Many people worry when their ear hurts while coughing. But, it usually means you have a common cold or upper respiratory infection. At Liv Hospital, we know ear pain during coughing is a common problem.
Congestion and Eustachian tube dysfunction are big reasons for this pain. The common cold can also cause ear pain because of congestion or infection complications. Knowing why your ear hurts when you cough helps you know when to see a doctor.
Why your ear hurts coughing: Learn about referred pain via the vagus nerve and the role of Eustachian tube pressure changes.
Ear pain and coughing are linked by our body’s anatomy. When we cough, it affects our ears because of shared pathways. This connection is not just a coincidence.
Ear pain is common during colds and flu. The Eustachian tube helps balance ear pressure. But, when it’s blocked by congestion, problems arise.
Studies show that in many colds, the middle ear pressure drops. This is because the Eustachian tube gets blocked. The body’s fight against infection causes more mucus and swelling.
Coughing changes pressure in the chest, affecting the Eustachian tube. This can lead to ear pain if the tube is blocked or not working right.
Knowing how ear pain and coughing are connected helps us manage symptoms. By understanding the Eustachian tube’s role and the effects of infections, we can reduce discomfort.
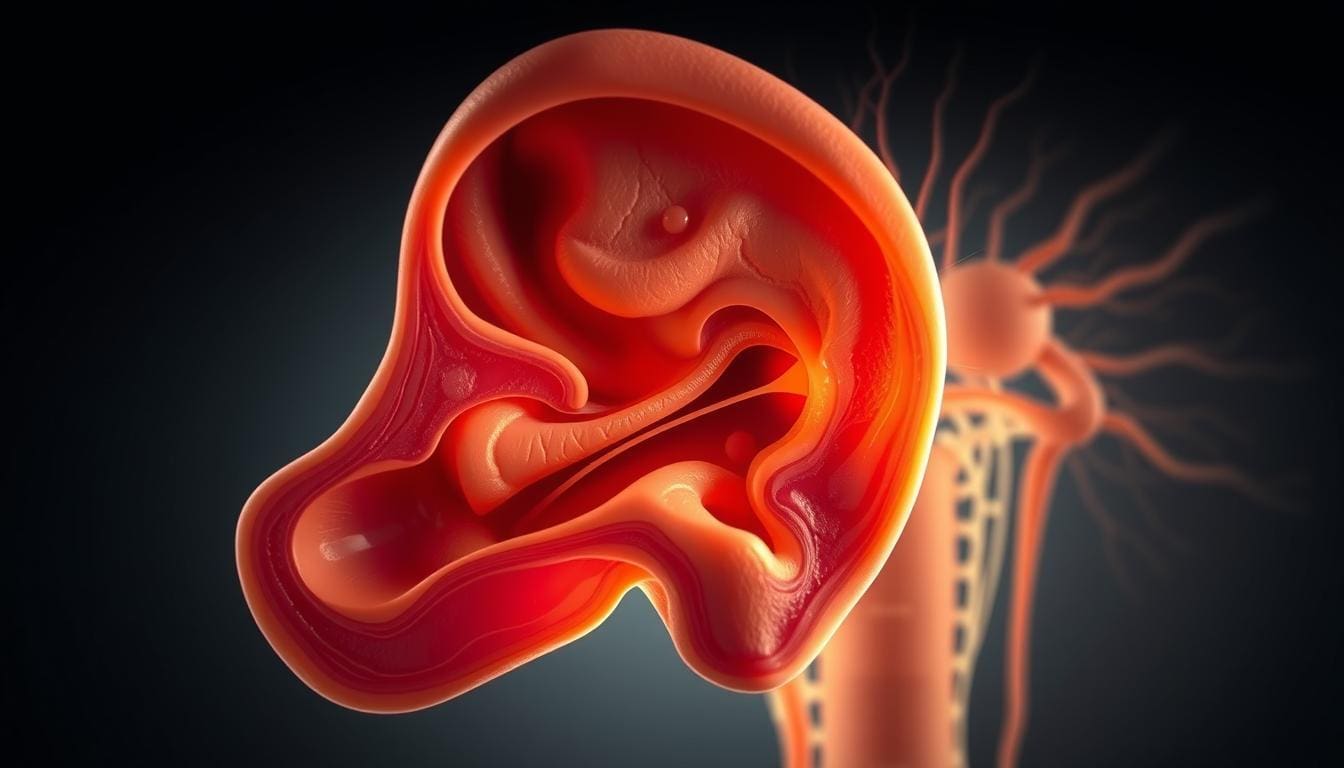
To understand why ear pain happens when we cough, we need to know about the ear’s structure and how it works. The ear is a complex system that helps us hear and stay balanced.
