The thyroid gland is a key part of our body, found in the neck. It helps control how our body grows and works. At Liv Hospital, we use the latest imaging tech to check on thyroid health. A big part of this is the CT thyroid gland scan.
A CT scan of the thyroid gland gives us important details. It helps us see thyroid nodules, cysts, and if the gland is too big. This info is key for diagnosing and treating thyroid diseases. It lets us create treatment plans that fit each patient’s needs.
Key Takeaways
- CT thyroid gland scans help find thyroid nodules and cysts.
- Advanced imaging tech makes diagnosis more accurate.
- Thyroid CT scans check if the gland is too big.
- Liv Hospital’s team focuses on patient care.
- CT scans are vital for managing thyroid diseases.
The Fundamentals of CT Thyroid Gland Imaging
CT thyroid gland imaging is key in diagnosing and managing thyroid issues. It gives us detailed images of the thyroid gland. This helps us spot and track different thyroid problems.
What is a CT Scan of the Thyroid Gland?
A CT scan of the thyroid gland is a non-invasive test. It uses X-rays and computer tech to show detailed images of the thyroid and nearby areas. It’s great for checking the thyroid’s size, shape, and position, and for finding any oddities like nodules or tumors.
For some scans, we might use a contrast agent to make certain parts clearer. Studies on the National Center for Biotechnology Information show that contrast agents can really help improve CT scan accuracy.
When Physicians Recommend Thyroid CT Scans
Doctors suggest thyroid CT scans for many reasons. They’re used to check thyroid nodules or goiter, to see if the gland is too big, or if there are symptoms like trouble swallowing or neck pain. A CT scan can also help guide biopsies or other procedures.
We suggest a thyroid CT scan when other tests, like ultrasound, don’t give clear results. Or when we need more detailed info. The choice to do a CT scan depends on the patient’s specific needs and what the doctor thinks is best.
Normal Thyroid CT Scan: Anatomy and Dimensions
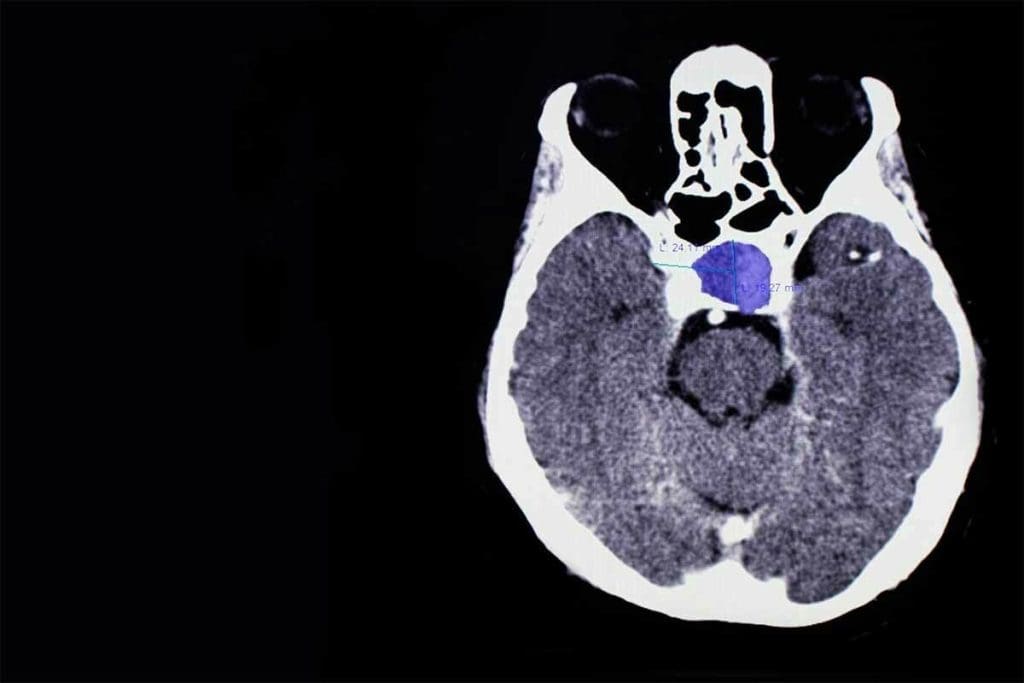
It’s key to know the standard look and size of the thyroid gland on CT scans for correct diagnosis. When looking at a thyroid CT scan, it’s important to grasp the normal anatomy and how it looks on images.
