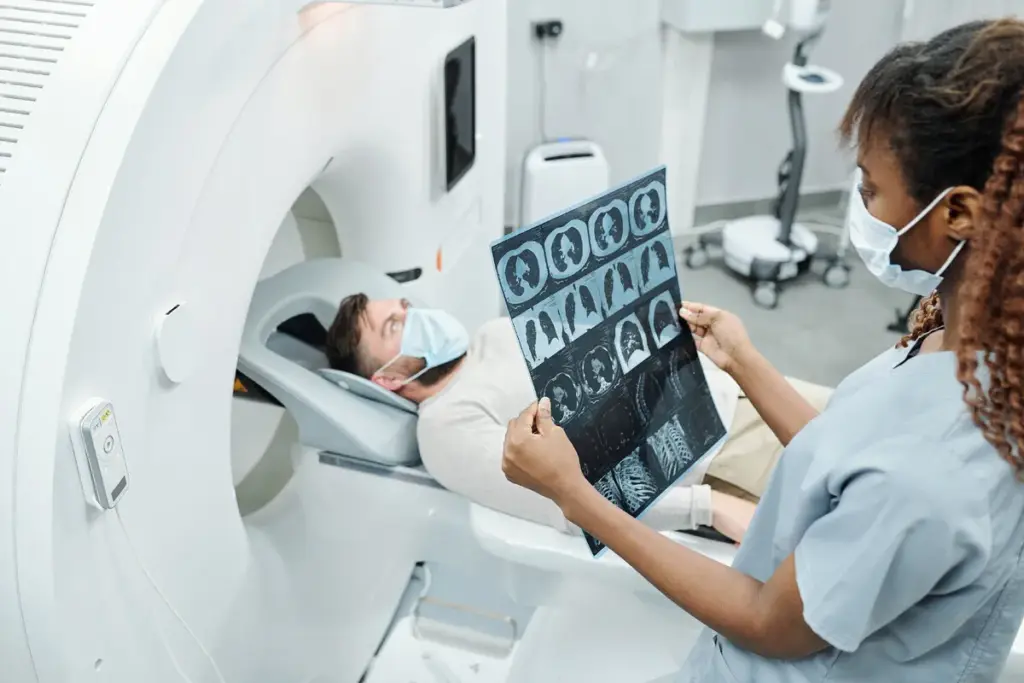
Former NFL star Deion Sanders recently revealed his bladder cancer diagnosis, sparking a conversation about the importance of bladder cancer screening. At Deion Sanders’ age, it’s crucial to understand how cancer is detected.
Does a ct scan detect tumors? Yes, but not all. Get best facts. Cystoscopy is vital to see inside. It finds dangerous lesions scans miss.
Bladder cancer, like many other forms of cancer, requires early detection for effective treatment. One common method of detection is through a CT scan. But the question remains, can a CT scan accurately detect cancer bladder issues?
Key Takeaways
- CT scans are a common diagnostic tool for detecting various health issues, including bladder cancer.
- Deion Sanders publicly sharing his diagnosis highlights the importance of cancer awareness.
- Early detection is key to treating bladder cancer effectively.
- Bladder cancer screening methods vary, but CT scans are among the most reliable.
- Understanding the diagnostic process can help alleviate concerns about cancer detection.
Understanding CT Scans and Their Purpose
Computed Tomography (CT) scans have revolutionized the field of medical imaging, providing unparalleled insights into the human body. These scans are a crucial diagnostic tool, enabling healthcare professionals to visualize internal structures in detail.
What is a CT Scan?
A CT scan is a non-invasive medical imaging test that uses X-rays and computer technology to produce detailed cross-sectional images of the body’s internal structures. It is particularly useful for diagnosing and monitoring a wide range of medical conditions.
How Does a CT Scan Work?
During a CT scan, the patient lies on a table that slides into a large, doughnut-shaped machine. The machine rotates around the patient, emitting X-rays that are absorbed by the body’s tissues to varying degrees. The X-ray data is then reconstructed by a computer into detailed images.
