Reading a CT scan accurately is key in today’s medicine. It helps doctors spot different tissue densities and body parts. CT scans use X-rays, a type of radiation, to create images.
Doctors take X-rays from many angles and use detectors to see how much is absorbed. Knowing how to read a CT scan is vital for making diagnoses. Need help with CT scan interpretation? This essential guide provides step-by-step instructions on reading images and anatomy.
Key Takeaways
- CT scans are created using X-rays and measure tissue density.
- Accurate interpretation relies on recognizing anatomical structures.
- Understanding attenuation is key for effective diagnosis.
- CT scans can be used with or without contrast to see different body parts.
- Knowing the orientation is important when reading CT scans, often using the transverse plane.
The Fundamentals of CT Scan Technology
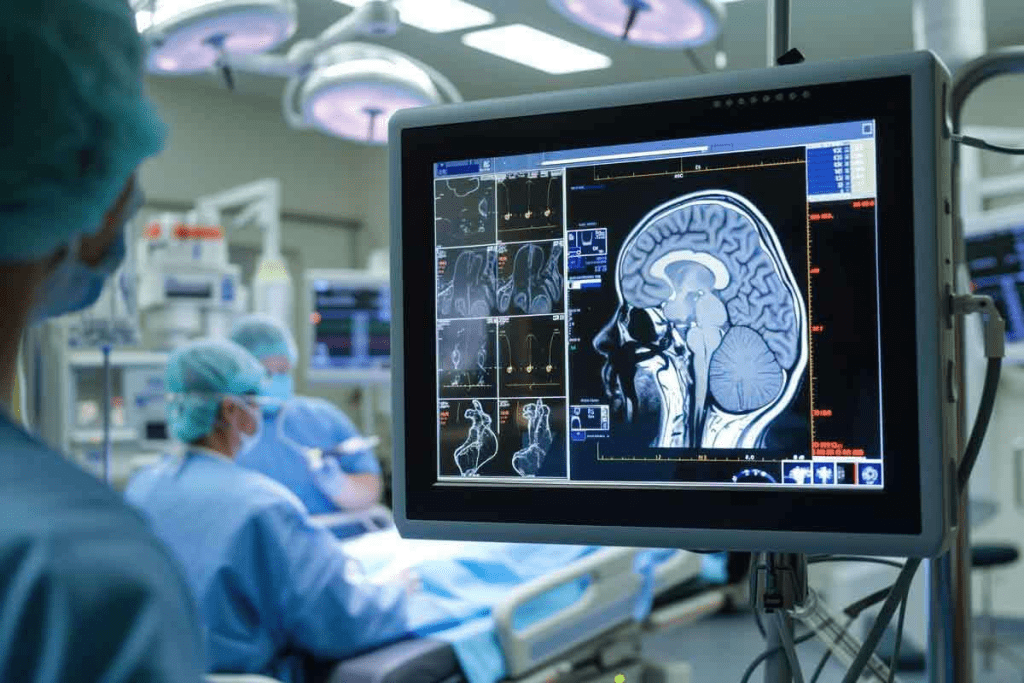
CT scans use X-rays to show what’s inside the body. They are key in modern medicine. Doctors use them to see inside the body clearly.
How CT Imaging Works
CT imaging measures how X-rays change as they go through the body. This change depends on the body part’s density. For example, bone absorbs more X-rays than soft tissues.
The scanner has an X-ray tube and detectors that move around the patient. They collect data from many angles. Then, special algorithms turn this data into detailed images.
Hounsfield Units and Tissue Density Measurement
The scanner measures how X-rays change in Hounsfield Units (HU). Water is 0 HU. Denser materials have positive HU, and less dense ones have negative.
- Bone: Has high HU values (around +1000)
- Soft Tissues: Have intermediate HU values (around +40 to +80)
- Air: Has low HU values (around -1000)
Knowing Hounsfield Units helps doctors understand CT scans. It lets them see different tissues and find problems.
Types of CT Scans and Their Applications
There are many CT scans, each for different uses:
- Non-contrast CT: Finds acute hemorrhage, kidney stones, and tumors.
- Contrast-enhanced CT: Uses contrast to show blood vessels and lesions.
- High-resolution CT: Shows small details, great for lung scans.
- CT Angiography: Looks at blood vessels and vascular diseases.
Each CT scan has its own benefits. Doctors pick the right one for each case.
