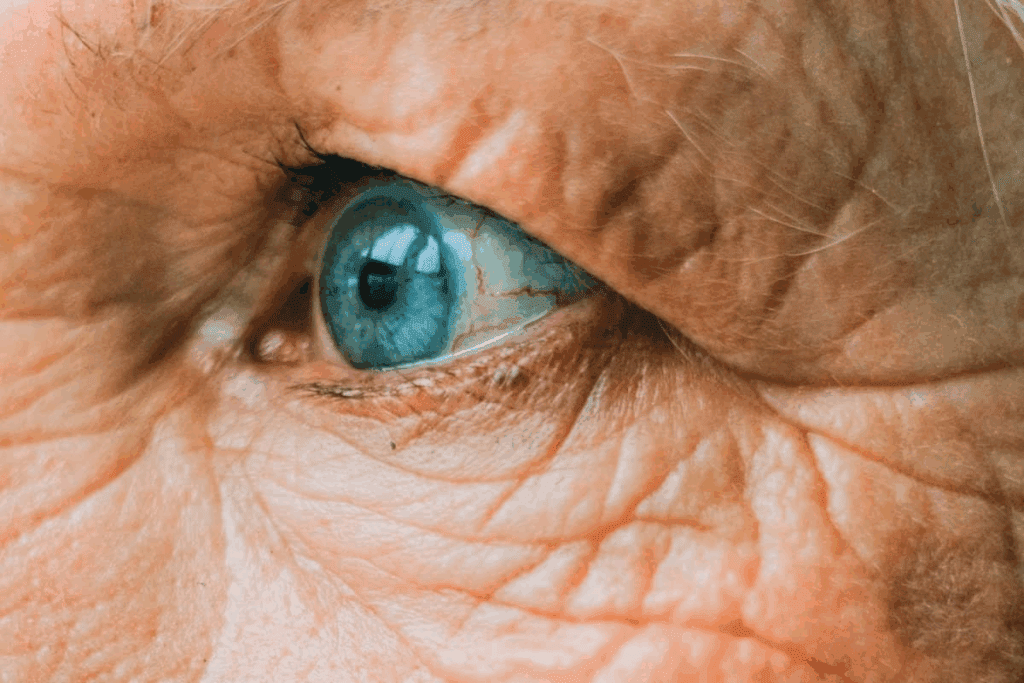
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye problem that can cause blindness if not treated. It damages the blood vessels in the retina. Anyone with diabetes is at risk, no matter the type.diabetes and yellow eyes12 Key Causes and Treatments for Ankle Swelling, Pain, and Bruising
The longer you have diabetes, the more likely you are to get diabetic retinopathy. But, catching it early and managing blood sugar well can stop it. At Liv Hospital, our team works together to help people with diabetes keep their eyes healthy.
Key Takeaways
- Diabetic retinopathy is a leading cause of preventable blindness in working-aged adults worldwide.
- Anyone with diabetes is at risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
- Early detection and timely medical intervention are key to preventing vision loss.
- Keeping blood sugar levels in check can prevent diabetic retinopathy.
- A team approach is vital for caring for people with diabetes.
Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy: A Leading Cause of Preventable Blindness
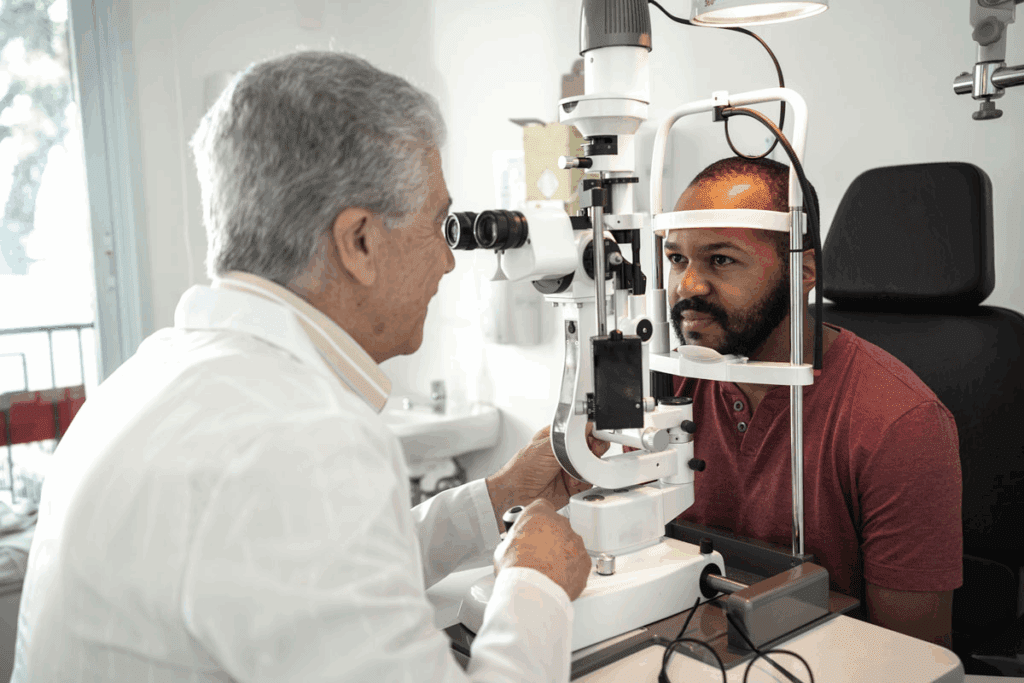
It’s key for people with diabetes to know about diabetic retinopathy to keep their eyes healthy. This condition harms the blood vessels in the retina, which can cause blindness. We’ll look at how diabetes affects the retina and the global impact.
Global Statistics and Prevalence
Diabetic retinopathy is a big health problem worldwide. About 26.4 percent of those with diabetes have this condition. Of those, 5.1 percent face serious vision problems. This shows why it’s so important to be aware and manage it well.
| Population | Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy | Vision-Threatening Complications |
|---|---|---|
| Global Diabetes Population | 26.4% | 5.1% |
| Type 1 Diabetes | Higher prevalence due to longer disease duration | More frequent |
| Type 2 Diabetes | Significant prevalence due to larger population | Common |
How Diabetes Damages the Retina
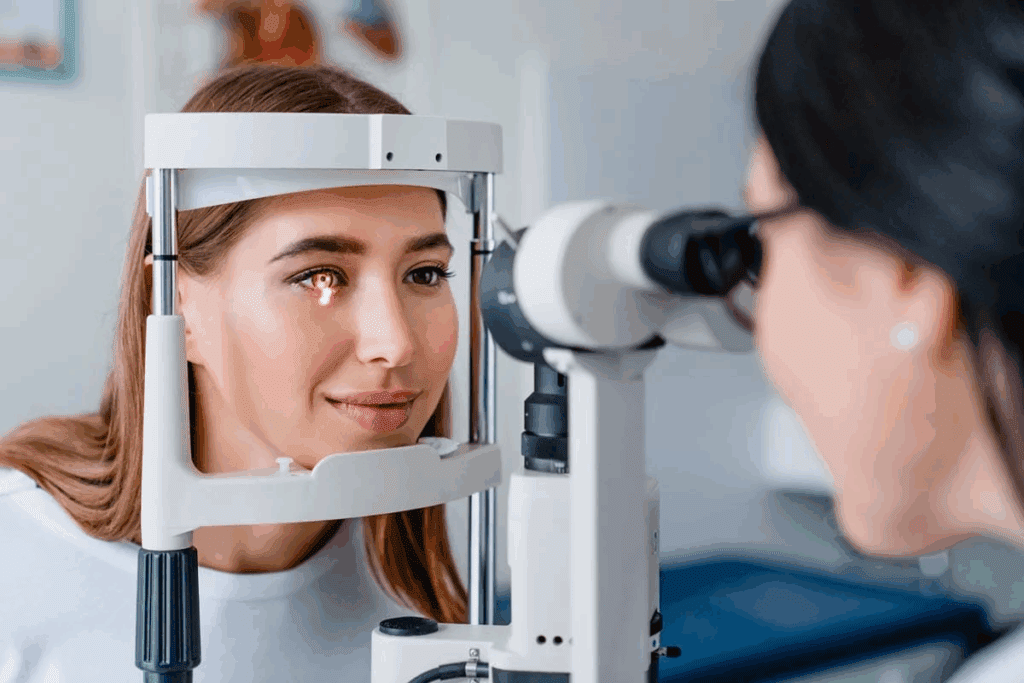
Diabetic retinopathy happens when blood vessels in the retina get damaged. High blood sugar levels harm these tiny vessels, cutting off the retina’s blood supply. This can cause serious problems, including background retinopathy and more severe forms.