Common Uses of CT Scans
CT scans are versatile and have numerous applications in medical diagnosis. Some of the common uses include:
- Diagnosing and monitoring cancer
- Guiding biopsies and other interventional procedures
- Detecting internal injuries and bleeding
- Diagnosing vascular diseases
|
Application |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Cancer Diagnosis |
CT scans help in detecting tumors, staging cancer, and monitoring treatment response. |
|
Guiding Procedures |
CT scans are used to guide biopsies, drainages, and other minimally invasive procedures. |
|
Trauma and Injury |
CT scans quickly identify internal injuries, such as bleeding or organ damage. |
|
Vascular Diseases |
CT scans diagnose vascular conditions, including aneurysms and blockages. |
The CU Anschutz medical campus is renowned for its advanced medical research and treatment facilities, including the use of CT scans in cancer diagnosis and treatment. Institutions like these are at the forefront of medical innovation, providing high-quality care to patients.
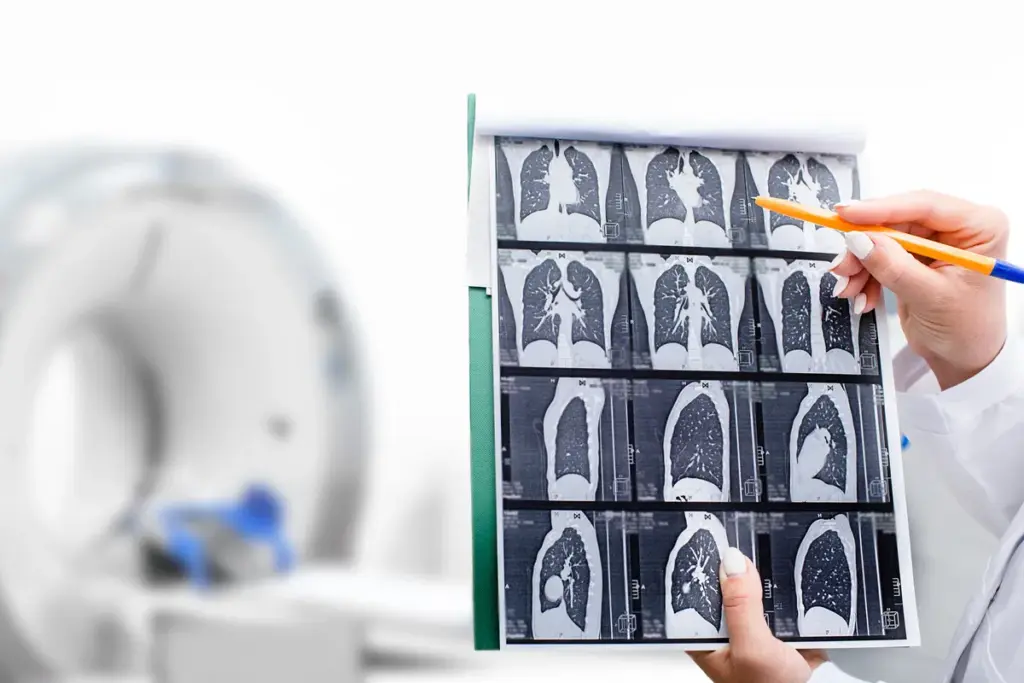
Types of Tumors Detected by CT Scans
The versatility of CT scans allows them to detect a wide range of tumors, from benign growths to malignant cancers. This capability is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Benign vs. Malignant Tumors
Understanding the difference between benign and malignant tumors is essential for determining the appropriate course of action. Benign tumors are non-cancerous and typically do not spread to other parts of the body, whereas malignant tumors are cancerous and can metastasize.
Key differences between benign and malignant tumors include:
- Growth Rate: Benign tumors usually grow slowly, while malignant tumors can grow rapidly.
- Invasion: Malignant tumors invade surrounding tissues, whereas benign tumors tend to remain localized.
