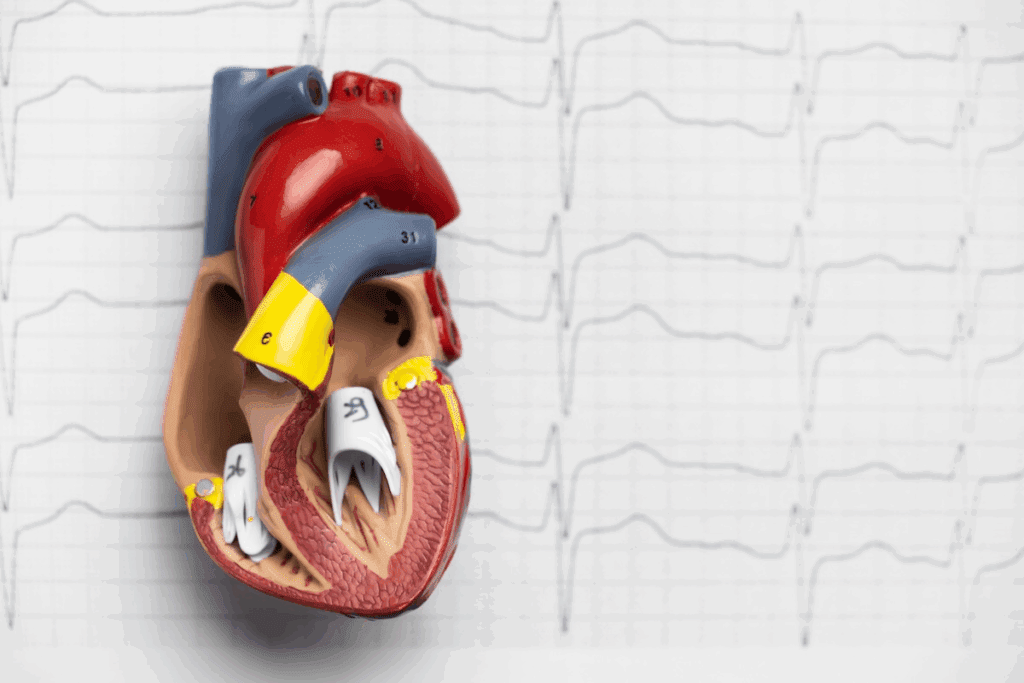
Knowing the heart’s anatomy is key for doctors and students. It’s important to label a heart diagram right for learning and medical work.
We know how vital it is to understand the heart’s parts well. At Liv Hospital, we aim to help international patients get top-notch medical care. We also offer detailed education and support.
Learning the main parts of a heart diagram helps doctors make right diagnoses and plans. In this guide, we’ll cover the 12 key labels for a heart diagram. This will give you a full view of the heart’s structure.

Accurate heart labeling is key for learning and medical diagnosis. It helps us grasp the heart’s complex parts and their roles. This is essential for spotting and fixing heart issues. Learn the labeled diagram of heart with key parts and functions explained clearly.
The heart has layers like the tough myocardium and the thin pericardium. There’s also the inner endocardium. Labeling these parts is critical for seeing how they help blood flow. Important labels include the right and left atria, ventricles, and major blood vessels.
Heart labeling is vital for both students and doctors. It’s key for spotting and treating heart problems. By labeling correctly, we get a clearer picture of the heart’s role in our bodies.
“The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood through the circulatory system, supplying oxygen and nutrients to the body’s tissues and removing carbon dioxide and other wastes.” – American Heart Association
In schools, labeling helps teach heart anatomy. Doctors use it for diagnosing and treatment. Labeling is used in many ways, from teaching to medical care.
Understanding the heart’s anatomy through labeling helps us better diagnose and treat heart issues. This leads to better health outcomes for patients.

The right atrium is a key part of the heart, acting as the main entry for blood that’s low in oxygen. Knowing where it is, how it’s built, and what it does helps us understand how blood moves around our body.
