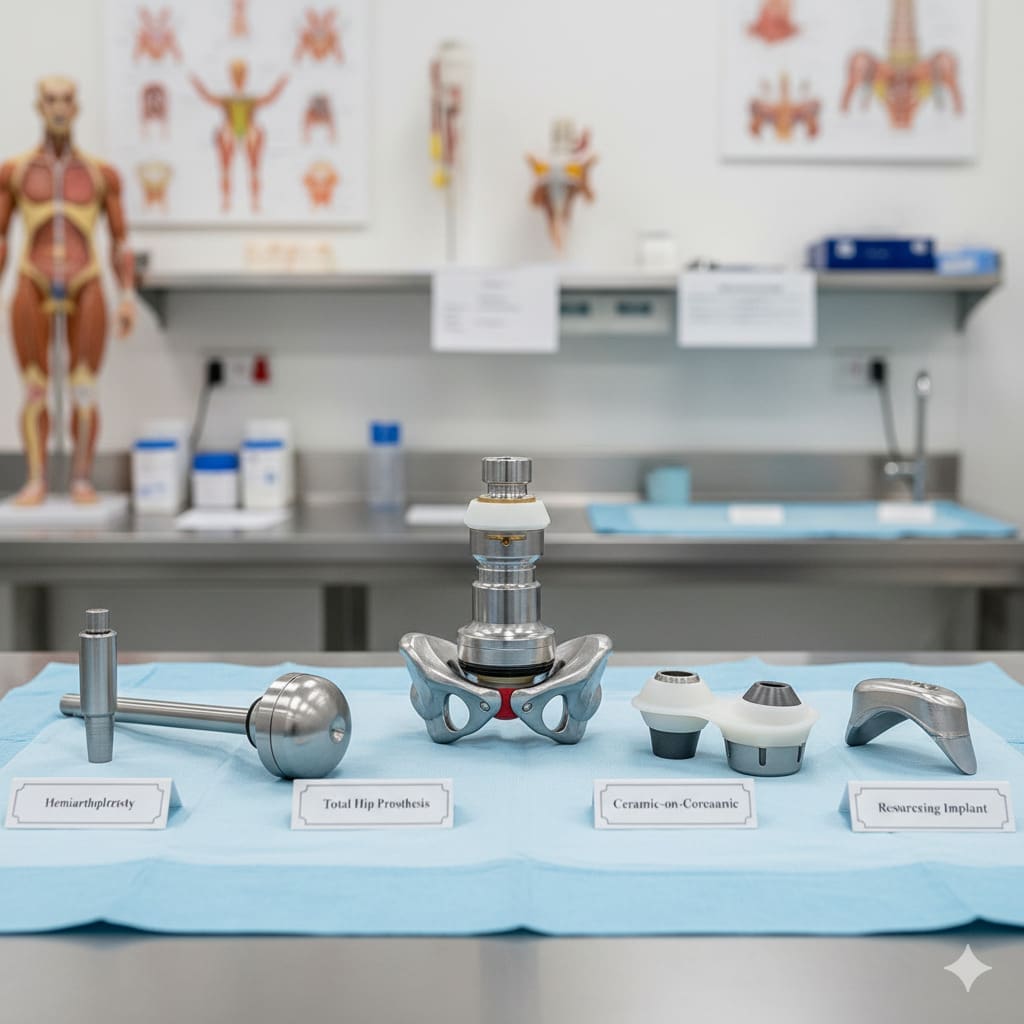
When you think about hip replacement surgery, knowing the hip prosthesis options is key. Recent studies show many types of hip implants. Each has its own good points and possible downsides.
At Liv Hospital, we focus on patient care in musculoskeletal health. We use the most up-to-date methods and materials. We’ll look at the main choices, materials, and risks of hip replacement. This will help you understand what to expect.
Key Takeaways
- Several variations of hip prosthesis are available, each with its benefits and risks.
- Liv Hospital uses the latest evidence-based techniques and materials.
- Understanding the different materials used in hip implants is important.
- Potential risks are linked to hip replacement surgery.
- Orthopedic surgeons at Liv Hospital are trusted for their expertise.
Understanding Hip Replacement Surgery
Hip arthroplasty, or total hip replacement, is a surgery for severe hip joint problems. It replaces the damaged or arthritic hip with an artificial one. This helps to ease pain and improve movement.
