Ear pain with a cold is a common problem for millions. When a cold virus causes swelling, it blocks the Eustachian tube. This can trap fluid in the middle ear, leading to pain and serious issues.
At Liv Hospital, we know how important it is to find relief. Our team is here to offer trusted advice to manage cold-related ear pain effectively.
There are many ways to ease the pain of a common cold earache. We’ll look at over-the-counter remedies and medical options for quick relief.
If you have a cold and ears hurt, learn quick solutions to relieve the ear pain caused by pressure buildup in the middle ear.
Globally, ear pain from colds is a big problem for healthcare. It often comes from issues like acute otitis media. This affects many people all over the world.
Studies show that colds and ear infections caused over 8 million lost years of life in 2021. This shows how common the issue is. Acute otitis media is a big reason for ear pain from colds, often happening with or after colds.
A study found that otitis media affects many, in both rich and poor countries. It bothers both kids and adults. This makes it clear we need better ways to handle ear pain from colds.
The cost of ear pain from colds is huge, with millions spent on healthcare each year. This includes doctor visits, medicines, and sometimes surgery. People’s lives are also affected, with symptoms ranging from mild to severe.
The ripple effect of ear pain from colds goes beyond the person. It affects families and communities too. Lost work and caring for sick family members add to the cost.
“The global health burden of upper respiratory infections and related complications like otitis media is a pressing concern that requires a full public health approach.”
It’s important to understand the global impact of ear pain from colds. This helps us create better health plans and treatments. By tackling this issue, we can make life better for those affected and ease the financial load on healthcare systems worldwide.
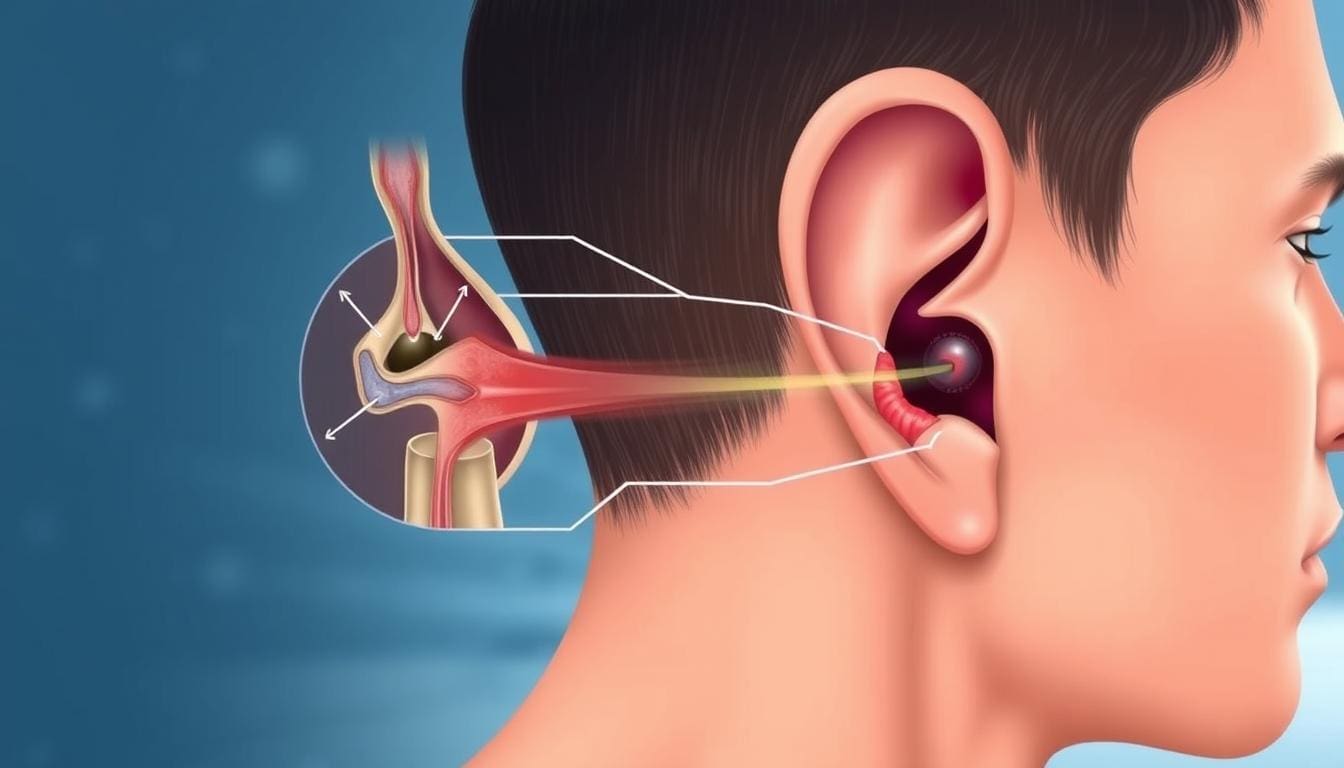
A head cold and ear pain are closely linked. This is because of how our body’s respiratory system works. When we get a cold, the virus can spread to our ears, causing pain and discomfort.
