Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It affects many parts of the body, with the skin being the second most frequently affected. Cutaneous manifestations happen in 70 to 85 percent of people with the disease. It’s important to recognize these symptoms early and get expert care.
At Liv Hospital, we use international best practices and academic rigor. We help you understand and spot the key cutaneous symptoms of SLE. Our patient-centered approach ensures we give our international patients the care they need.
Key Takeaways
- Cutaneous manifestations are a common symptom of SLE, occurring in 70 to 85 percent of patients.
- Early recognition of skin manifestations is key for effective management.
- Liv Hospital provides complete care for international patients with SLE.
- Our approach combines international best practices with academic rigor.
- Understanding cutaneous symptoms is vital for delivering complete care.
Understanding Lupus Erythematosus and Its Cutaneous Impact
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a complex autoimmune disease. It affects the skin and other organs. Knowing how it impacts the skin is key to caring for patients.
What is Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)?
SLE is a chronic autoimmune disorder. It can affect many organs, including the skin, kidneys, and joints. Symptoms vary greatly from person to person, with flares and remission periods.
Prevalence and Demographics
SLE affects 17 to 48 people per 100,000 worldwide. It mostly hits women, with a ratio of 8 to 9 women for every man. Knowing this helps us understand the disease better.
The Skin-Lupus Connection
Most people with lupus develop skin diseases, known as cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Symptoms range from mild to severe, including rashes and sensitivity to sunlight.
The link between lupus and skin health is complex. It involves genetics, environment, and immune system issues. Grasping this connection is essential for managing the disease.
Classification of Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus
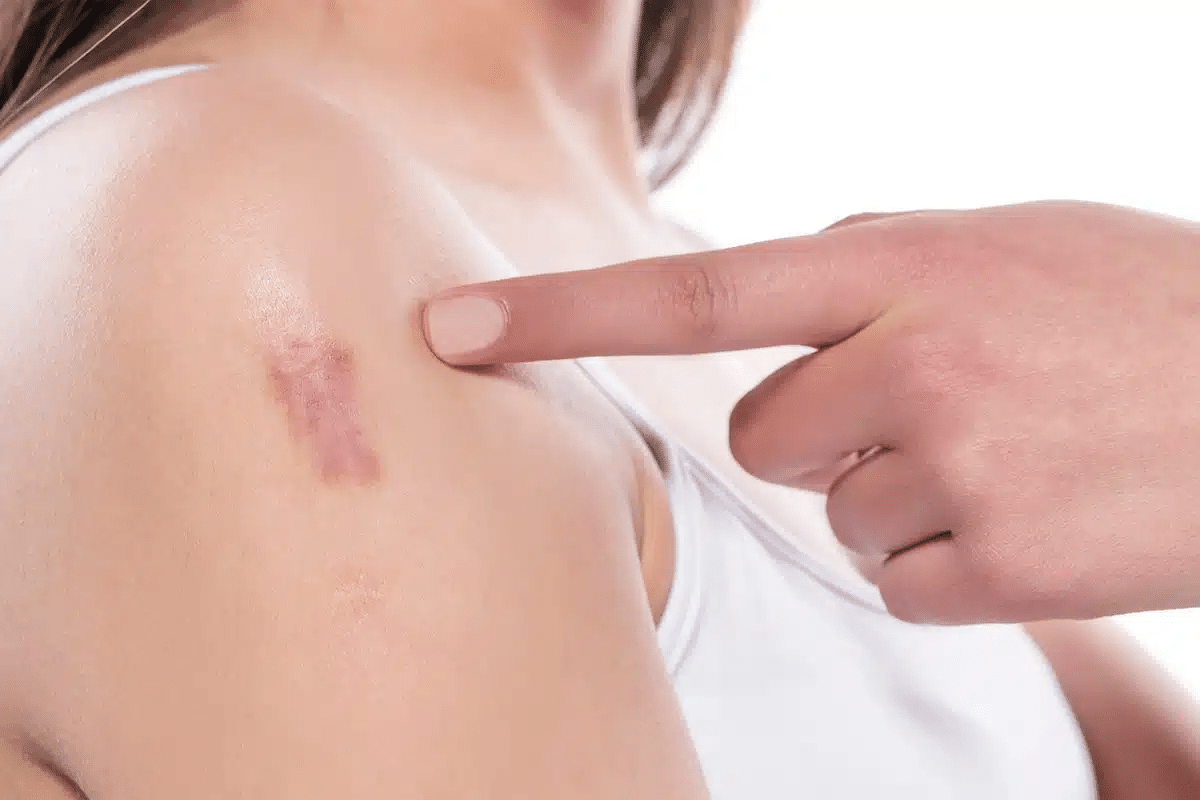
It’s key to know the different types of Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus for diagnosis and treatment. This condition is split into three main types: Acute, Subacute, and Chronic. Each type has its own skin symptoms and how long they last.
