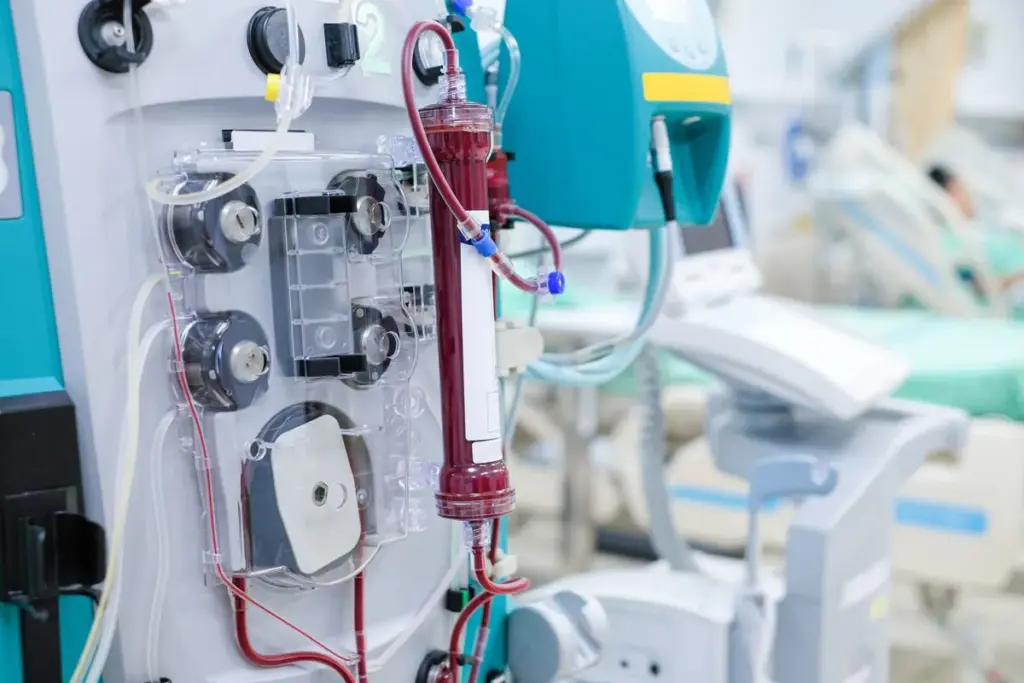

Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, or ECMO, is a life-saving therapy. It’s used when a patient’s heart and lungs can’t work right on their own. This complex procedure can be tough on the body, and it’s important to know the challenges it brings.
Patients on ECMO treatment often face serious health issues. While it saves lives, it can also cause long-term problems like pain, anxiety, and brain issues. As healthcare workers, we know how vital it is to support patients fully after ECMO treatment.
Key Takeaways
- ECMO is a life-support therapy for critical heart and lung failure.
- The treatment can have significant physical demands and possible complications.
- Patients may face long-term issues like pain, anxiety, and brain problems.
- Comprehensive support is key for patients recovering from ECMO treatment.
- Understanding ECMO’s effects is vital for better patient outcomes.
What Is ECMO and How Does It Support Critical Patients?