The right atrium is found on the right side of the heart, near the top. It gets blood from the body through the superior and inferior vena cava. Its design helps move blood to the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve. The walls of the right atrium contract to push blood towards the ventricle, keeping the flow going.
The right atrium is important for the circulatory system. It holds deoxygenated blood and pumps it to the right ventricle. This is a key step for blood to go to the lungs and get oxygen. The right atrium’s work is tied to how well the heart pumps blood.
To label a heart model or diagram, you need to spot the right atrium’s unique features. Look for its position among other heart parts and the presence of the superior and inferior vena cava. Correctly labeling the right atrium is key to grasping the heart’s layout.
| Feature | Description |
| Location | Right upper side of the heart |
| Blood Source | Superior and inferior vena cava |
| Valve | Tricuspid valve |
The left atrium is a key part of the heart. It gets oxygen-rich blood from the pulmonary veins. This makes it vital for the heart’s work.
The left atrium is on the heart’s left upper side. It connects to the pulmonary veins, which carry blood from the lungs. The left atrium’s position is key for its job, as it receives blood before it goes to the left ventricle.
Teaching heart anatomy often includes the left atrium. It helps students grasp the heart’s layout and how it works. Correct labeling is vital for pinpointing the heart’s parts, like the left atrium.
The left atrium is essential in pulmonary circulation. It gets oxygen-rich blood from the lungs through the pulmonary veins. This blood then moves to the left ventricle through the mitral valve. This step is vital for keeping the body oxygenated, as the blood then spreads to the body.
“The left atrium is a key structure in the heart’s ability to manage oxygenated blood return from the lungs.”
To spot the left atrium on a heart diagram, look at its position. It’s usually found at the back and linked to the pulmonary veins. Noticing these points helps in correctly labeling the heart.
Medical and nursing students often practice labeling the heart. These exercises help them learn the heart’s layout and its role. By doing so, they can better identify the left atrium and other important heart parts.
The right ventricle is one of the heart’s four chambers. It pumps blood to the lungs for oxygen. This is key for the body’s oxygen supply.
The right ventricle has unique features and boundaries. It’s separated from the left ventricle by the interventricular septum. This wall keeps oxygenated and deoxygenated blood separate.
The right ventricle’s walls are thinner than the left’s. It pumps blood to the lungs over a shorter distance and at lower pressure.
The right ventricle gets deoxygenated blood from the right atrium through the tricuspid valve. It then sends this blood to the lungs via the pulmonary artery, which starts at the right ventricle’s base.
The right ventricle is key in the circulatory system. It makes sure deoxygenated blood goes to the lungs for oxygen. This balance is vital for the body’s health.
Any problem with the right ventricle can cause serious heart issues. These include pulmonary hypertension or right ventricular failure. Knowing how the right ventricle works is important for diagnosing and treating these problems.
On heart diagrams, the right ventricle is shown as being in front of the left ventricle. It’s connected to the pulmonary artery. The labelled heart diagram helps us see where the right ventricle is in relation to other heart parts.
| Feature | Description |
| Location | Anterior to the left ventricle |
| Connection | Pumps blood to the lungs via the pulmonary artery |
| Boundary | Separated from the left ventricle by the interventricular septum |
Understanding the right ventricle’s structure, function, and how it’s shown on diagrams is important. Heart diagrams with labels help medical professionals learn and practice. They show how the heart’s chambers, valves, and major vessels work together.
The left ventricle is the heart’s main muscle. It pumps blood full of oxygen to the body. This is key for the heart’s work in the circulatory system.
The left ventricle has thick walls. These walls help push blood into the aorta, the biggest artery. This is because it needs more power than the right ventricle.
Its walls are thicker than other heart parts. This lets it handle the high pressure needed to pump blood all over the body.
The left ventricle is key for systemic circulation. It pumps blood into the aorta. Then, the blood goes to different parts of the body, bringing oxygen and nutrients.
