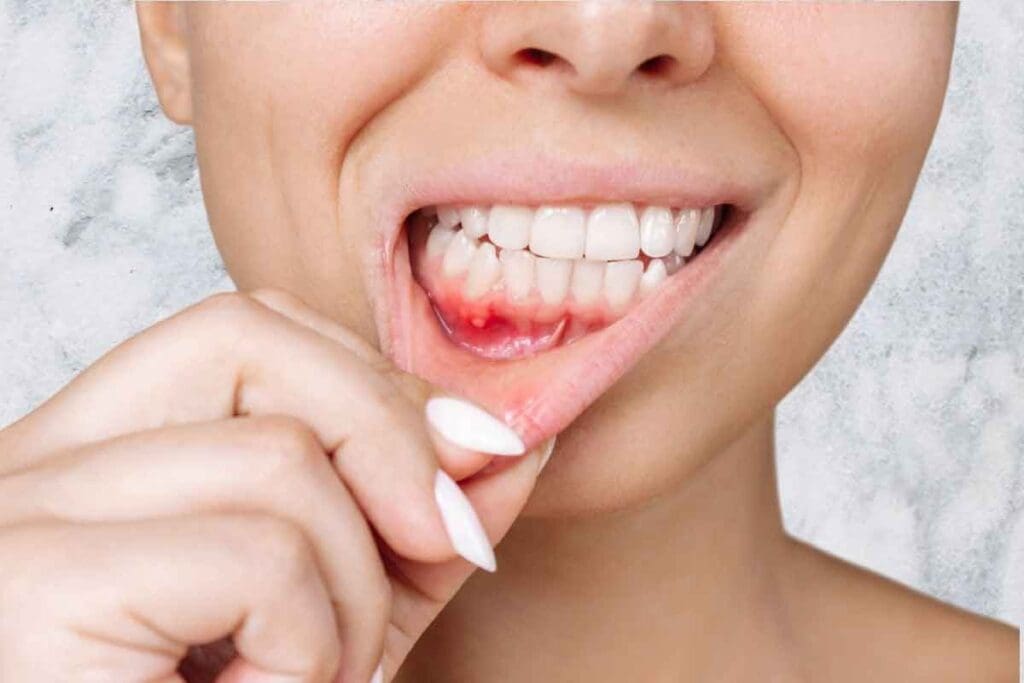
Bleeding gums might not just mean gum disease. Liv Hospital, a top healthcare provider, says it can also signal leukemia. This is a blood cancer that makes too many bad white blood cells.
Leukemia can make platelet counts drop. This leads to symptoms like bleeding gums. It’s key to link oral health to leukemia for early treatment.
Liv Hospital stresses knowing the mouth signs of leukemia. By spotting these, people can get help fast.
Key Takeaways
- Bleeding gums can be an early symptom of leukemia.
- Leukemia is a type of blood cancer affecting white blood cell production.
- Low platelet count due to leukemia can cause bleeding gums.
- Recognizing oral health signs is key to early detection.
- Liv Hospital emphasizes the importance of awareness about leukemia mouth symptoms.