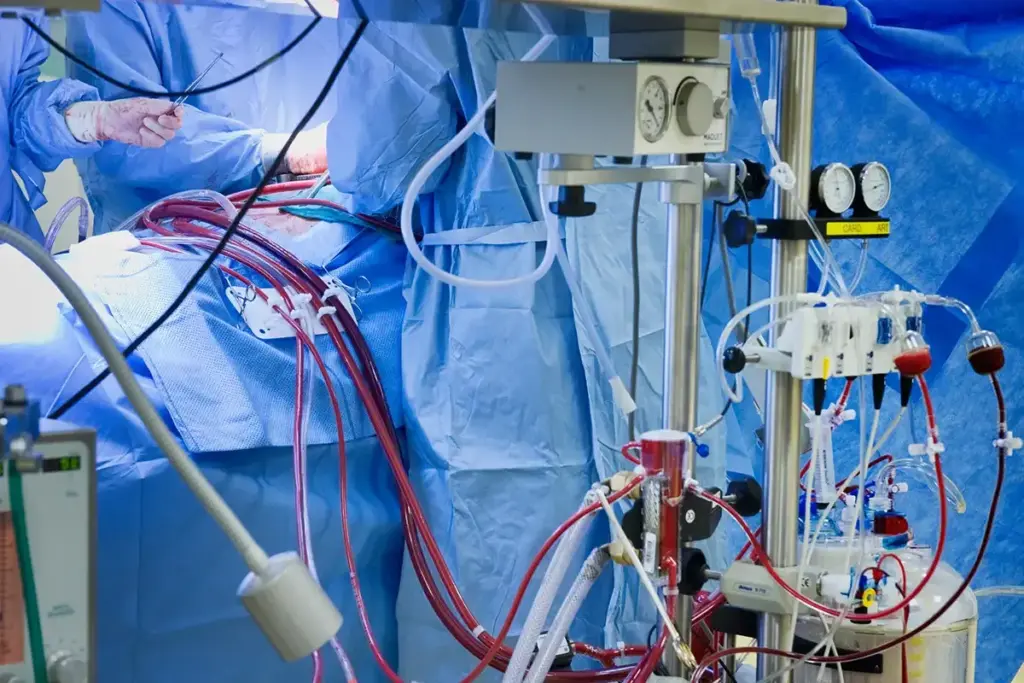
When other treatments don’t work, ECMO steps in to save critical patients. ECMO, or Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation, is a high-tech way to help those with severe heart or lung problems.
Defining Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) is a life-saving therapy. It takes over the heart and lungs’ work by using a bypass machine, called the ECMO machine. This machine oxygenates the blood and removes carbon dioxide before returning it to the patient.
Doctors turn to ECMO when other treatments fail. TheExtracorporeal Life Support Organization (ELSO) says ECMO helps patients with severe respiratory and cardiac issues.
The Mechanics Behind ECMO Life Support
ECMO’s process is complex and needs careful handling. The ECMO machine has a membrane oxygenator for oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange. There are different ECMO types, like Veno-Arterial (VA ECMO) and Veno-Venous (VV ECMO), each for specific needs.
VA ECMO is for patients needing both heart and lung support. It uses major veins and arteries. VV ECMO, on the other hand, supports the lungs but keeps the heart working. It uses two major veins.
Choosing between VA ECMO and VV ECMO depends on the patient’s condition. Knowing about ECMO’s mechanics and types is key to effective patient care.
The ECMO Procedure: Understanding the Physical Intervention
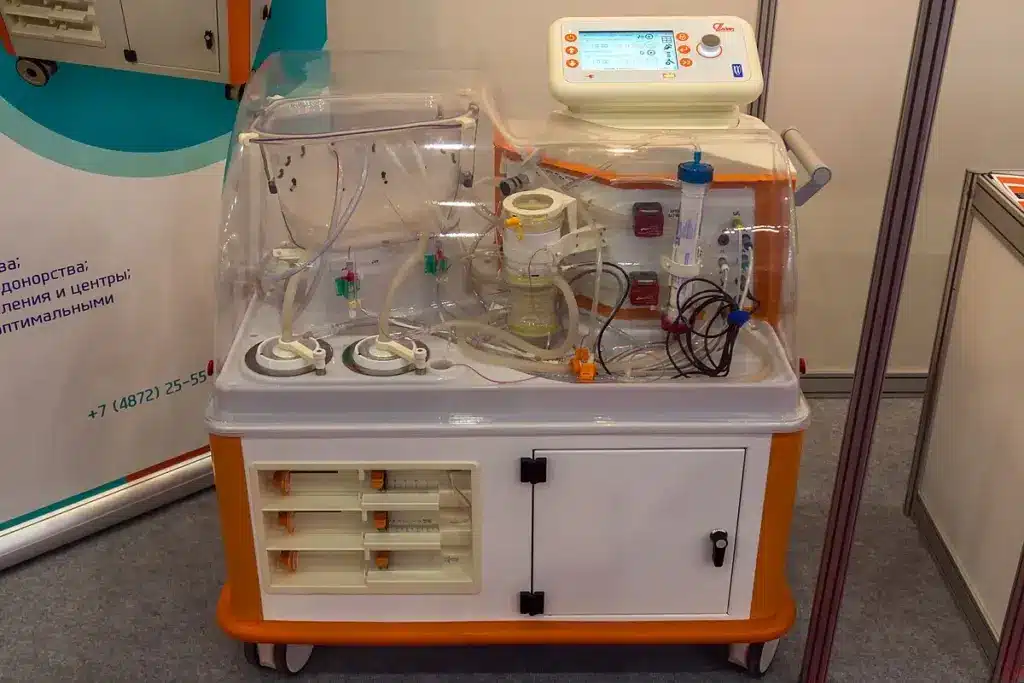
Starting ECMO support is a big step. It involves a key process called cannulation. This process is essential for ECMO therapy to work. It allows blood to be taken from the body, oxygenated, and then returned.
Cannulation Process and Initial Body Response
The cannulation process means putting big tubes into major blood vessels. Doctors use special tools like ultrasound to guide them. This helps avoid problems and makes sure the tubes are in the right place.
Initial Body Response: When the tubes are put in and ECMO starts, the body reacts right away. You might see changes in blood pressure, heart rate, and how blood flows. Keeping an eye on these is key to keeping the patient stable.
How Blood Circulation Changes During Support
ECMO changes how blood flows. It can make the heart work less hard in some cases. Or, it can help with breathing in others.
|
ECMO Type |
Blood Circulation Changes |
Clinical Implications |
|---|---|---|