In heart anatomy labeling, the left ventricle is highlighted. It’s important for understanding heart function and spotting heart problems.
To spot the left ventricle on heart diagrams, look for the thick chamber on the left. It’s the biggest and most muscular. Its apex points down towards the left hip.
When looking at labels for the heart, the left ventricle is noted for its role and position. Knowing its anatomy is important for learning and medical work.
Labeled heart diagrams are essential for doctors. They help show the heart’s layout clearly. These diagrams are also great for teaching, helping students grasp the heart’s complex parts.
The aorta is the largest artery in our body. It’s key for spreading oxygenated blood everywhere. At Liv Hospital, we focus on the aorta’s role to give top-notch care to our patients.
The aorta starts from the left ventricle and goes up before curving back and down. It passes through the chest and belly. Along the way, it splits into important branches.
These branches supply blood to the head, neck, and arms. They also feed the organs in the chest and belly.
Some major branches include:
The aorta’s main job is to send oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body. It does this through its branches, which get smaller as they go further away.
The aorta’s elastic properties help it stretch when the heart beats and snap back when it relaxes. This keeps blood flowing smoothly all the time.
“The aorta is more than just a passive conduit for blood; it’s a dynamic organ that plays a critical role in maintaining blood pressure and ensuring adequate perfusion of vital organs.”
Experts note.
Correctly labeling the aorta on heart diagrams is key for learning and medical use. It’s important to mark its different parts, like the ascending aorta, aortic arch, and descending aorta.
Use clear labels and avoid confusion. Make sure the labels are easy to read. Stick to standard terms and follow established names for parts of the body.
The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs. It’s a key part of the circulatory system. Knowing how it works helps us understand the heart’s role.
The pulmonary artery starts in the right ventricle of the heart. It’s a wide artery that splits into two branches. These branches go to the right and left lungs.
Key Features:
The pulmonary artery’s main job is to move deoxygenated blood to the lungs. This is essential for blood to get oxygen. Then, the oxygen-rich blood goes to the body.
| Characteristics | Description |
| Origin | Right ventricle of the heart |
| Branching | Divides into right and left pulmonary arteries |
| Function | Transports deoxygenated blood to the lungs |
On a heart diagram, the pulmonary artery is easy to spot. It starts in the right ventricle and splits into two branches. Knowing this helps us see how blood moves.
Learning about the pulmonary artery helps us understand the heart better. Activities that label the heart parts help students see how blood flows. This makes learning about the heart’s anatomy more fun and clear.
The pulmonary veins are unique because they carry oxygenated blood. They are key to keeping our bodies supplied with oxygen. They transport oxygen-rich blood from the lungs back to the heart.
There are usually four pulmonary veins, with two from each lung. They send oxygenated blood to the left atrium. Knowing how these veins are arranged helps us understand how blood gets back to the heart.
The pulmonary veins are essential for the heart’s function. They make sure oxygenated blood gets back to the heart. From there, it’s sent to the rest of the body. Problems with these veins can cause serious health issues.
Key functions of the pulmonary veins include:
When we label the heart, it’s important to include the pulmonary veins. They show how the heart’s parts work together. These veins are marked on diagrams to show their role in the circulatory system.
Learning to label the pulmonary veins helps students and professionals understand the heart better. It shows how oxygenated blood is circulated in the body. Accurate labeling is key to grasping the heart’s anatomy and function.
The superior and inferior vena cava are key veins. They carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart. Knowing about the vena cava helps us understand the heart’s structure and its role in the body.
The superior and inferior vena cava serve different areas. The superior vena cava carries blood from the upper body, like the head and arms. On the other hand, the inferior vena cava brings blood from the lower body, such as the legs.
The vena cava is essential for venous return. This is how deoxygenated blood gets back to the heart. Without it, the heart can’t pump blood to the lungs for oxygen.