The Hidden Connection Between Oral Health and Blood Cancer
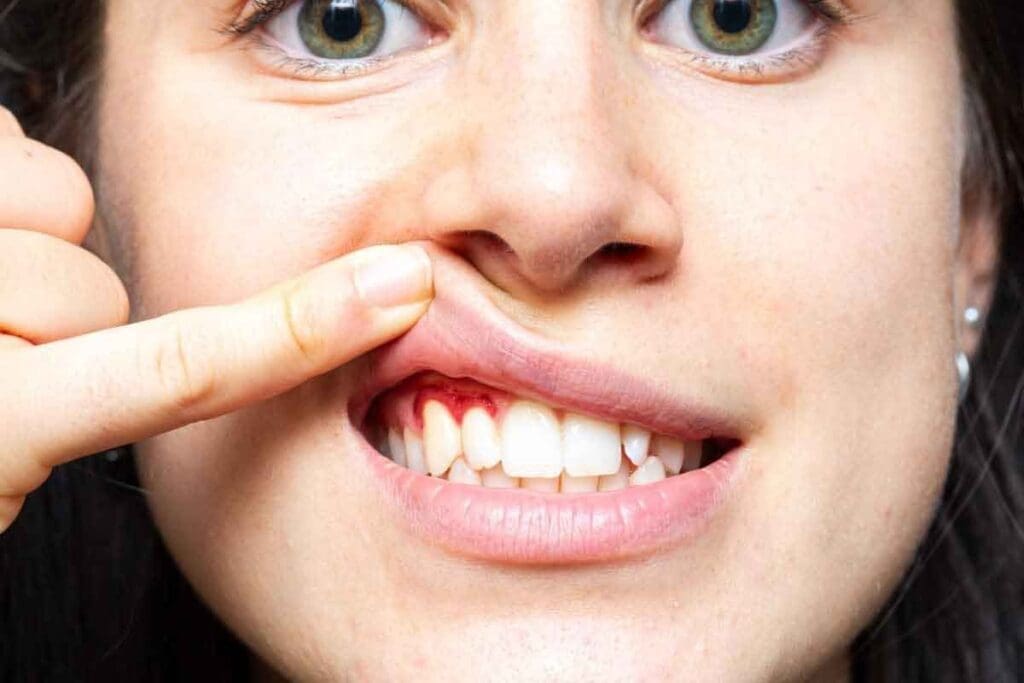
The mouth can show early signs of leukemia. This is important for catching the disease early.
How Leukemia Manifests in the Mouth
Leukemia can cause bleeding gums, swollen gums, and mouth ulcers. It happens because of abnormal white blood cells. These cells disrupt normal blood production.
In some cases, leukemia can make gums swell and hurt. This is called leukemic gingivitis. Gums may bleed easily.
Why Oral Symptoms Often Go Unrecognized
People often think oral symptoms of leukemia are just gum disease. This can lead to a delay in getting medical help.
| Oral Symptom | Common Misdiagnosis | Leukemia Indicator |
| Bleeding Gums | Gingivitis | Low platelet count |
| Swollen Gums | Gum Disease | Leukemic infiltration |
| Mouth Ulcers | Viral Infection | Immune system suppression |
It’s important to know the difference between common gum problems and leukemia symptoms. This can help get medical help sooner.
Understanding Leukemia: Types and Blood Cell Disruption

Leukemia is a cancer that affects the blood. It disrupts the normal production of blood cells. This can lead to health problems like trouble fighting infections and controlling bleeding.
Common Types of Leukemia
There are many types of leukemia, each with its own traits. The main ones are:
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): A fast-moving disease that affects lymphoid cells.
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): A type that affects myeloid cells and can get worse quickly if not treated.
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): A slower type that affects lymphoid cells.
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML): A type that affects myeloid cells and progresses slowly.
How Abnormal White Blood Cells Affect the Body
Leukemia causes the body to make abnormal white blood cells. These cells take over the bone marrow, leaving less room for healthy cells. This can cause:
- Increased risk of infections because there are fewer normal white blood cells.
- Bleeding problems from low platelet counts.
- Anemia from fewer red blood cells.
Knowing these effects helps us spot leukemia symptoms early. It’s important to get medical help right away.
Early Stage Leukemia Bleeding Gums: The Critical Warning Sign
Bleeding gums might not just mean bad oral hygiene. It could also signal leukemia early. This symptom happens when platelet counts drop, which are key for blood to clot.
Decreased Platelet Counts and Clotting Problems
Leukemia messes with the bone marrow, where platelets are made. This messes up platelet production, leading to thrombocytopenia. This condition makes it hard for blood to clot, causing easy bruising and bleeding, like bleeding gums.
Leukemia affects the body’s ability to make normal blood cells. As it gets worse, abnormal white blood cells take over the bone marrow. This includes the cells that help with clotting.
