Last Updated on November 4, 2025 by mcelik
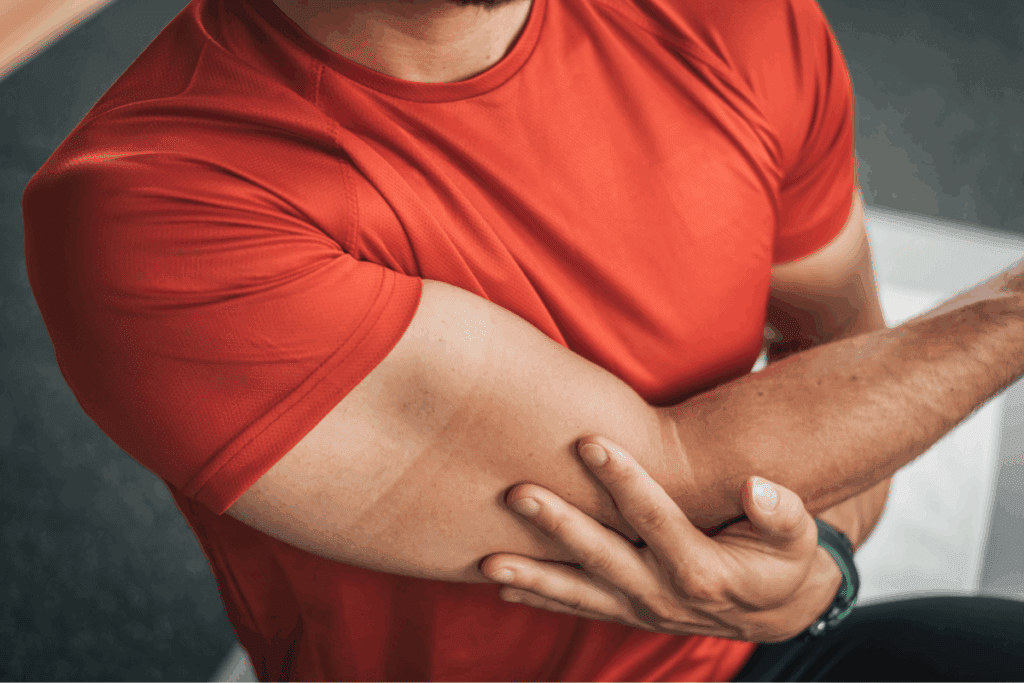

The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon. This clinical test detects large tears weakness in the shoulder, helping doctors determine the severity of rotator cuff injuries.
We’ll dive into the drop arm test, covering what it is, its history, and its use in finding muscle weakness. Knowing about this test helps doctors and patients deal with shoulder injuries better and choose the right treatment approach.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
Over the years, the test has changed to be more accurate and useful. We’ve made improvements in how it’s done and understood. This makes it a trusted way to detect muscle tears and identify large muscle tears.

Knowing the shoulder’s anatomy is key for doctors to treat shoulder problems well. The shoulder joint is very complex and mobile. It has many bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments that help it move a lot.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
The rotator cuff is made of several muscles and tendons. It has four muscles: the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis. These muscles and tendons help keep the shoulder stable and allow for different movements.
The rotator cuff muscles do several things:
Rotator cuff injuries are common, mainly in athletes and those who do hard activities. The usual injuries are:
These injuries can happen from sudden trauma, repeated strain, or wear and tear over time. Identifying muscle weakness signs and finding big muscle tears are key for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding these common injuries and how they affect the shoulder is important for doctors. It helps them give accurate diagnoses and plan effective treatments.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
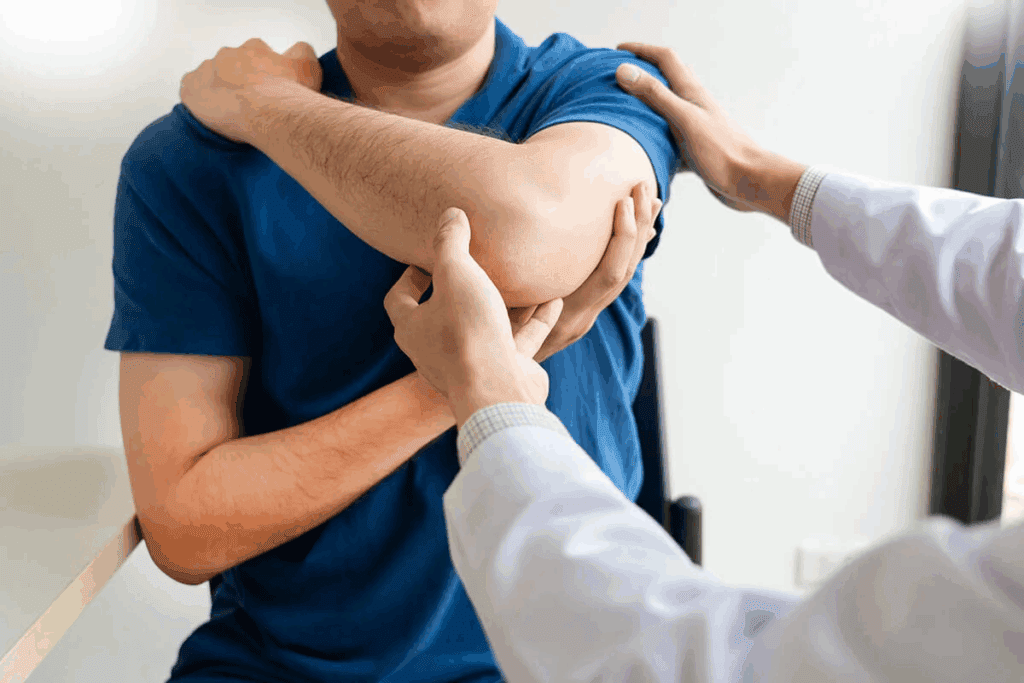
The test checks if a patient can hold their arm in a certain way. They hold their arm at 90 degrees of abduction, with the thumb down. Then, we see if they can keep it there or if it drops.
If the patient feels pain or weakness and the arm drops, the test is positive. This means there’s a big injury, like a large rotator cuff tear. The test shows that the rotator cuff can’t hold the arm up against gravity anymore.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
The table below shows what the drop arm test means for rotator cuff injuries.
| Test Outcome | Indication | Possible Injury |
| Arm drops suddenly | Positive test | Large rotator cuff tear |
| Arm held steady | Negative test | No significant tear |
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
It’s also good to tell the patient to relax their shoulder muscles. This makes the test more accurate and less likely to miss something because of muscle tightness.
The way the examiner does the test is very important. They should stand next to the patient and gently hold their arm. Smooth, controlled movements help to see how well the patient’s shoulder is working.
| Examiner Action | Patient Response |
| Raise the patient’s arm to 90 degrees abduction | Hold the arm in this position |