The vena cava’s main tasks are:
Correctly labeling the vena cava in heart diagrams is important. It helps in education and medical use. It’s key to clearly show both the superior and inferior parts.
Good labeling methods include:
Understanding the vena cava’s role and labeling it well in diagrams helps us learn about the heart. It also helps in diagnosing and treating heart issues.
Heart valves are key to making sure blood moves in one direction through the heart. They are essential for good blood flow and heart health. We use labeled heart diagrams to learn about the different valves and their roles.
The semilunar valves, made up of the aortic and pulmonary valves, stop blood from flowing back into the ventricles.
The tricuspid valve is between the right atrium and ventricle. It makes sure blood goes from the right atrium to the right ventricle, not the other way around.
The mitral valve, also called the bicuspid valve, is between the left atrium and ventricle. It lets blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle, keeping it from going back.
Labeled heart diagrams are important for doctors. To spot valve structures:
| Valve Type | Location | Function |
| Aortic Valve | Between left ventricle and aorta | Prevents backflow into left ventricle |
| Pulmonary Valve | Between right ventricle and pulmonary artery | Prevents backflow into right ventricle |
| Tricuspid Valve | Between right atrium and right ventricle | Prevents backflow into right atrium |
| Mitral Valve | Between left atrium and left ventricle | Prevents backflow into left atrium |
The heart’s septum is key in keeping oxygenated and deoxygenated blood separate. It’s a tissue wall that divides the heart into right and left sides. This ensures blood flows smoothly and efficiently through the heart.
The septum has two main parts: the interatrial septum and the interventricular septum. The interatrial septum splits the right and left atria. The interventricular septum splits the right and left ventricles. Both are vital for keeping blood types separate.
“The septum is a critical structure that ensures the heart functions properly,” say cardiac specialists. It helps the heart pump blood well to the body.
The septum’s main job is to keep blood from mixing between chambers. This is key for efficient oxygen delivery to the body’s tissues. Without a working septum, the heart can’t circulate oxygenated blood well.
Imaging methods like echocardiography, MRI, and CT scans help see the septum. Knowing how to read these images is important for diagnosing and treating heart issues.
Doing heart structure labeling activities can really help understand the septum. By labeling heart diagrams, people can see how different structures work together and how blood flows.
We’ve looked into the heart’s complex anatomy and why labeling is key. Knowing heart anatomy well is vital for doctors and students. It’s the base for understanding the heart’s parts and how they work together.
Labeling heart diagrams correctly is key in learning and medical work. It helps people understand the heart’s detailed structure and its role in blood flow. By learning the 12 main labels, we get a full picture of the heart’s anatomy.
Good heart anatomy knowledge is critical for making accurate diagnoses and treatments. As we improve in medical education, the need for precise heart and blood system labeling grows. This ensures doctors can give top-notch care.
The heart has four main chambers. These are the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. Knowing these chambers is key to understanding how the heart works.
The right atrium is where deoxygenated blood comes back to the heart. It gets this blood from the body through the vena cava.
The left ventricle is the heart’s main pump. It sends oxygen-rich blood to the whole body. This makes it very important for the circulatory system.
The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs. It’s a key part of the circulatory system.
Heart valves make sure blood flows only one way through the heart. There are different types of valves. They all work together to control blood flow.
Labeling the heart diagram is very important. It helps students and doctors learn about the heart’s parts. This includes its chambers, valves, and major vessels.
The 12 essential labels include the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. Also, the aorta, pulmonary artery, and pulmonary veins. The vena cava, heart valves, septum, and other key structures are also included.
Knowing heart anatomy is key for accurate diagnosis and treatment. It helps doctors understand the heart’s parts and how they work.
The septum is a vital structure. It separates the heart into right and left sides. It’s important for the heart’s function.
Accurate heart labeling is very important in clinical practice. It helps doctors diagnose and treat heart conditions well. This ensures the best care for patients.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!
WhatsApp us