What is Hip Arthroplasty?
Hip arthroplasty is a surgery where the damaged hip parts are swapped for artificial ones. The hip is a ball-and-socket joint. In a healthy hip, the ball fits smoothly into the socket.
When the joint is damaged, hip arthroplasty can fix it. The surgery replaces both the ball and socket with artificial parts. These parts are made of metal, ceramic, or plastic.
The choice of materials and design depends on the patient’s age, activity level, and the surgeon’s choice.
Common Terminology in Hip Replacement
It’s important for patients to know the terms used in hip replacement surgery. This helps them make informed decisions about their treatment. Here are some common terms:
- Hip Prosthesis: The artificial device used to replace the hip joint.
- Bearing Surface: The surfaces of the prosthesis that come into contact with each other, such as the ball and socket.
- Cemented Fixation: A method of securing the prosthesis to the bone using bone cement.
- Uncemented Fixation: A method where the prosthesis is designed to encourage bone growth onto its surface for stability.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Hip Arthroplasty | Surgical procedure to replace the hip joint |
| Bearing Surface | Surfaces of the prosthesis in contact |
| Cemented Fixation | Method of securing prosthesis using bone cement |
| Uncemented Fixation | Method encouraging bone growth for stability |
Knowing these terms and the basics of hip arthroplasty helps patients understand their treatment options. It allows them to make informed decisions about their care.
Why Hip Replacements Are Performed
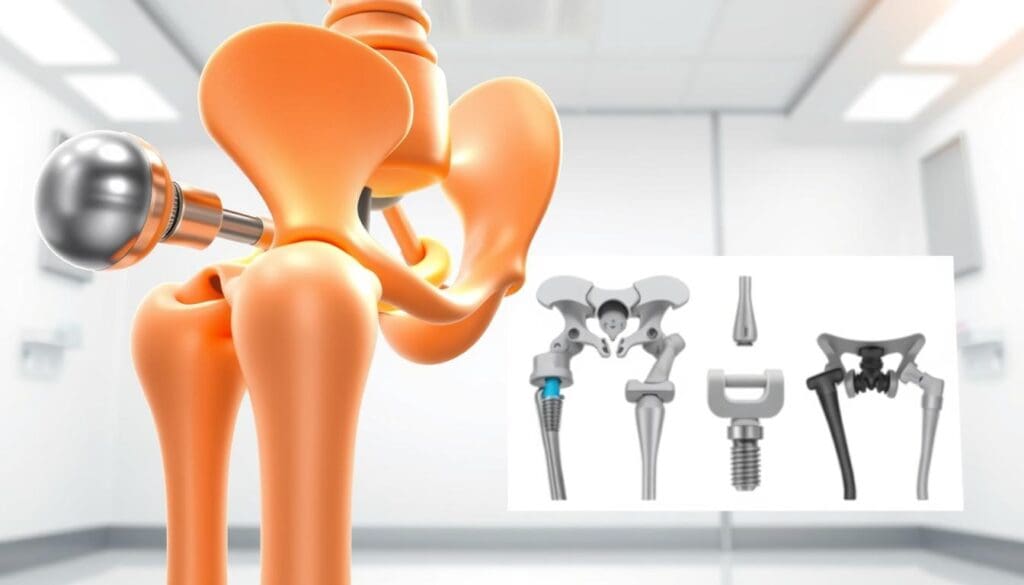
Hip replacements are done for several reasons. These include severe joint damage from osteoarthritis, fractures, and chronic pain. This pain can make daily life hard. Knowing why hip replacements are needed helps patients and doctors choose the best treatment.
Advanced Osteoarthritis
Advanced osteoarthritis is a top reason for hip replacement. This disease wears down the cartilage in the hip, causing pain. When other treatments don’t work, surgery is an option. We use artificial hip models to fix the joint and stop the pain.
Hip Fractures
Hip fractures, often from falls or osteoporosis, also lead to surgery. In older adults, these fractures can make it hard to move around. Hip replacement helps fix the damage and lets patients move freely again. The hip implant design depends on the fracture and the patient’s health.