It’s vital to catch and manage diabetic retinopathy early to avoid losing vision. Knowing how diabetes harms the retina helps people protect their eye health.
The Connection Between Diabetes and Yellow Eyes: Warning Signs to Watch For
[Add image here]
Diabetes can cause many eye problems, including yellow eyes. This is a serious issue that needs quick attention. We will look at the early signs of diabetic eye issues and when to get medical help.
Early Symptoms of Diabetic Eye Problems
In the early stages of diabetic retinopathy, some people might not notice anything wrong. But as it gets worse, they might see blurry vision, floaters, or dark spots in their sight. It’s important to watch for these changes and see a doctor if they don’t go away or get worse.
Some common early signs include:
- Blurred vision or double vision
- Floaters or dark strings floating in the field of vision
- Changes in vision, such as seeing rings or halos around lights
- Dark or empty areas in the vision
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
If you suddenly lose your vision, have severe eye pain, or are very sensitive to light, get help right away. These signs can mean a serious problem like diabetic retinopathy or macular edema.
Regular eye exams are key for people with diabetes. They help catch problems early. By keeping an eye on your vision and knowing the warning signs, you can protect your sight.
Also, managing your diabetes well is important. High blood sugar can make eye problems worse. By working with your healthcare team and living a healthy lifestyle, you can lower the risk of serious eye issues.
Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy Development
Knowing the stages of diabetic retinopathy is key to managing it well and keeping your eyes healthy. This condition gets worse in steps, each with its own signs and effects on your vision. It starts with damage to the small blood vessels in the retina, moving from early to more serious stages.
Background Retinopathy: The Early Stage
Background retinopathy, or mild non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy, is the first sign. At this point, small blood vessels in the retina weaken, causing tiny bulges called microaneurysms. These can leak fluid, making the retina swell. Catching it early through eye exams is very important to stop it from getting worse.
Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR)
NPDR happens when more blood vessels get damaged. It shows up as hemorrhages, hard exudates, and cotton wool spots in the retina. The damage can vary, from mild to severe. Keeping blood sugar levels in check is key to slowing NPDR down.
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR)
PDR is the most serious stage of diabetic retinopathy. At this point, damaged blood vessels stop working, leading to new, fragile blood vessels growing in the retina. These new vessels can easily bleed, causing serious vision loss. Quick treatment, like laser therapy or anti-VEGF injections, is needed to stop vision from getting worse.
In summary, knowing about diabetic retinopathy’s stages is vital for managing it. Regular eye exams and early treatment can greatly help keep vision intact for people with diabetes.
Key Risk Factors That Accelerate Eye Damage
Several critical risk factors can speed up diabetic retinopathy, leading to severe sight loss if not managed. It’s key for those with diabetes to know these factors to protect their vision.
Blood Sugar Control and HbA1c Levels
Poor blood sugar control is a big risk for diabetic retinopathy. The HbA1c test shows blood sugar levels over two to three months. Keeping HbA1c below 7% can lower the risk of diabetic retinopathy. A study found tight blood glucose control can cut diabetic retinopathy risk by 76% in type 1 diabetes.
“The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT) clearly demonstrated that tight blood glucose control can significantly reduce the risk of diabetic retinopathy.”
Hypertension and Cardiovascular Health
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a major risk for eye damage in diabetes. High blood pressure can harm the retina’s blood vessels, making diabetic retinopathy worse. Managing high blood pressure with lifestyle changes and meds can lessen this risk. Good cardiovascular health is also linked to eye health, helping prevent diabetic retinopathy.
Early-Onset Diabetes and Disease Duration
The length of time with diabetes and when it starts are key risks for diabetic retinopathy. The longer someone has diabetes, the higher their risk. Those diagnosed with diabetes young are at higher risk of complications, including diabetic retinopathy, later. Early diagnosis and management are key to avoiding long-term issues.
Understanding and managing these risk factors can greatly reduce the risk of diabetic retinopathy. This helps protect vision for those with diabetes.
Essential Blood Sugar Management Strategies
To stop diabetic retinopathy, managing blood sugar is key. It needs a mix of taking medicine, changing your lifestyle, and keeping an eye on your levels.
Medication Adherence and Insulin Management
Sticking to your medicine and insulin is very important. Consistent medication adherence keeps blood sugar in check. This lowers the chance of diabetic retinopathy. Always talk to your doctor about your treatment plan.