Cold viruses cause ear pain mainly by blocking our nasal and throat areas. This blockage can lead to dysfunction of the Eustachian tube. This tube is key for air pressure in our ears. If it’s blocked, we feel ear pain and pressure.
The Eustachian tube keeps air pressure balanced in our ears. But during a cold, swelling and more mucus can block it. This leads to ear pain.
The Eustachian tube links our middle ear to the back of our nose and throat. It’s main job is to regulate air pressure and clear mucus from our middle ear. But during a cold, it can get vulnerable to blockage because of swelling and more mucus.
It’s important to understand how the Eustachian tube works and how it’s affected by colds. Knowing how to manage pressure and congestion can help ease ear pain.
Ear pain from a cold can be really uncomfortable. But knowing the symptoms is the first step to feeling better. When a cold virus hits, it can make your ears hurt in different ways.
Ear pain from a cold can feel different for everyone. But there are some common signs to watch for. These include:
These feelings happen because the cold virus can make your middle ear inflamed and filled with fluid. This leads to pain and discomfort.
It’s important to tell cold-induced ear pain apart from other ear issues. Unlike ear infections, which can be very painful and cause fever, cold-induced pain is usually just a dull ache. But if you notice:
you should get medical help right away. These could be signs of something more serious.
The way cold-induced ear pain symptoms get worse can vary. Sometimes, the pain goes away once the cold is gone. But sometimes, it can get worse or not go away if you get an ear infection. It’s key to watch your symptoms and get medical help if they get worse.
Knowing how symptoms progress can help you manage your condition better. It also tells you when to get more medical help.
Over-the-counter pain relievers are often the first choice for ear pain from colds. They offer quick relief, helping you get back to your day.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a top pick for ear pain. Ibuprofen is a well-known NSAID that fights inflammation and pain. It does this by stopping the body from making prostaglandins, which cause pain and swelling.
A study in the Journal of Pain Research shows NSAIDs like ibuprofen work well for acute pain. It stresses the need for the right dose for best pain relief.
Acetaminophen is another common pain reliever. It’s good for those who can’t take NSAIDs because of stomach problems or other reasons. Acetaminophen changes how the brain feels pain, giving relief without reducing swelling much.
“Acetaminophen is a versatile analgesic that can be used in various pain management scenarios, including ear pain due to colds.”
Medical Expert, Pain Management Specialist
To get the most relief from ear pain, it’s key to follow the right dosage for over-the-counter pain meds. The amount and how often you take it can change based on the drug and your health.
Medication | Adult Dosage | Frequency |
Ibuprofen | 200-400 mg | Every 4-6 hours |
Acetaminophen | 325-650 mg | Every 4-6 hours |
Always check the packaging or talk to a healthcare professional for specific dosing advice. This helps avoid bad interactions with other meds.
Decongestants are a good way to clear blockages and reduce pressure in the ear when you have a cold. A cold can make your nasal passages and Eustachian tube congested. This can cause ear pain and discomfort. Decongestants help clear this congestion, improving ear function and easing pain.
