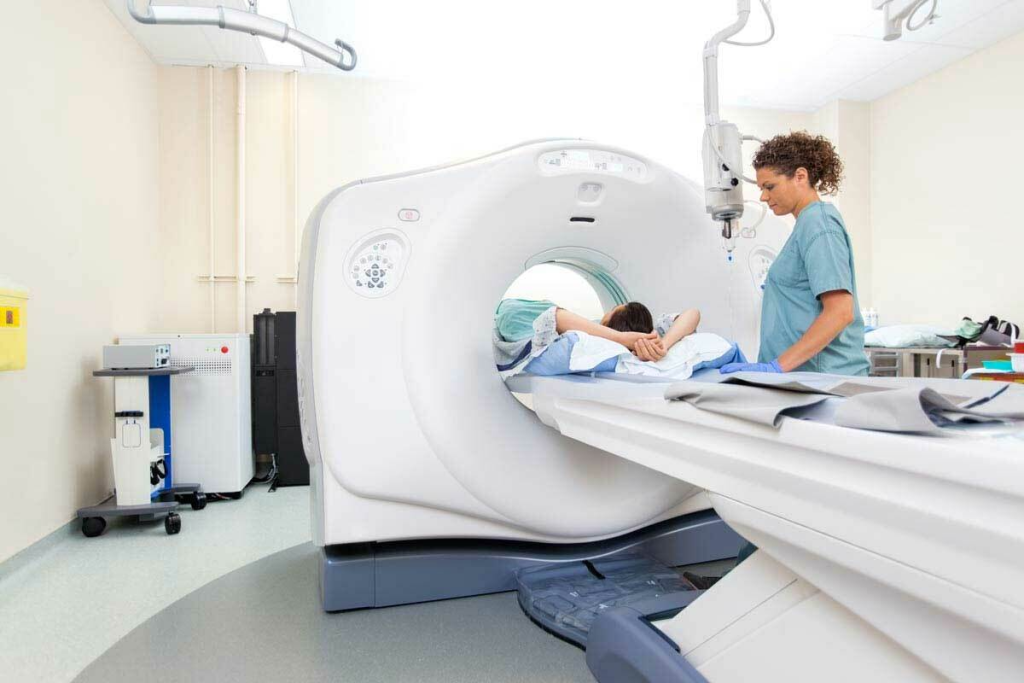
Finding bone cancer early can really help patients. At Liv Hospital, we use the latest tech and care to help patients. Many tests help find bone cancer, like imaging that shows the bone clearly. One of the most effective imaging tests is the CT scan bone cancer exam, which provides detailed cross-sectional images of bones to detect tumors and assess their extent. CT scans have high sensitivity and specificity in diagnosing bone cancer, aiding in early detection and treatment planning to improve patient outcomes.
.
To know if a growth is cancer, a biopsy might be needed. We stress the value of new diagnostic tools in better care.
It’s important to know the different types of bone cancer and their warning signs. This knowledge helps in early detection and treatment. Bone cancer is divided into primary and secondary types, each with its own characteristics and treatment options.
Primary bone cancer starts in the bones. Secondary bone cancer spreads to the bones from other cancers. Osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, and Ewing’s sarcoma are common primary bone cancers. Osteosarcoma often affects long bones.
Chondrosarcoma comes from cartilage cells. Ewing’s sarcoma is a fast-growing tumor that can happen in any bone. Secondary bone cancer comes from cancers like breast, prostate, lung, or kidney. It can greatly affect a patient’s life and chances of recovery.
It’s key to know the symptoms of bone cancer for early diagnosis. Symptoms include persistent bone pain, swelling, and tenderness. Some may have fractures without a big injury, known as pathological fractures.
Other signs include feeling tired, losing weight, and having a fever. These symptoms are not specific but should not be ignored.
| Type of Bone Cancer | Origin | Common Symptoms |
| Osteosarcoma | Bone cells | Bone pain, swelling |
| Chondrosarcoma | Cartilage cells | Pain, swelling, limited mobility |
| Ewing’s Sarcoma | Bone or soft tissue | Pain, swelling, fever |
| Secondary Bone Cancer | Metastasis from other cancers | Bone pain, fractures, weight loss |
Knowing about bone cancer types and symptoms is vital for early diagnosis and treatment. Recognizing these signs and understanding the different types of bone cancer helps patients get medical help early. This can lead to better outcomes.
