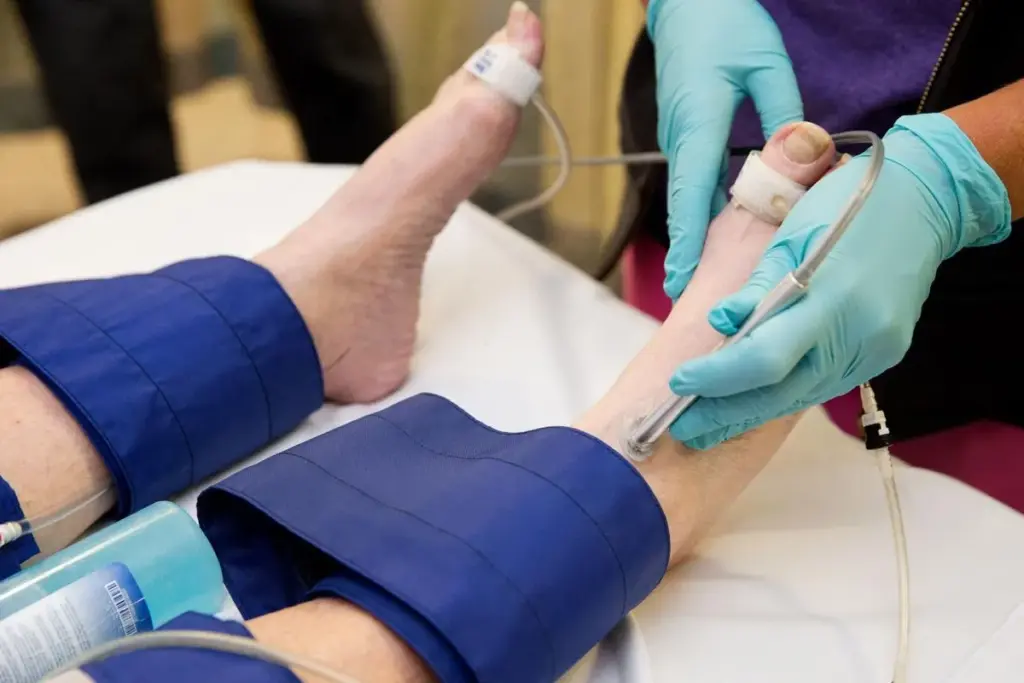
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) affects millions worldwide. It causes a lot of discomfort and can lead to serious health problems. One in three people over 50 with PAD may have blocked arteries in their legs, which can severely impact their quality of life angioplasty.
To address this issue, medical professionals often use stents. They help keep the blood flowing and prevent further blockages. But what happens after the procedure? Understanding leg positioning after angioplasty is key for a smooth recovery.
We will guide you through the importance of leg positioning after stent placement. We will also provide insights into what you can expect during your recovery.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) and its impact on leg health
- The role of stents in treating blocked arteries in the legs
- Importance of leg positioning after angioplasty for a smooth recovery
- What to expect during the recovery process
- Tips for managing leg health after stent placement
Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
It’s important to know about Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) if you have circulation problems. PAD is a condition that affects the arteries. If not treated, it can lead to serious health issues.
Common Causes of PAD
PAD happens when plaque builds up in the arteries, known as atherosclerosis. This can be caused by high blood pressure, diabetes, and smoking. These factors can harm the blood vessel lining, making it easier for blockages to occur.
Other risk factors include high cholesterol, obesity, and a family history of heart disease. Knowing these causes helps in preventing and managing PAD.
Symptoms and Warning Signs
PAD symptoms can vary but often include muscle pain or cramping in the legs during exercise, known as claudication. Other signs are weakness or numbness in the legs, coldness, sores, or weak pulses in the legs or feet.
Spotting these symptoms early is key, as PAD raises the risk of heart attack or stroke. If you notice any of these signs, get medical help to avoid worse problems.