| Slowly lower the patient’s arm to their side | Control the descent or drop the arm |
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
It’s also important to check the patient’s health before starting the test. Look at their medical history and current symptoms to make sure it’s safe and right for them.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
Understanding the test results is key. A positive test means there’s a big injury or tear. This is often seen in large tears weakness detection.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
The signs of a big tear or injury include:
Seeing these signs means the patient might need more tests and possibly treatment.
A negative test means the patient can lower their arm without pain or weakness. This suggests there might not be a big tear or rotator cuff injury.
But, a negative result doesn’t mean there’s no shoulder problem. Some injuries might not show up on this test. More tests and exams are needed for a full check-up.
The table below shows the main differences between positive and negative test results:
| Test Result | Indicators | Possible Diagnosis |
| Positive | Severe pain, inability to lower arm, visible weakness | Significant rotator cuff tear or large tears weakness |
| Negative | No significant pain, ability to lower arm smoothly | No large tear or significant rotator cuff injury |
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
The drop arm test’s sensitivity and specificity are important. Sensitivity means it correctly spots patients with rotator cuff tears. Specificity means it correctly spots those without the condition. Research shows the test’s sensitivity and specificity vary, making results interpretation critical.
For example, a study might say the test is 80% sensitive and 90% specific for rotator cuff tears. This means it correctly spots 80 out of 100 patients with tears. It also correctly spots 90 out of 100 patients without tears.
Several things can change how accurate the drop arm test is. Patient positioning is very important. If it’s not done right, the test might not work as it should. The examiner’s technique also matters, as different ways of doing the test can affect results.
Patient factors like pain, muscle guarding, and other shoulder problems can also affect the test. To get better results, healthcare providers need to know these factors. They should get proper training, position patients correctly, and consider the patient’s overall health.
Understanding what affects the drop arm test’s accuracy helps us use it better in clinics. This leads to better care for patients.
The drop arm test is very useful in both primary care and orthopedic evaluation. It helps find shoulder problems, like big rotator cuff tears and muscle weakness.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
It’s important for patients to know the test isn’t hard, but might hurt a bit if there’s an injury. We’re there to watch over them and make sure they’re okay.
To ease discomfort, we make sure patients are comfortable and in the right position. We teach them to tell us if they feel pain. This way, we can change how we do the test if needed.