Essential Equipment and Software for CT Scan Viewing

To read CT scans well, radiologists need special tools and tech. They must understand anatomy deeply. They also need the right equipment and software to see these images right.
PACS Systems and Viewing Software
PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) is key for storing and managing medical images. Radiologists need to view and interpret CT scans. The software with PACS lets them tweak images and mark important points.
Workstation Setup for Optimal Viewing
A good workstation is key for viewing CT scans. It needs high-resolution monitors to show detailed images. Correct orientation is also important. The setup should show images right, helping radiologists interpret them better.
Advanced Visualization Tools
Advanced tools are important for analyzing CT scans. Tools like multi-planar reconstruction (MPR), maximum intensity projection (MIP), and volume rendering help. They let radiologists see complex structures and problems clearly.
With PACS systems, the right software, a good workstation, and advanced tools, radiologists can read CT scans better. This approach is key to giving patients the best care.
Understanding CT Scan Orientation and Views
It’s key to know the various views and orientations of CT scans for good image interpretation. CT scans can be seen in many planes. This is important for diagnosing and treating medical conditions right.
Axial, Coronal, and Sagittal Planes
CT scans are mainly viewed in three main planes: axial, coronal, and sagittal. The axial plane is the most common. It shows images as if looking from below the patient, with the body sliced into horizontal sections. Axial images are usually seen from below, so the patient’s right side is on the left side of the image, and vice versa.
The coronal plane splits the body into front and back sections. It gives a view from the front or back. This plane is great for checking structures that span multiple axial slices. The sagittal plane splits the body into left and right sections. It offers a side view. It’s very useful for looking at midline structures or lesions.
Conventional Viewing Perspectives
When looking at CT scans, knowing the conventional viewing perspectives is vital. For axial images, the standard view is from below, as mentioned earlier. For coronal and sagittal reconstructions, the viewing convention is the same as axial images, with the patient’s right side on the left side of the image.
Right-Left Orientation on Screen
It’s very important to correctly identify right-left orientation on the screen for accurate interpretation. Most viewing software has markers or labels to show the patient’s orientation. It’s important to get used to these indicators to avoid mistakes.
By learning the different planes and orientations of CT scans, healthcare professionals can improve their diagnostic accuracy. This leads to better patient care.
CT Scan Interpretation: Basic Principles and Approach
Understanding CT scans well is key. It involves looking at how different things show up on the scan. This helps doctors spot problems and treat them right.
Systematic Review Methodology
Looking at CT scans step by step is important. This means checking the patient’s history and the scan itself. It also means looking at the scan from different angles.
- Reviewing the patient’s clinical history and relevant medical information
- Evaluating the CT scan images in multiple planes (axial, coronal, sagittal)
- Assessing the quality of the scan and identifying any artifacts
- Analyzing the attenuation characteristics of various tissues and structures
Analyzing Attenuation Differences
How different things show up on a CT scan is very important. The Hounsfield scale helps doctors tell tissues apart. Each tissue has its own number on this scale.
| Tissue Type | Hounsfield Unit (HU) Range |
| Bone | 1000+ |
| Soft Tissue | 40-80 |
| Fat | -100 to -50 |
| Air | -1000 |
Normal vs. Abnormal Findings
It’s important to know what’s normal and what’s not on a CT scan. Abnormal things can be tumors, broken bones, or infections.
- Masses or tumors
- Fractures or bony abnormalities
- Inflammation or infection
- Vascular abnormalities
By following a set of steps and understanding CT scans, doctors can make accurate diagnoses. This helps in treating patients better.
Window Settings and Their Impact on Visualization
Choosing the right window settings is key to seeing CT scan images clearly. These settings change how bright or dark the image looks. This helps doctors see different parts of the body better.
Each setting is for a specific part of the body. By tweaking the window level and width, doctors can make certain areas stand out. This makes it easier to spot problems.
Soft Tissue Windows
Soft tissue windows are for looking at soft body parts. They have a narrow window width to show contrast well. This is great for checking organs and finding tumors or swelling.
Bone Windows
Bone windows focus on bones. They have a wider window width to show bone details clearly. This is perfect for seeing fractures, bone diseases, or wear and tear.
Lung Windows
Lung windows are for the lungs. They have high contrast to spot lung problems like nodules or infections. These windows are key for diagnosing lung diseases.
