Cardiovascular diseases are a big worry worldwide. Stent placement is a common way to fix blocked or narrowed arteries. Recent studies show that stent placement isn’t just for older people; younger folks are getting them too. Knowing the average age for stent placement helps us understand heart health trends and what affects them. Detailing what is the average age for a stent placement and discussing the statistical average age for stent placement among cardiac patients.
We look into the details of stent placement ages. This tells us a lot about heart health. Things like lifestyle, genetics, and conditions like coronary artery disease play big roles in who gets a stent.
Key Takeaways
- The age demographic for stent placement varies widely.
- Lifestyle and genetics significantly influence the need for stent placement.
- Coronary artery disease is a major factor in stent placement.
- Younger individuals are increasingly undergoing stent placement.
- Understanding stent placement ages provides insights into cardiovascular health trends.
The Science Behind Stent Procedures
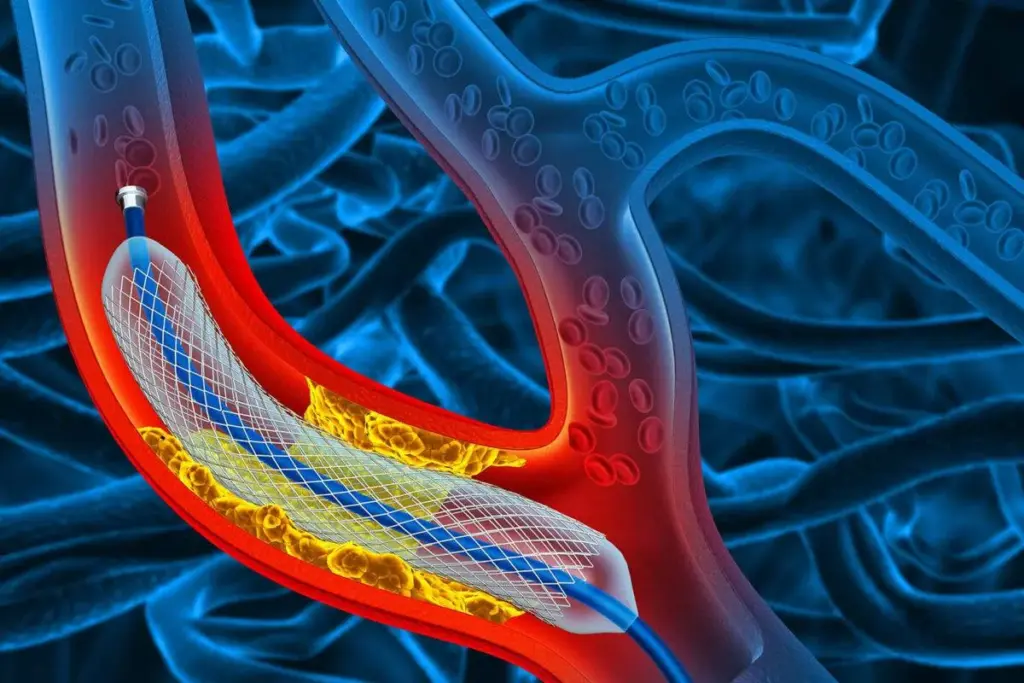
Stent procedures are a big part of interventional cardiology. This field has made huge strides in recent years. We’ll look into how stents work to open blocked arteries.
Definition and Function of Stents
A stent is a small, mesh tube that opens up blocked arteries. It helps blood flow better and lowers heart attack risks. Stents are made from metal or polymer and stay in the artery forever.
To place a stent, doctors follow these steps:
- Angiography to see the blocked artery
- Balloon angioplasty to widen it
- Stent deployment to keep it open
Types of Stents Used in Modern Medicine
There are many stent types, each for different needs. Here are the main ones:
|
Type of Stent |
Description |
Advantages |
|---|---|---|
|
Bare-Metal Stents |
Made from metal mesh |
Less expensive, easier to place |
|
Drug-Eluting Stents |
Coated with medication to prevent restenosis |
Reduced risk of artery re-narrowing |
|
Bioresorbable Stents |
Made from materials that dissolve over time |
Reduces long-term complications, restores natural artery function |
Choosing the right stent depends on many things. These include the patient’s health history, the blockage’s location and severity, and overall health. Knowing these helps find the optimal age for stent placement and improves patient outcomes.