- Metastasis: Only malignant tumors can spread to other parts of the body.
Types of Cancers Typically Detected
CT scans are effective in detecting various types of cancers, including lung, liver, and pancreatic cancers. Early detection of these cancers can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
|
Cancer Type |
Detection Capability |
|---|---|
|
Lung Cancer |
Highly detectable due to CT scans’ ability to image lung structures clearly. |
|
Liver Cancer |
CT scans can identify liver lesions and tumors, aiding in early diagnosis. |
|
Pancreatic Cancer |
CT scans help in detecting pancreatic tumors and assessing their resectability. |
Non-Cancerous Growths
Apart from detecting malignant tumors, CT scans can also identify non-cancerous growths such as cysts and adenomas. Accurate diagnosis of these growths is vital to avoid unnecessary treatments.
Examples of non-cancerous growths detected by CT scans include:
- Cysts in the kidneys or ovaries
- Adenomas in the adrenal glands
- Benign tumors in the thyroid gland
The Role of CT Scans in Cancer Diagnosis
Cancer diagnosis has been significantly enhanced by the use of CT scans, which provide detailed insights into tumor presence, size, and location. This diagnostic tool is crucial for identifying cancer at an early stage, thereby improving treatment outcomes.
Initial Screening and Detection
Initial screening and detection are critical in the fight against cancer. CT scans are often used as a first-line imaging test to detect tumors, especially in individuals with a high risk of cancer or those exhibiting symptoms. The detailed images produced by CT scans enable healthcare providers to identify abnormalities that may indicate cancer.
The process involves the patient being positioned on a table that slides into a CT scanner, which rotates around the body, capturing images from multiple angles. These images are then reconstructed into detailed cross-sectional pictures of the body’s internal structures.
Staging of Cancer
Once cancer is detected, cancer staging becomes essential for determining the extent of the disease. CT scans play a vital role in this process by providing information on the size of the tumor, its location, and whether it has spread to nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the body. Accurate staging is critical for developing an effective treatment plan.
- Determining tumor size and location
- Identifying lymph node involvement
- Detecting metastasis to other organs
Monitoring Treatment Response
Monitoring treatment response is another crucial aspect of cancer management where CT scans prove invaluable. By conducting regular CT scans, healthcare providers can assess how well the cancer is responding to treatment, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy. This information helps in adjusting the treatment plan as needed.
In some cases, procedures like cath removal may be relevant, especially if a patient has undergone interventions that involve catheter placement. CT scans can help in assessing the success of such procedures and the overall health of the patient post-intervention.
By leveraging the diagnostic capabilities of CT scans, healthcare providers can offer more personalized and effective care to cancer patients, from initial diagnosis through treatment and follow-up.
Limitations of CT Scans in Tumor Detection
Despite their widespread use, CT scans have several limitations in tumor detection that need to be understood. While they are a valuable diagnostic tool, their effectiveness can be influenced by various factors.
False Positives and Negatives
One of the significant limitations of CT scans is the occurrence of false positives and false negatives. A false positive result can lead to unnecessary anxiety and additional testing, as it indicates the presence of a tumor when there is none. On the other hand, a false negative result can be particularly dangerous, as it may miss a tumor that is actually present, potentially delaying diagnosis and treatment.
Studies have shown that the rate of false positives and negatives can vary depending on the type of tumor, the quality of the CT scan equipment, and the expertise of the radiologist interpreting the images. For instance, a study found that false negatives can occur in up to 10% of cases for certain types of tumors.
Sensitivity to Tumor Types
CT scans are not equally effective in detecting all types of tumors. Their sensitivity can vary significantly depending on the tumor’s location, size, and characteristics. For example, CT scans are generally more effective in detecting larger tumors and those located in areas with less movement, such as the liver or kidneys.
- Tumors in the bladder can be challenging to detect due to the bladder’s variable filling state and the potential for bladder cancer symptoms to be similar to those of other conditions.