|
VA ECMO |
Reduced cardiac workload, altered blood pressure |
Cardiac rest, possible recovery |
|
VV ECMO |
Enhanced oxygenation, minimal direct cardiac impact |
Support for respiratory failure, reduced lung workload |
It’s important to understand these changes. This helps doctors manage the patient’s care and make ECMO work better. They need to keep watching and adjusting things to meet the patient’s needs.
Different Types of ECMO and Their Bodily Impact
ECMO therapy is not a one-size-fits-all treatment; it comes in various forms, each designed to address specific critical care needs. The type of ECMO used depends on the patient’s condition, the underlying cause of their illness, and the level of cardiac and respiratory support required.
VA ECMO: Effects on Cardiovascular System
Veno-arterial (VA) ECMO is used when both the heart and lungs need support. It reduces the heart’s workload, allowing it to rest and recover. This approach can be lifesaving in cases of severe cardiac failure or cardiogenic shock. But, VA ECMO means the ECMO circuit handles a lot of blood circulation, affecting the heart.
The use of VA ECMO can change blood pressure and flow, affecting vital organs. It also carries risks like bleeding or vascular injury from the cannulation process. Despite these challenges, VA ECMO is a critical tool for managing severe cardiac dysfunction.
VV ECMO: Respiratory System Implications
Veno-venous (VV) ECMO is mainly used for patients with severe respiratory failure. It oxygenates the blood outside the body, allowing the lungs to rest. This can be very helpful when conventional ventilation strategies fail.
While VV ECMO doesn’t directly support the heart, it can help by reducing strain from hypoxemia and hypercapnia. But, careful consideration is needed to avoid complications like infection or thrombosis.
Hybrid ECMO Approaches and Complication Rates
In some cases, hybrid or combined ECMO approaches are used, tailoring therapy to the patient’s needs. These approaches offer flexibility but also add complexity and risks. The decision to use a hybrid ECMO approach must be carefully weighed against the benefits and risks.
Complication rates for ECMO therapy vary widely. They depend on the type of ECMO, the patient’s condition, and the center’s experience. Understanding these factors is key to optimizing ECMO therapy and minimizing its impact.