If you take insulin, knowing how to use it right is important. Continuous education and support from doctors helps manage insulin well.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring Benefits
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) gives you real-time blood sugar info. CGM benefits include better blood sugar control and less chance of low blood sugar. It also shows how food and exercise affect your blood sugar.
CGM lets you spot patterns in your blood sugar. This helps you act fast to avoid problems like diabetic retinopathy.
How to Prevent Eye Damage from Diabetes Through Diet
Eating right is vital for managing blood sugar and avoiding eye damage from diabetes. Nutritional guidelines suggest eating lots of veggies, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins.
Try to eat less sugary foods and fats. Hydration is also key, so drink lots of water all day.
With a healthy diet and other management strategies, people with diabetes can lower their risk of diabetic retinopathy. This helps protect their eyesight.
Lifestyle Modifications to Protect Your Vision
Making lifestyle changes is key to protecting your vision if you have diabetes. By adopting healthier habits, you can lower the risk of eye problems like diabetic retinopathy.
Nutrition Guidelines for Eye Health
Eating a balanced diet is essential for eye health. Foods rich in lutein and zeaxanthin, like spinach and kale, help protect the retina.
- Eat a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables.
- Include omega-3 fatty acids from fish like salmon and sardines.
- Choose whole grains over refined ones for better health.
Vitamins C and E, zinc, and beta-carotene are also important for your eyes. Eating foods with these nutrients can help prevent eye pain from diabetes.
Exercise Recommendations to Improve Circulation
Regular exercise boosts blood flow, which is good for your eyes. It helps control blood sugar and lowers the risk of diabetic retinopathy.
- Do at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week.
- Do strength training exercises two times a week.
- Yoga and Pilates can improve flexibility and well-being.
Good circulation ensures your eyes get the oxygen and nutrients they need.
Smoking Cessation and Alcohol Moderation
Smoking and drinking too much alcohol can worsen diabetic retinopathy. Quitting smoking and drinking in moderation are important steps to protect your vision.
| Benefit | Smoking Cessation | Alcohol Moderation |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced Risk of Eye Disease | Significantly reduces the risk of diabetic retinopathy | Lowers the risk of eye damage associated with excessive drinking |
| Overall Health Improvement | Improves cardiovascular health and reduces cancer risk | Reduces the risk of liver disease and other health issues |
By changing your lifestyle, people with diabetes can better manage their condition and protect their vision.
In conclusion, making lifestyle changes is vital for preventing diabetic retinopathy. Focus on nutrition, exercise, and avoid harmful habits like smoking. This way, you can improve your eye health and overall well-being.
The Critical Importance of Regular Eye Screenings
For people with diabetes, regular eye exams are key to their care. Managing diabetes is not just about blood sugar control. It also means protecting your vision. Early detection and treatment of diabetic retinopathy are vital to avoid blindness.
Screening Frequency Based on Diabetes Type
Eye screening frequency varies with diabetes type. Generally, yearly dilated eye exams are recommended for those with diabetes. Pregnant women or those with gestational diabetes might need more frequent checks. Always follow your healthcare provider’s advice for eye care.
- Individuals with type 1 diabetes should have their first eye exam within five years of their diagnosis.
- Those with type 2 diabetes should have an eye exam at the time of diagnosis.
- Pregnant women with diabetes or gestational diabetes may need more frequent screenings as recommended by their doctor.
What to Expect During a Diabetic Eye Exam
During a diabetic eye exam, your eye care professional will check for diabetic retinopathy and other eye issues. The exam includes:
- A visual acuity test to assess your vision.
- A dilated eye exam to inspect the retina for any damage.
- Imaging tests, such as optical coherence tomography (OCT), to capture detailed images of your retina.
This detailed examination helps your healthcare provider catch issues early, when they are easier to treat.
Benefits of Early Detection
Early detection of diabetic retinopathy through regular eye screenings has many benefits. It allows for timely intervention, which can prevent disease progression and vision loss. In some cases, it may even avoid the need for diabetes eye operation. Early management of diabetic retinopathy can greatly improve your quality of life by preserving your vision.
Understanding diabetic retinopathy stages, including bdr ophthalmology or background diabetic retinopathy, is key. Background diabetic retinopathy is an early stage where the retina shows damage signs. Early detection and management can significantly prevent further complications.