- Small tumors or those in complex anatomical locations, such as the pancreas, may also be difficult to identify accurately.
Factors Affecting Accuracy
Several factors can affect the accuracy of CT scans in tumor detection. These include:
- The quality of the CT scan machine and the technology used.
- The expertise and experience of the radiologist interpreting the scan.
- Patient factors, such as body size and the presence of other medical conditions.
Understanding these limitations is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients. It highlights the importance of using CT scans as part of a comprehensive diagnostic approach, potentially including additional imaging techniques or biopsies, to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning.
Importance of Follow-Up Tests
CT scans are just the first step in the diagnostic process; follow-up tests are essential for accuracy and effective treatment planning. After a CT scan, healthcare providers often recommend additional tests to gather more detailed information about the detected tumor.
Additional Imaging Techniques
In many cases, additional imaging techniques are used to supplement the information obtained from a CT scan. These may include MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), PET (Positron Emission Tomography) scans, or ultrasound. Each of these imaging modalities provides unique information that can help in diagnosing and staging tumors.
For instance, MRI is particularly useful for examining soft tissue tumors, while PET scans can help determine the metabolic activity of a tumor, indicating whether it is benign or malignant.
- MRI: Useful for soft tissue examination
- PET scans: Help determine tumor metabolic activity
- Ultrasound: Provides real-time images and is useful for guided biopsies
Role of Biopsies in Diagnosis
A biopsy involves taking a sample of tissue from the suspected tumor for microscopic examination. This procedure is crucial for determining whether a tumor is benign or malignant and for identifying the specific type of cancer.
Biopsies can be performed using various techniques, including needle biopsies guided by imaging technologies like ultrasound or CT scans. The tissue sample is then examined by a pathologist to provide a definitive diagnosis.
|
Biopsy Type |
Description |
Guidance |
|---|---|---|
|
Needle Biopsy |
Minimally invasive, involves removing tissue or cells |
Ultrasound or CT scan |
|
Surgical Biopsy |
More invasive, involves removing a larger tissue sample |
Surgical procedure |
When is Cystoscopy Recommended?
Cystoscopy is a procedure that allows direct visualization of the inside of the urinary bladder and urethra. It is particularly useful for diagnosing conditions affecting the urinary tract, such as bladder cancer.
During a cystoscopy, a flexible or rigid scope is inserted through the urethra into the bladder. This procedure can help identify tumors, stones, or other abnormalities within the urinary tract.
Understanding the anatomy of the urinary bladder and prostate is essential for interpreting the results of a cystoscopy. The urinary bladder is a hollow organ that stores urine, and the prostate gland surrounds the urethra in males.
The detailed examination provided by cystoscopy can significantly aid in the diagnosis and treatment planning for urinary tract conditions.
How to Prepare for a CT Scan
Understanding what to expect before, during, and after a CT scan can significantly reduce anxiety. A CT scan is a sophisticated imaging test that helps diagnose various medical conditions. Being prepared is key to a smooth and successful procedure.
Pre-Scan Instructions
To prepare for a CT scan, follow these steps:
- Clothing: Wear loose, comfortable clothing. You may be asked to change into a gown.
- Metal Objects: Remove any metal objects such as jewelry, glasses, or hairpins.
- Contrast Material: If your scan requires contrast material, you may be asked to drink a liquid or have an IV line placed.
- Medications: Inform your doctor about any medications you’re taking, especially if you have diabetes or kidney disease.
- Allergies: Disclose any allergies, particularly to iodine or contrast materials.
For patients requiring a urinary catheter kit, it’s essential to follow the specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider regarding its use before the scan.
What to Expect During the Procedure
During the CT scan, you’ll lie on a table that slides into a large, doughnut-shaped machine. The procedure is typically painless and takes about 10 to 30 minutes. Here are some key aspects to expect:
- The table will move slowly through the scanner.
- You may hear clicking or whirring sounds.
- If contrast material is used, you might feel a slight pinch from the IV needle.
