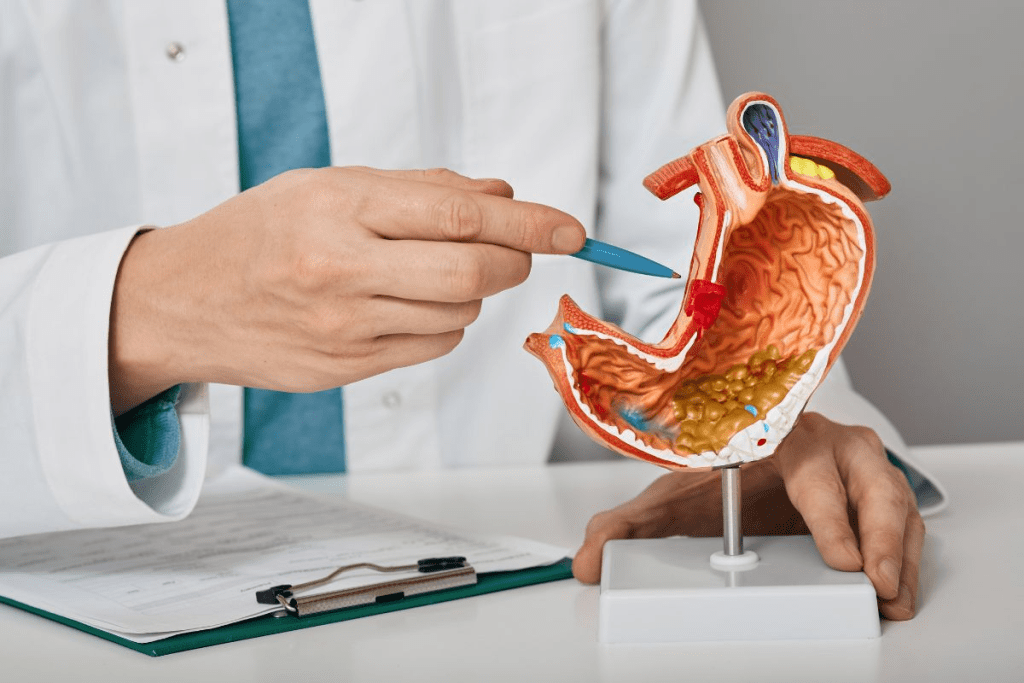
Understanding the role of a gastroenterologist is key to digestive health. We often see “GI doctor” and “gastroenterologist” used in the same way. But what do they really mean?
A gastroenterologist is a medical specialist who deals with the gut and related organs. In short, a GI doctor and a gastroenterologist are the same. They focus on issues with your digestive system.
Knowing what a gastroenterologist does helps us choose the right healthcare for our gut problems. Whether it’s a simple issue or a complex one, a gastroenterologist is the expert to see.
Key Takeaways
- A GI doctor and a gastroenterologist are in the same medical specialty.
- Gastroenterologists diagnose and treat digestive health disorders.
- Understanding the role of a gastroenterologist helps in making informed healthcare choices.
- Gastroenterologists specialize in conditions affecting the gastrointestinal tract.
- Consulting a gastroenterologist is essential for complex digestive disorders.
Understanding Medical Terminology in Digestive Health
Knowing the language of gastroenterology is key for both patients and doctors. It helps in making sure the right diagnosis and treatment are given. Gastroenterology deals with the digestive system, including the digestive tract, gallbladder, liver, bile ducts, and pancreas.
Official Terms in Gastroenterology
Gastroenterology uses special terms for conditions, procedures, and the digestive system’s anatomy. For example, “GI” stands for “gastrointestinal,” meaning the digestive tract. A gastroenterologist is a doctor who deals with the digestive system and related organs.
Some important terms in gastroenterology are:
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus.
- Endoscopy: a way to see the upper digestive tract.
- Colonoscopy: a way to look inside the whole colon.
The Misconception of “Gastrologist” as a Medical Specialty
Many think a gastrologist is a specialist in digestive diseases. But the correct term is gastroenterologist. The term ‘gastrologist’ is not recognized in modern medicine. It’s often used incorrectly instead of ‘gastroenterologist.’ This mix-up can cause confusion between doctors and patients.
Understanding these terms and the role of gastroenterologists helps patients. It makes it easier for them to understand their care and treatment options in gastroenterology.