Standard Appearance of Thyroid on CT
The thyroid gland looks a certain way on CT scans. It is homogeneous and hyperdense compared to the muscles around it because of its high iodine. The gland wraps around the trachea, with two lobes joined by the isthmus.
Typical Dimensions of Thyroid Lobes
The size of the thyroid gland varies among people, but there are general guidelines for what’s normal. The thyroid lobes are measured by their length, depth, and width.
| Dimension | Normal Range |
| Craniocaudal (Length) | 4-6 cm |
| Anteroposterior (Depth) | 1.5-2.5 cm |
| Transverse (Width) | 1.5-2.5 cm |
Knowing these dimensions and the normal look of the thyroid gland on CT scans helps spot abnormalities. It also sets the stage for more detailed diagnostic checks.
Insight 1: CT Scan With Contrast Thyroid Enhancement
Contrast in CT scans greatly improves thyroid imaging accuracy. We use CT scans with contrast to get detailed thyroid gland images. These images are key for diagnosing and managing thyroid conditions.
Benefits of Thyroid CT With Contrast
Contrast agents make thyroid structures and lesions more visible during CT scans. This is great for spotting and understanding thyroid nodules, tumors, and other issues. Contrast-enhanced CT scans show how blood flows through thyroid lesions. This helps doctors plan surgeries and understand thyroid diseases better.
Using contrast in thyroid CT scans has many benefits:
- Improved detection of small lesions
- Enhanced characterization of thyroid nodules
- Better visualization of the relationship between the thyroid gland and surrounding structures
Contrast vs. Non-Contrast Thyroid Imaging
Both contrast-enhanced and non-contrast CT scans are useful for thyroid imaging. Non-contrast CT scans are good for finding calcifications in thyroid nodules and seeing the thyroid’s overall shape. But contrast-enhanced CT scans give more info that’s vital for diagnosis and treatment planning.
| Feature | Non-Contrast CT | Contrast-Enhanced CT |
| Detection of Calcifications | Excellent | Limited |
| Characterization of Nodules | Limited | Excellent |
| Vascularity Assessment | No | Yes |
In conclusion, the choice between contrast-enhanced and non-contrast CT scans depends on the clinical question and the needed information. We often use both scans together to fully understand thyroid anatomy and pathology.
Insight 2: Detecting Thyroid Nodules Through CT Imaging
Finding thyroid nodules accurately is key for managing thyroid health. CT scans are a big help in this area. With better imaging, spotting these nodules is getting easier.
CT scans help us see thyroid nodules clearly. They show details of the gland that can’t be felt by hand. This is important for finding nodules that are hard to see.
Characteristics of Nodules on Thyroid CT Scan
Thyroid nodules on CT scans look different. Some are hypodense, appearing less dense than the gland. Others might be isodense or hyperdense. The look of a nodule can tell us something about it.
A study says, “It’s important to know what thyroid nodules look like on CT scans to figure out if they might be cancer.”
“CT scans can spot signs that might mean a nodule is cancerous, like irregular shapes or tiny calcium spots.”
Calcified Thyroid Nodules on CT
Calcium in thyroid nodules is a big deal. CT scans are great at finding calcium, which can mean the nodule is either benign or cancerous. The way calcium is arranged, like microcalcifications, is a red flag for cancer.
We look at the calcium in nodules to decide what to do next. The type of calcium and other details help us decide if more tests or treatment are needed.
In short, CT scans are a key tool for finding and understanding thyroid nodules. Knowing how to read these scans helps us care for patients with thyroid issues better.
Insight 3: Thyroid Cyst CT Scan Identification
CT scans are key in telling cystic from solid thyroid nodules. They help doctors decide the best treatment. Thyroid cysts are filled with fluid and can be seen on CT scans. It’s important to tell them apart from solid nodules.
Differentiating Cysts from Solid Nodules
On a thyroid gland CT scan, cysts look like well-defined, less dense areas. “Hypodense” means they are less dense than the thyroid tissue around them. This is a key sign of cysts.
But, not all less dense nodules are cysts. Some might be solid nodules that just look less dense.
To tell cysts from solid nodules, doctors look at several things on the CT scan:
- Density: Cysts are less dense than solid nodules.