Looking into stent procedures shows that age for placement varies. This depends on the stent type and the patient’s condition.
Common Medical Conditions Requiring Stent Placement
Some medical conditions make stent placement more likely. Stents help treat heart diseases, improving life quality. We’ll look at the main conditions that often need stents.
Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD) often needs stents. It happens when arteries narrow or block due to plaque. This can cause heart attacks.
Stents are used during angioplasty to keep arteries open. This improves blood flow to the heart.
The American Heart Association says CAD is the top cause of death globally. Stents have changed heart care, making treatment less invasive.
“The use of stents in coronary artery disease has significantly improved patient outcomes by reducing the risk of heart attacks and improving overall cardiac health.”American College of Cardiology
Peripheral Artery Disease
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) also needs stents. It affects arteries outside the heart, mainly in the legs. This causes pain and limits movement.
Stenting opens blocked arteries, improving blood flow and easing symptoms. PAD is common, hitting older adults hard. Stents can greatly improve their lives by reducing pain and improving mobility.
|
Condition |
Typical Age Group Affected |
Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
|
Coronary Artery Disease |
45-75 years |
Chest pain, shortness of breath |
|
Peripheral Artery Disease |
50-80 years |
Leg pain, cramping during activity |
Other Conditions Requiring Stent Intervention
Other conditions also need stents. Carotid artery disease is treated with stents to prevent stroke. Renal artery stenosis, affecting kidney blood supply, is also stented.
The age for stent placement varies by condition. Knowing these conditions and treatments is key for doctors and patients.
Understanding these conditions shows how vital stenting is. It improves patient outcomes and quality of life.
Average Age for Stent Placement: Current Statistics
Knowing the average age for stent placement is key for doctors and patients. Looking at current stats, we see many factors play a role in when people get stents.
US Data on Stent Procedure Demographics
In the US, stent data shows a detailed picture. Studies say the average age for coronary stent implantation is about 65 years. This number changes based on heart disease rates and new medical tech.
Looking closer at demographics, we learn:
- Men tend to get stents younger than women.
- Having diseases like diabetes and high blood pressure can lower the stent age.
- Where you live in the US can also change the average age due to different healthcare access.
International Comparisons of Stent Recipient Ages
Comparing US data to the rest of the world shows interesting differences. For example:
- In some European countries, the average age for stents is over 67 years.
- On the other hand, some Asian countries have an average age under 60 years. This might be because of lifestyle and genetics.
These global comparisons show why it’s vital to look at health trends, lifestyle, and healthcare systems. They help us understand the typical age for stent surgery worldwide and what affects it.
Age Distribution Across Different Types of Stents
Stent placement ages vary by stent type, showing different patient demographics. Stents treat many conditions, like coronary artery disease and peripheral artery disease. Knowing the age ranges for each stent type helps tailor treatments to patients.
Coronary Stent Age Patterns
Coronary stents are used a lot for coronary artery disease (CAD). Most people getting these stents are over 60. The average age for getting a coronary stent is about 65, showing CAD’s commonality in older adults.
Key age-related trends for coronary stents include:
- Patients under 50: Less common, often associated with early-onset CAD or genetic predispositions.
- Patients between 60-75: Most common age range, reflecting the peak prevalence of CAD.
- Patients over 80: Increasingly common due to aging populations and improved survival rates.
Peripheral Vascular Stent Demographics
Peripheral vascular stents treat peripheral artery disease (PAD). Most patients getting these stents are over 65. The average age for these stents is a bit higher than coronary stents, often because PAD is diagnosed later.
Notable demographics for peripheral vascular stents include:
- Higher prevalence in older adults, with a significant increase in patients over 70.
- Association with comorbidities such as diabetes and hypertension.
- Increasing use in younger patients with lifestyle-related PAD.
Neurovascular Stent Age Statistics
Neurovascular stents treat brain blood vessel conditions like aneurysms and intracranial stenosis. The age range for these stents varies by condition. For example, aneurysm treatments might have younger patients, while intracranial stenosis treatments might have older ones.
Age-related observations for neurovascular stents include:
- A wider age range compared to coronary or peripheral stents.
- Younger patients are more commonly associated with aneurysm treatments.
- Older patients are more frequently treated for intracranial stenosis.
Stent Placement in Young Adults (Under 40)
Stent placement in people under 40 is interesting. It often comes with special risks and health concerns. We’ll look into why and what it means for young adults.