The ear has three main parts: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. The outer ear catches sound waves and sends them into the ear canal. The middle ear has air and the eardrum, which sends sound to the inner ear. The inner ear turns these vibrations into signals for our brain.
The Eustachian tube links the middle ear to the back of the throat. It’s key for keeping air pressure equal. When we swallow or yawn, it opens to let air in or out, keeping pressure balanced.
Pressure equalization is how the Eustachian tube keeps middle ear air pressure steady. It opens and closes to let air flow, keeping pressure balanced. This balance is vital for hearing and avoiding ear pain, like during coughing.
Knowing how the ear works, and the Eustachian tube’s role, helps us understand ear pain from coughing. It shows how important it is to keep our ears healthy.
Coughing can make your ear hurt because of the sudden pressure change. This isn’t just a random thing. It’s because of how our ears and breathing system work together. Knowing why this happens can help you feel better and know what to do.
Coughing makes your chest pressure go up, which can hurt your ear. The Eustachian tube helps keep ear pressure even. But when you cough, it can get strained and cause earache.
“The pressure changes during coughing can be significant enough to cause discomfort in the ear,” as noted by medical professionals. This is true, mainly for people with cough earache from colds.
The Eustachian tube links your middle ear to your nose and throat. When you have a cold, mucus can block it. This blockage stops the tube from working right, causing ear pain when i cough.
Fluid in the middle ear also causes ear pain when coughing. If the Eustachian tube is blocked, fluid can build up. This can make your ear feel full or painful, often linked to earache and runny nose.
“The relationship between coughing and ear pain is closely linked to the Eustachian tube’s function and the presence of fluid in the middle ear.”
In summary, ear pain from coughing comes from pressure changes, Eustachian tube blockage, and fluid buildup. Knowing this can help you manage and reduce the discomfort of cough earache.
Ear pain from coughing often means there’s an issue that needs fixing. We’ll look at common causes and what they mean for you.
Colds are a big reason for ear pain when you cough. They bring symptoms like sneezing, coughing, and sore throats. Viruses can block the Eustachian tube, causing ear pain.
Ear pain from colds comes from nasal and Eustachian tube inflammation. A blocked Eustachian tube makes ears feel full or pressurized, worse when you cough.
Sinusitis, or inflamed sinuses, can also cause ear pain. The sinuses and ears are linked by the Eustachian tube. Sinus pressure can make ear pressure worse, making coughing hurt more.
Sinusitis and ear pain are closely linked. Treating sinusitis can help with ear pain. Sinusitis can block the Eustachian tube, affecting ear pressure.
Otitis media happens when germs from the nose and throat get into the ear. It causes ear pain, fever, and hearing loss. Coughing can make this pain worse.
Knowing why ear pain happens when coughing is key. If it’s from otitis media, you might need to see a doctor to avoid serious problems.
It can be hard to tell if your ear pain is from an ear infection or a cold. But, there are clear signs to look for. Both can cause ear pain and coughing, but they have different causes and symptoms.
Ear infections, or otitis media, cause inflammation and fluid in the middle ear. You might notice:
Ear infections are more common in children. They get six to ten colds a year, increasing their risk of ear infections.
Colds are viral infections that affect the upper respiratory tract. They don’t directly cause ear infections but can lead to ear pain. Common cold symptoms include:
Adults get two to four colds a year. Their symptoms are usually milder, but ear pain can occur, mainly if they have ear or respiratory issues.
It’s important to watch how long and how bad your symptoms are. If ear pain lasts or comes with fever, hearing loss, or discharge, see a doctor.
Knowing the signs of ear infections and colds helps you figure out why your ears hurt. This way, you can manage your symptoms or get help when needed.
Coughing and sneezing can sometimes cause ear pain due to sudden pressure changes. These actions lead to unexpected pain in the ears. The science behind this is tied to how pressure changes affect our ears.