Brain Windows
Brain windows are for the brain. They help find bleeding, strokes, or tumors. In emergencies, they’re vital for quick brain condition checks.
Knowing how to use different window settings is critical for reading CT scans right. By adjusting these settings, doctors can find more problems. This helps care for patients better.
| Window Setting | Typical Window Level | Typical Window Width | Primary Use |
| Soft Tissue | 40-50 HU | 300-400 HU | Evaluating organs and soft tissue abnormalities |
| Bone | 500-700 HU | 1500-2000 HU | Assessing bone morphology and detecting bone lesions |
| Lung | -500 to -600 HU | 1500-2000 HU | Evaluating lung parenchyma and detecting pulmonary abnormalities |
| Brain | 30-40 HU | 80-100 HU | Assessing brain structures and detecting neurological conditions |
Cross-Sectional Anatomy in CT Imaging
Cross-sectional anatomy is key to understanding CT scans. It helps doctors diagnose and treat many health issues. Detailed images from CT scans are essential for accurate diagnoses.
CT scans give a full view of the body’s inside parts. This helps doctors see anatomy in three dimensions. It’s very helpful for complex areas like the head, neck, chest, belly, pelvis, and muscles.
Head and Neck Anatomy
The head and neck have important structures like the brain, eyes, sinuses, and big blood vessels. On a CT scan, you can see the brain’s different parts and the ventricles. The eyes and sinuses are also clear, helping doctors spot problems like fractures, tumors, or infections.
Thoracic Anatomy
The chest area has the lungs, heart, and big blood vessels. CT scans of the chest let doctors check the lungs, heart, and blood vessels. The lung windows setting is great for looking at lung tissue. The mediastinal windows are better for the heart and big blood vessels.
| Structure | Visibility on CT | Clinical Significance |
| Lung Parenchyma | Highly visible on lung windows | Assessment of nodules, infiltrates, and emphysema |
| Mediastinal Structures | Visible on mediastinal windows | Evaluation of lymphadenopathy, tumors, and vascular abnormalities |
| Pleura | Visible on lung windows | Detection of effusions, pneumothorax, and pleural thickening |
Abdominal and Pelvic Anatomy
The belly and pelvis have vital organs like the liver, spleen, pancreas, kidneys, and gut. CT scans are great for checking these organs for problems like tumors, cysts, and inflammation.
Using contrast can make some structures, like the gut and blood vessels, clearer.
Musculoskeletal Anatomy
CT scans are very useful for the muscles and bones. They help spot complex fractures, bone tumors, and wear and tear. The detailed images let doctors see bones and soft tissues well.
Step-by-Step Guide to Reading a Head CT Scan
Learning to read a head CT scan is key for spotting neurological issues. It shows the brain’s layout and any oddities.
Identifying Normal Brain Structures
To understand a head CT scan, knowing the brain’s layout is first. The scan shows the brain in shades of gray. Each shade means different tissue types.
- Gray Matter: Looks grayer because it has more water.
- White Matter: Looks whiter because of fatty sheaths around nerves.
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF): Looks dark or black because it’s very watery.
Recognizing Common Pathologies
After spotting normal parts, look for common problems. These include:
- Hemorrhages: Show up as bright white spots because of blood.
- Infarctions: Look like dark spots, showing areas without blood flow.
- Tumors: Appear as dense masses, sometimes with swelling around them.
Assessing for Hemorrhage, Edema, and Mass Effect
When checking a head CT scan, look for signs of bleeding, swelling, and mass effect. Bleeding shows up as bright spots. Swelling is dark areas around injuries. Mass effect means brain parts are pushed out of place.
- Hemorrhage: Find bright spots, often seen after injuries or aneurysms.
- Edema: Spot dark areas around injuries, showing swelling.
- Mass Effect: Look for brain shifts, ventricular compression, or herniation.
By carefully looking at these signs, doctors can spot and treat brain issues with head CT scans.
How to Read a Chest CT Scan
To read a chest CT scan well, one must look at the lung’s inner part for any issues. They should also check the area in the middle of the chest and the outer lining of the lungs. This method helps check the whole chest area.
Lung Parenchyma Assessment
The lung’s inner part is where air and blood exchange. On a CT scan, look for any odd shapes or spots. These scans are great at finding lung tumors early.