Short-term Physical Demands of ECMO on Vital Organs
ECMO support is a complex medical intervention. It requires careful consideration of its short-term physical demands on vital organs. When patients are placed on ECMO, their bodies undergo significant stress, affecting the heart, lungs, and other vital organs. Understanding these demands is key for effective patient care.
Heart and Circulatory System Stress
The heart and circulatory system face a lot of stress during ECMO therapy. The extracorporeal circuit can change blood flow and pressure, causing cardiac strain. Vascular access for cannulation can also affect circulatory stability. We must closely monitor cardiac function to mitigate these risks.
In some cases, ECMO support can be beneficial for the heart. It allows the heart to rest and recover. This depends on the type of ECMO used; for instance, veno-arterial (VA) ECMO can have different effects compared to veno-venous (VV) ECMO. VA ECMO provides both cardiac and respiratory support, while VV ECMO mainly supports respiratory function.
Lung Response During Mechanical Oxygenation
The lungs undergo significant changes during ECMO, mainly when mechanical oxygenation is used. Reduced need for ventilation can be beneficial, allowing the lungs to rest. This is helpful in cases of severe lung injury. Yet, prolonged inactivity can lead to lung atrophy or complications like pneumonia.
Careful management of ventilator settings and regular assessment of lung function are essential. The goal is to support the lungs during the critical phase while preventing further injury.
Liver and Digestive System Changes
ECMO can also impact the liver and digestive system. Changes in blood flow and the systemic inflammatory response can affect liver function. Monitoring liver enzymes and bilirubin levels is critical for early detection of issues.
Nutritional support is another critical aspect. The metabolic demands of patients on ECMO can be high. Ensuring adequate nutrition while avoiding complications like cholestasis or gut dysmotility is a delicate balance that healthcare providers must maintain.
Neuropsychiatric Effects: How ECMO Impacts the Brain
ECMO is a lifesaving treatment for critical patients. It has big effects on the brain. Understanding these effects is key to giving the best care.
Pain Experiences During and After Treatment
Pain is a big issue in ECMO care. The treatment is very invasive. Effective pain management strategies are needed to help patients feel better.
Patients feel pain differently. So, care must be tailored to each person. Sedation and analgesia help with pain but can have side effects. Careful titration of sedatives and analgesics is needed to manage pain without harming the patient.
Anxiety and Depression Following ECMO Support
Anxiety and depression are common after ECMO. They can make recovery harder. Early identification and intervention are key. Psychological support is a big part of care for ECMO patients.
Studies show up to 41% of ECMO patients have long-term anxiety and depression. Multidisciplinary care teams are vital. They provide the support and resources needed for mental health.
Sleep Disturbances and Management Approaches
Sleep issues are a big problem for ECMO patients. They affect recovery and well-being. Strategies to promote better sleep include a good sleep environment and managing pain.
Managing sleep is complex. Collaboration between healthcare providers and patients is needed. Together, they can create effective sleep plans to help patients recover better.
Neurocognitive Consequences of ECMO Therapy
As ECMO therapy becomes more common, it’s key to know its effects on the brain. This therapy, though lifesaving, can harm patients’ brain function and thinking skills.
Memory and Cognitive Function Impairments
Research shows many ECMO patients face brain problems. 38% of patients struggle with memory, focus, and quick thinking after ECMO. These issues can make everyday tasks hard.
Many factors cause these brain problems. These include the illness itself, the ECMO treatment, and the care that follows. We need to look at all these when checking patients’ brain health after ECMO.
Long-term Neurological Outcomes
It’s vital to know how ECMO affects the brain long-term. This knowledge helps us support and help patients recover better. Some patients may keep facing brain and thinking problems, which can lower their quality of life.