Acute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (ACLE)
ACLE starts suddenly and is linked to other body diseases. It shows up as a malar rash, a butterfly-shaped mark on the cheeks and nose. ACLE is very sensitive to UV light, making it worse with sun exposure. Medical Expert, triggering an immune response and rashes in Lupus patients.
Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (SCLE)
SCLE has less severe but more widespread lesions than ACLE. Its lesions are often papulosquamous or annular and also sensitive to UV light. This type of Lupus is linked to specific autoantibodies, like anti-Ro/SSA.
Chronic Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (CCLE)
CCLE includes discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE), the most common type. DLE has disc-shaped lesions that can cause scarring and harm if not treated. CCLE can happen with or without other body diseases.
We understand the many ways Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus can show up. We’re dedicated to giving each patient the care they need, using the latest medical knowledge and treatments.
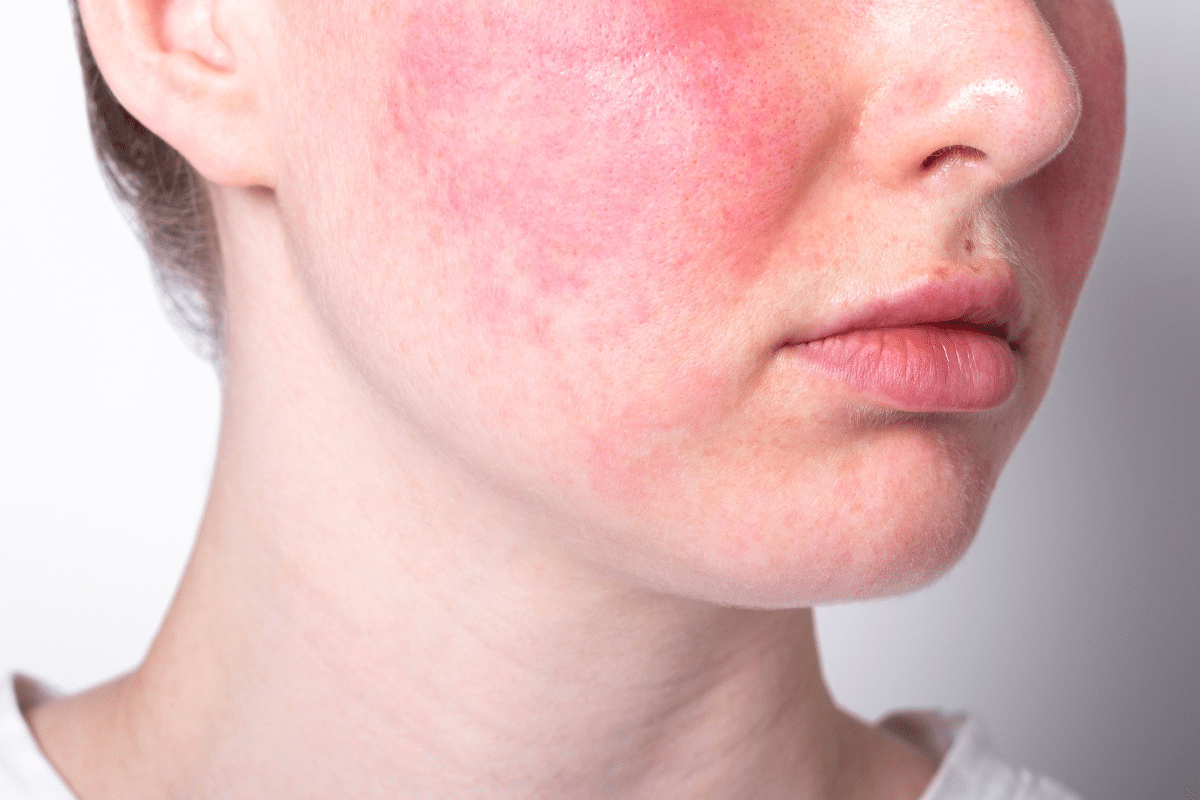
Malar Rash: The Classic Butterfly Pattern
Malar rash, also known as a butterfly rash, is a key sign of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). It shows up in about 20.4 percent of SLE patients. This makes it a big clue for doctors to diagnose the condition.