Why Bleeding Occurs Without Injury or Gum Disease
Bleeding gums in leukemia patients can happen without any injury or gum disease. This is because of clotting problems caused by the disease. Even simple actions like brushing teeth can cause bleeding because of the fragile blood vessels and clotting issues.
In some cases, the bleeding can be severe and hard to stop. This shows the need for quick medical help. It’s important to know why bleeding happens to get the right treatment.
Case Studies: When Bleeding Gums Led to Diagnosis
There are cases where bleeding gums led to a leukemia diagnosis. For example, a patient might go to the dentist for gum bleeding. Then, tests show they have leukemia.
These stories show how important it is for dentists to watch for signs of serious diseases like leukemia. They also remind patients to pay attention to their symptoms.
Distinguishing Leukemia-Related Bleeding from Common Gingivitis
Telling apart gum disease from leukemia-related bleeding is key for quick medical help. Both can cause gum bleeding, but the reasons and signs are different.
Characteristics of Normal Gum Disease
Gingivitis, a common gum disease, comes from poor oral care. It leads to plaque and swelling. Symptoms include:
- Red, swollen gums
- Bleeding when brushing or flossing
- Bad breath
- Tender gums
Gingivitis can be treated with dental cleanings and better oral care. But, if ignored, it can turn into periodontitis. This is a serious infection that harms the gums and teeth.
Red Flags That Suggest Something More Serious
While gingivitis can cause bleeding, some signs point to leukemia. Look out for:
| Symptom | Gingivitis | Leukemia-Related Bleeding |
| Bleeding Frequency | Typically, during brushing or flossing | Spontaneous and excessive bleeding |
| Gum Appearance | Red, swollen, tender | Pale, swollen, and possibly infiltrated with leukemic cells |
| Associated Symptoms | Bad breath, tender gums | Fatigue, weight loss, frequent infections |
Spontaneous and excessive gum bleeding without reason is a big warning sign. Also, if gums look pale or are swollen with leukemic cells, it might be leukemia. Other signs like fatigue, weight loss, and frequent infections with gum bleeding need a closer look.
It’s important to know these differences for early detection and the right treatment. Dentists are key in spotting these signs and telling apart gingivitis from leukemia.
7 Key Mouth Symptoms of Early Leukemia to Monitor
Leukemia often shows signs in the mouth that need quick action. Spotting these signs early can help in getting the right treatment fast.
1. Spontaneous and Excessive Gum Bleeding
One key sign of early leukemia is bleeding gums without reason. This happens because there are fewer platelets, making blood hard to clot. If your gums bleed a lot without injury, see a doctor right away.
2. Swollen, Spongy Gum Tissue
Leukemia can also make gums swell and feel spongy. Leukemic cells in the gums make them big and sore. This can hurt and make it hard to clean your teeth.
3. Persistent Gum Pain Without Clear Cause
Gum pain that won’t go away is another warning sign. Leukemia can cause this pain because of the cancer cells in the gums.
4. Recurring Mouth Ulcers and Sores
Ulcers and sores in the mouth that keep coming back are also a sign. A weak immune system from leukemia leads to these infections.
Other important mouth symptoms to watch for include:
- Pale mucous membranes
- Dry mouth or xerostomia
- Changes in the tongue’s appearance or function
| Oral Symptom | Possible Cause |
| Spontaneous Gum Bleeding | Low platelet count |
| Swollen Gum Tissue | Infiltration of leukemic cells |
| Recurring Mouth Ulcers | Compromised immune system |
“Early detection of leukemia is key to good treatment. Knowing the mouth symptoms can help catch it early.”
— Medical Expert
It’s important to watch for these symptoms and get medical help if they don’t go away or get worse. Finding leukemia early can greatly improve treatment outcomes.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) and Its Direct Infiltration of Gum Tissue
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) can directly affect gum tissue, causing swelling and bleeding. It’s a blood cancer that grows fast and fills the bone marrow with abnormal cells. This stops normal blood cells from being made.