To grasp the full impact of ECMO on the brain, let’s look at some data:
|
Neurocognitive Outcome |
Percentage Affected |
Potential Interventions |
|---|---|---|
|
Memory Impairments |
25% |
Cognitive Rehabilitation |
|
Attention Deficits |
20% |
Attention Training Programs |
|
Processing Speed Issues |
18% |
Neuropsychological Support |
|
Other Cognitive Impairments |
15% |
Multidisciplinary Rehabilitation |
Knowing these brain effects helps us tailor support and rehab for ECMO patients. This way, we can improve their long-term health and well-being.
Functional Limitations and Physical Rehabilitation Needs
Patients on ECMO therapy often struggle with moving and doing daily tasks. They need a detailed rehab plan to get stronger and more functional. This is key to overcoming the challenges they face after ECMO.
Mobility Challenges Post-ECMO
After ECMO, patients find it hard to move around. The treatment’s long downtime and invasive nature weaken muscles. We’ve seen that starting to move early helps a lot in improving their health.
Starting physical therapy early helps a lot. It includes exercises made just for the patient. These aim to build muscle strength and improve flexibility.
Daily Activity Restrictions and Adaptations
Patients also face hurdles in doing everyday tasks. Simple actions like bathing and eating become hard due to weakness. We advise patients and their caregivers to find ways to manage these tasks better.
Occupational therapy is very helpful. It teaches patients how to do daily tasks more easily. This is key to improving their life quality and recovery.
Timeline for Physical Recovery
The time it takes for patients to recover varies. It depends on how long they were on ECMO, their health before, and the rehab program. Most start to see big improvements in 6 to 12 weeks after leaving the hospital. But, full recovery can take even longer.
|
Recovery Phase |
Timeline |
Key Milestones |
|---|---|---|
|
Initial Recovery |
0-6 weeks |
Regaining basic mobility, managing pain |
|
Intermediate Recovery |
6-12 weeks |
Improving strength, increasing independence in daily activities |
|
Advanced Recovery |
3-6 months |
Enhancing physical function, returning to more complex activities |
It’s important to know that 52% of patients face functional impairments after ECMO. This shows the need for personalized rehab plans. Understanding these needs helps us support patients better on their path to recovery and a better life.
Renal Complications: The Leading ECMO Challenge
ECMO therapy is life-saving but often leads to renal complications. These issues complicate patient care and recovery. It’s key to understand the causes and find effective ways to manage them.
Mechanisms of Kidney Injury During Support
Kidney injury from ECMO can come from hypotension, inflammation, and nephrotoxic agents. ECMO’s non-pulsatile flow also affects kidney function by changing blood flow patterns.
It’s important to see kidney injury in ECMO patients as a complex issue. This includes their pre-existing kidney conditions, the reason for ECMO, and the effects of treatment drugs.
Comparison Between Conventional and Hybrid Approaches
Conventional and hybrid ECMO methods have different risks and benefits for kidneys. Conventional ECMO might lead to more kidney problems because of longer use and increased inflammation.
Hybrid ECMO, which mixes different methods or adds other support, might help by being more tailored and possibly shorter in duration.
“The choice between conventional and hybrid ECMO approaches should be guided by individual patient needs and the potential for reducing renal complications.” -Expert Opinion
Prevention and Management Strategies
To prevent kidney problems in ECMO patients, we need a detailed plan. This includes choosing patients carefully, watching their kidney function closely, and using strategies to protect their kidneys.
- Keeping blood pressure right and fluid levels balanced is key.
- Try to avoid nephrotoxic agents.
- Use drugs that help kidneys work better.
It’s also wise to have early detection plans for kidney injury. And to have a clear plan for managing kidney issues when they happen.
Bleeding Risks and Anticoagulation Management
ECMO therapy is life-saving but comes with big bleeding risks. It’s important to manage these risks carefully. ECMO support needs a balance to prevent clotting in the circuit and avoid bleeding.
Increased Bleeding Vulnerability
The ECMO circuit exposes blood to a large artificial surface. This triggers an inflammatory response and activates coagulation pathways. This can increase the risk of bleeding, mainly in patients with coagulopathy or those undergoing invasive procedures.