- You may be asked to hold your breath at times to ensure clear images.
Post-Scan Care
After the scan, you can usually resume your normal activities unless your doctor advises otherwise. If you received contrast material, you might be monitored for a short period for any adverse reactions. Here are some general guidelines:
|
Post-Scan Instructions |
Details |
|---|---|
|
Hydration |
Drink plenty of water to help flush out the contrast material. |
|
Monitoring |
Watch for any unusual symptoms such as rash, itching, or difficulty breathing. |
|
Results |
Your doctor will discuss the results with you, usually within a few days. |
By understanding the process and following these guidelines, you can make your CT scan experience as smooth as possible.
Discussing Results with Your Doctor
The moment you’ve been waiting for – receiving your CT scan results – can be both relieving and confusing. It’s a critical juncture where understanding the information presented is key to moving forward with your care.
Understanding Your CT Scan Report
Your CT scan report is a detailed document that outlines the findings of your scan. It’s essential to comprehend what this report means for your health. The report will typically describe the presence, size, and location of any abnormalities, including tumors. Pay close attention to the language used; your healthcare provider can help clarify any medical jargon.
When reviewing your report, look for sections that summarize the findings and recommendations for next steps. If there’s anything you don’t understand, don’t hesitate to ask your doctor to explain it in simpler terms.
Questions to Ask Your Healthcare Provider
Being proactive about your health means asking the right questions. When discussing your CT scan results, consider asking:
- What do the results indicate about my condition?
- Are there any additional tests or scans needed?
- What are the potential treatment options?
- How will we monitor the progress of my treatment?
Having a list of questions ready can help ensure that you cover all your concerns during your consultation.
Importance of Clear Communication
Clear communication with your healthcare provider is vital. It’s not just about understanding your diagnosis but also about feeling comfortable with the information shared. Don’t hesitate to seek a second opinion if you’re unsure about your diagnosis or treatment plan.
As seen in various health journeys, including that of public figures like Deion Sanders, clear and timely communication can significantly impact one’s ability to cope with and manage their health condition.
By being informed and engaged, you can work collaboratively with your healthcare team to make the best decisions for your health.
Patient Experiences and Perspectives
Tumor detection is not just a medical process; it’s a personal journey that affects patients and their loved ones deeply. The experience can be daunting, but hearing the stories of those who have walked this path can provide comfort and insight.
Real-Life Stories of Tumor Detection
Many patients have shared their stories of tumor detection, highlighting the challenges they faced and the resilience they discovered within themselves. For instance, a patient diagnosed with bladder cancer might undergo a series of treatments, including bladder cancer therapy, and emerge stronger on the other side.
“I was shocked by my diagnosis, but the support of my family and the guidance of my healthcare team made all the difference. Through bladder cancer therapy, I was able to navigate the treatment process with more confidence.”
These stories are not just about the medical journey; they’re also about the emotional impact of diagnosis and the various coping strategies that patients employ.
Emotional Impact of Diagnosis
The moment of diagnosis can be incredibly challenging. Patients often report feeling overwhelmed, anxious, and uncertain about the future. The emotional impact of a tumor diagnosis can be just as significant as the physical aspects.
- Fear of the unknown
- Anxiety about treatment outcomes
- Concerns about the impact on family and friends
Understanding these emotional responses is crucial for providing comprehensive care. Healthcare providers are increasingly recognizing the importance of addressing the emotional and psychological needs of their patients.
Coping Strategies
Patients and their families have developed various coping strategies to deal with the challenges of tumor detection and treatment. These can include:
- Seeking support from family, friends, and support groups
- Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as meditation or yoga
- Staying informed about their condition and treatment options
By sharing these stories and strategies, we hope to provide a sense of community and support for those currently navigating their own tumor detection journey.
Conclusion: The Value of CT Scans in Healthcare
CT scans play a vital role in modern healthcare, offering a powerful diagnostic tool for detecting tumors and other conditions. The diagnostic capabilities of CT scans have revolutionized the way healthcare providers diagnose and treat patients.