The Mechanism of Gum Infiltration in AML
AML cells spread from the bone marrow to the gums. This is because AML grows and moves to different parts of the body. It leads to leukemic gingivitis, a gum disease unlike the usual kind caused by bad oral hygiene.
Leukemic cells in the gums cause inflammation and swelling. This makes the gums bigger and more likely to bleed, even without injury.
Distinctive Features of Leukemic Gingivitis
Leukemic gingivitis from AML has unique signs. These include:
- Spontaneous bleeding without any obvious cause
- Swollen and spongy gum texture
- Persistent pain or discomfort in the gums
- Ulcerations or sores in the mouth
These symptoms are often more severe than regular gum disease.
Visual Identification of AML-Related Gum Changes
A dental professional can spot gum changes linked to AML. These include:
| Characteristic | Description |
| Gum Swelling | Enlargement of the gums due to infiltration by leukemic cells |
| Gum Color Change | A change in the color of the gums, often appearing redder or purplish |
| Bleeding | Spontaneous bleeding from the gums, even without trauma |
Spotting these signs early is key to diagnosis and treatment. Dental professionals are essential in catching these signs. Regular dental visits are vital.
Dentists as Frontline Detectors: The Crucial Role in Early Diagnosis
Dentists are key in spotting leukemia early by finding important oral signs. They are often the first to see these signs during regular check-ups.
What Dental Professionals Look For During Examinations
Dentists search for signs of leukemia during dental exams. They look for:
- Spontaneous and excessive gum bleeding
- Swollen, spongy gum tissue
- Unexplained gum pain
- Recurring mouth ulcers and sores
Vigilance is key in spotting these symptoms early. This can lead to quick medical help.
The Medical Referral Process for Suspected Blood Disorders
If a dentist thinks a patient might have leukemia, they send them to a doctor. This step is vital for quick care.
The process includes:
- Initial assessment by the dentist
- Referral to a hematologist or oncologist
- Comprehensive blood tests and other diagnostic procedures
Collaborative Care Between Dental and Oncology Teams
Diagnosing and treating leukemia needs teamwork between dentists and oncologists. Dentists share important info about the patient’s mouth health. This helps in planning treatment and managing side effects.
Collaboration between healthcare teams ensures patients get all-around care. This care lasts from diagnosis to treatment and beyond.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention for Oral Symptoms
Certain oral symptoms need immediate attention because they might signal serious conditions like leukemia. Many oral health issues are harmless. But some symptoms can point to serious health problems that need quick medical check-ups.
Oral health is tied to overall health. Changes in the mouth can be the first sign of a serious condition. It’s important to know the warning signs and when to seek help.
Urgent Warning Signs That Shouldn’t Be Dismissed
If you notice any of these symptoms, get medical help right away:
- Spontaneous and excessive gum bleeding that doesn’t stop after applying pressure.
- Persistent gum pain or swelling that doesn’t get better with oral care or over-the-counter treatments.
- Recurring mouth ulcers or sores that are unusually large, painful, or last a long time.
These symptoms might mean leukemia or another serious health issue. Getting medical help quickly can help find the cause and the right treatment.
Preparing for Your Medical Appointment
Before your medical appointment, prepare by gathering information that can help with the diagnosis. Here’s a guide to help you:
| Information to Provide | Why It’s Important |
| Detailed description of your symptoms | Helps healthcare providers understand your condition |
| Medical history, including any previous diagnoses or treatments | Provides context for your current symptoms |
| List of medications you’re currently taking | Assists in identifying possible causes or interactions |
Being ready for your appointment can make the diagnostic process better. It ensures you get the right care.
The Diagnostic Journey: From Oral Symptoms to Leukemia Diagnosis
Oral symptoms can be an early warning sign of leukemia. This starts a diagnostic process with several key steps. When these symptoms are found, tests are done to see if leukemia is present and what type it is.
Initial Blood Work and What It Reveals
The first step in diagnosing leukemia is blood work. This includes a complete blood count (CBC) to check for abnormal levels of white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. “Abnormal blood counts can indicate the presence of leukemia, but further testing is needed to confirm the diagnosis,” say medical professionals.