Decongestants are available in two forms: oral and nasal. Oral decongestants, like pseudoephedrine, are taken by mouth and work throughout your body. Nasal decongestants are applied directly to your nasal passages with sprays or drops. They offer quick relief but have different effects and durations.
Oral Decongestants: These last longer, often 12 to 24 hours. But, they take longer to start working than nasal decongestants.
Nasal Decongestants: They work fast, often in minutes. But, their effects last only 4 to 6 hours. It’s important to use them as directed to avoid rebound congestion.
Decongestant Type | Onset Time | Duration of Action |
Oral | 30-60 minutes | 12-24 hours |
Nasal | Within minutes | 4-6 hours |
Decongestants reduce swelling in the nasal passages and Eustachian tube. This improves the tube’s function. The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the back of the nose and throat. It helps equalize ear pressure.
When this tube is blocked by a cold, it can cause ear pain. Decongestants clear this blockage, restoring normal pressure in the ear.
Following the recommended dosage and usage guidelines for decongestants is key. Oral decongestants should be taken every 12 hours. Nasal decongestants should not be used for more than 3 to 5 days to avoid rebound congestion.
It’s best to follow the product’s instructions or get advice from a healthcare professional. They can help you use decongestants safely for cold-induced ear pain.
Using a warm compress is a great way to ease ear pain from a cold. It boosts blood flow and cuts down swelling. This simple trick can bring quick relief.
To use a warm compress, soak a clean cloth in warm water. Make sure it’s damp but not wet. You can also use a microwave-safe bag filled with rice or a special warm compress pack.
Heat it for a few seconds until it’s warm but not too hot.
Key steps to follow:
The compress should be warm, not hot. Test it against your forearm to make sure it’s comfy. Start with shorter sessions (5-7 minutes) and adjust as needed.
Important considerations:
For better results, try using warm compresses with other treatments. Decongestants and pain relievers can help with pain and congestion.
Combination therapy benefits:
Adding warm compresses to your cold relief plan can help manage ear pain. It makes you feel better overall.
Steam therapy and adjusting humidity can help with ear pain from colds. It loosens mucus and reduces congestion. This makes breathing easier and relieves ear pressure.
To make a good steam treatment, boil water, then take it off the heat. Lean over the pot with a towel on your head to trap the steam. Be careful not to get too close to the hot water to avoid burns. You can also use a steam inhaler for a safer option.
“Steam inhalation is a simple, non-invasive method that can provide significant relief from nasal congestion and ear pain,” says Medical Expert, an ENT specialist.
Humidifiers help keep the room’s moisture right, which is good for your nasal passages and Eustachian tube. It’s recommended to keep the humidity level between 40% to 60%.
You can do steam therapy several times a day as needed. But make sure the water is clean to avoid bacteria and mold. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for humidifiers and steam inhalers.
Adding steam therapy and adjusting humidity to your cold relief plan can help ease ear pain. It can also make you feel better overall during a cold.
Equalizing ear pressure is key when you have ear pain from colds. There are many ways to do this. The Eustachian tube helps keep ear pressure balanced. When it’s blocked by a cold, the Valsalva and Toynbee maneuvers can help.
The Valsalva maneuver is easy. You pinch your nose, close your mouth, and blow gently through your nose. This opens the Eustachian tube and balances ear pressure. To do it right, follow these steps:
Be gentle with the Valsalva maneuver to avoid hurting your eardrum or making it worse.
The Toynbee maneuver is another way to balance ear pressure. It involves swallowing while pinching your nose. This opens the Eustachian tube, letting air in and balancing pressure. Here’s how to do it:
An alternative is the jaw exercise. It moves your jaw to open the Eustachian tube.
Jaw exercises can also help. They move your jaw to open the Eustachian tube. Some good ones are:
Do these exercises often to keep the Eustachian tube working and ease ear pain from colds.
Many people are turning to natural remedies and herbal solutions for ear pain from a cold. These options can offer relief without the side effects of some medicines.
Natural remedies have been used for centuries to treat ear pain. Garlic oil eardrops, tea tree oil, and ginger or turmeric supplements are among the most effective.
Garlic oil is great for fighting infections and ear pain. You can buy it or make your own by mixing garlic oil with olive or coconut oil.