- Margins: Cysts have clear edges, while solid nodules have irregular ones.
- Enhancement: After contrast, cysts don’t show much enhancement. Solid nodules enhance more.
Hypodense Thyroid Nodule on CT Scan
A hypodense thyroid nodule might be a cyst, but more tests are needed to be sure. Hypodensity can also mean a solid nodule with necrosis or hemorrhage. So, a hypodense nodule needs careful checking.
A hypodense thyroid nodule could be a benign cyst or a complex cyst. It could also be a solid nodule with cystic changes. Treatment depends on the CT scan findings and other health factors.
By spotting thyroid cysts on CT scans, doctors can plan better treatments. This could be watching, draining, or surgery. The detailed info from CT scans helps doctors make the best choices for patients.
Insight 4: Evaluating Thyroid Enlargement with CT
CT scans are key in checking thyroid gland size. They help figure out why it’s enlarged. Thyroid growth can be caused by many things, like inflammation, autoimmune diseases, or tumors.
Causes of Thyroid Gland Enlargement
Several things can make the thyroid gland grow. Autoimmune diseases like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis can cause it to swell. Other reasons include Graves’ disease and iodine deficiency.
Thyroid growth can also be due to nodules or cysts. These can be harmless or cancerous. Sometimes, the whole gland grows, or just certain parts.
CT Findings in Diffuse vs. Nodular Enlargement
CT scans show what thyroid enlargement looks like. If the gland grows all over, it looks the same on CT. It might show up differently on scans with contrast, depending on the cause.
But if the gland grows in spots, CT scans can spot these areas. They show how big and what they look like.
For example, some nodules might be harmless, while others could be cancerous. CT scans also show how these nodules relate to nearby tissues. This helps doctors plan surgery.
Using CT scans to check thyroid growth helps us understand the cause. This guides treatment, whether it’s medicine or surgery.
Insight 5: Preoperative Planning Using CT of Thyroid
CT scans have changed how we plan for thyroid surgery. They help surgeons make better choices. We use CT scans to get key info for surgery.
Surgical Guidance and Anatomical Mapping
CT scans give us detailed anatomical mapping. This is key to seeing how the thyroid gland relates to other parts. It helps surgeons plan the safest way to operate.
With CT scans and contrast, we see the thyroid gland and nearby important structures clearly. This helps lower the chance of problems during surgery.
Assessment of Tumor Extension
Understanding how far a tumor has spread is also important. CT scans show us the size, location, and how deep the tumor goes. This helps decide the best surgery plan for each patient.
We look at the tumor’s details and how it affects nearby areas with CT scans. This helps us plan the surgery and predict any challenges.
By combining CT scan info with other tests, we make a detailed plan. This plan increases the chance of a good surgery result.
Insight 6: Abnormal Thyroid CT Scan Findings
Finding abnormal results on a thyroid CT scan is key to diagnosing and treating thyroid diseases. These findings can show a variety of conditions, from harmless nodules to cancerous tumors.
Identifying Malignant vs. Benign Features
Radiologists examine thyroid CT scans for specific signs. They look for features that suggest a nodule or lesion might be cancerous. Signs of cancer include irregular shapes, tiny calcium spots, and growth into nearby tissues.
Benign features, on the other hand, show up as smooth edges, uniform density, and no invasion. But, it’s important to remember that some cancerous nodules can look like harmless ones, and vice versa.
| Feature | Malignant | Benign |
| Margins | Irregular | Smooth |
| Calcifications | Microcalcifications | Coarse calcifications |
| Invasion | Present | Absent |
Recurrent Disease Detection
Thyroid CT scans are also important for spotting disease return in thyroid cancer patients. By comparing new scans to old ones, doctors can find signs of disease coming back, like new nodules or bigger ones.
Finding the disease early means doctors can act fast, which can greatly help patients. So, regular thyroid CT scans are a big part of caring for thyroid cancer patients.
Insight 7: Advanced Applications of CT Scan Thyroid Gland
Advanced CT scan techniques have changed how we manage thyroid disease. Now, we can see the thyroid gland in detail. This helps us make more accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
CT scans have many uses in thyroid disease management. One key benefit is being able to tell normal from abnormal thyroid structures. This is important for catching diseases early, when they are easier to treat.