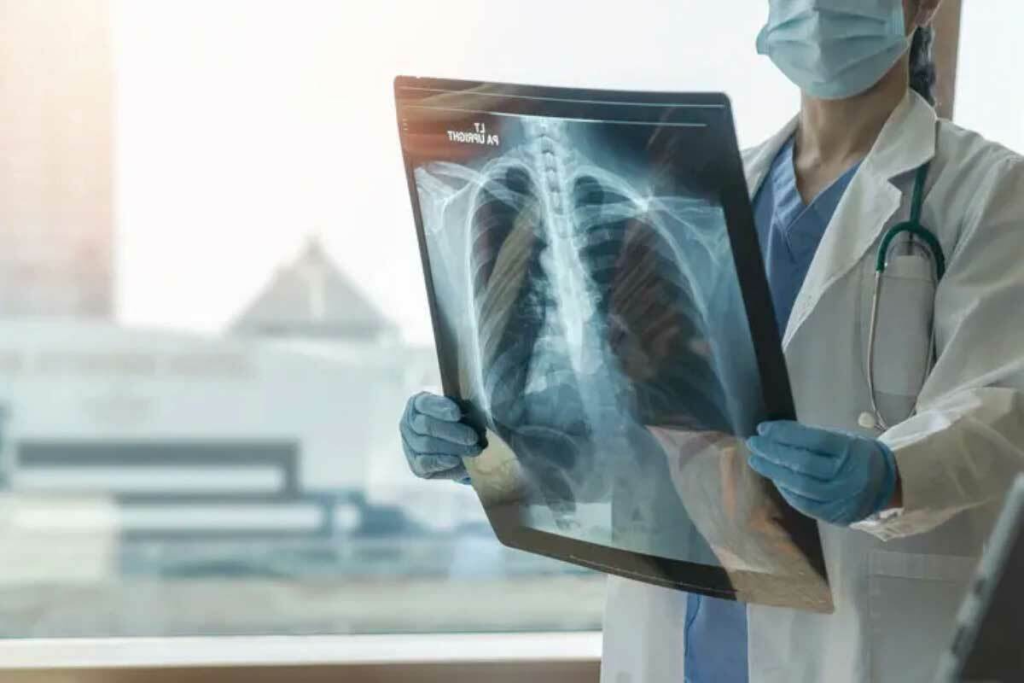
When symptoms hint at bone cancer, the journey starts with a detailed first check. Most people first reach out to their GP. This first step is key to further tests.
The first doctor visit is a big step in finding out if you have bone cancer. The doctor will ask about your health history and do a physical check. They look for signs like ongoing bone pain, swelling, or unexplained fractures.
A detailed physical check is important. It helps find any issues that need further looking into. The doctor will check your overall health for signs of bone cancer.
Doctors say, “A complete first check is essential to decide what to do next for those suspected of having bone cancer.”
After the first check and physical, figuring out the right tests comes next. This means choosing which tests will confirm or rule out bone cancer.
What tests you get depend on your symptoms, health history, and the physical check. Tests like X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, and blood work are common for bone cancer.
When doctors think bone cancer might be present, they often start with X-rays. X-rays use a small amount of radiation to see inside your body, focusing on bones. They help find bone issues that need more checking.
X-rays show bone problems by taking pictures of the bones inside. They’re great for spotting fractures, bone lesions, or tumors. Cancer can change bones, making them look different on an X-ray.
Even though X-rays are good for starting, they have limits. They might not show soft tissues or the exact bone issue. More tests are often needed to be sure.
Getting an X-ray for bone cancer is quick and usually painless. The technician will set you up, and the machine will take pictures. It’s over in a few minutes. You might need to hold your breath or stay very calm.
Knowing how X-rays help find bone cancer is important. They’re a key first step, but more tests might follow to get a full picture.
CT scans are key in finding bone cancer. They give a full view of tumors. A CT scan uses X-rays and a computer to show inside your body. It’s great for seeing the size, shape, and where they are.
CT scans show bone tumors in 3D detail. Doctors can then see how big and where the tumors are. This helps figure out the cancer’s stage and how to treat it.
The clear images from CT scans also show how tumors relate to nearby tissues. This is important for planning surgery.
New CT tech uses AI, making diagnosis better. AI helps find small issues that might be missed. This makes diagnosing bone cancer more accurate.
CT scans also help with biopsies for bone cancer. They guide the biopsy needle to the right spot. This makes the biopsy results more reliable.
CT-guided biopsies are great for hard-to-reach tumors. They help doctors get the right tissue for testing.
Together, CT scans, AI, and biopsies help doctors better diagnose and treat bone cancer. This means better care for patients.
Diagnosing bone cancer often uses different imaging methods. MRI is key because it can see soft tissues well. MRI stands for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. It uses magnetism and radio waves to show the body’s inside details.
MRI has many benefits for bone cancer checks. It can see bone marrow and soft tissues clearly. This helps doctors know how big the tumor is and plan surgery.