A CBC can show signs like anemia, low platelet count, or too many white blood cells. These signs can point to leukemia.
Advanced Testing: Bone Marrow Biopsy and Imaging
If blood work suggests leukemia, advanced testing follows. A bone marrow biopsy is done to check for cancerous cells in the bone marrow. This involves taking a sample of bone marrow for detailed examination.
Imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or PET scans are also used. They help see if leukemia has spread to other parts of the body.
Understanding Your Test Results
It’s key to understand your test results. A leukemia diagnosis is confirmed when cancerous cells are found in the blood or bone marrow. The type of leukemia is based on the specific cells affected and their characteristics.
“The diagnosis of leukemia is not just about confirming the presence of cancer; it’s about understanding the specific type and its implications for treatment,” said a leading oncologist.
Next Steps After Diagnosis
After a leukemia diagnosis, talking about treatment options with a healthcare provider is next. This may include chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or a bone marrow transplant. The choice depends on the type and stage of leukemia.
It’s vital for patients to work closely with their healthcare team. This helps create a personalized treatment plan.
Conclusion: Vigilance and Early Action Save Lives
Being careful about your mouth health is key to spotting leukemia early. Signs like sudden gum bleeding and swollen gums are important to watch for. They can help doctors find and treat leukemia quickly.
Spotting leukemia early can greatly improve treatment results. Knowing the signs and acting fast can really help patients. It’s important for both dentists and everyone else to know about leukemia.
Linking mouth health to leukemia helps people stay healthy. Going to the dentist regularly and watching for unusual mouth symptoms is important. It’s part of taking care of your overall health.
Staying alert and spreading the word about leukemia can lead to quicker action. This can save lives. Working together, we can make a big difference in finding and treating leukemia.
FAQ
What is the connection between bleeding gums and leukemia?
Bleeding gums can be a sign of leukemia. This is because leukemia affects blood cell production. Platelets, which help with clotting, are often impacted.
How does leukemia affect oral health?
Leukemia can cause bleeding gums and swollen gums. It also leads to recurring mouth ulcers. This happens because leukemic cells invade the oral tissues.
What are the common types of leukemia?
Common types include Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) and Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). There’s also Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) and Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML).
Can bleeding gums be a sign of early-stage leukemia?
Yes, bleeding gums can be an early sign of leukemia. This is true if the bleeding is spontaneous or excessive. It may show a problem with platelet production.
How can I distinguish between normal gum disease and leukemia-related bleeding?
Leukemia bleeding is often spontaneous or excessive. Normal gum disease bleeds when you brush or floss. It also has symptoms like pain or inflammation.
What role do dentists play in detecting leukemia?
Dentists are key in spotting early leukemia signs. They notice unusual symptoms like gum infiltration or unexplained bleeding during routine exams.
What are the key mouth symptoms of early leukemia?
Early leukemia symptoms include spontaneous gum bleeding and swollen gums. You might also have persistent gum pain and recurring mouth ulcers.
How is leukemia diagnosed?
Diagnosing leukemia involves blood tests, bone marrow biopsies, and imaging studies. These confirm leukemic cells and determine the disease’s type and extent.
What should I do if I’m experiencing symptoms that might be related to leukemia?
If you have symptoms like unexplained bleeding or swollen gums, see a doctor quickly. Early diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve your chances.
Can Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) directly affect gum tissue?
Yes, AML can directly affect gum tissue. This leads to symptoms like swollen, painful, or bleeding gums. It’s a sign of leukemic gingivitis.
How can I prepare for a medical appointment if I suspect I have leukemia?
To prepare, list your symptoms, medical history, and questions. Be ready to discuss your health and any concerns you have.
References
Jureller, A., & Wernisch, J. (2022). The recognition of oral manifestations of haematological disease saves lives: a case report. Bulletin of the National Research Centre, 46(1), 239. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9440743/



