Differentiating Normal from Abnormal Structures
CT scans use advanced technology to show clear images of the thyroid gland. Doctors can spot abnormalities like nodules or cysts. They can also learn about their characteristics.
For example, a CT scan can tell if a nodule is benign or cancerous by looking at its appearance and density. Here’s a table showing the differences:
| Characteristics | Benign Nodules | Malignant Nodules |
| Density | Typically hypodense or isodense | Often hyperdense or heterogeneous |
| Margins | Well-defined margins | Irregular or infiltrative margins |
| Calcifications | Coarse or eggshell calcifications | Microcalcifications |
Role in Diagnosis and Management of Thyroid Diseases
CT scans are key in diagnosing and managing thyroid diseases. They give doctors important info for treatment plans.
For instance, CT scans can show how big a tumor is or if cancer has spread. Knowing this helps doctors choose the best treatment, like surgery or radiation.
By using advanced CT scan tech, we can better diagnose and manage thyroid diseases. This leads to better care for patients.
Conclusion: The Evolving Role of CT in Thyroid Evaluation
CT scans are key in checking and treating thyroid diseases. They give us detailed views of the thyroid, helping us understand and manage thyroid issues better.
Thyroid CT scans help doctors spot thyroid nodules and check for thyroid growth. They also help plan surgeries carefully. These scans show important details about thyroid nodules and disease extent.
CT technology keeps getting better, helping us diagnose and treat thyroid diseases more accurately. As CT scans improve, we’ll get even clearer images. This will help patients get better care and results.
In short, CT scans are vital for thyroid health checks. They help doctors give better care to patients with thyroid issues. This leads to better health outcomes for everyone.
FAQ
What is a CT scan of the thyroid gland?
A CT scan of the thyroid gland uses X-rays and computer tech to show detailed images. It helps doctors see the thyroid gland’s shape and find any problems.
When is a thyroid CT scan recommended?
Doctors suggest thyroid CT scans for several reasons. They use them when they think there might be thyroid disease. They also use them to check thyroid nodules, see if the thyroid is too big, or plan for surgery.
What is the standard appearance of the thyroid gland on a CT scan?
The normal thyroid gland looks like two lobes on a CT scan. It’s usually 4-6 cm long and 1-2 cm thick. Its density is mostly even.
What are the benefits of using contrast in thyroid CT scans?
Contrast makes some parts of the thyroid gland clearer on CT scans. It helps doctors see different types of thyroid diseases better. This gives them more information for diagnosis and treatment.
How do CT scans help in detecting thyroid nodules?
CT scans help find thyroid nodules by showing their size, location, and details. They can spot calcification, which is important for checking if a nodule might be cancerous.
What does a hypodense thyroid nodule on a CT scan indicate?
A hypodense thyroid nodule means it’s less dense than the rest of the thyroid. This could mean it’s cystic or necrotic. Doctors usually need to do more tests to figure out what it is.
How do CT scans differentiate between thyroid cysts and solid nodules?
CT scans tell the difference between thyroid cysts and solid nodules by looking at their density and shape. Cysts are usually well-defined and less dense. Solid nodules are denser and might look more complex.
What are the causes of thyroid gland enlargement, and how do CT scans help?
Thyroid gland enlargement can happen for many reasons, like goiter or Graves’ disease. CT scans help see how big the enlargement is and what kind it is. This helps doctors understand the problem better.
How do CT scans contribute to preoperative planning for thyroid surgery?
CT scans give surgeons detailed info about the thyroid gland and nearby areas. This helps them plan the best surgery for each patient. It helps them understand how big the disease is and where it is.
What are the abnormal findings on a thyroid CT scan?
Abnormal findings on a thyroid CT scan include nodules, cysts, calcification, and signs of cancer. These need more tests and treatment to figure out what’s going on.
How do CT scans detect recurrent thyroid disease?
CT scans find thyroid disease that comes back by spotting new or bigger lesions. This is key to catching and treating recurrence early.
References:
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2017). What Are the Radiation Risks from CT? https://www.fda.gov/radiation-emitting-products/medical-x-ray-imaging/what-are-radiation-risks-ct
- Singh, V. (2023). CT Patient Safety And Care. StatPearls (NCBI Bookshelf). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK567800/


































