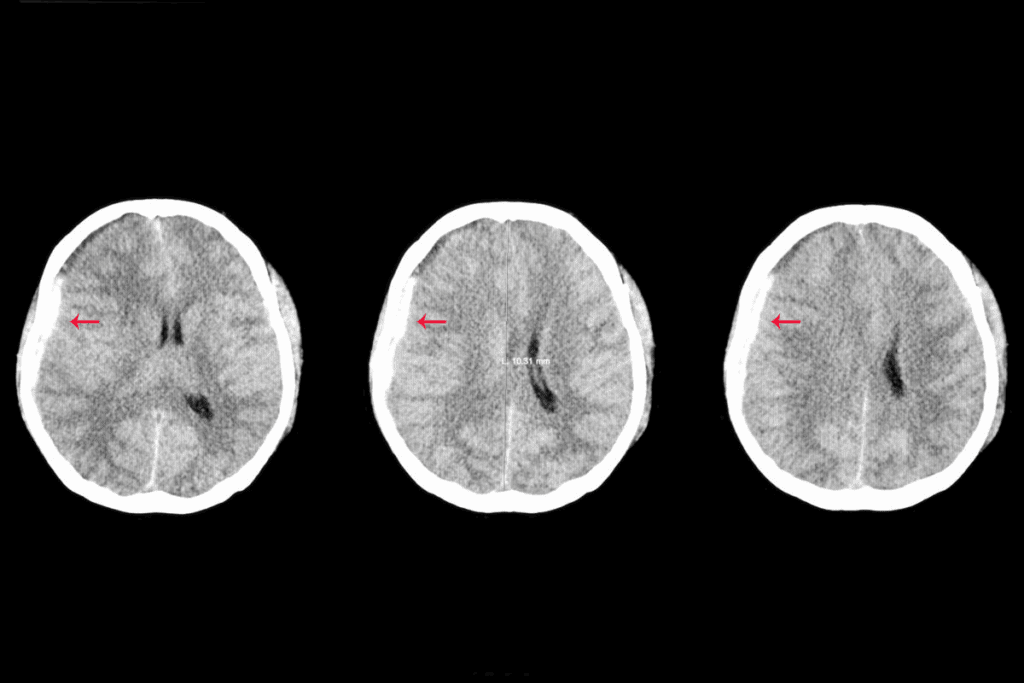
At Liv Hospital, we specialize in treating brain aneurysms with a new method called endovascular coiling. This method uses a thin catheter to reach the aneurysm in the brain. There, platinum coils are placed to stop blood flow and seal the aneurysm.
This way, we can prevent rupture and lower the risk of problems. Johns Hopkins Medicine says this method is as good as open surgery but safer and quicker.
Key Takeaways
- Endovascular coiling is a minimally invasive treatment for brain aneurysms.
- Platinum coils are used to induce clot formation and seal off the aneurysm.
- This technique blocks blood flow into the aneurysm, preventing rupture.
- Endovascular coiling is considered a safer alternative to open surgery.
- Liv Hospital’s team of experts specializes in this advanced treatment.
Understanding Brain Aneurysms
Brain aneurysms are weak spots in the brain’s blood vessels that can balloon and possibly rupture. This can lead to serious health issues, like stroke and even death. We will look into the basics of brain aneurysms, including their causes, risk factors, symptoms, and how they are diagnosed.
What Is a Brain Aneurysm?
A brain aneurysm, also known as a cerebral aneurysm, is a bulge or sac in a blood vessel in the brain. It happens when the vessel wall weakens, causing it to balloon out. This bulge can put pressure on the brain tissue and nerves. If it ruptures, it can cause bleeding in the brain, known as a subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can lead to the development of a brain aneurysm. These include:
- Genetic predisposition: People with a family history of brain aneurysms are more likely to get one.
- High blood pressure: Hypertension can weaken blood vessel walls, making them more prone to aneurysm formation.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and raises blood pressure, increasing the risk.
- Age and gender: Brain aneurysms are more common in adults and slightly more prevalent in women.