Chronic Pain and Joint Dysfunction
Chronic pain and joint problems, like those from osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, can make daily tasks hard. When other treatments don’t help, surgery can restore function and stop the pain. Choosing the right hip replacement options can greatly improve a patient’s life.
In summary, hip replacement surgery is key for many hip issues. Understanding why it’s needed helps patients and doctors make the best choices for care.
Evolution of Hip Prosthesis Technology
Advances in hip prosthesis technology have changed orthopedic surgery a lot. They offer new hope to those with hip problems. The journey of hip prosthesis development has seen many milestones and new ideas.
Historical Development
The idea of hip replacement started in the late 19th century. But, it wasn’t until the 20th century that we saw the modern hip prosthesis. Early attempts used ivory and rubber, but they didn’t work well because of material issues.
In the mid-20th century, using stainless steel and cobalt-chromium alloys changed things. These materials made hip prosthetics last longer. Surgery also became less invasive, making recovery faster and scarring less.
| Decade | Significant Advancements | Materials Used |
|---|---|---|
| 1950s | Introduction of metallic hip prosthetics | Stainless Steel, Cobalt-Chromium Alloys |
| 1960s | Development of cemented hip replacements | Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) cement |
| 1980s | Advancements in cementless fixation | Porous-coated and hydroxyapatite-coated implants |
| 2000s | Introduction of highly crosslinked polyethylene | Highly crosslinked polyethylene |
Modern Advancements
Today, hip prosthesis technology keeps getting better. This is thanks to new materials and surgical methods. Modern prosthetics are made to last longer and work better with the body. The use of ceramic and highly crosslinked polyethylene has made them last longer.
Surgery has also improved a lot. Now, we use computer-assisted navigation and robotic surgery. These help place implants more accurately, leading to better results and faster recovery.
The future of hip prosthesis technology is exciting. Ongoing research is looking into new materials and technologies. As we keep exploring, patients will see even better results from hip replacement surgery.
Different Types of Hip Prosthesis: The 5 Key Options
There are many hip joint replacement options, each with its own features. The right choice depends on the patient’s age, how active they are, and the doctor’s advice. We’ll look at the main types of hip prostheses, focusing on their materials and how they’re fixed in place.
Classification Based on Bearing Surfaces
Hip prostheses are sorted by the materials of their moving parts. The moving parts are called the bearing surfaces. The main types are:
- Metal-on-Polyethylene: This is common, with a metal ball and a plastic socket.
- Ceramic-on-Polyethylene: This has a ceramic ball and a plastic socket, wearing less than metal-on-polyethylene.
- Ceramic-on-Ceramic: This is very durable, with both parts made of ceramic.
- Metal-on-Metal: This type is less used now because of metal ion concerns, with both parts metal.
Each type has its benefits and downsides. For example, metal-on-polyethylene prostheses are common but might wear faster than ceramic-on-ceramic ones.
Classification Based on Fixation Methods
Hip prostheses are also grouped by how they’re attached to the bone. The main ways are:
- Cemented Fixation: Uses bone cement to hold the prosthesis in place.
- Uncemented Fixation: This is a tight fit that allows bone to grow into it over time.
- Hybrid Fixation: Combines cement and press-fit methods for a mix of stability and growth.
The choice between these methods depends on the bone quality, patient age, and the doctor’s choice. We’ll look at these factors more in the next sections, giving a full view of hip replacement options.
In summary, knowing about the different hip prostheses is key for patients and doctors. By looking at the materials and how they’re fixed, we can choose the best option for each person.
Metal-on-Polyethylene Hip Prosthesis: The Traditional Option
The hip implant designs include the metal-on-polyethylene hip prosthesis. It’s a traditional and widely used option. This prosthesis is known for its durability and functionality in hip replacement surgery.
Design and Components
The metal-on-polyethylene hip prosthesis has a metal femoral head and a polyethylene acetabular liner. The metal part is made from cobalt-chromium or titanium alloys. These materials are strong and safe for the body.
The polyethylene liner is made from ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE). It’s chosen for its wear resistance and ability to reduce friction. The design aims for smooth movement between the metal and polyethylene parts. This reduces wear and tear over time.
Advantages and Limitations
The metal-on-polyethylene hip prosthesis has a long history of use. It has been improved over the years to better outcomes. It’s also more affordable than newer technologies, which is a big plus for many patients.