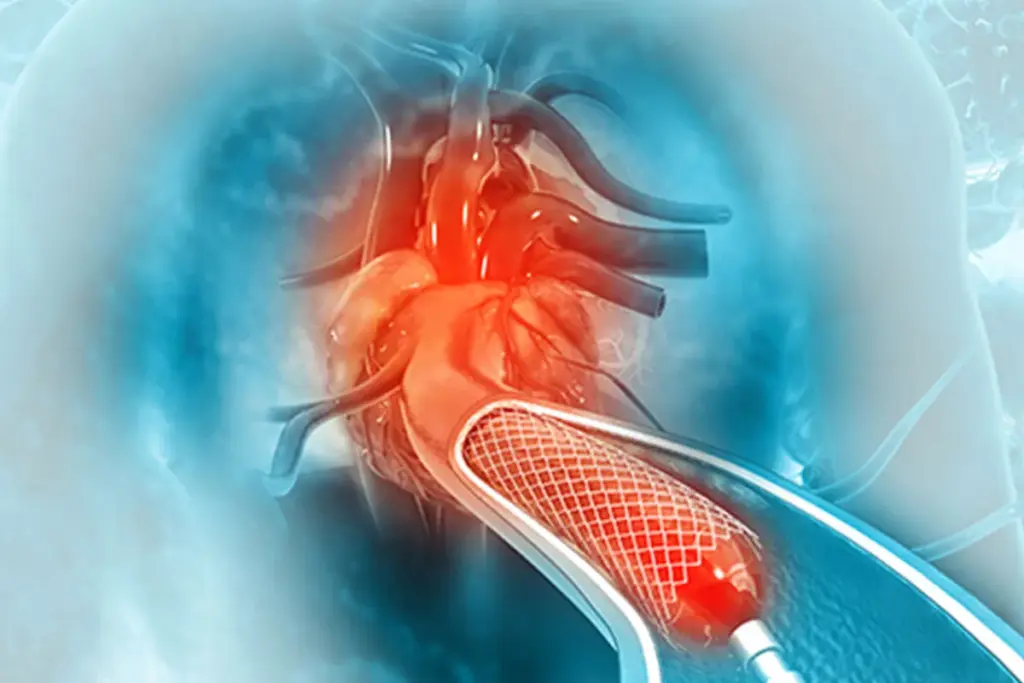
What Are Leg Stents?
Leg stents are small, metal mesh tubes used after angioplasty. This procedure widens narrowed or blocked arteries. They are key in treating Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD), which narrows or blocks leg arteries.
Stents keep arteries open, improving blood flow to the legs. This is vital for PAD patients. It helps reduce leg pain when walking and boosts quality of life.
Types of Vascular Stents Used in Legs
There are several vascular stents for leg arteries, each for different needs. The main types are:
- Bare-metal stents: Traditional, made from metal mesh. They support the artery’s openness.
- Drug-eluting stents: Coated with medication to prevent artery narrowing. Ideal for those at high risk of restenosis.
- Bioresorbable stents: Dissolve in the body over time. They offer temporary support and may reduce long-term issues.
|
Stent Type |
Description |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Bare-metal |
Made from metal mesh |
Provides structural support |
|
Drug-eluting |
Coated with medication |
Reduces risk of re-narrowing |
|
Bioresorbable |
Dissolves over time |
Temporary support, fewer long-term complications |
How Stents Improve Blood Flow
Stents keep arteries open, ensuring blood flow to leg muscles. This reduces pain during walking and boosts mobility.
Stent placement is key in angioplasty. It combines with angioplasty for better results and less artery narrowing.
Medical Conditions Requiring Leg Stents
Leg stents are needed for people with certain vascular problems. These problems affect blood flow to the legs. They can cause pain and limit how well you can move. We’ll look at the main conditions that need leg stents, like atherosclerosis, claudication, and critical limb ischemia.
Atherosclerosis in Lower Extremities
Atherosclerosis is when plaque builds up in arteries, narrowing them. This can reduce blood flow to the legs. Atherosclerosis in the legs is a big part of peripheral artery disease (PAD).