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact |
| Genetics | Family history of aneurysms | Increased likelihood |
| Hypertension | High blood pressure | Weakens vessel walls |
| Smoking | Damages blood vessels | Increases risk |
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of a brain aneurysm can vary based on its location and size. Some aneurysms may not show symptoms until they rupture. Others may cause:
- Headaches
- Nausea and vomiting
- Confusion or altered mental state
- Seizures
Diagnosis usually involves imaging tests like CT scans, MRI, or cerebral angiography. These tests help visualize the aneurysm and assess its size and location.
Understanding brain aneurysms is key for early detection and effective management. Recognizing risk factors and symptoms helps individuals seek medical attention quickly. This can prevent severe complications.
The Coiling Procedure: A Detailed Look
Endovascular coiling is a modern way to treat brain aneurysms. It stops blood from flowing into the aneurysm sac. This method is less invasive than traditional surgery.
Definition and Medical Purpose
The coiling procedure uses coils to block blood flow into the aneurysm sac. This reduces the risk of rupture. Coil embolization is done through a catheter in the blood vessels.
Once the coils are in place, they help form blood clots. This isolates the aneurysm from the bloodstream.
We choose endovascular coiling for patients with high-risk aneurysms. The choice depends on the aneurysm’s size, location, and shape.
History and Development of Endovascular Techniques
The first coils were developed in the 1990s. Over time, coil technology has improved a lot. Now, we have bioactive and complex coils.
Endovascular techniques have evolved a lot. Research and development keep improving patient care. New coil designs and delivery systems are being explored.
When Coiling Is Recommended
Coiling is suggested for high-risk aneurysms. The choice depends on the aneurysm’s details and the patient’s health.
- Aneurysm size and location
- Aneurysm morphology and neck size
- Patient’s clinical condition and comorbidities
- Presence of symptoms or previous rupture
We consider these factors to choose the best treatment for each patient. This ensures the best outcome.
Patient Eligibility for Coil Embolization
To see if coil embolization is right for you, we look at your aneurysm and health. We check many things to decide if this treatment is best.
Ideal Candidates for the Procedure
People with small to medium aneurysms and easy-to-reach locations are often good candidates. Those with unruptured aneurysms might also be considered, as it can stop a rupture.
We also look at your medical history. This includes things like high blood pressure, diabetes, and past vascular problems. This helps us spot any risks and prepare for them.
Contraindications and Limitations
Some conditions might make coil embolization not the best choice. This includes large or giant aneurysms, complex shapes, and sensitive locations. Those with severe vascular disease or serious health issues might also face challenges.
| Condition | Potential Impact on Coil Embolization |
| Large or Giant Aneurysms | May require additional or alternative treatments |
| Complex Aneurysm Morphology | Can complicate coil deployment and stability |
| Severe Vascular Disease | Increases procedural risks and complicates access |
Pre-Procedure Assessment
Before we start, we do a detailed check to see if you’re a good fit. This includes detailed imaging studies like digital subtraction angiography and 3D rotational angiography. These help us see the aneurysm’s shape.
We also review your medical history and do lab tests. This helps us understand your health and any risks the procedure might have.
How Endovascular Coiling Works
Endovascular coiling involves placing coils in an aneurysm to block it from blood flow. This method is complex and needs great skill. We’ll look at how it isolates aneurysms, the types of coils used, and how blood clots form.
The Basic Mechanism of Aneurysm Isolation
Endovascular coiling fills the aneurysm with coils to promote clotting. These coils are made to be safe for the body and help blood clots form. By filling the aneurysm, we lower the risk of rupture and stop it from growing.
Types of Aneurysm Coils
There are many types of aneurysm coils, each with its own benefits. The right coil depends on the aneurysm’s size, shape, and location, and the patient’s health.
| Coil Type | Description | Benefits |
| Bare Platinum Coils | Made of platinum, these coils are highly biocompatible and promote clotting. | Effective in inducing clot formation, easy to deploy. |
| Coated Coils | Coated with materials that enhance clotting, such as hydrogel or polyglycolic acid. | Improved clot formation, reduced risk of coil compaction. |
| 3D Coils | Designed to conform to the shape of the aneurysm, providing better filling. | Effective in treating complex aneurysms, improved packing density. |
Blood Clot Formation Process
The clotting process is key to endovascular coiling’s success. When coils are placed in the aneurysm, they start clotting. This clot isolates the aneurysm from blood flow, lowering rupture risk.
