems like bleeding or fluid buildup in the belly.
The table below lists some belly and digestive symptoms linked to clotting disorders:
| Symptom | Description | Possible Complication |
| Abdominal Pain | Severe pain due to internal clotting | Mesenteric Ischemia |
| Nausea and Vomiting | Associated with abdominal pain and clotting | Dehydration, Electrolyte Imbalance |
| Changes in Bowel Habits | Diarrhea or constipation due to clotting effects on intestinal blood flow | Intestinal Obstruction, Ischemia |
Knowing about these symptoms and their risks is key to catching clotting disorders early. If you’re experiencing these signs, talk to a doctor for the right care.
Sign #7: Subtle and Easily Missed Blood Clotting Disease Symptoms
The seventh sign of a clotting disorder is subtle and easy to miss. It requires a sharp eye to spot. These signs are so fine that they often go unnoticed until they become serious.
Fatigue and General Malaise
Fatigue is a common sign. It’s a constant tiredness that doesn’t get better with rest. General malaise, feeling generally unwell, can also be a sign of clotting disorders. These symptoms are hard to pinpoint, making diagnosis tricky.
Symptoms That Only Appear During Specific Events
Some people only feel symptoms during certain times or situations. For example, symptoms can get worse when you’re stuck in one place for a long time, like on a long flight or in bed. Spotting these patterns is key to catching the problem early.
The Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular health check-ups are key to catching clotting disorders early. Doctors can check your overall health, spot risks, and do screenings during these visits. It’s important for those with a family history of clotting or other risks to stay on top of their health and talk openly with their doctor.
By knowing these subtle signs and going for regular check-ups, people can catch and manage clotting disorders better.
Diagnostic Testing for Blood Clotting Disorders
Diagnostic testing is key in finding and treating blood clotting disorders. Getting the right diagnosis is vital for the right treatment and to avoid serious issues.
Complete Blood Count and D-dimer Tests
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) checks the blood’s different parts, like red and white cells and platelets. It can’t diagnose clotting disorders alone but gives insight into blood health. The D-dimer test is more specific for clotting. It looks at D-dimer, a protein from dissolving blood clots. High D-dimer levels suggest a blood clot.
Genetic Testing for Inherited Clotting Disorders
Genetic testing is key for inherited clotting disorders. It can spot conditions like Factor V Leiden thrombophilia and Prothrombin G20210A mutation. Knowing the genetic cause helps doctors give better treatment and prevention plans.
Imaging Studies for Clot Detection
Imaging studies are essential for finding blood clots. Ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are used. These help find where and how big the clots are, guiding treatment.
In summary, tests and imaging are used together to diagnose and manage blood clotting disorders. Knowing about these tests helps both patients and doctors.
Treatment Options and Management Approaches
Treating clotting disorders requires a mix of anticoagulant meds, surgery, and lifestyle changes. It’s important to know all the treatment options and how they fit each patient’s needs.
Anticoagulant Medications
Anticoagulants are key in managing clotting disorders. They stop new clots from forming and prevent existing ones from growing. Common ones include warfarin, apixaban, and rivaroxaban. The right choice depends on the patient’s condition and other health factors.
“Anticoagulation therapy needs close monitoring,” a clinical guideline says. Regular blood tests help adjust dosages and avoid risks.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is sometimes needed for clotting disorders. Thrombectomy removes clots from blood vessels. It’s considered when other treatments fail or when there’s a high risk of serious problems.
A specialist might suggest surgery for big clots causing severe symptoms or a high risk of pulmonary embolism. The decision depends on the patient’s health and condition details.
Lifestyle Management with Clotting Disorders
Lifestyle changes are vital in treating clotting disorders. This includes eating right, staying active, and avoiding sitting too long. Patients are told to keep a healthy weight, stop smoking, and drink less alcohol to lower risks.
“Lifestyle changes can greatly help manage clotting disorders,” a healthcare provider says. These changes can improve life quality and treatment results. By making these changes, patients can manage their condition better and lower the chance of future clots.
It’s important to keep up with doctor visits to check on the condition and adjust treatment plans. Combining medical treatment with lifestyle changes helps people with clotting disorders live full and active lives.
Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
Clotting disorders can be influenced by genetics, lifestyle, and environment. Knowing these factors helps in preventing them.
Who Is at Higher Risk for Clotting Disorders?
Some people are more likely to get clotting disorders. This includes:
- Family history of clotting disorders
- Previous history of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE)
- Genetic conditions such as Factor V Leiden or Antithrombin III deficiency
- Age, with risk increasing after 40 years
- Obesity and sedentary lifestyle
- Cancer and its treatment
Knowing these risks helps in early treatment and management.
Lifestyle Modifications to Reduce Risk
Changing your lifestyle can lower clotting disorder risk. These changes include:
- Regular physical activity to improve circulation
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on veins
- Avoiding prolonged periods of immobility
- Staying hydrated to prevent blood concentration
- Avoiding smoking, which damages blood vessels
These habits can help reduce the risk of clotting disorders.
Medical Interventions for Prevention
Medical help is key for those at high risk. This includes:
- Anticoagulant medications to prevent clot formation
- Use of compression stockings to improve blood flow
- Intermittent pneumatic compression devices for hospitalized patients
Comparison of Prevention Strategies
| Prevention Strategy | Target Group | Effectiveness |
| Lifestyle Modifications | General Population | High |
| Anticoagulant Medications | High-Risk Individuals | Very High |
| Compression Stockings | Individuals with Mobility Issues | Moderate |
In conclusion, understanding risk factors and prevention strategies is key. By combining lifestyle changes with medical help, individuals can lower their risk of clotting disorders.
Conclusion: When to Seek Medical Help
It’s important to know the signs of clotting disorders to get help quickly. Look out for pain in your limbs, trouble breathing, changes in your brain, unusual bleeding, skin color changes, or belly pain. If you see these signs, you should see a doctor right away.
Getting help early can really help people with clotting disorders. Knowing your body and when to get help can save lives.
If you might be at risk because of your family history, age, or other reasons, talk to your doctor. They can help you prevent problems and watch for any issues.
Keep an eye on your health and don’t wait to get help if you think something’s wrong. Being proactive can help manage your symptoms better.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of a clotting disorder?
Symptoms include pain, swelling, and redness in the limbs. You might also have trouble breathing or feel neurological issues. Other signs are unusual bleeding, skin problems, and stomach issues.
How is a clotting disorder diagnosed?
Doctors use several tests to diagnose. These include a complete blood count and D-dimer tests. They also do genetic testing and imaging like ultrasound or CT scans.
What is the difference between a bleeding disorder and a clotting disorder?
Bleeding disorders make it hard for blood to clot, leading to too much bleeding. Clotting disorders, on the other hand, cause blood clots that block blood flow.
What are the risk factors for developing a clotting disorder?
Risk factors include genetics, age, and being overweight. Other factors are not moving much, surgery, cancer, and certain health conditions.
Can clotting disorders be prevented?
Some risks can’t be changed, but you can lower your risk. This includes exercising regularly, staying at a healthy weight, and avoiding sitting for too long.
What are the treatment options for clotting disorders?
Treatments include medicines to prevent clotting, surgery, and lifestyle changes. These help manage symptoms and prevent more clots.
How can I manage my condition if I have a clotting disorder?
Managing your condition means following your treatment plan and making healthy lifestyle choices. Regular check-ups are also important to keep your condition under control.
What should I do if I experience symptoms of a clotting disorder?
If you have symptoms, get medical help right away. Early treatment can greatly improve your outcome.
Are there any specific tests that can detect clotting disorders?
Yes, tests like D-dimer, complete blood count, and genetic testing can help find clotting disorders.
Can clotting disorders be treated with surgery?
Sometimes, surgery is needed to remove a clot or fix damage from a clotting disorder.
How do anticoagulant medications work in treating clotting disorders?
These medicines stop new clots from forming and prevent existing ones from growing. This reduces the risk of serious problems.
References:
- Streiff, M. B., et al. (2016). Guidance for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Blood Advances, 1(1), 105-114. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4715858/



