Causes of Early-Onset Arterial Blockages
Young adults getting stents often have certain health issues. These can include genetic predispositions, lifestyle choices, or other health problems. For example, some people might have a condition called familial hypercholesterolemia. This can cause heart disease early on, leading to stent placement.
Lifestyle choices also matter a lot. Smoking, eating too much saturated fat, and not being active can cause blockages early. Knowing these risks helps prevent and manage heart disease in the young.
Long-term Implications for Younger Recipients
Stent placement in young adults has big long-term effects. They might face challenges like stent failure or need more treatments later. So, it’s important to watch their heart health closely.
Also, young stent users might live longer. This means they could face problems with stent durability and might need more surgeries. This shows why ongoing cardiovascular care and healthy living are key.
Middle-Aged Stent Recipients (40-60 Years)
The average age for getting a cardiac stent is often between 40 and 60. This age range is key for heart health. People in this group often face a mix of lifestyle and genetic risks that lead to needing a stent.
Risk Factors Prevalent in This Age Group
Several risk factors are common among middle-aged stent recipients. These include:
- Hypertension: High blood pressure is a big risk for heart disease.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are more likely to get coronary artery disease.
- Smoking: Smoking greatly increases the risk of heart disease and stent need.
- High Cholesterol: High levels of LDL cholesterol can cause artery plaque buildup.
- Family History: A family history of heart disease raises the risk for middle-aged people.
These factors often work together, making cardiovascular events more likely in this age group.
Treatment Approaches and Considerations
Treating middle-aged stent recipients involves both immediate stent placement and long-term plans. We tailor treatments to each person’s specific risk factors.
Some important considerations are:
- Lifestyle Modifications: We encourage healthier lifestyles, like better diets and exercise.
- Medication Management: We use meds to control conditions like high blood pressure and cholesterol.
- Monitoring: Regular checks to see how well the stent is working and if heart disease is getting worse.
By using a full treatment plan, we can help improve outcomes for middle-aged stent recipients.
Stent Procedures in Older Adults (60-75 Years)
As people age from 60 to 75, their hearts change a lot. This can make stent placement more complex. We know these changes affect how well stents work.
Age-Related Cardiovascular Changes
Older adults face heart changes like stiffer arteries and less flexible blood vessels. They also have more health issues like high blood pressure and diabetes. These factors can make stent placement harder and change how well it works after.
When deciding on stents for older adults, we look at their health closely. Their overall health and any other health problems are key. They help us understand the good and bad sides of stent placement.
Benefit-Risk Assessment for This Age Group
Figuring out the good and bad of stents for older adults is complex. We look at their health, heart disease, and how stents might improve their life. We balance the benefits, like feeling better and moving easier, against the risks, like complications and ongoing care needs.
Choosing to get a stent is a personal decision for older adults. We consider their medical needs and what they value most. Our goal is to give care that fits each person’s unique situation.
Elderly Patients and Stent Interventions (75+ Years)
Elderly patients face unique challenges with stent placement due to age and health issues. When considering stent procedures for those 75 and older, we must balance benefits and risks. Our goal is to enhance their quality of life.
Special Considerations in Geriatric Cardiology
In geriatric cardiology, multiple health issues make stent decisions harder. Comprehensive geriatric assessment is key to understanding a patient’s health and recovery chances. We look at cognitive function, physical strength, and chronic conditions to decide on stent suitability.
Elderly patients need personalized treatment plans based on their medical history and current health. This approach helps reduce risks and increase stent benefits.
Quality of Life Outcomes After Stent Placement
When evaluating stent success in the elderly, quality of life outcomes are key. We look at procedure success and its effect on function, symptom relief, and well-being. Research shows stent placement can greatly improve quality of life by easing symptoms and improving mobility.
But, we must also consider the risks of stent placement in the elderly. Careful patient selection and meticulous post-procedure care are essential to avoid complications and ensure the best results.
By focusing on the patient and using new stent technology and techniques, we can better help elderly patients. As the population ages, understanding stent placement in older adults will become more critical for healthcare providers.
Gender Differences in Stent Placement Age
The age at which people get stents varies by gender. This is because men and women face different heart health risks. Hormones also play a role in when and how well stents work.