Key factors influencing clot formation include:
- Coil material and design
- Aneurysm size and shape
- Patient’s coagulation status
Understanding endovascular coiling’s mechanism and success factors helps us see its benefits and risks. Our goal is to give full care and support to those undergoing this treatment.
Step-by-Step Guide to the Coiling Procedure
Understanding the coiling procedure is key. It’s a treatment for brain aneurysms. Coils are used to block the aneurysm sac.
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Preparation is vital before starting. This includes checking the patient’s health history and doing imaging tests. Doctors also talk about the procedure’s risks and benefits.
Patients get instructions on what to do before the procedure. This includes fasting and managing medications. Our team makes sure everything is ready for a smooth procedure.
Anesthesia Administration
The procedure is done under general anesthesia. This keeps the patient comfortable and prevents movement. An anesthesiologist watches the patient’s vital signs during the procedure.
General anesthesia helps our team work efficiently and safely. It ensures the best results for the patient.
Catheter Insertion and Navigation
Inserting and navigating the catheter is a key step. A small cut is made in the groin, and the catheter is inserted into the femoral artery. Fluoroscopy guides the catheter to the aneurysm.
This careful navigation is essential for placing coils correctly in the aneurysm.
Coil Deployment Technique
With the catheter in place, the coils are deployed. Soft, platinum coils are pushed through the catheter into the aneurysm. They cause clotting, isolating the aneurysm from the bloodstream.
The deployment is watched closely with imaging. This ensures the coils are placed right and the aneurysm is blocked effectively.
| Step | Description | Key Considerations |
| Pre-Procedure Preparation | Comprehensive patient assessment and imaging | Medical history, imaging studies, patient education |
| Anesthesia Administration | General anesthesia for patient comfort | Anesthesiologist expertise, patient monitoring |
| Catheter Insertion and Navigation | Catheter navigation to the aneurysm site | Fluoroscopic guidance, precision |
| Coil Deployment Technique | Deployment of coils into the aneurysm sac | Real-time imaging, coil placement accuracy |
Advanced Imaging in Coiling Surgery
Advanced imaging is key for diagnosing and treating brain aneurysms during coiling. These technologies give us clear views of the aneurysm and the blood vessels around it. This helps make sure the treatment works well.
Digital Subtraction Angiography
Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) is a vital tool in coiling surgery. It uses a contrast agent to show blood vessels and aneurysms. DSA gives us live images, helping us place coils accurately.
To start DSA, a catheter is put into the femoral artery. It’s then guided to the aneurysm. A contrast agent is injected, and X-ray images are taken. These images show the aneurysm’s details, like size and shape.
3D Rotational Angiography
3D Rotational Angiography gives us a 3D view of the aneurysm and blood vessels. It’s great for complex cases, helping us understand the aneurysm’s shape and its position.
With 3D images, we can better plan the coiling. We can see the aneurysm’s shape and choose the best coil setup. This lowers the risk of problems and improves results.
Real-Time Monitoring Systems
Real-time monitoring is essential in coiling surgery. It lets us change the procedure if needed. These systems show images as we place coils, helping us see if the treatment is working.
Using DSA, 3D rotational angiography, and real-time monitoring, we can safely treat brain aneurysms through coiling.
Supplementary Devices in Aneurysm Treatment
Advanced treatments for aneurysms often use special devices to help. These devices work with coiling to make treatments more effective. They are very helpful for complex cases.
Stent-Assisted Coiling for Wide-Necked Aneurysms
Stent-assisted coiling helps treat wide-necked aneurysms. A stent is placed across the aneurysm neck. This creates a support that keeps coils from moving into the main artery.
Benefits of Stent-Assisted Coiling:
- Enhanced stability for coil deployment
- Improved packing density
- Reduced risk of coil protrusion into the parent artery
Flow Diverters
Flow diverters are used in aneurysm treatment. They change blood flow to help the aneurysm close off. They are great for complex aneurysms that are hard to treat with just coiling.