Benefits of Garlic Oil Eardrops:
Tea tree oil and lavender oil are soothing. Tea tree oil fights microbes, and lavender oil eases pain and promotes calm. Apply them around the ear or use in a warm compress.
Essential Oil | Benefits | Application Method |
Tea Tree Oil | Antimicrobial, reduces inflammation | Topical application or warm compress |
Lavender Oil | Relieves pain, promotes relaxation | Topical application or warm compress |
Ginger and turmeric are anti-inflammatory. Taking them as supplements or in teas can help reduce inflammation and ear pain.
Ginger: Has compounds like gingerol, which fights inflammation.
Turmeric: Contains curcumin, a strong anti-inflammatory.
Adding these natural remedies to your routine can help with ear pain from a cold. Always talk to a healthcare professional before trying new treatments.
When kids get ear pain from a cold, we need special ways to help. Their Eustachian tubes are different, making them more likely to get blocked and hurt.
Helping kids with ear pain means using methods that fit their age. For older kids, medicines like acetaminophen can work if given the right amount based on their size and age.
Younger kids need comfort more than anything. Gently massaging their ears and using warm compresses can help. Also, making sure they drink plenty of water helps thin out mucus.
“Keeping your child upright can help drain the Eustachian tube and reduce pressure.”
Talking to kids about their ear pain is key. Using simple words and being reassuring helps them understand and feel safe.
By using these methods, we can make ear pain from colds easier for kids. This makes their recovery less scary and more manageable.
It’s important to know when to see a doctor for ear pain caused by a cold. Many cases can be treated at home. But, some symptoms might mean a serious issue that needs a doctor’s help.
Some signs could mean serious problems from ear pain due to a cold. These include:
Ear infections can happen as a cold complication. Look out for these signs:
Symptom | Description |
Persistent ear pain | Pain that lasts more than a few days or gets worse |
Fever | Especially in kids, a fever might mean an ear infection |
Hearing difficulties | Muffled hearing or trouble responding to sounds |
If you or your child shows warning signs or ear infection symptoms, see a doctor. At the visit, a healthcare professional will:
Seeing a doctor early can stop serious problems and help with treatment. This reduces the chance of lasting effects.
It’s important to understand how a head cold can cause ear pain. We’ve looked at ways to ease this discomfort. These include using over-the-counter pain meds, trying natural remedies, and using techniques to balance ear pressure.
Most ear pain from a cold isn’t serious. You can handle it with home remedies and some over-the-counter treatments. But, knowing when to see a doctor is key to avoid bigger problems.
By using the relief methods we talked about, you can lessen ear pain from a cold. It’s vital to get relief quickly and properly to feel better during a cold.
If your ear pain doesn’t go away or is very bad, see a doctor. They can check you out and give the right treatment. Taking care of yourself and getting medical help when needed is the best way to manage ear pain from a cold.
Ear pain with a cold often comes from congestion. It’s also due to the Eustachian tube not working right. This causes pressure imbalance in the ears.
Try over-the-counter pain meds, decongestants, or warm compresses. Steam therapy and pressure-equalizing techniques can also help.
NSAIDs like ibuprofen and acetaminophen are good for ear pain from a cold.
Decongestants reduce nasal congestion. This helps the Eustachian tube work better and eases ear pressure.
Yes, a warm compress on the affected ear can ease pain and discomfort.
Steam therapy loosens mucus and reduces congestion. This promotes drainage and relieves ear pressure.
Yes, natural remedies like garlic oil eardrops, tea tree oil, and ginger supplements can help with ear pain and inflammation.
Manage cold symptoms, use nasal decongestants, and practice good ear hygiene to prevent ear pain.
Seek medical help for severe ear pain, fever, discharge, or hearing loss. These could be signs of a complication or ear infection.
Yes, kids can get ear pain from a cold. Use age-appropriate pain relief like acetaminophen or ibuprofen. Comfort them with warm compresses.
Look out for severe ear pain, fever, discharge, hearing loss, or dizziness. These are signs of complications and need immediate medical attention.
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. (n.d.). Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536942/
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!
WhatsApp us