Clinical Characteristics and Appearance
The malar rash looks like a butterfly on the cheeks and nose. It’s usually red and can make the skin more sensitive to sunlight.
Medical Expert. Werth says that skin symptoms can show what’s happening inside the body. She stresses how important it is to notice and treat skin issues.
Triggers and Exacerbating Factors
Several things can make the malar rash worse or start it. These include:
- Exposure to sunlight
- Stress
- Infections
Knowing what causes these problems helps manage the condition better.
Differential Diagnosis from Similar Conditions
It’s important to tell malar rash apart from other skin issues. Conditions that might look similar include:
|
Condition |
Characteristics |
|---|---|
|
Rosacea |
Flushing, papules, and pustules, typically without the butterfly pattern |
|
Contact Dermatitis |
Localized reaction to allergens or irritants, not necessarily in a butterfly distribution |
|
Erysipelas |
Acute infection with distinct borders, often accompanied by fever |
Getting a correct diagnosis needs a careful look and thinking about the whole situation.
Discoid Lupus Erythematosus: Scarring Skin Lesions
Scarring skin lesions are a key feature of discoid lupus erythematosus. This condition is closely linked to systemic lupus erythematosus. DLE can cause lasting scarring, setting it apart from other types of cutaneous lupus.
Identifying Features and Distribution
DLE lesions are usually disc-shaped and can appear anywhere on the body. They often show up on sun-exposed areas like the face, ears, and scalp. These lesions can be red, scaly, and sometimes have follicular plugging.
Key Features of DLE Lesions:
- Disc-shaped appearance
- Potential for scarring and permanent damage
- Commonly found on sun-exposed areas
- Can be accompanied by symptoms like erythema and scaling
Progression and Long-term Complications
If not treated, DLE lesions can cause serious scarring and disfigurement. Scalp scarring can lead to permanent hair loss. It’s important to monitor and treat early to avoid long-term issues.
|
Complication |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Scarring |
Permanent damage to the skin, potentially leading to disfigurement |
|
Hair Loss |
Scarring on the scalp can result in irreversible hair loss |
|
Skin Discoloration |
Lesions can cause changes in skin pigmentation |
Relationship to Systemic Disease
DLE is mainly a skin condition but is linked to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Patients with DLE should be checked for systemic symptoms. A skin biopsy can help differentiate DLE from other conditions and guide treatment.
Healthcare providers must be aware of the risk of systemic involvement in DLE patients. They should manage the condition properly.
Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (SCLE) Manifestations
SCLE is a key part of lupus and needs attention for its skin symptoms. It affects about 11.1 percent of people with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Doctors must know about it.
SCLE has two main types of skin lesions: papulosquamous and annular. These lesions help doctors diagnose SCLE and cause discomfort for patients.
Papulosquamous and Annular Variants
The papulosquamous variant of SCLE has scaly papules that can grow into plaques. These look like psoriasis, so doctors must be careful when diagnosing.
The annular variant has a ring-like pattern with clear centers. It can look like other skin conditions, so doctors need to examine it closely.
Photosensitivity and Environmental Triggers
Photosensitivity is a key feature of SCLE. UV radiation makes skin lesions worse. Medical Expert.
Things like UV exposure can make SCLE symptoms worse. Teaching patients about protecting themselves from the sun is very important.
Association with Specific Antibodies
SCLE often has anti-Ro/SSA antibodies. Finding these antibodies helps doctors diagnose SCLE and understand how it works.