The mechanism of action for flow diverters involves:
- Redirecting blood flow away from the aneurysm
- Promoting intra-aneurysmal thrombosis
- Encouraging aneurysm occlusion over time
Balloon-Assisted Techniques
Balloon-assisted coiling uses a balloon to help place coils. The balloon is inflated across the aneurysm neck. This prevents coils from moving into the main artery and allows for more coils to be packed.
Advantages of Balloon-Assisted Coiling:
- Improved coil stability during deployment
- Enhanced coil packing density
- Reduced risk of coil migration
Intrasaccular Flow Disruptors
Intrasaccular flow disruptors are placed inside the aneurysm sac. They disrupt blood flow, promote clotting, and lower the risk of rupture.
The benefits of intrasaccular flow disruptors include:
- Effective disruption of aneurysmal blood flow
- Promotion of intra-aneurysmal thrombosis
- Potential for reduced aneurysm recurrence
Using these devices can greatly improve aneurysm treatment results. They are very helpful for complex and challenging cases.
Benefits of Endovascular Coiling
Endovascular coiling offers many benefits, like shorter recovery times and fewer complications. It’s a popular choice because it’s effective in stopping aneurysms from rupturing. Plus, it’s a minimally invasive method.
Minimally Invasive Advantage
Endovascular coiling is known for being minimally invasive. It doesn’t require a big cut like traditional surgery. Instead, a small puncture in the groin is made to access the femoral artery. This way, the catheter and coils can reach the aneurysm site without causing much damage.
Key advantages of the minimally invasive approach include:
- Smaller incisions, resulting in less scarring
- Reduced risk of infection
- Less post-operative pain
Reduced Recovery Time
Patients who get endovascular coiling usually recover faster than those who have open surgery. The procedure’s minimally invasive nature means less tissue damage. This leads to a quicker recovery time.
| Recovery Aspect | Endovascular Coiling | Open Surgery |
| Hospital Stay | 1-3 days | Several weeks |
| Return to Normal Activities | A few days to a week | Several weeks to months |
Lower Complication Rates
Endovascular coiling has fewer complications than traditional surgical clipping. Its minimally invasive nature lowers the risk of issues like infection, bleeding, and damage to brain tissue.
Effectiveness in Preventing Rupture
Endovascular coiling is very effective in preventing aneurysm rupture. It works by isolating the aneurysm from the bloodstream. This greatly reduces the risk of rupture and its severe consequences.
The benefits of coiling in preventing rupture include:
- Immediate reduction in the risk of rupture
- Long-term protection against re-bleeding
- Minimally invasive follow-up procedures for monitoring
Potential Risks and Complications
It’s important to know the risks of coiling before you decide on this treatment. Endovascular coiling is a common and effective way to treat brain aneurysms. But, it’s not without its risks.
Procedure-Related Complications
Complications can happen during or right after the coiling procedure. These might include:
- Thromboembolic events, where a blood clot forms and potentially causes a stroke
- Aneurysm rupture during the procedure, a serious complication that requires immediate attention
- Vasospasm, a condition where the blood vessels constrict or spasm
- Access site complications, such as bleeding or hematoma at the catheter insertion site
We do our best to avoid these risks. We carefully choose our patients, use precise techniques, and watch them closely during and after the procedure.
Long-Term Risks
There are also long-term risks to consider with endovascular coiling. These include:
- Coil compaction, where the coils become compressed over time
- Aneurysm recurrence, where the treated aneurysm re-forms or grows back
- In-stent thrombosis, a condition where a blood clot forms within a stent
It’s key to have regular check-ups to watch for these long-term risks.
Coil Compaction and Aneurysm Recurrence
Coil compaction and aneurysm recurrence are major long-term risks. Coil compaction happens when the coils used to fill the aneurysm get compressed. This can lead to the aneurysm coming back.
| Risk Factor | Description | Management Strategy |
| Coil Compaction | Coils become compressed over time | Regular follow-up imaging, possible additional coiling |
| Aneurysm Recurrence | Aneurysm re-forms or grows back | Additional coiling or other treatments |
Managing Complications
It’s vital to manage complications well for the success of endovascular coiling. This means:
- Promptly recognizing complications
- Appropriate medical or interventional treatment
- Close monitoring and follow-up
We focus on educating our patients and providing follow-up care to manage and reduce these risks.