What is a GI Doctor? Roles and Responsibilities
A GI doctor, or gastroenterologist, is key in solving digestive health problems. They are medical experts focused on the GI tract and liver. They diagnose and treat various disorders and diseases.
Definition of a Gastroenterologist
A gastroenterologist is trained to handle GI tract and liver issues. They manage many conditions, like inflammatory bowel disease and liver disorders. They also treat gastroesophageal reflux disease and colorectal cancer.
These doctors have up to six years of extra training after medical school. This prepares them for diagnosing and treating diseases. They can do endoscopies and colonoscopies.
The roles and responsibilities of a gastroenterologist include:
- Diagnosing and treating gastrointestinal and liver disorders
- Performing endoscopic procedures to visualize the GI tract
- Managing chronic conditions such as IBD and GERD
- Providing preventive care, including colorectal cancer screening
- Collaborating with other healthcare professionals to provide complete care
Knowing what a gastroenterologist does helps patients understand their care. It shows the specialized help they offer for digestive health issues.
The Extensive Education Path of Becoming a GI Doctor
Gastroenterologists go through a long education path. This prepares them for their important role in healthcare. They learn a lot in school and through clinical training. This makes sure they can handle many digestive health problems.
Medical School and Internal Medicine Residency
First, they go to medical school for four years after getting a bachelor’s degree. There, they learn a lot about medicine. They also get practical experience in clinics.
Then, they do a three-year residency in internal medicine. This lets them work with adult diseases, including GI issues. It’s key for learning about the digestive system and health.
In their residency, they learn to manage many conditions. This includes diabetes and hypertension, and GI disorders. It’s important for understanding the digestive system and health.
Gastroenterology Fellowship Training
After internal medicine, they apply for a gastroenterology fellowship. These programs are competitive and last three years. Here, they learn more about the digestive tract and liver.
They get a lot of practice with endoscopic procedures and managing GI diseases. They work with experienced doctors to improve their skills. This makes them proficient GI doctors.
Board Certification Requirements
To be a board-certified gastroenterologist, they must pass the Gastroenterology Certification Exam. This exam checks their knowledge and skills. It makes sure they can give good care to patients.
Board certification is not just once. They must keep up with education and show they are committed to their field. This keeps them up-to-date with new gastroenterology knowledge.
In short, becoming a GI doctor takes a lot of education and training. From medical school to fellowship and board certification, they learn a lot. This training helps them give top-notch care to patients with digestive health issues.
Common Digestive Conditions Treated by Gastroenterologists
Gastroenterologists play a key role in diagnosing and treating digestive diseases. They handle a wide range of conditions in the gastrointestinal tract. This includes both common and rare diseases.
Common Conditions: Gastroenterologists often deal with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), and Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD). IBD includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. These conditions can greatly impact a person’s life, making them need thorough care.
Symptoms and Diagnosis: People with these conditions might have stomach pain, diarrhea, constipation, and weight loss. Doctors use a patient’s medical history, physical check-ups, endoscopies, and imaging to diagnose.
Treatment Approaches: Treatment plans are made to fit each patient’s needs. They can include lifestyle changes, medications, or more advanced treatments. Our aim is to reduce symptoms, manage the condition well, and enhance the patient’s health.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) management through lifestyle changes and medication.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) treatment focuses on symptom relief and dietary adjustments.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) management involves medication, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgery.
Diagnostic and Treatment Procedures in Gastroenterology
Gastroenterologists use advanced tools and treatments to help patients. The field has grown a lot. Now, there are many ways to diagnose and treat stomach and bowel problems.
Endoscopic Procedures
Endoscopy is a key tool in gastroenterology. It lets gastroenterologists see inside the upper digestive system. A colonoscopy is also important. It checks the colon for polyps, cancer, and other issues.
New endoscopic technology has made these procedures better. For example, capsule endoscopy lets us see the small intestine without traditional endoscopy.
Therapeutic Interventions
Therapeutic interventions in gastroenterology include medicines and advanced endoscopic treatments. Gastrointestinal specialists use these methods to manage long-term and sudden conditions.
| Procedure | Description | Common Applications |
| Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) | A technique that combines endoscopy and fluoroscopy to diagnose and treat conditions related to the bile and pancreatic ducts. | Pancreatitis, bile duct obstruction |
| Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) | A procedure that uses a flexible tube with an ultrasound device to obtain images and samples of the digestive tract and surrounding tissues. | Cancer staging, evaluating gastrointestinal lesions |
| Colonoscopy | A procedure that allows visualization of the inside of the colon and rectum, enabling the removal of polyps and the collection of tissue samples. | Colorectal cancer screening, diagnosis of colon diseases |
About 60“70 million people in the U.S. have gastrointestinal diseases each year. Colonoscopy screenings can cut colorectal cancer by up to 60%. These numbers highlight the need for good diagnostic and treatment methods in gastroenterology.