Male vs. Female Age Patterns
Men tend to get stents earlier than women. Men usually get them in their early to mid-60s. Women often wait until their late 60s or early 70s.
This age gap is due to many factors. Hormones and lifestyle choices are big ones. For example, estrogen helps protect women’s hearts before menopause. But after menopause, women’s heart risks rise, making them more like men’s.
Hormonal and Physiological Factors
Hormones, like estrogen, affect when and how well stents work. Estrogen helps women’s hearts before they stop menstruating. Other differences, like body size and health conditions, also play a part.
These factors are important for planning treatment. Doctors need to think about these differences when deciding on stent placement.
Key Considerations:
- Gender differences in cardiovascular risk factors
- Hormonal influences on heart health
- Physiological variations between men and women
Knowing these differences helps doctors give better care. This leads to better results for both men and women getting stents.
Socioeconomic and Racial Factors Affecting Stent Procedure Age
Healthcare access and genetic factors differ among various groups. These differences affect when people get stents. It’s important to understand these factors to ensure fair treatment for everyone.
Healthcare Access Disparities
People from lower-income backgrounds often face delays in medical care. This can lead to more severe heart problems. As a result, they might need stents at a younger age.
Areas with less access to healthcare tend to have more heart disease. This means stents are placed earlier in these communities. In contrast, wealthier areas with better healthcare tend to have older stent recipients.
|
Socioeconomic Status |
Average Age for Stent Placement |
Healthcare Access Index |
|---|---|---|
|
Low |
55 |
60 |
|
Middle |
62 |
75 |
|
High |
68 |
90 |
Genetic and Environmental Influences
Genetics and environment also shape when stents are placed. Some racial groups are more at risk for heart disease due to their genes. For example, people of South Asian descent are at higher risk for heart problems.
Environmental factors like diet and pollution can make these risks worse. A diet full of bad fats and lacking in fruits and veggies can speed up heart disease. This might mean stents are needed sooner.
Understanding how socioeconomic status, race, and healthcare outcomes interact is key. This knowledge helps doctors tailor care to meet the needs of different patients. It can lead to better heart health for all.
Determining the Optimal Age for Stent Insertion
Cardiologists look at many things to decide when to put in a stent. They don’t just look at how old the patient is. They check the patient’s health fully.
Medical Criteria for Timing Interventions
When to put in a stent depends on several medical factors. These include how bad the symptoms are and if the patient has other health issues. We use these to figure out how urgent the procedure is and what risks there might be.
Important things to consider are:
- The extent of arterial blockage
- The patient’s overall cardiovascular health
- Presence of other health conditions
- Previous medical interventions
Balancing Immediate Need vs. Long-term Outcomes
It’s important to balance the need for a stent now with what might happen later. We think about the benefits of acting quickly and the risks that might come up later.
|
Age Group |
Immediate Benefits |
Long-term Considerations |
|---|---|---|
|
Under 40 |
Relief from acute symptoms |
Potential for future complications, need for repeat procedures |
|
40-60 |
Improved quality of life, reduced risk of heart attack |
Management of risk factors, lifestyle adjustments |
|
60+ |
Symptom management, improved survival |
Considerations for comorbidities, procedural risks |
By looking at all these factors, we can find the best time for a stent for each patient. This way, we make sure they get the best care possible.
Recovery and Prognosis Based on Patient Age
The age of a patient getting a stent affects their recovery and future health. Looking at different age groups shows age’s big role in recovery and long-term health.
Post-Procedure Complications by Age Group
Older patients face more problems after a stent procedure than younger ones. This is because older people often have other health issues and are less strong. Common issues include:
- Bleeding at the access site
- Vascular complications
- Renal failure
- Cardiac arrhythmias
Younger patients usually have fewer issues and heal faster. But, lifestyle and risk factors like smoking or diabetes can affect everyone’s recovery.
Long-Term Survival Rates Across Age Demographics
Survival rates after getting a stent also change with age. Younger patients tend to live longer than older ones. This is because older people face more health problems and their risk of death increases with age.
Important factors for long-term survival include:
- The type of stent used (e.g., drug-eluting vs. bare-metal stents)
- Following the doctor’s advice on medication
- Making healthy lifestyle choices (like eating right and exercising)
- Managing other health conditions
Knowing these factors helps us give better care to patients of all ages. This improves their chances of a good outcome after getting a stent.