Key benefits of MRI in bone cancer diagnosis include:
Special MRI plans are used for bone tumor checks. These plans might include T1-weighted and T2-weighted images, and studies with contrast.
| MRI Sequence | Application in Bone Tumor Evaluation |
| T1-weighted | Provides detailed anatomy and is useful for assessing bone marrow |
| T2-weighted | Highlights fluid-containing structures and is sensitive to changes in soft tissues |
| Contrast-enhanced | Helps in identifying tumor vascularity and assessing the extent of tumor spread |
MRI is often chosen over other methods in some cases. For example, when detailed soft tissue checks are needed or when tumors are in complex areas.
The choice of imaging modality depends on various factors, including the specific clinical question, the location of the suspected tumor, and the patient’s overall condition.
Bone cancer detection often uses imaging and lab tests, including blood work. Blood tests aren’t a sure way to find bone cancer. But they help a lot in figuring out what’s wrong and how to treat it.
Blood tests can hint at bone cancer by looking at certain enzymes and proteins. Alkaline phosphatase, for example, is linked to bone growth. High levels might mean bone cancer is present. Other markers, like lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) check how active cells are.
But, these markers aren’t just for bone cancer. They can also show up in other health issues. For example, high alkaline phosphatase can mean bone fractures, liver disease, or other cancers. So, while these markers are useful, they need to be looked at with other test results.
There’s no single blood test for bone cancer. Blood tests can’t say for sure if you have a bone tumor. To diagnose bone cancer, doctors use X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs, and then take a biopsy.
Even if blood tests can’t directly find bone cancer, they’re key for checking overall health. They help figure out how far the disease has spread. This is important for planning treatment.
These tests are very important for cancer staging and treatment planning. They help doctors see how well treatment is working and make changes if needed.
PET scans are key in finding bone cancer by showing metabolic activity in tumors. They use radioactive materials to spot changes in body tissues.
PET scans inject a radioactive tracer into the body. Tumors, being more active, take up more tracer. This makes tumors visible during the scan.
This method helps us see the tumor’s size and activity. It’s vital for diagnosing bone cancer and planning treatment.
Using PET and CT scans together boosts accuracy. The PET scan shows metabolic activity, while the CT scan gives detailed images. This combo helps pinpoint tumors and their size.
This combination is great for seeing if cancer has spread. It’s key for staging and treatment planning.
| Diagnostic Tool | Information Provided | Use in Bone Cancer |
| PET Scan | Metabolic activity of tumors | Identifying tumor presence and behavior |
| CT Scan | Anatomical details | Precise location and extent of tumors |
| PET-CT Combination | Both metabolic and anatomical information | Enhanced accuracy in diagnosis and staging |
During a PET scan, patients get a radioactive tracer and lie in a scanner. It’s painless but you must stay very quiet for a bit.
One thing to think about is radiation. While it’s small, it’s important. We make sure scans are worth the risk and try to keep exposure low.
We focus on making patients comfortable and informed about radiation. We want to support them every step of the way.
The bone biopsy is key to diagnosing bone cancer. It gives a detailed look at the tumor. This helps doctors know if it’s cancer, what type, and how far it has spread. It also guides treatment choices.
There are two main bone biopsy types: needle and surgical. A needle biopsy uses a thin needle to take a bone tissue sample. It’s less invasive and has less risk of complications, with quicker recovery.
A surgical biopsy requires an incision to reach the tumor. It’s used for larger samples or hard-to-reach tumors. This method gives a bigger sample for detailed analysis.
The biopsy starts with preparation, like imaging tests to find the tumor. It’s done under local anesthesia to keep the patient comfortable. Recovery time depends on the biopsy type.
Needle biopsy recovery is quick, with little discomfort. Patients can get back to normal fast.
Surgical biopsy recovery takes longer, sometimes a few days. Doctors give specific care instructions to help with healing and prevent infection.
After the biopsy, the sample is examined under a microscope. This is called histopathological analysis. It helps find cancer cells and understand the tumor’s characteristics.
Molecular testing also checks for genetic markers or mutations. This info helps tailor treatments based on the tumor’s behavior.
Bone scans use special materials to see how bones work and find cancer. They are tests that use a tiny bit of radioactive material. This helps doctors find and watch bone conditions, like cancer.
A bone scan starts with a small radioactive tracer injected into a vein. This tracer lights up active bones. It’s usually a technetium-based compound.
After the injection, it takes a few hours for the tracer to spread. During this time, you can move around and do normal things.
The scanning part has you lying on a table. A gamma camera takes pictures of your skeleton. It shows where the bones are most active. This can mean cancer, fractures, or infections.
The bone scan is great for finding cancers in bones, even if they started somewhere else.