Recovery and Follow-Up After Brain Aneurysm Coiling
After a brain aneurysm coiling, patients start a recovery phase. This phase needs careful watching and follow-up care. It’s key for the procedure’s success and the patient’s health.
Hospital Stay Duration
The time in the hospital after coiling varies. It depends on the patient’s condition and the procedure’s complexity. Usually, patients stay a few days. During this time, their health is closely watched.
Post-Procedure Restrictions
Patients should avoid hard work and heavy lifting after coiling. We give each patient specific guidelines. These are based on their needs and the procedure details.
Follow-Up Imaging Schedule
Regular imaging tests are part of the care plan after coiling. We check if the coiling worked and watch for complications. These tests, like angiography, are done at times set by the doctor.
Long-Term Monitoring
Long-term checks are key to keep the aneurysm closed and catch problems early. We help patients plan for long-term follow-ups. This might include regular imaging and doctor visits.
Following the care plan helps patients get better and lowers the risk of problems. We’re dedicated to supporting patients through their recovery.
Conclusion
We’ve looked into brain aneurysm coiling, a complex treatment for cerebral aneurysms. Endovascular coiling is a big step forward. It’s a less invasive and effective way to treat patients at risk of aneurysm rupture.
Understanding the procedure, its benefits, and risks helps patients and doctors make better choices. As technology gets better, coiling’s role in treating aneurysms will grow. This brings new hope to those affected.
Coiling offers quick recovery times and fewer complications, making it a good choice for some patients. It’s key to carefully choose who gets this treatment and do thorough checks before starting. This ensures the best results.
We’re always working to improve endovascular coiling. Our goal is to provide top-notch healthcare and support to patients worldwide. Brain aneurysm coiling shows how far we’ve come in treating complex health issues. We’re excited to see how it will continue to evolve.
FAQ
What is a brain aneurysm coiling procedure?
Brain aneurysm coiling is a minimally invasive treatment. It involves placing platinum coils inside the aneurysm. This helps form a clot and prevents it from rupturing.
How does coil embolization work?
Coil embolization involves placing coils in the aneurysm sac. This causes clotting and isolates the aneurysm. It reduces the risk of rupture.
What are the benefits of endovascular coiling?
Endovascular coiling is minimally invasive. It has a lower risk of complications and faster recovery. It’s also effective in preventing aneurysm rupture.
What are the risks associated with coiling?
Coiling is generally safe but carries risks. These include procedure-related complications and aneurysm recurrence. Proper follow-up care can manage these risks.
Who is a candidate for coil embolization?
Suitable candidates have aneurysms that fit coiling criteria. Their health must also allow for the procedure.
What is the role of advanced imaging in coiling surgery?
Advanced imaging, like digital subtraction angiography, is key. It provides detailed information on the aneurysm’s anatomy and coiling effectiveness.
What are supplementary devices used in aneurysm treatment?
Devices like stent-assisted coiling and flow diverters enhance coiling. They are used for wide-necked aneurysms and improve treatment outcomes.
What is the recovery process like after brain aneurysm coiling?
Recovery involves a short hospital stay and minimal restrictions. Follow-up imaging is needed to check the coiling’s success and watch for complications.
How is aneurysm recurrence managed after coiling?
Recurrence is managed with additional treatments. This includes further coiling or other endovascular methods. Long-term monitoring ensures the aneurysm remains closed.
What is considered a main benefit of endovascular coiling?
A key benefit is its minimally invasive nature. This reduces complications and promotes faster recovery compared to open surgery.
What is the purpose of using coils made of platinum in aneurysm treatment?
Platinum coils promote clotting. They are designed to fill the aneurysm effectively. This isolates it from blood flow and reduces rupture risk.
Can coiling be used for all types of brain aneurysms?
Coiling is suitable for many aneurysms. Its use depends on size, location, shape, and the patient’s health.
References:
- Zhao, J. (2017). Current treatment strategies for intracranial aneurysms. Stroke and Vascular Neurology, 2(3), 148-157.











