Gout is a metabolic disorder that affects millions of adults in the USA. It causes sudden and severe attacks of pain, swelling, and tenderness. We will explore the connection between low-dose aspirin use and the risk of recurrent gout attacks.
Research has shown that low-dose aspirin can increase the risk of recurrent gout attacks by nearly 80 percent. This is because aspirin influences uric acid levels. It can trigger or worsen gout symptoms. Understanding this relationship is key for treating patients with both cardiovascular health and gout issues.
Key Takeaways
- Low-dose aspirin can increase the risk of recurrent gout attacks.
- Gout is a metabolic disorder characterized by acute and chronic inflammatory responses.
- Aspirin affects uric acid metabolism, potentially exacerbating gout symptoms.
- Understanding the connection between aspirin use and gout is essential for optimizing treatment.
- Patients managing both cardiovascular health and gout require informed medical guidance.
Understanding Gout and Its Rising Prevalence
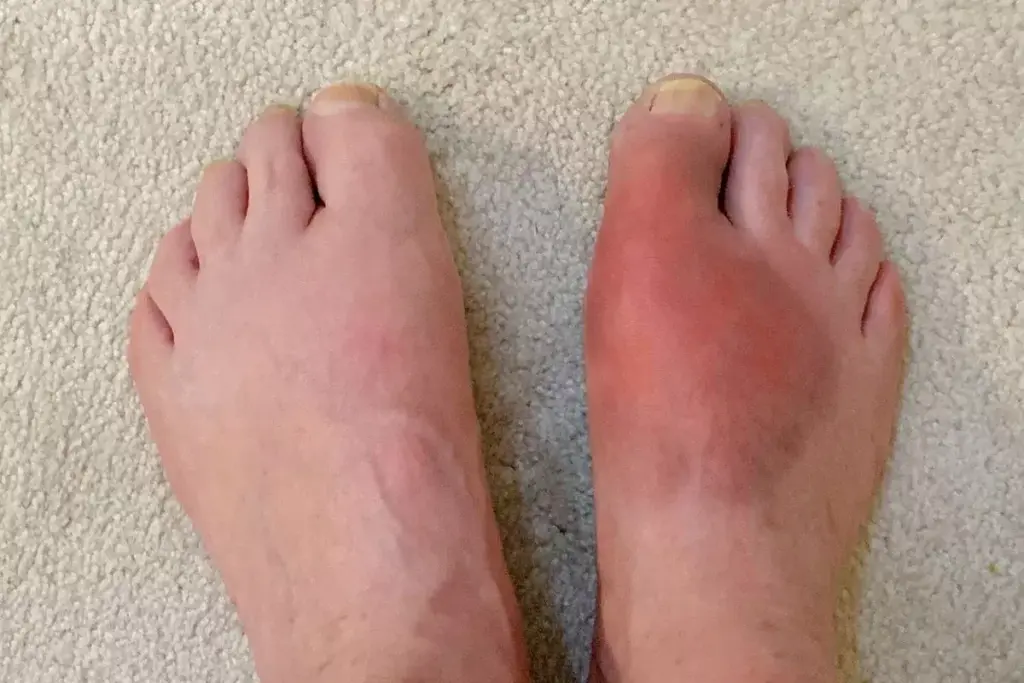
Gout, a complex form of arthritis, is becoming more common in the United States. It affects millions of adults. This condition causes sudden, severe pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in one or more joints, often in the big toe. Knowing about gout is key to managing its symptoms and preventing future attacks.
What is Gout and What Causes It?
Gout happens when there’s too much uric acid in the blood. This can lead to sharp, needle-like crystals forming in a joint or tissue. This causes pain, inflammation, and swelling. Elevated uric acid levels can come from making more uric acid, not getting rid of it, or a mix of both.
Genetics, diet, obesity, certain medicines, and health issues like kidney disease can raise uric acid levels. Diet plays a big role, as foods high in purines (like red meat, seafood, and alcohol) increase uric acid. On the other hand, eating more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can lower the risk of gout.
Gout Statistics in the United States
In the United States, about 8.3 million adults have gout. The number of people with gout has been going up over the years. Some groups are more affected than others.
Men are more likely to get gout than women, but this changes with age. Women’s uric acid levels go up after menopause. Knowing these stats and why gout happens is important for managing and preventing it. Healthcare providers can help patients control their symptoms and improve their lives by tackling the root causes of gout.
The Connection Between Aspirin and Gout
It’s important to know how aspirin affects uric acid levels for those with gout. Aspirin is used for heart health but has a tricky relationship with gout.
How Aspirin Affects Uric Acid Metabolism
Aspirin’s impact on uric acid levels depends on the dose. At low doses, it can block the excretion of uric acid. This can lead to high uric acid levels in the blood, a problem for gout patients.
Studies show that taking low-dose aspirin can increase the risk of gout attacks. This is because it changes how the kidneys handle uric acid, making it harder to get rid of.
The Kidney’s Role in Aspirin-Related Hyperuricemia
The kidneys are key in managing uric acid, and aspirin’s effect on this can raise gout risk. Low doses of aspirin can reduce the kidneys’ ability to remove uric acid, causing blood levels to rise. But, higher doses can help get rid of uric acid, lowering blood levels.
It’s vital to understand how aspirin affects uric acid levels for gout patients. By adjusting aspirin doses and watching uric acid levels, doctors can help prevent gout attacks.
Aspirin Dosage and Its Impact on Gout Risk
It’s important to know how aspirin dosages affect gout risk. The impact of aspirin on gout is not simple. It changes a lot with the dosage.
Low-Dose Aspirin (325 mg or less)
Low-dose aspirin is often used for heart health. But, it can harm those with gout. Research shows that low-dose aspirin can raise the risk of gout attacks.
It does this by making it harder for the kidneys to get rid of uric acid. This leads to higher levels of uric acid in the blood. This is bad news for gout sufferers.
Baby Aspirin (81 mg) and Gout Attacks
Baby aspirin, at 81 mg, is good for the heart. But, even this small dose can mess with uric acid levels. This can cause gout attacks in some people.
Those taking baby aspirin should watch their gout closely. It’s important to be aware of this risk.
Higher Doses of Aspirin (3+ grams): Different Effects
But, higher doses of aspirin (over 3 grams) have a uricosuric effect. This means they help get rid of uric acid. It might lower the risk of gout attacks.
Yet, taking such high doses is risky. They can cause side effects. Doctors usually don’t recommend them without careful thought.
When it comes to aspirin and gout, we need to think carefully. Knowing how different doses affect gout risk helps make better choices about using aspirin.
Conclusion: Balancing Cardiovascular Benefits and Gout Risk
We’ve looked into how aspirin affects gout and heart health. Aspirin can change how uric acid works in the body, which might make gout worse. But, for those at risk of heart disease, the benefits of aspirin must be considered against the risks.
People with gout or at risk need to think carefully about taking aspirin. Other treatments might be better to avoid gout while keeping the heart safe. We should keep an eye on uric acid levels and change treatments as needed to stop gout attacks.
It’s important to know how aspirin impacts gout. By understanding what affects uric acid, we can decide on aspirin use wisely. This way, we can enjoy the heart benefits of aspirin without harming our gout.
FAQ
Does aspirin cause gout or trigger gout attacks?
How does aspirin affect uric acid metabolism?
What is the impact of low-dose aspirin on gout risk?
Is baby aspirin (81 mg) bad for gout?
Can higher doses of aspirin have a different effect on gout?
What exacerbates gout?
How can gout risk be mitigated in patients taking aspirin?
Is aspirin good or bad for gout?
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3902644/