Diagnostic Capabilities and Patient Care
The value of CT scans lies in their ability to provide detailed images of internal structures, enabling healthcare providers to identify tumors and other abnormalities with high accuracy. This information is crucial for developing effective treatment plans.
Encouraging Open Dialogue
Maintaining an open dialogue with healthcare providers is essential for patients undergoing CT scans. By understanding the results and implications of their scans, patients can make informed decisions about their care. The CU Cancer Center is a prime example of a facility that prioritizes patient education and care.
Advancements in Imaging
The future of imaging in tumor detection is promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and technique. As imaging capabilities continue to evolve, we can expect even more accurate and effective diagnosis and treatment of tumors.
FAQ
What is a CT scan, and how does it detect tumors?
A CT (Computed Tomography) scan is a medical imaging test used to produce detailed cross-sectional images of the body. It detects tumors by using X-rays and computer technology to create images of the inside of the body, helping doctors identify abnormalities.
Can a CT scan detect all types of tumors?
While CT scans are highly effective in detecting many types of tumors, their ability to detect certain tumor types can be limited. Factors such as tumor size, location, and type can affect detection.
What is the difference between benign and malignant tumors?
Benign tumors are non-cancerous and typically do not spread to other parts of the body, whereas malignant tumors are cancerous and can invade surrounding tissues and metastasize to other areas.
How does a CT scan help in cancer diagnosis and treatment?
CT scans play a crucial role in cancer diagnosis by detecting tumors, staging cancer, and monitoring treatment response. They help doctors assess the effectiveness of treatments and make informed decisions about patient care.
What are the limitations of CT scans in tumor detection?
CT scans can have limitations, including false positives and negatives, and varying sensitivity to different tumor types. Factors like image quality and interpreter expertise can also impact accuracy.
What follow-up tests are typically recommended after a CT scan?
Depending on the CT scan results, additional imaging techniques, biopsies, or procedures like cystoscopy may be recommended to further diagnose or monitor conditions.
How can I prepare for a CT scan?
Preparation for a CT scan may include following specific dietary instructions, removing jewelry or metal objects, and potentially using a contrast agent. Your healthcare provider will provide detailed pre-scan instructions.
How do I understand my CT scan report?
Understanding your CT scan report involves reviewing the findings with your healthcare provider, who can explain the results in the context of your overall health and any necessary next steps.
What is the role of biopsies in diagnosing tumors detected by CT scans?
Biopsies involve taking a sample of tissue from a suspected tumor for pathological examination. They are crucial in confirming whether a detected tumor is benign or malignant.
How does the anatomy of the urinary bladder and prostate relate to CT scans?
Understanding the anatomy of the urinary bladder and prostate is essential for interpreting CT scans that involve these areas. Accurate imaging helps in diagnosing and treating conditions affecting these organs.
What is the importance of clear communication with healthcare providers about CT scan results?
Clear communication with your healthcare provider ensures that you understand your CT scan results, the implications for your health, and the appropriate steps to take next.
Are CT scans used for monitoring treatment response in cancer patients?
Yes, CT scans are commonly used to monitor how well cancer treatments are working by assessing changes in tumor size and spread over time.
Can CT scans detect non-cancerous growths?
Yes, CT scans can detect non-cancerous growths, such as benign tumors or cysts, in addition to malignant tumors.
What is the significance of Deion Sanders’ bladder cancer diagnosis in the context of CT scans?
Deion Sanders’ public disclosure of his bladder cancer diagnosis highlights the importance of medical imaging, including CT scans, in detecting and managing cancer.
How do CT scans contribute to the early detection of bladder cancer?
CT scans can contribute to the early detection of bladder cancer by providing detailed images that help identify tumors and other abnormalities in the bladder.
Reference
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28677000/




