The plaque is made of fat, cholesterol, and other blood substances. Over time, it can harden and block the arteries. This blockage can cause pain when walking, known as claudication.
|
Condition |
Description |
Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
|
Atherosclerosis |
Buildup of plaque in arterial walls |
Pain during walking, coldness in legs |
|
Claudication |
Pain in legs during exercise due to reduced blood flow |
Pain in legs or buttocks during activity |
|
Critical Limb Ischemia |
Severe reduction in blood flow to the limbs |
Severe pain at rest, ulcers, gangrene |
Claudication and Critical Limb Ischemia
Claudication is pain in the legs or buttocks when you’re active. It’s because of not enough blood flow. It goes away when you rest. Critical limb ischemia (CLI) is a more serious case where you have pain even when sitting or lying down. It can cause ulcers or gangrene.
Both claudication and CLI show serious atherosclerosis in the legs. Claudication can really affect your life, but CLI is a serious threat to your limb. Leg stents help by opening up blocked or narrowed arteries to improve blood flow.
Understanding these conditions helps us see why leg stents are important. They help improve blood flow, lessen symptoms, and stop the disease from getting worse.
Benefits of Leg Stent Placement
Stent placement in the legs helps restore blood flow. This relieves symptoms of Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) and prevents serious problems. It’s a key treatment for those with PAD, improving health and well-being.
Improved Quality of Life
Leg stent placement greatly improves life for PAD patients. It eases pain, cramping, and fatigue. This lets patients do daily tasks more easily and move around better.
a top vascular surgeon, says, “Leg stent placement has changed PAD treatment. It lets patients be independent and live better lives.”
“The insertion of stents in the legs has been a game-changer for many of our patients, allowing them to walk further and live more actively.”
Preventing Serious Complications
Leg stent placement also prevents serious PAD complications. It keeps blood flowing, avoiding gangrene and amputation. These are risks when PAD is not treated well.
|
Benefits |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Improved Mobility |
Restored blood flow enables patients to walk further and engage in physical activities. |
|
Pain Reduction |
Alleviation of pain and cramping associated with PAD. |
|
Prevention of Complications |
Reduced risk of gangrene and amputation. |
Choosing leg stent placement is a big decision. But, it’s backed by solid evidence and expert advice. This treatment promises a better life and less chance of serious issues.
The Angioplasty and Stenting Procedure Explained
Exploring the angioplasty and stenting procedure is key. Knowing the steps and what to expect can ease worries. It prepares patients for the treatment ahead.
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Before angioplasty and stenting, health and artery condition tests are conducted. These tests include blood work and imaging studies like angiography. They help doctors plan the procedure.
Patients are told to stop certain medications. Following the doctor’s instructions is vital for a good outcome.
Step-by-Step Process
The procedure has several steps:
- The patient lies on a table, and the area is cleaned and numbed.
- A small incision is made, and a catheter with a balloon is guided to the blocked artery.
- The balloon is inflated to widen the artery, and a stent is placed to keep it open.
- The catheter is removed, and the incision is closed.
Types of Anesthesia Used
Anesthesia types vary in angioplasty and stenting. Local anesthesia is often used to numb the area. This lets the patient stay awake. Sometimes, conscious sedation is used to relax the patient.
Knowing about the procedure and anesthesia can make patients feel more at ease. It helps them prepare for their treatment.
Access Sites for Leg Stent Procedures
Finding the best access site is key in leg stent procedures. The right site can greatly affect treatment success and recovery.
Femoral Artery Access
The femoral artery is a top choice for leg stent procedures. It’s popular because it’s easy to get to and most doctors know how to use it. It’s in the groin, making it a direct path to the lower limb arteries.
Using the femoral artery has many benefits, including:
- It’s big and easy to access
- Doctors are very familiar with it
- Procedures can be done with just local anesthesia
Alternative Access Points
While the femoral artery is common, other sites might be used based on the patient’s body and the blockage’s location. Other sites include:
- Radial artery access: It’s becoming more popular for its lower risk of complications.