But, there are downsides. The polyethylene liner can wear out, leading to bone loss and the need for more surgery. Also, it may not last as long as newer materials, which could be a problem for younger, more active patients.
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Established track record | Polyethylene wear and tear |
| Cost-effective | Risk of osteolysis |
| Wide range of sizes available | Potential need for revision surgery |
Ideal Candidates
This prosthesis is best for older patients or those with lower activity levels. It’s also an option for patients who can’t use more advanced materials due to health reasons.
“The choice of hip prosthesis depends on several factors, including patient age, activity level, and overall health. The metal-on-polyethylene option remains a reliable choice for many patients undergoing hip replacement surgery.”
In conclusion, the metal-on-polyethylene hip prosthesis is a well-established choice in hip replacement surgery. It has its limitations, but its advantages make it suitable for many patients. Understanding the design, components, and patient-specific factors is key to choosing the right prosthesis.
Ceramic-on-Polyethylene Hip Prosthesis: Reduced Wear Option
The ceramic-on-polyethylene hip prosthesis is a big step forward in hip replacement tech. It has less wear than other options. This prosthesis mixes a ceramic ball with a polyethylene liner. It’s strong and reliable for those getting hip surgery.
Design and Components
This prosthesis has a ceramic ball and a polyethylene cup. Ceramic materials are hard and don’t wear down easily. Polyethylene acts as a shock absorber, helping to prevent bone fractures.
The parts are designed to work well together. This reduces the chance of problems. Using ceramic and polyethylene together cuts down on wear debris. This helps avoid osteolysis and implant loosening.
Advantages and Limitations
Ceramic-on-polyethylene hip prostheses wear down less than metal ones. This means they last longer and are less likely to need to be replaced.
But, there are some downsides. Ceramic parts can break more easily than metal ones. But, new ceramic tech has made this risk much lower.
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Reduced wear rate | Potential for ceramic fracture |
| Lower risk of osteolysis | Higher cost compared to some other options |
| Improved longevity of the implant |
Ideal Candidates
Many patients can benefit from ceramic-on-polyethylene hip prostheses. They’re great for those at risk of osteolysis or who are very active. Ideal candidates are usually younger or have a longer life expectancy. This is because they wear down less, lasting longer.
Choosing the right hip prosthesis depends on many things. These include the patient’s age, how active they are, and their bone quality. We help patients pick the best option for them, based on their needs and what they prefer.
Ceramic-on-Ceramic Hip Prosthesis: The Durable Option
The ceramic-on-ceramic hip prosthesis is a big step forward in hip replacement tech. It’s a durable choice for those with hip damage or arthritis. This prosthesis is made to last a long time.
Design and Components
Ceramic-on-ceramic hip prostheses are all ceramic. This makes them hard and resistant to wear. They have a ceramic ball and socket that move smoothly together. The ceramic materials reduce the chance of metal debris and corrosion, which is good for patients looking for a long-lasting hip replacement.
Advantages and Limitations
One big plus of ceramic-on-ceramic hip prostheses is their exceptional wear resistance. This means they can last longer. They also cause fewer problems with local tissue reactions. But, there’s a chance of ceramic fracture and squeaking sounds in some cases.
We need to think about these points when deciding if ceramic-on-ceramic hip prostheses are right for someone.
Ideal Candidates
Ceramic-on-ceramic hip prostheses are best for younger, more active people. Those who are very active or might be sensitive to metal can really benefit from this prosthesis. But, the choice should depend on the patient’s needs and health, including bone quality.
Knowing about ceramic-on-ceramic hip prostheses helps patients make better choices about their treatment.
Metal-on-Metal Hip Prosthesis: The Controversial Option
The metal-on-metal hip prosthesis has sparked a lot of debate in the orthopedic field. It has unique features and risks. We will look into its design, benefits, and drawbacks, and discuss the concerns it raises.
Design and Components
Metal-on-metal hip prostheses have both the ball and socket made of metal alloys, like cobalt-chromium or titanium. This design aims to offer a durable and long-lasting option compared to others.
Key Components:
- Metal ball (cobalt-chromium or titanium alloy)
- Metal socket (cobalt-chromium or titanium alloy)
- Stem (usually made from titanium alloy)
Advantages and Limitations
One big plus of metal-on-metal hip prostheses is their durability and lower wear rates. This is great for younger, more active patients.