Key features to evaluate in the lung parenchyma include:
- Nodule size and location
- Presence of calcifications or fat within nodules
- Consolidations or infiltrates
- Ground-glass opacities or interstitial lung disease
Mediastinal Structures Evaluation
The middle part of the chest has important stuff like the heart and big blood vessels. On a CT scan, check if these things are normal in size and shape. Look for any signs that something might be wrong.
| Mediastinal Structure | Normal Characteristics | Abnormal Characteristics |
| Lymph Nodes | Small, less than 1 cm | Enlarged, greater than 1 cm |
| Thyroid Gland | Homogeneous, normal size | Nodules, enlargement |
| Heart and Great Vessels | Normal size and configuration | Enlargement, aneurysms |
Pleural and Chest Wall Examination
Also, check the outer lining of the lungs and the chest wall. Look for fluid, thickening, or calcium deposits. Also, watch for any odd growths or breaks in the chest wall.
“The accurate interpretation of chest CT scans requires a thorough understanding of thoracic anatomy and pathology, as well as attention to detail to identify subtle abnormalities.” –
Radiology Expert
By carefully looking at a chest CT scan, doctors can spot many chest problems. This includes lung cancer and issues with the outer lining of the lungs.
Abdominal CT Scan Interpretation Techniques
To understand abdominal CT scans, knowing the normal anatomy is key. These scans help check the liver, spleen, pancreas, and more. They give detailed images of these organs and systems.
Liver, Spleen, and Pancreas Assessment
Checking the liver, spleen, and pancreas means looking at their size and shape. The liver should look the same all over and have a smooth edge. The spleen is usually the same but less dense than the liver. The pancreas is checked for size, shape, and any unusual growths or stones.
Key features to assess in the liver, spleen, and pancreas:
- Liver: Homogeneity, contour, presence of lesions
- Spleen: Size, homogeneity, presence of lesions
- Pancreas: Size, contour, presence of masses or calcifications
Gastrointestinal Tract Evaluation
Looking at the gastrointestinal tract means checking the bowel wall and lumen. The wall should be even, and the lumen should be normal in size. Any unusual growths or changes are noted.
Key features to assess in the gastrointestinal tract:
- Bowel wall thickness
- Lumen diameter
- Presence of masses or lesions
Genitourinary System Analysis
The genitourinary system, like the kidneys and bladder, is checked for size and function. Kidneys are looked for any growths or stones. Ureters and bladder are checked for blockages or growths.
| Organ | Key Features to Assess |
| Kidneys | Size, shape, presence of masses or cysts |
| Ureters | Diameter, presence of obstruction |
| Bladder | Wall thickness, presence of masses |
By carefully checking these areas, doctors can understand CT scans well. They can spot many health issues, from simple to serious ones needing quick action.
How to Read a CT Scan for Cancer
CT scans are key in finding cancer. It’s important to read them right for treatment plans. Looking at a CT scan for cancer means checking many details.
Identifying Suspicious Masses and Nodules
First, we look for odd masses and nodules in CT scans. These might be tumors. Their look can tell us if they’re bad.
Key features to look for include:
- Size and shape of the mass or nodule
- Location within the organ or tissue
- Density and homogeneity
- Margins and borders
- Presence of calcifications or necrosis
Contrast Enhancement Patterns
How a CT scan shows contrast is very telling. Contrast agents help us see different tissues and problems.
The pattern of enhancement can indicate:
- The vascularity of the lesion
- The presence of necrosis or cystic components
- The presence of malignancy
Staging and Metastasis Assessment
After finding a suspicious spot, we check the cancer’s stage and if it has spread. CT scans help us see how far the disease has gone.
| Cancer Stage | CT Scan Findings |
| Localized | Tumor confined to the organ of origin |
| Regional | Spread to nearby lymph nodes or tissues |
| Distant Metastasis | Spread to distant organs or lymph nodes |
Follow-up and Surveillance Protocols
After diagnosing and staging, we use CT scans to check how treatment is working. We also watch for any signs of cancer coming back. Knowing when and how to do follow-ups is key to managing cancer.
Key considerations include:
- How often to have follow-up scans
- What to look for to see if treatment is working
- Signs that cancer might be coming back
Common Pitfalls and Artifacts in CT Scan Interpretation
Artifacts and pitfalls in CT imaging can affect scan results. It’s key to know their causes and effects. Understanding these challenges helps in giving accurate diagnoses.