When we cough, air is pushed out of the lungs quickly. This creates a big pressure change in the body. The Eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the back of the nose and throat, is affected by this change.
The Eustachian tube helps balance the pressure in the ears with the outside environment. During a cough, the tube opens and closes fast. This can cause ear pain.
The sudden increase in pressure during a cough goes to the middle ear through the Eustachian tube. This quick change can be uncomfortable or painful. It’s worse if the Eustachian tube is blocked or not working right.
Sneezing also involves a sudden release of air, similar to coughing. The pressure changes during a sneeze can affect the Eustachian tube and middle ear, causing pain. The physics behind sneezing and ear pain is similar to coughing.
To show the similarities and differences between coughing and sneezing in relation to ear pain, consider the following table:
Action | Pressure Change | Effect on Eustachian Tube | Potential for Ear Pain |
Coughing | Sudden increase in thoracic pressure | Rapid opening and closing | High |
Sneezing | Forceful expulsion of air | Rapid opening and possible blockage | High |
Both coughing and sneezing can cause ear pain due to sudden pressure changes. Knowing how these mechanisms work can help find ways to ease ear pain during these actions.
Several factors can increase the chance of ear pain when coughing. These include age and any health conditions you might have. Knowing these can help you prevent ear pain and get the right treatment.
Children and adults have different ear structures. This affects how likely they are to get ear pain from coughing. Children are more likely to get ear infections because their Eustachian tubes are shorter and more horizontal. This makes it easier for bacteria to reach the middle ear.
Adults have longer, more vertical Eustachian tubes. This makes it harder for bacteria to get through. But, adults with ear or breathing problems can also get ear pain from coughing.
Having ear or breathing problems before can make ear pain from coughing more likely. Conditions like chronic ear infections, sinusitis, or allergies can cause Eustachian tube problems. This makes it harder for the ear to adjust pressure when you cough.
People with a history of ear infections or breathing issues like asthma or COPD need to be careful. These conditions can make coughing worse and increase ear pain risk.
Season and environment also affect ear pain from coughing. For example, during cold and flu season, more people get respiratory infections. This means more ear pain from coughing.
Things like allergens, smoking, or pollution can irritate your breathing. This can make coughing worse and put more pressure on the Eustachian tube. Knowing this can help you avoid these triggers.
Risk Factor | Description | Impact on Ear Pain |
Anatomical Differences | Children’s Eustachian tubes are shorter and more horizontal | Increased risk of ear infections and pain |
Pre-existing Conditions | Chronic otitis media, sinusitis, allergies | Eustachian tube dysfunction, increased ear pain |
Seasonal Factors | Cold and flu season, allergen exposure | Increased respiratory infections, ear pain |
Ear pain from coughing can be really uncomfortable. But, there are simple home remedies that can help. These methods aim to ease the pain and find the cause.
It’s important to balance ear pressure to stop ear pain from coughing. The Toynbee maneuver is one way to do this. It involves swallowing while pinching your nose.
Another method is the Valsalva maneuver. This is when you gently blow air through your nose while it’s closed. Trying these can help your ears feel better.
Yawning or chewing gum can also help. They open the Eustachian tube. This tube connects your middle ear to your nose and throat, balancing pressure.
OTC decongestants and antihistamines can help with ear pain from coughing. Decongestants reduce nasal stuffiness, which can cause ear pressure. Antihistamines are good if allergies are making your ears hurt.
Medication Type | Use | Examples |
Decongestants | Relieve nasal congestion | Pseudoephedrine, Phenylephrine |
Antihistamines | Counteract allergic reactions | Diphenhydramine, Loratadine |
Putting a warm compress on your ear can help. The warmth eases the pain. You can use a warm washcloth or a low setting heating pad.
Using essential oils like tea tree or eucalyptus oil can also help. They have anti-inflammatory properties. But, always mix these oils with a carrier oil and test them first to avoid any bad reactions.
By using these home remedies, you can manage ear pain from coughing. This will make you feel more comfortable.
Cough-related ear pain can be managed with various treatments. It’s important to find the cause to choose the right treatment.
Antibiotics are needed for bacterial infections like sinusitis or otitis media. They don’t work on viral infections, so they’re only used when it’s confirmed to be bacterial.