At times, we might use gentle moves or support to help them. Our aim is to keep them comfortable while getting the right results.
By teaching patients about the test and easing their discomfort, we make the experience better. This helps us get more accurate results with our advanced technology.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
The Drop Arm Test isn’t perfect. It can give wrong results sometimes. This can happen because of how the test is done, the patient’s cooperation, or other shoulder problems.
Factors that may lead to false results include:
| Factor | Potential Impact |
| Inadequate examiner technique | May lead to false-negative results |
| Patient guarding or pain | Can result in false-positive findings |
| Presence of other shoulder conditions | May complicate test interpretation |
When doing a physical therapy check-up, think about these points. You might want to use other tests too to really understand the tear severity.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
There are other ways to check the shoulder’s health. These include:
Using these tests together helps understand the shoulder better. It makes finding muscle tears easier.
Imaging tests are important for confirming what physical exams find. Common ones are:
By combining these tests with the Drop Arm Test, doctors can make better diagnoses. This leads to more effective treatments for muscle tears.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
We’ll look at two main conditions it can diagnose: rotator cuff tears and other shoulder issues. Knowing about these conditions helps doctors plan better treatments.
Rotator cuff tears are common shoulder injuries found with the drop arm test. These happen when the tendons that connect muscles to bones get damaged.
Key aspects of rotator cuff tears include:
The test checks if the rotator cuff muscles and tendons are okay. A positive test means there’s a big tear. This helps doctors decide what to do next.
The drop arm test also helps find other shoulder problems. These include:
| Condition | Description | Symptoms |
| Impingement Syndrome | Compression of the rotator cuff tendons | Pain during arm movement, mostly overhead |
| Tendinitis | Inflammation of the tendons | Pain, swelling, and less mobility |
| Adhesive Capsulitis (Frozen Shoulder) | Stiffness and inflammation of the shoulder joint | Severe stiffness, pain, and limited movement |
Even though it’s mainly for rotator cuff tears, the drop arm test gives insights into shoulder function. It can also show signs of other problems.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
After a diagnosis from the Drop Arm Test, doctors and patients can talk about treatment. They will choose between non-surgical and surgical options. This depends on how bad the condition is, the patient’s health, and what they prefer.
Many people with shoulder problems like rotator cuff tears start with non-surgical treatment. This usually includes rest, physical therapy, and medicine to control pain and swelling.
If non-surgical methods don’t work or the problem is severe, surgery might be needed. The type of surgery depends on the diagnosis and what the patient needs.
| Surgical Option | Description | Typical Recovery Time |
| Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair | Minimally invasive surgery to fix torn tendons. | 4-6 months |
| Open Rotator Cuff Repair | Traditional open surgery for more complex tears. | 6-9 months |
It’s key for patients to talk about the pros and cons of each option with their doctor. This helps them make a well-informed choice.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
Good rehab not only eases pain but also brings back shoulder strength and function. This lets patients get back to their daily life and sports. Our rehab plans are made just for each patient. We consider the injury’s severity and the patient’s health goals.
Physical therapy is a key part of fixing shoulder injuries. Our therapy plans help with healing, improve movement, and build muscle around the shoulder.
A physical therapy evaluation is done at the start. It checks the patient’s condition, including tear severity assessment, and makes a treatment plan just for them.
The time it takes to recover can change a lot. It depends on the injury’s severity and how well the treatment works. Generally, patients see these milestones:
Regular checks are done to see how the patient is doing. The rehab plan might be changed if needed. We stress the importance of following the therapy plan to get the best results.
With a thorough rehab program, patients see big improvements in shoulder function and life quality.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon.
The drop arm test helps find big tears and weakness in the shoulder. It’s mainly for the rotator cuff.
First, the patient holds their arm in a certain way. Then, they slowly lower it. This checks if they can control the movement.
If the test is positive, it means there’s a big injury or tear in the shoulder. This is often in the rotator cuff.
The test might not always be right. It can give false results. So, it’s best used with other tests for a sure diagnosis.
The test’s accuracy depends on how it’s done and the patient’s position. Its results can vary.
Yes, it’s good for primary care. It’s simple and works well to check for shoulder injuries.
Treatment can be physical therapy or surgery. It depends on how bad the injury is.
Patients can tell the examiner if it hurts. They can also adjust their position to feel less pain.
Physical therapy is key after a diagnosis. It helps patients get their shoulder strong and mobile again.
Yes, some medical conditions or injuries make the test not work well. It might hurt or not be accurate.
The drop arm test is designed to identify significant rotator cuff tears, particularly those affecting the supraspinatus tendon
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!