Several factors increase the bleeding risk in ECMO patients:
- Systemic anticoagulation to prevent circuit thrombosis
- Contact of blood with the non-endothelial surface of the ECMO circuit
- Inflammatory response to the ECMO circuit
- Potential for platelet dysfunction
Special Considerations in Trauma Patients
Trauma patients on ECMO face a high risk of bleeding. This is because their injuries may not be fully assessed at ECMO start. Managing these patients needs a team effort. It considers injury severity, need for surgery, and bleeding risk.
|
Risk Factor |
Description |
Management Strategy |
|---|---|---|
|
Systemic Anticoagulation |
Use of anticoagulants to prevent circuit clotting |
Close monitoring of coagulation parameters, adjustment of anticoagulant dose |
|
Circuit Design |
Material and design of the ECMO circuit |
Selection of circuits with improved biocompatibility |
|
Patient Condition |
Pre-existing coagulopathy or organ dysfunction |
Careful patient selection, close monitoring |
Balancing Clotting Prevention and Bleeding Risk
Managing anticoagulation in ECMO patients is complex. It’s about balancing clotting prevention and bleeding risk. Strategies include:
- Monitoring of coagulation parameters and adjustment of anticoagulation therapy
- Use of point-of-care testing to assess coagulation status
- Implementation of protocols for the management of bleeding and thrombosis
By managing these risks carefully, we can improve ECMO patient care and outcomes.
Immune System Response to ECMO Treatment
ECMO therapy sets off a mix of immune reactions, from inflammation to suppression. It’s vital to understand these responses to care for patients well.
Inflammatory Reactions to the ECMO Circuit
The ECMO circuit can cause a big inflammatory response. This happens when blood touches the artificial surfaces of the circuit. The immune system’s cells and proteins get activated.
Key factors contributing to inflammation include:
- The material composition of the ECMO circuit
- The flow characteristics within the circuit
- The presence of any circuit components that may leach into the blood
We tackle this inflammation by designing the circuit carefully. We choose materials that are good for the body and adjust flow rates.
Infection Susceptibility During Support
Patients on ECMO face a higher risk of infections. This is because of the therapy’s invasive nature and the critical illness it treats.
Keeping a close eye on patients and strict infection control are key. We do regular cultures, take good care of cannula sites, and use antibiotics wisely.
Long-term Immune Function After ECMO
How ECMO affects the immune system long-term is something we’re studying. While it saves lives, it might change how the immune system works. This could make patients more prone to infections and affect their health later.
We’re dedicated to keeping up with patients after ECMO. We watch for any lasting effects on their immune system.
Metabolic and Nutritional Challenges During ECMO Support
ECMO patients face unique metabolic and nutritional challenges. These challenges affect their health and recovery. Understanding these challenges is key to providing the best care.
Altered Metabolism and Energy Requirements
Patients on ECMO have a different metabolic rate. This is due to their critical illness and the ECMO process. “Their metabolic demands are high, and their energy needs are different,” say critical care nutrition experts.
This altered metabolism means they need more energy. Adjustments in nutrition are necessary to meet these needs.
The ECMO circuit can also cause inflammation. This makes metabolic regulation harder. So, nutrition must be tailored to counteract these effects. Patients need enough calories and proteins to aid in recovery.
Nutritional Support Protocols and Importance
Nutritional support is vital in ECMO care. It helps in recovery and outcomes. Adequate nutrition keeps the gut healthy, boosts the immune system, and aids in wound healing.
Personalized nutritional plans are essential for ECMO patients. They must consider the patient’s energy needs, micronutrients, and the best way to deliver nutrition. Early enteral nutrition is often recommended for better outcomes. But, decisions should be based on the patient’s condition.
A critical care specialist says, “Nutritional support in ECMO patients is not just about calories. It’s about the complex relationship between nutrition, inflammation, and organ function.” This highlights the need for a team approach to nutritional care in ECMO patients.