Preventive Strategies to Delay Stent Necessity
Preventive measures can delay or prevent stent needs. Keeping arteries healthy lowers the risk of needing a stent.
Lifestyle Modifications for Arterial Health
Lifestyle changes are key to stopping arterial diseases from getting worse. Important changes include:
- Eating a healthy diet full of fruits, veggies, and whole grains
- Doing regular physical activity to boost heart health
- Quitting smoking to lessen artery damage
- Managing stress with meditation or yoga
Medical Management Before Stent Intervention
Medical care is also vital in avoiding stent needs. This includes:
- Keeping high blood pressure in check with meds and lifestyle
- Controlling diabetes with diet, exercise, and meds
- Managing cholesterol with diet and statins if needed
Good management of these conditions can help avoid stents. It improves life quality and outcomes.
Knowing stent placement age data and the optimal age for stent insertion helps tailor prevention. It’s based on individual risk and health.
Technological Advances Affecting Stent Placement Age Range
Modern technology is changing the age limits for stent placement. With new medical advancements, more people are getting stents. This is a big change in who can get stent procedures.
Evolution of Stent Materials and Design
New stent materials and designs are key to this change. Drug-eluting stents are now used, which lower the chance of blockages coming back. This makes stents a good option for people of all ages.
Stent technology has improved a lot. For example, bioresorbable stents are being made. They act as a temporary support and then dissolve, which could lead to fewer complications later on.
|
Stent Type |
Material |
Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
|
Bare-metal Stents |
Stainless Steel or Cobalt-Chromium |
Simple Design, Cost-effective |
|
Drug-eluting Stents |
Metal with Drug Coating |
Reduced Risk of Restenosis |
|
Bioresorbable Stents |
Biodegradable Polymers or Metals |
Temporary Scaffolding, Reduced Long-term Complications |
Minimally Invasive Techniques and Their Impact on Age Criteria
New, less invasive techniques are also changing stent placement ages. These methods lead to fewer problems and quicker healing. This makes them better for older patients.
Robot-assisted stent placement is becoming more common. It improves accuracy and allows for more complex procedures. This helps patients of all ages get stents.
As technology keeps getting better, more people will be able to get stents. This means more treatment options for everyone, no matter their age.
Conclusion
Knowing when stents are usually implanted is key in heart care. The age for stent procedures changes a lot. This depends on health issues, money status, and new stent tech.
Looking into this, we see many factors affect stent ages. Better heart care and stent tech are always getting better. This might change the average age for stents and help more people.
Healthcare teams can give better care by understanding these factors. As heart care gets better, who gets stents will change. This shows how health and disease are managed differently over time.
FAQ
What is the average age for stent placement?
The age for stent placement varies. It depends on the stent type and the medical condition. Coronary stents often involve older people due to heart disease.
How does age influence the outcome of stent placement?
Age affects stent placement outcomes. Older patients might face more complications and have different survival rates than younger ones.
What are the typical age ranges for different types of stent placements?
Stent placement ages differ by type. Coronary stents often involve older adults due to heart disease. Peripheral and neurovascular stents have different demographics based on their conditions.
Can young adults undergo stent placement?
Yes, young adults under 40 can get stents. It’s rare but can happen due to genetics, lifestyle, or health conditions.
How do socioeconomic and racial factors affect the age of stent placement?
Socioeconomic status and race impact stent placement age. This is due to healthcare access, lifestyle, and genetics.
What are the key considerations for determining the optimal age for stent insertion?
Choosing the right age for stent insertion requires careful thought. It depends on symptoms, health conditions, and long-term benefits.
Are there gender differences in the age at which individuals undergo stent placement?
Yes, gender influences stent placement age. It’s due to different risk factors and hormonal effects.
How can preventive strategies delay the necessity for stent placement?
Preventive measures like lifestyle changes and managing conditions can delay or prevent stent need.
What impact do technological advances have on the age range for stent placement?
Advances in stent technology and techniques can expand stent placement to more ages. This makes stents a viable option for more patients.
What is the typical recovery process like after stent placement, and how does age affect it?
Recovery after stent placement varies with age. Older patients might face more complications and need closer monitoring.
How do medical conditions like coronary artery disease influence the average age for stent placement?
Conditions like coronary artery disease affect stent placement age. They are more common in older people.
References
New England Journal of Medicine. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1002358