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Durable and potentially long-lasting | Risk of metal ion release into the bloodstream |
| Lower wear rates | Potential for adverse local tissue reactions |
| Suitable for active patients | Higher risk of revision surgery |
-Dr. an orthopedic surgeon, says, “Metal-on-metal hip prostheses have benefits but are limited due to metal ion release and local tissue reactions.”
“The metal-on-metal hip replacement was initially hailed as a revolutionary option due to its durability. But, its use has been marred by controversy over its safety and health risks.”
Concerns and Current Status
The main worries with metal-on-metal hip prostheses are metal ion release and local tissue reactions. These issues have led to a decrease in their use.
The medical community is closely watching the long-term effects of these prostheses. There’s a move towards more personalized hip replacement options. Now, metal-on-metal hip prostheses are used more carefully, often for specific patients.
We are dedicated to giving our patients the best care. We consider the latest research and advancements in hip replacement technology.
Hybrid Hip Prosthesis Systems: The Customized Option
Hybrid hip prosthesis systems are a big step forward in orthopedic tech. They offer customized solutions for those with complex hip issues. These systems mix the best parts of different materials and tech.
Combining Different Materials
Hybrid hip systems use various materials for their benefits. For example, a ceramic head with a polyethylene liner reduces wear and boosts durability. We also use titanium and cobalt-chromium alloys for their strength and safety.
By combining different parts, surgeons can make a prosthesis that fits each patient’s needs perfectly.
Hybrid systems are flexible, allowing for personalized treatment plans. This leads to better results and happier patients. They’re great for those with special needs or past issues with regular prostheses.
Specialized Applications
These systems are perfect for patients with unique needs or past problems. They can handle bone loss or deformity, making the hip joint more stable and functional. We team up with patients and surgeons to find the best hybrid setup for each case.
Hybrid hip systems meet a wide range of patient needs. They’re good for both young, active people and older patients needing gentler treatments.
Materials Used in Hip Prosthesis Construction
We use metals, ceramics, and polymers to make hip prostheses. Each material is chosen for its durability, how well it fits with the body, and how it works. This choice is key for the prosthesis’s success.
Metals: Cobalt-Chromium, Titanium, and Stainless Steel
Metals are strong and last long, making them great for hip prostheses. Cobalt-chromium alloys are top picks because they’re tough and wear well. Titanium is chosen for its light weight and how well it bonds with bone.
Stainless steel is durable and resists corrosion, but it wears faster than other metals. It’s used less often for this reason.
Ceramics: Alumina and Zirconia
Ceramics like alumina and zirconia are used for their wear resistance and safety. Alumina is very hard and has low friction, which helps the prosthesis last longer. Zirconia is strong and tough, perfect for areas needing extra durability.
Ceramics are best for younger, more active people because they wear down less.
Polymers: Highly Crosslinked Polyethylene
Highly crosslinked polyethylene is a polymer used in hip prostheses, mainly for the liner. It’s been improved to last longer and reduce bone damage. The crosslinking makes it more durable against wear and damage.
This material is often paired with metal or ceramic heads. It offers a good mix of durability and wear resistance.
Choosing materials for hip prostheses is complex. It depends on the patient’s age, activity level, and body needs. Knowing the benefits of each material helps doctors make the best choices for patients.
Selecting the Right Hip Prosthesis
Choosing the right hip prosthesis is a big decision. It needs a deep understanding of what each patient needs. We look at many factors to find the best option for each person.
Patient Age and Activity Level Considerations
Age and how active a patient is matter a lot. Younger, more active people might need stronger prosthetics. Older or less active people might do better with other types that last longer.
We also think about how much a patient moves. For example, younger patients might get prosthetics made of durable materials that last longer.
Metal Sensitivity and Allergies
Some people might be allergic to metals in prosthetics, like cobalt or nickel. We look for signs of these allergies. Then, we suggest prosthetics made of safer materials like ceramic or titanium.
Using materials that are less likely to cause an allergic reaction is key. Titanium is a good choice for people with metal allergies because it’s safe for the body.
Anatomical and Bone Quality Factors
The shape and strength of a patient’s bones are also important. Patients with weak bones might need special prosthetics or ways to attach them.