SCLE and certain autoantibodies show how complex its immune system is. Knowing this helps doctors treat SCLE better.
Alopecia in Lupus: Patterns and Presentations
Hair loss is common in Lupus patients, affecting nearly half of those with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). It can greatly affect a patient’s life, impacting their self-esteem and well-being. We focus on addressing this issue fully.
Non-scarring vs. Scarring Alopecia
Alopecia in Lupus can be non-scarring or scarring. Non-scarring is more common and can be reversed. Scarring, on the other hand, causes permanent hair loss by destroying follicles. Knowing the difference is key to the right treatment.
Non-scarring alopecia in Lupus looks like diffuse hair thinning, similar to telogen effluvium. It’s often caused by Lupus’s systemic inflammation. In contrast, scarring alopecia has scarring lesions on the scalp, leading to permanent hair loss.
Lupus Hair (“Lupus Hairs”)
“Lupus hairs” are fragile, brittle hairs seen in Lupus patients. They break easily and are linked to active disease. Finding “Lupus hairs” can mean the disease is active and treatment might need to change.
“The presence of ‘Lupus hairs’ can be a significant indicator of disease activity, necessitating a thorough assessment and possibly a change in treatment strategy.”
Management Approaches for Hair Loss
Managing alopecia in Lupus requires a detailed plan. For non-scarring alopecia, the focus is on controlling Lupus. This might include systemic corticosteroids, antimalarials, or immunosuppressants. For scarring alopecia, acting quickly is key to prevent more hair loss.
|
Management Approach |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Systemic Corticosteroids |
Used to reduce inflammation and control disease activity |
|
Antimalarials |
Effective in managing skin and joint manifestations of Lupus |
|
Immunosuppressive Agents |
Reserved for severe cases of Lupus, including those with significant hair loss |
We stress the need for a complete approach to hair loss in Lupus patients. This includes photoprotection, gentle hair care, and addressing the emotional impact of alopecia.
Skin Lesions in Lupus Erythematosus: Vasculitis and Raynaud’s Phenomenon
Vasculitis and Raynaud’s phenomenon are common skin issues in lupus patients. They can cause different skin problems, affecting people’s lives. We will look at the signs and problems these conditions bring.
Cutaneous Vasculitis Manifestations
Cutaneous vasculitis in lupus can show up as palpable purpura, which are purple spots you can feel. It happens when blood vessels get inflamed, causing skin problems. These issues can be mild or severe and affect different parts of the skin.
Patients with cutaneous vasculitis might get ulcerations and necrosis in serious cases. This makes it hard to treat. Vasculitis often means the disease is more complex, needing detailed treatment plans.
Raynaud’s Phenomenon in Lupus Patients
Raynaud’s phenomenon is when blood vessels in the fingers and toes narrow in cold or stress. This can be a big problem for lupus patients, as it can cut off blood flow to the hands and feet.
Managing Raynaud’s involves changing your lifestyle, like staying warm and avoiding stress. Doctors might also use vasodilators to help blood flow better.
Digital Ulcers and Nail Fold Changes
Digital ulcers are a problem caused by poor blood flow in the fingers and toes. They can hurt and be hard to heal, making it tough for patients and doctors.
Nail fold changes, like telangiectasias and capillary abnormalities, are also seen in lupus patients. These signs can show the disease’s impact on blood vessels and how active it is.
It’s key to take good care of wounds and prevent digital ulcers. Watching nail fold changes can help doctors understand the disease better and make treatment plans.
Oral and Mucosal Manifestations of Lupus
Lupus erythematosus is complex, showing up in the mouth and on mucous membranes. These symptoms can really affect a person’s life. They need care that covers all these symptoms.
Oral Ulcers and Their Characteristics
Oral ulcers are common in lupus patients. They can hurt and show up in different parts of the mouth. These ulcers often come back and can make eating and talking hard.
|
Characteristics |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Location |
Oral mucosal surfaces |
|
Appearance |
Variable, often with a red or white appearance |
|
Symptoms |
Painful, potentially impacting eating and speaking |
Nasal and Ocular Involvement
Lupus can also hit the nasal and eye areas. Nasal issues might cause ulcers or crusts. Eye problems can lead to things like episcleritis or scleritis.