Bone scans are better than X-rays or CT scans because they show bone activity. They’re good for finding conditions not seen on other scans.
They cover more of the body than MRI, spotting many diseases at once. But MRI shows soft tissues better. So, bone scans are often used with other tests for a full view.
Getting ready for a bone scan is easy. You might not eat or drink for a few hours. Remove any metal jewelry or objects.
After the scan, you can go back to your usual activities. Drinking lots of water helps get rid of the tracer. Side effects are rare, but some people might feel a bit off.
We know tests can worry you. Our team is here to help and support you. We want you to feel informed and at ease.
We use a detailed plan to find bone cancer, combining many tests for the best results. Finding bone cancer often means first checking for other health issues that might look like cancer. This careful method helps us give the most accurate diagnosis, which is key to good treatment plans.
Our diagnostic plan includes many tests and checks. We start with basic exams and then use X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans. Each test gives us important information about the bone and the tissues around it.
Using these tests together helps us figure out the type and stage of bone cancer. For example, X-rays show bone problems, but CT scans show the tumor’s shape and size in 3D. MRI scans are great for looking at soft tissues around the bone.
Multidisciplinary tumor boards are key in diagnosing. These teams include experts from oncology, radiology, and pathology who discuss patient cases together. This teamwork makes sure all parts of the diagnosis are considered, leading to better treatment plans.
After confirming bone cancer, staging is next. Staging shows how far the cancer has spread. This info is key for planning the right treatment.
Knowing the stage helps pick the best treatments, like surgery, chemo, or radiation. It also gives important info on what to expect, helping patients and families understand the disease’s likely course.
| Stage | Description | Typical Treatment Approach |
| Stage I | Cancer is localized and has not spread. | Surgery, possibly followed by observation. |
| Stage II | Cancer is localized but more aggressive. | Surgery, possibly with chemo or radiation. |
| Stage III | Cancer has spread to other parts of the body. | Systemic treatments like chemo, targeted therapy, or immunotherapy. |
The field of bone cancer detection is changing fast with new tech. We’re always looking to improve how we find and treat bone cancer. This means better care for our patients.
Liv Hospital is leading the way in these new methods. We use the latest tools like liquid biopsy and next-generation imaging. This helps us find bone cancer more accurately and quickly.
Liquid biopsy is a non-invasive way to find bone cancer. It looks at DNA in the blood to understand the tumor. This helps doctors make better treatment plans and track the disease.
New imaging tech is changing how we see bone cancer. MRI and CT scans now show tumors more clearly. This means doctors can plan treatments better and help patients more.
The benefits of these new imaging tools are many:
At Liv Hospital, we’re all about the latest tech for our patients. Our team creates treatment plans that use the newest diagnostic tools. This means our patients get the best care possible.
We’re always looking for new ways to help our patients. By using the latest tech, we can give them accurate diagnoses and effective treatments. This helps them have better outcomes.
Understanding bone cancer diagnosis can be tough, but knowing the tests helps. We’ve looked at tests like X-rays, CT scans, MRI, PET scans, and biopsies. Each one is key in finding bone cancer and knowing how far it has spread.
Getting a correct bone cancer diagnosis is very important. It helps doctors plan the best treatment. At Liv Hospital, we use the latest tech to give our patients accurate diagnoses and care.
As we get better at finding bone cancer, new tests will help patients even more. Knowing about the tests and working with doctors makes facing a bone cancer diagnosis easier.
Doctors use imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, MRI, and PET scans to find bone cancer. They also do lab tests and bone biopsies.
Blood tests can’t directly find bone cancer. But, they can show signs like high alkaline phosphatase levels. These tests help plan treatment and check how far the cancer has spread.
Yes, MRI is great for seeing bone marrow and tissues around it. It’s very good at finding bone cancer and seeing how big it is.
Yes, CT scans show detailed 3D images of bone tumors. They help doctors see how big the tumor is. New AI CT systems are even better at finding cancer.
PET scans show where bone tumors are active. When used with CT scans, they make finding cancer more accurate. They also help see if cancer has spread.
A bone biopsy takes a bone sample for testing. It’s done by removing a piece of bone. The sample is then checked to see if there’s cancer.
A bone scan shows how bones are working. It can find bone cancer and see if it’s spread. It’s often used with other tests.
Yes, a knee X-ray might show bone problems, like tumors. But X-rays aren’t always good at finding bone cancer. More tests are usually needed.
Staging is key to knowing how far bone cancer has spread. It helps doctors plan the best treatment. Knowing the stage helps predict how well a patient will do.
Yes, new tech like liquid biopsy and next-gen imaging are getting better at finding bone cancer. Liv Hospital uses the latest tech to help patients.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!
WhatsApp us