Treatment Options When Retinopathy Develops
Managing diabetic retinopathy requires a variety of treatments. Each treatment is chosen based on the individual’s needs. These options help manage the condition and prevent vision loss.
Laser Therapy and Anti-VEGF Injections
Laser therapy is a common treatment for diabetic retinopathy. It uses laser burns to reduce swelling in the retina. Laser therapy can significantly reduce the risk of blindness in patients with diabetic retinopathy. Anti-VEGF injections are another option. They involve injecting medications into the eye to stop blood vessel growth.
Anti-VEGF injections have revolutionized the treatment of diabetic retinopathy. They offer a targeted approach to reduce swelling and improve vision. These injections are given monthly and can greatly improve vision in some patients.
Surgical Interventions for Advanced Cases
In advanced cases, surgery may be needed. Vitrectomy is a surgery that removes the vitreous gel and blood. This surgery can restore vision and prevent further loss. Surgical interventions are often used with other treatments for advanced diabetic retinopathy.
Emerging Treatments and Clinical Trials
Research into diabetic retinopathy is ongoing. Several new treatments are showing promise. Clinical trials are exploring new medications that target inflammation and oxidative stress. These emerging treatments offer hope for improved outcomes in patients with diabetic retinopathy. Joining clinical trials can provide access to new treatments and help advance medical knowledge.
It’s important to understand the treatment options for diabetic retinopathy. Working closely with healthcare providers helps develop a personalized treatment plan. This plan protects vision and reduces the risk of blindness. The question of whether diabetes can make you blind is a significant concern. But with proper management and treatment, the risk can be greatly reduced.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Eye Health with Diabetes
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious problem that can cause vision loss if not treated. By managing your diabetes well, making healthy lifestyle choices, and getting regular eye exams, you can lower your risk of losing your vision. We want to help you take charge of your eye health by knowing the risks and acting early.
Symptoms like diabetic retinopathy floaters or red eyes can signal eye damage. If you notice red eyes and diabetes, get medical help right away. Early eye screenings can catch problems before they get worse, helping you get the right treatment.
Following the advice in this article can help keep your vision safe and your life quality high. We urge you to work with your healthcare team to manage your diabetes and watch your eye health. Together, we can keep your vision and overall health in top shape.
FAQ
What is diabetic retinopathy and how does it affect vision?
Diabetic retinopathy is a diabetes complication that harms the retina. It can lead to blindness. It damages vision by causing blood vessels in the retina to bleed or leak fluid.
What are the early symptoms of diabetic eye problems?
Early signs include blurry vision, floaters, bloodshot eyes, and yellow eyes. It’s important to notice these signs early to get medical help.
How does diabetes damage the retina?
High blood sugar levels from diabetes harm the retina’s blood vessels. This leads to diabetic retinopathy.
What are the stages of diabetic retinopathy?
The stages are background retinopathy, non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR), and proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR). Each stage shows the disease getting worse.
How can blood sugar control prevent eye damage from diabetes?
Keeping blood sugar levels in check helps prevent eye damage. This can be done through medication, insulin, and glucose monitoring.
What lifestyle changes can help protect vision in diabetes?
Eating right, exercising, quitting smoking, and drinking less alcohol can protect your vision. These lifestyle changes are important.
How often should I have my eyes screened for diabetic retinopathy?
People with diabetes should get an eye exam at least once a year. The exact frequency depends on the type of diabetes.
What can I expect during a diabetic eye exam?
A diabetic eye exam includes a visual acuity test and a dilated eye exam. It might also include imaging tests like OCT to check the retina.
What are the treatment options for diabetic retinopathy?
Treatments include laser therapy, anti-VEGF injections, and surgery for advanced cases. New treatments are also being tested in clinical trials.
Can diabetic retinopathy be prevented?
While you can’t prevent diabetic retinopathy completely, you can lower the risk. This is done through good blood sugar control, regular eye exams, and a healthy lifestyle.
How does hypertension affect diabetic retinopathy?
High blood pressure can make diabetic retinopathy worse. It puts extra strain on the retina’s blood vessels.
What is the impact of disease duration on diabetic retinopathy?
The longer you have diabetes, the higher your risk of diabetic retinopathy. Early diagnosis and management are key.
Are there any dietary adjustments that can help prevent eye damage from diabetes?
Yes, eating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, lutein, and zeaxanthin can help eye health. These nutrients are important.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2913095/


