The Impact of GI Specialists on Public Health
GI specialists have a big role in public health. They help prevent diseases and manage chronic conditions. They improve the lives of people with digestive problems.
Colorectal Cancer Screening and Prevention
Screening for colorectal cancer can lower its rates. GI specialists are key in these efforts. They help find and remove polyps before they turn into cancer.
Management of Chronic Digestive Disorders
GI specialists are essential for chronic digestive diseases like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. They give patients the care they need to live better. They use medicine, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgery to help manage these conditions.
Prevalence of Gastrointestinal Diseases in the United States
Gastrointestinal diseases are common in the U.S. They affect many people. GI specialists diagnose and treat these diseases. They help with issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and more.
Multidisciplinary Approach to Digestive Health Care
A team effort is key to good digestive health care. We know that gastroenterology works with other medical fields. This teamwork helps give patients the care they need.
Collaboration with Other Medical Specialties
Gastroenterologists team up with surgeons, radiologists, and nutritionists. They work together to tackle tough gut problems. This team effort makes sure patients get care that fits their needs.
For example, when it comes to gut cancer, gastroenterologists team up with oncologists and surgeons. They plan treatments that might include endoscopy, surgery, and chemo. For chronic gut issues, working with dietitians and psychologists helps too. It boosts patient results and life quality.
LivHospital shows the high standards of this field. It aims to lead globally with academic methods and a focus on teamwork.
Academic Protocols and Research Advancements
Gastroenterology keeps getting better thanks to new research and tech. Academic rules help make sure care is up-to-date and effective.
Research covers many areas, like new tests and treatments. For example, better endoscopy tools help diagnose and treat gut diseases. Also, studying the gut’s microbes is revealing new ways to handle gut issues.
By working together and keeping up with research, we offer top-notch care to our patients.
Conclusion: The Value of Specialized Gastroenterological Care
Getting care from a gastroenterologist or GI doctor is key for complex digestive issues. It helps improve health and quality of life. These specialists have a lot of education and training to help with digestive health.
Choosing a GI specialist is very important. Patients get the newest treatments and care plans made just for them. This includes endoscopic procedures and more.
Gastroenterologists are important for public health. They help with cancer screening and managing chronic diseases. Their skills are vital for dealing with common digestive problems in the U.S.
In short, specialized care for digestive health is a must, not a luxury. We urge people to find these specialists for top-notch care. This leads to better health for everyone.
FAQ’s:
What is a GI doctor, and what do they specialize in?
A GI doctor, or gastroenterologist, is a specialist. They deal with the digestive system, like the esophagus and stomach. They also work on the small intestine and colon.
What is the difference between a gastroenterologist and a gastrologist?
“Gastrologist” is not a real medical term. It’s often confused with a gastroenterologist. A gastroenterologist is a doctor who focuses on digestive system disorders.
What kind of training does a gastroenterologist receive?
Gastroenterologists get a lot of education. They go to medical school, then do a residency in internal medicine. After that, they have a gastroenterology fellowship. They also get board-certified.
What are some common digestive conditions treated by gastroenterologists?
They treat many conditions. This includes acid reflux and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). They also handle inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and colorectal cancer.
What diagnostic procedures do gastroenterologists use?
They use many tests. These include endoscopy and colonoscopy. They also use imaging tests to diagnose and manage digestive issues.
How do gastroenterologists contribute to public health?
They are key to public health. They promote screening for colorectal cancer. They also manage chronic digestive disorders and address gastrointestinal diseases.
What is the importance of a multidisciplinary approach in digestive health care?
A team approach is vital. It involves gastroenterologists, surgeons, and radiologists. This ensures patients get the best care for complex digestive issues.
How do I know if I need to see a gastroenterologist?
See a gastroenterologist for ongoing or severe symptoms. This includes pain, diarrhea, or constipation. They can help with proper evaluation and treatment.
References
- WebMD. (2024). What does a gastroenterologist do? https://www.webmd.com/ibs/what-does-a-gastroenterologist-do