We check the bones to pick the right prosthesis. For example, someone with osteoporosis might get a prosthesis that helps their bones grow into it.
| Patient Factor | Consideration | Prosthesis Option |
|---|---|---|
| Age and Activity Level | Durability and wear resistance | Ceramic-on-ceramic or highly crosslinked polyethylene |
| Metal Sensitivity | Hypoallergenic materials | Titanium or ceramic prostheses |
| Bone Quality | Stable fixation and integration | Specialized coatings or designs for bone ingrowth |
By looking at these factors, we can choose the best hip prosthesis. This helps make sure the surgery is a success for the patient.
Risks and Complications of Hip Prosthesis
It’s important to know the risks of hip prosthesis before deciding on hip replacement surgery. Hip replacement is usually safe and works well. But, there are possible complications to be aware of.
Short-Term Complications
Complications can happen during or right after surgery. These include:
- Infection: There’s a chance of infection with hip replacement surgery.
- Blood Clots: Blood clots can form in the legs or lungs, a condition known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
- Nerve Injury: There’s a risk of nerve damage during surgery, which can result in numbness, tingling, or weakness.
We use antibiotics to prevent infection and anticoagulant medications to reduce blood clot risk.
Long-Term Complications
Complications can also happen months or years after surgery. These include:
- Dislocation: The artificial hip joint can dislocate, which is more common in the early period after surgery.
- Wear and Tear: Over time, the components of the hip prosthesis can wear out, potentially leading to the need for revision surgery.
- Wear Debris: Tiny particles can be generated from the wear of the prosthetic components, potentially causing inflammation or bone loss.
Knowing about these long-term complications is key for managing expectations and making informed decisions. We closely monitor the condition of the hip prosthesis and address any issues quickly.
By understanding both short-term and long-term risks, patients can make better choices and aim for the best outcomes.
Conclusion
Knowing about the different hip prosthesis types is key for those getting hip replacement surgery. We’ve talked about many options, like metal-on-polyethylene and ceramic-on-ceramic. Each has its own benefits and considerations.
Research shows that some hip prostheses work better than others. For example, those with a full HA coated compaction stem lead to better results. A study in the BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders journal found positive outcomes with a certain design.
Choosing the right hip prosthesis is a big decision. It depends on the patient’s age, how active they are, and their body’s needs. By learning about the different types, patients can make better choices. We aim to give clear, helpful information to support patients during their hip replacement journey.
What are the different types of hip prosthesis available?
We have many hip prosthesis options. These include metal-on-polyethylene, ceramic-on-polyethylene, and ceramic-on-ceramic. We also have metal-on-metal and hybrid systems. Each has its own benefits and features.
How is the right hip prosthesis selected for a patient?
We look at several factors to choose the right hip prosthesis. These include the patient’s age, activity level, and metal sensitivity. We also consider anatomical and bone quality factors.
What are the common materials used in hip prosthesis construction?
We use different materials for hip prostheses. These include metals like cobalt-chromium, titanium, and stainless steel. We also use ceramics like alumina and zirconia, and polymers like highly crosslinked polyethylene. These materials help create durable and compatible prostheses.
What are the risks and complications associated with hip prosthesis?
Like any surgery, hip prosthesis has risks and complications. These include infection, dislocation, wear and tear, and loosening. We closely monitor and manage these issues.
How have advancements in hip prosthesis technology improved outcomes?
Advances in hip prosthesis technology have made them better. They are now more durable, have less wear, and are more compatible. This has led to better results and happier patients.
What is the difference between metal-on-polyethylene and ceramic-on-ceramic hip prostheses?
Metal-on-polyethylene prostheses are traditional and common. Ceramic-on-ceramic prostheses, on the other hand, offer less wear and better durability. They are a good choice for younger, more active patients.
Are there any specific considerations for patients with metal sensitivity or allergies?
Yes, we consider metal sensitivity and allergies when choosing a hip prosthesis. We choose alternative materials or designs to reduce the risk of adverse reactions.
References
News-Medical.Net: Research identifies best materials for long-lasting hip implants
PubMed Central (NCBI): Metal-on-Metal Hip Arthroplasty and the Development of Pseudotumors: A Systematic Review




