Motion and Breathing Artifacts
Motion artifacts happen when patients move during scans. This causes blurring or streaking. Breathing artifacts are a big problem in scans of the chest and belly.
- Effects: Blurring, streaking, or duplication of structures.
- Mitigation: Patient instruction, breath-holding techniques, and faster scanning protocols.
Beam Hardening and Streak Artifacts
Beam hardening creates dark streaks or bands due to dense materials. Streak artifacts come from metal or dense contrast.
- Causes: Dense materials like bone or metal, high-density contrast agents.
- Correction: Using metal artifact reduction algorithms, adjusting scanning parameters.
Partial Volume Effects
Partial volume effects occur when structures are only partly in the slice. This averages out values, hiding details.
- Impact: Loss of detail, inaccurate measurement of lesion size or density.
- Minimization: Thinner slices, overlapping reconstructions.
Strategies to Overcome Interpretation Challenges
To improve CT scan accuracy, several strategies help:
- Optimize scanning protocols: Adjusting parameters to minimize artifacts.
- Use advanced reconstruction techniques: Implementing algorithms to reduce noise and improve image clarity.
- Enhance patient preparation: Instructions to minimize motion and breathing artifacts.
- Cross-reference with other imaging modalities: When necessary, to clarify findings.
Understanding and tackling these common issues improves CT scan accuracy. This leads to better patient care.
Conclusion
Accurate ct scan interpretation is key for patient care and treatment planning. Understanding CT scan technology, equipment, and software is essential for analyzing images well.
Liv Hospital focuses on international best practices and academic standards. This shows how important precise ct scan interpretation is. By using a systematic approach to read CT scans, healthcare workers can improve diagnosis and patient care.
Good ct scan interpretation means knowing anatomy, window settings, and common mistakes. Radiologists and clinicians can better diagnose and manage health issues by mastering these skills.
Medical imaging keeps getting better, so staying current is vital. Healthcare professionals can offer top care by keeping up with new techniques and technologies. This way, they can use ct scan interpretation and reading to guide treatment plans.
FAQ
What is a CT scan and how does it work?
A CT scan uses X-rays and computer tech to show detailed images of the body. It works by moving an X-ray machine around the body. This captures images from different angles, then makes detailed pictures.
What are Hounsfield Units and how are they used in CT scans?
Hounsfield Units (HU) measure tissue density on CT scans. They help show how different tissues absorb X-rays. This helps doctors see and understand different body parts.
How do I interpret the orientation of a CT scan?
CT scans are viewed in three planes: axial, coronal, and sagittal. Knowing these views is key to understanding the scan. The axial view is horizontal, the coronal is frontal, and the sagittal is a side view.
What is the importance of window settings in CT scan interpretation?
Window settings adjust the contrast and brightness of CT images. They help doctors see different body parts better. This is important for accurate diagnosis.
How do I identify normal and abnormal findings on a CT scan?
To spot normal and abnormal findings, analyze the images carefully. Look for differences in tissue density and know the normal anatomy. Abnormal findings might include tumors or fractures.
What are some common pitfalls and artifacts in CT scan interpretation?
Common issues in CT scans include motion artifacts and streaks. These can distort images. Knowing these problems helps doctors make accurate diagnoses.
How do I read a CT scan for cancer?
To read a CT scan for cancer, look for suspicious areas. Analyze how tissues react to contrast. Also, check for cancer spread and follow-up plans. Knowing anatomy and pathology is key.
What are the different types of CT scans and their applications?
There are many CT scan types, like non-contrast and contrast-enhanced scans. Each is used for different medical needs. They help diagnose and monitor various conditions.
How do I analyze the liver, spleen, and pancreas on an abdominal CT scan?
When looking at the liver, spleen, and pancreas, check their size and shape. Note any abnormalities like tumors. Also, look at nearby structures for any issues.
What is the role of PACS systems in CT scan viewing?
PACS systems manage and share medical images, including CT scans. They are vital for healthcare professionals to view and discuss scans. This helps in accurate diagnosis and treatment.
References
Telford, J. J., Rosenfeld, G., & Zakkar, S., et al. (2021). Patients’ Experiences and Priorities for Accessing Gastroenterology Care. Journal of the Canadian Association of Gastroenterology, 4(1), 3“9. https://academic.oup.com/jcag/article-abstract/4/1/3/5610049


