Here are some key points about when antibiotics are necessary:
Healthcare providers may prescribe medications for pain and inflammation. These can include:
These medications are chosen based on the specific diagnosis and the patient’s overall health.
Often, cough-related ear pain is a symptom of an underlying respiratory condition. Treating the underlying cause is key to alleviating ear pain. This may involve:
By addressing the root cause, we can alleviate ear pain and improve respiratory health.
It’s important to prevent ear pain when we have respiratory infections. Coughing and congestion can cause ear pain due to pressure changes. By taking steps to prevent ear pain, we can stay comfortable and healthy.
Keeping ear pressure stable is key to avoiding ear pain. Drinking lots of water helps thin out mucus and eases congestion. This keeps the Eustachian tube working right, balancing ear pressure.
Using nasal decongestants is another good move. They cut down nasal congestion, which helps the Eustachian tube and prevents ear pain. But, it’s important to follow the directions to avoid getting worse congestion.
Additional techniques include:
Lessening coughing is vital to prevent ear pain. Using cough suppressants or expectorants can help. Suppressants cut down on coughing, while expectorants make it easier to cough up mucus.
Good respiratory hygiene is also key. Avoiding irritants like smoke and strong smells helps. Also, staying in a clean, well-ventilated area is important.
Other strategies include:
By using these proactive methods, we can greatly reduce ear pain from respiratory infections. This improves our comfort and health.
It’s important to know when to see a doctor for ear pain and coughing. Many times, ear pain is just a minor issue. But sometimes, it can be a sign of something serious that needs quick medical help.
Some symptoms with ear pain and coughing mean you should see a doctor right away. These include:
When you see your doctor for ear pain and coughing, they will check you thoroughly. They might do:
Knowing why you have ear pain and coughing is key to getting the right treatment. By getting medical help when needed, you can make sure any problems are fixed right away.
Understanding ear pain and coughing is key to feeling better. We’ve seen how coughing can cause ear pain. This usually happens because of problems with the Eustachian tube or fluid in the middle ear.
Ear pain from coughing can come from many sources. These include colds, sinus infections, and middle ear infections. Luckily, most of these issues get better by themselves, like during a cold.
There are many ways to treat ear pain from coughing. You can try home remedies like warm compresses or decongestants. Or, you might need antibiotics for infections. Also, there are steps you can take to keep your ears healthy and reduce coughing.
In short, ear pain from coughing is not usually a big deal. With the right treatment, you can feel better. But, if your symptoms don’t go away or get worse, it’s best to see a doctor. They can check for any serious problems that need their help.
Ear pain when coughing often comes from the Eustachian tube. It can’t handle the pressure changes during coughs. This leads to discomfort.
Yes, coughing can lead to earache. It’s because of the pressure changes in the ear. This can cause Eustachian tube dysfunction or make existing ear conditions worse.
Sneezing, like coughing, can cause sudden pressure changes in the ear. This can lead to ear pain if the Eustachian tube is blocked or not working right.
To ease ear pain when coughing, try equalizing ear pressure. You can do the Toynbee maneuver, use over-the-counter decongestants, or apply warm compresses.
Ear pain when coughing might mean an ear infection. But, it’s not the only reason. Look for fever, discharge, or hearing loss to confirm an infection.
Ear infections have severe ear pain, fever, or hearing loss. A cold has a runny nose, sneezing, and congestion. Knowing these differences helps figure out the cause of ear pain.
Risk factors include anatomical differences, like in children. Also, pre-existing ear or respiratory conditions and seasonal factors that worsen respiratory infections.
See a doctor for severe ear pain, fever, discharge, hearing loss, or if symptoms get worse. These could be signs of a serious condition.
Yes, you can prevent it. Keep ear pressure balanced with yawning or chewing. Use medications to reduce coughing. Also, manage any respiratory conditions.
Yes, try over-the-counter decongestants, warm compresses, and methods to balance ear pressure. The Toynbee maneuver or yawning can help.
Medical treatments include antibiotics for infections, pain and inflammation meds, and treatments for underlying respiratory conditions. These help alleviate symptoms.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). Sore Throat. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/community/for-patients/sore-throat.html
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!
WhatsApp us