- Brachial artery access: Though rare, it’s used when other sites can’t be used.
Choosing alternative sites depends on the patient’s needs and the doctor’s skills.
Do Angioplasty with Stenting Need to Keep Their Leg Straight?
After angioplasty with stenting, many wonder if they must keep their leg straight. This is key for a smooth recovery and to avoid complications.
Immediate Post-Procedure Positioning Requirements
Right after the procedure, patients must keep their leg straight. This is to lower the risk of bleeding or hematoma at the access site. The time needed can change based on the technique, catheter size, and patient health.
Scientific Rationale Behind Leg Positioning
Keeping the leg straight after angioplasty helps prevent bleeding and aids in clotting at the access site. When the femoral artery is accessed, as in leg angioplasty, it stops the clot at the puncture site from moving.
“The primary mechanism by which keeping the leg straight aids in recovery is by minimizing movement at the arterial puncture site, which helps in forming a stable clot and lowers the risk of bleeding complications.”
To show why leg positioning is important, here’s a table on post-angioplasty leg care:
|
Aspect |
Recommendation |
Rationale |
|---|---|---|
|
Leg Positioning |
Keep leg straight |
Prevent bleeding and promote hemostasis |
|
Duration |
2-4 hours |
Based on clinical guidelines and patient condition |
|
Activity Level |
Limited activity |
Reduce risk of complications |
As the table shows, keeping the leg straight is vital in post-angioplasty care. Following these guidelines helps patients avoid complications and recover smoothly.
Post-Angioplasty Leg Care Guidelines
Recovering well after angioplasty means following key leg care steps. Patients must pay close attention to their leg care to avoid any issues during recovery.
Hospital Recovery Protocol
In the hospital, doctors watch the patient’s leg closely. Right after the procedure, the leg is kept straight to stop bleeding and help it heal. They also look out for any signs of trouble, like bleeding, pain, or swelling.
Hospital care includes:
- Regular checks on the access site
- Monitoring for signs of bleeding or hematoma
- Managing pain effectively
- Ensuring the patient is comfortable and informed about their care
First 24-48 Hours After Procedure
The first 24-48 hours are very important for recovery. Patients should rest and avoid hard activities during this time. We suggest:
- Keeping the leg straight for a few hours after the procedure
- Avoiding heavy lifting, bending, or hard exercise
- Following medication instructions carefully
- Monitoring for any unusual symptoms or complications
It’s also key to follow up with healthcare providers as told to make sure recovery is going well.
By sticking to these guidelines, patients can lower the risk of problems and help their leg heal. Taking good care of your leg after angioplasty is vital for the best results from the procedure.
Importance of Straight Leg After Angioplasty
Keeping the leg straight after angioplasty is key to a smooth recovery. It ensures the stent works right and helps avoid extra problems. This step is not just a suggestion; it’s essential for a good outcome.
Preventing Complications at the Access Site
One big reason for straight leg positioning is to avoid issues at the access site. This is where the catheter was put in for the procedure. Problems like bleeding or swelling can happen here. Straightening the leg helps lower these risks.
“The importance of proper leg positioning cannot be overstated in the prevention of access site complications post-angioplasty.”
|
Complication |
Description |
Prevention Measure |
|---|---|---|
|
Bleeding |
Bleeding at the access site |
Keeping the leg straight |
|
Hematoma |
Collection of blood outside the blood vessels |
Leg immobilization |
|
Pseudoaneurysm |
A leakage of arterial blood from an artery into the surrounding tissue |
Strict bed rest |
Optimizing Stent Placement and Healing
Keeping the leg straight also helps with stent placement and healing. Getting the stent in the right spot is key for blood flow. A straight leg makes this easier.
Proper stent placement is vital for avoiding problems later. Doctors say the stent’s position is critical for the procedure’s success.
In summary, keeping the leg straight after angioplasty is very important. It’s a simple action that greatly helps the procedure’s success. It prevents access site problems and ensures the stent works well.
When Can You Bend Your Leg After Stent Placement?