Genital Lesions in Lupus
Genital lesions are rare but can happen in lupus. They look like mouth ulcers and can hurt. Managing these lesions means using creams and sometimes medicines to control symptoms.
We offer full care for these symptoms. Our goal is to help our patients manage their lupus well.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Cutaneous Lupus
Managing cutaneous lupus starts with a precise diagnosis. This guides the treatment plan. We know how complex diagnosing this condition can be. Tailoring treatment to each patient’s needs is key.
Skin Biopsy Techniques and Findings
A skin biopsy is a key tool for diagnosing cutaneous lupus. It involves taking a small skin sample for a microscope check. The biopsy can confirm the diagnosis by showing skin inflammation and damage.
We use different biopsy methods, like punch and excisional biopsies. The right method is important for an accurate diagnosis.
Topical and Systemic Treatment Options
Treatment for cutaneous lupus varies based on the disease’s severity. Topical corticosteroids work for mild cases. For more severe cases, systemic medications like antimalarials or immunosuppressants are needed.
We also consider biologics and new treatments for those who don’t respond to usual treatments. Our goal is to control symptoms, prevent flare-ups, and protect the skin.
Photoprotection and Lifestyle Modifications
Photoprotection is vital for managing cutaneous lupus. We teach patients about using broad-spectrum sunscreens and wearing protective clothing. Avoiding peak sun hours also helps prevent UV-induced flare-ups.
Lifestyle changes are also important. Eating well, managing stress, and not smoking can help control the disease. These habits can slow the disease’s progression.
By accurately diagnosing and treating cutaneous lupus, along with lifestyle advice, we help patients manage their symptoms. This improves their quality of life.
Conclusion: Living with Cutaneous Lupus
Managing cutaneous lupus erythematosus needs a full plan. This includes medical treatment and changes in lifestyle. We know a detailed strategy is key to controlling symptoms and improving life quality for patients.
People with cutaneous lupus can live active lives with the right care. Our healthcare team is committed to top-notch care and support. We make sure international patients get the best treatment for their condition.
Good management of cutaneous lupus combines different treatments and lifestyle changes. By taking a whole-body approach to lupus care, we help patients manage their condition well. This way, they can stay healthy and live well with lupus.
FAQ
What are the common skin manifestations of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)?
SLE can cause several skin issues. These include a malar rash, discoid lupus erythematosus, and subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. It can also lead to alopecia, cutaneous vasculitis, and oral ulcers.
What is the difference between Acute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (ACLE) and Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (SCLE)?
ACLE starts suddenly and is linked to other disease activity. SCLE, on the other hand, has papulosquamous or annular lesions. It’s often caused by photosensitivity.
How is Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) diagnosed and treated?
DLE is diagnosed by looking at the skin and doing a biopsy. Treatment includes topical corticosteroids, antimalarials, and immunosuppressants. These help manage symptoms and prevent scarring.
What is the relationship between Lupus and hair loss?
Lupus can lead to hair loss. This can be either non-scarring or scarring. Managing the disease and addressing hair loss are key.
Can Lupus cause oral and mucosal lesions?
Yes, Lupus can cause oral ulcers and affect the nose, eyes, and genitals. It’s important to get proper care to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
How is cutaneous Lupus diagnosed?
Diagnosing cutaneous Lupus involves a clinical exam, skin biopsy, and lab tests. These confirm Lupus-specific skin lesions and rule out other conditions.
What are the treatment options for cutaneous Lupus?
Treatments include topical corticosteroids, antimalarials, and immunosuppressants. Photoprotection measures are also used to manage symptoms and prevent disease progression.
How can photosensitivity be managed in patients with cutaneous Lupus?
Managing photosensitivity involves avoiding the sun, wearing protective clothing, and using broad-spectrum sunscreens. This prevents UV-induced skin damage.
What is the role of skin biopsy in diagnosing cutaneous Lupus?
Skin biopsy is key in confirming Lupus-specific skin lesions. It helps differentiate cutaneous Lupus from other conditions, guiding treatment.
Can cutaneous Lupus be associated with systemic disease?
Yes, cutaneous Lupus can be linked to systemic disease. It’s important to evaluate for systemic involvement to ensure proper care.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3410306/