Patients often ask when they can bend their leg after a stent placement. The recovery is a slow return to normal movement. It’s important to know when it’s safe to move.
Gradual Return to Normal Movement
Right after the procedure, patients are told to keep their leg straight. This helps the site heal and the stent work better. Usually, bending the leg can start in 24 to 48 hours. But, this can change based on your health and what your doctor says.
It’s good to move slowly to avoid problems. Start with small bends and straightens to help blood flow and prevent stiffness. Always listen to your doctor about how much and how often to move.
Signs That Indicate Safe Movement
When you start bending your leg, look for these signs of safe movement:
- Mild pain is okay, but sharp or severe pain means stop right away.
- Swelling or bruising at the site should be watched. If it gets worse, get medical help.
- Look out for bleeding or a big bruise at the site.
By watching for these signs and following your doctor’s advice, you can safely bend your leg again. Always talk to your doctor if you’re worried about your recovery.
Potential Complications of Leg Stent Procedures
It’s important to know about the risks of leg stent procedures. Leg stents help treat peripheral artery disease (PAD). But, like any medical treatment, there are possible dangers.
Access Site Complications
Access site complications are common with leg stent procedures. These happen where the catheter goes into the artery.
- Hematoma or bleeding
- Pseudoaneurysm formation
- Arteriovenous fistula
- Infection
To lower these risks, we plan carefully before the procedure. We use precise techniques during it. And we watch closely after it’s done.
Stent-Related Complications
Stent-related problems can affect how well the procedure works. These issues might include:
- Stent thrombosis (clot formation within the stent)
- Stent restenosis (re-narrowing of the stented segment)
- Stent migration or malposition
We do everything we can to avoid these problems. This includes using the right anticoagulation therapy. And we carefully choose and place the stent.
When to Seek Emergency Care
It’s key for patients to know when to get help right away. If you have any of these symptoms after a leg stent procedure, go to the emergency room:
- Severe pain or swelling in the leg
- Coldness or paleness of the leg
- Weakness or numbness in the leg
- Signs of infection, such as fever or redness at the access site
- Chest pain or shortness of breath
Acting fast can make a big difference. It can help prevent serious problems.
Recovery Timeline After Leg Stent Placement
After a leg stent placement, patients follow a recovery timeline to heal well. This timeline has different stages, each with its own goals and milestones.
First Week Post-Procedure
The first week is key for a good recovery. Patients should:
- Rest and avoid hard activities
- Watch the access site for any issues
- Take their meds as told
- Go to all follow-up appointments
Keeping the leg straight right after is important to avoid problems and ensure the stent works right. As they start doing normal things again, they should listen to their body and not overdo it.
Weeks 2-4 Recovery Milestones
In weeks 2-4, patients see big improvements. Key points include:
- Getting more mobile and able to do more
- Feeling better from Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
- Staying on a heart-healthy path with diet and exercise
During this time, knowing when it’s safe to bend the leg is important. Following the doctor’s advice is key for a smooth recovery.
Long-Term Recovery Expectations
In the long run, patients keep getting better and face fewer risks if they stick to their recovery plan. Expectations include:
- Keeping blood flow to the leg better
- Lowering the chance of heart problems with lifestyle changes and meds
- Going to regular check-ups to watch the stent and blood vessels
Knowing the recovery timeline helps patients heal and improve their blood flow. The process involves watching closely, making lifestyle changes, and following doctor’s orders.
Living with Leg Stents: Long-Term Care and Maintenance
Getting leg stents is just the start. Patients must focus on long-term care to get the most from the procedure. This means sticking to follow-up appointments and making lifestyle changes. These steps help keep the stent working well and improve blood flow.
Follow-up Appointments and Imaging
After getting leg stents, regular check-ups with your doctor are key. These visits help your doctor see how the stent is doing. They also check for any problems and make needed changes. Tests like ultrasound or angiography might be used to check the stent and artery.
It’s important to keep up with your follow-up schedule. Usually, you’ll see your doctor at 3, 6, and 12 months after the procedure. Then, you’ll go every year. But, your doctor might want to see you more often based on your health and needs.
|
Follow-up Interval |
Typical Procedures |
Purpose |
|---|---|---|
|
3 months |
Ultrasound, clinical assessment |
Assess stent patency, check for restenosis |
|
6 months |
Ultrasound, review of symptoms |
Monitor stent performance, adjust treatment plan if needed |
|
12 months |
Angiography, comprehensive evaluation |
Detailed assessment of stent and artery condition |
Lifestyle Modifications for Stent Longevity
Along with regular check-ups, making lifestyle changes can help your stent last longer. Quitting smoking is very important. Smoking can make your stent less effective. Eating well and staying active are also key.
It’s also important to manage risk factors like high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol. Working with your doctor to control these can make a big difference.
By following up regularly and making healthy choices, people with leg stents can see better blood flow and quality of life. It’s a team effort between patients and doctors to get the best results.
Conclusion
Understanding leg stents in treating Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is key for patients. Leg stents help improve blood flow and ease PAD symptoms.
After angioplasty, keeping legs in the right position is important. This helps the stent work better and heal faster. Following post-procedure guidelines and staying healthy can greatly improve life quality and prevent serious issues.
In summary, leg stents are a valuable treatment for PAD. With the right care, they can offer lasting relief. We urge patients to collaborate with their healthcare team for the best results after stent placement and angioplasty.
FAQ
Do you need to keep your leg straight after angioplasty with stenting?
Yes, it’s important to keep your leg straight after angioplasty with stenting. This helps prevent complications and ensures proper healing.
How long do I need to keep my leg straight after stent placement?
The time you need to keep your leg straight varies. It depends on the procedure and your doctor’s advice. It’s usually a few hours to a few days.
What are the benefits of keeping my leg straight after angioplasty?
Keeping your leg straight helps prevent bleeding or hematoma at the access site. It also reduces the risk of stent displacement. This promotes optimal stent placement and healing.
Can I bend my leg after stent placement?
You can bend your leg again as your healthcare provider advises. This is usually after a certain period following the procedure.
What are the signs that indicate it’s safe to bend my leg after stent placement?
Your healthcare provider will tell you when it’s safe to move your leg. This depends on the absence of complications, stable stent placement, and satisfactory wound healing.
What are the possible complications of leg stent procedures?
Complications can include bleeding or hematoma at the access site. Stent-related issues like stent thrombosis or restenosis are also possible.
When should I seek emergency care after leg stent placement?
Seek emergency care if you have severe pain, swelling, or bleeding at the access site. Also, if you experience chest pain, shortness of breath, or severe leg pain.
What is the recovery timeline after leg stent placement?
Recovery time varies. You can usually return to normal activities in a few weeks. Full recovery may take several weeks to a few months.
What long-term care and maintenance are required for patients living with leg stents?
Long-term care includes regular follow-up appointments and imaging tests. Lifestyle changes like exercise, a healthy diet, and quitting smoking help maintain the stent.
How do leg stents improve blood flow?
Leg stents keep the artery open, improving blood flow to the affected limb. This reduces symptoms like claudication and pain.
What are the common causes of Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)?
PAD is often caused by atherosclerosis, smoking, diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
What are the symptoms and warning signs of PAD?
Symptoms include leg pain or cramping during exercise, coldness or numbness in the legs, and weak or absent pulses in the legs.
Does having a pacemaker or ICD affect the angioplasty and stenting procedure?
A pacemaker or ICD may need special care during angioplasty and stenting. Your healthcare provider will give you necessary precautions.
Can I experience sharp pain at the pacemaker site after the procedure?
Some discomfort or pain at the pacemaker site is possible. But, severe or persistent pain should be reported to your healthcare provider.
What is the recovery process like after ICD implant?
Recovery after ICD implant includes a short hospital stay and rest. You’ll gradually return to normal activities with specific instructions from your healthcare provider.
References
The Lancet. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(13)61289-7/fulltext