Patient Selection: Who Faces Higher Physical Risks on ECMO
Choosing the right patients for ECMO is a detailed process. It looks at many factors to lessen physical harm. Doctors must check a patient’s health, past medical history, and the risks of ECMO therapy.
Age-Related Considerations and Outcomes
Age is key in picking patients for ECMO. Older people might face more risks because of less strength and health issues. Research shows older patients often stay in the hospital longer and have more problems.
But, age isn’t the only thing that matters. We look at how well a patient can function and how serious their illness is. A detailed check-up can help find out if older patients will really benefit from ECMO.
Pre-existing Conditions That Increase Physical Strain
Existing health problems are also important in choosing patients for ECMO. Issues like heart failure, COPD, and diabetes can make ECMO harder. These patients need extra care and watching to lower risks.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Patients with heart problems are at higher risk of heart issues during ECMO.
- Respiratory Diseases: COPD can make lung care during ECMO tricky, needing changes in ventilator settings.
- Metabolic Disorders: Diabetes and other metabolic issues need close watching to avoid problems during ECMO.
Risk Assessment Before ECMO Initiation
Doing a full risk check is key before starting ECMO. We look at the patient’s health, lab results, and scans to guess possible problems. We use scores and our best judgment to decide if ECMO is right for each patient.
“The decision to start ECMO should be made for each patient separately, considering their risks and benefits.”
By picking the right patients for ECMO and managing their risks, we can make the treatment safer and more effective.
Survival Rates vs. Quality of Life: The Complete Picture
ECMO’s impact goes beyond just keeping patients alive. It also affects their quality of life in big ways. We need to look at both survival rates and life quality after treatment.
Statistical Outcomes Across Patient Populations
Survival rates for ECMO patients change a lot. This depends on the patient’s condition, age, and the ECMO type. For example, some patients live beyond 60% of cases, but they might face long-term health issues.
We must look at these numbers to really get how ECMO works.
|
Patient Population |
Survival Rate (%) |
Long-term Impairment Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
|
Adult Respiratory Failure |
55-65 |
30-40 |
|
Pediatric Cardiac Arrest |
40-50 |
20-30 |
|
Neonatal Respiratory Distress |
70-80 |
10-20 |
Long-term Functional Status After Survival
It’s key to know how well ECMO patients do long-term. Many recover well, but some face lasting physical, mental, or emotional issues. We must study these outcomes to give better care.
Key factors influencing long-term functional status include:
- Pre-existing health conditions
- Duration of ECMO support
- Intensity of post-ECMO rehabilitation
Patient Perspectives on Post-ECMO Life
What patients say about ECMO is very important. Their stories help us understand the real effects of ECMO. This helps us improve care for future patients.
“After ECMO, my journey was not just about surviving but learning to live again. The support I received was critical in my recovery.” – ECMO Survivor
Looking at both numbers and personal stories helps us see ECMO’s full impact. It shows how it saves lives and improves life quality.
How Leading Hospitals Minimize ECMO’s Physical Impact
Top hospitals are always improving their care to lessen ECMO’s effects on patients. They use new protocols, specialized teams, and technology to help patients. This approach aims to reduce complications and make treatment easier.
Evolving Protocols to Reduce Complications
Top hospitals update their ECMO care plans regularly. They use the latest research to make sure care is the best it can be. For example, they might change how they monitor patients or manage blood thinners.
Some important updates include:
- Enhanced Monitoring: They use new systems to catch and fix problems fast.
- Personalized Care Plans: They tailor treatment to each patient, considering their health history and current condition.
- Multidisciplinary Teams: They bring together experts from different fields to manage care fully.
A study on theNational Center for Biotechnology Information shows how updates in care plans can improve patient results.
Specialized ECMO Teams and Patient Outcomes
Having a specialized ECMO team is key. These teams include doctors, nurses, and others with ECMO experience. They help manage ECMO treatment and make important decisions for patient recovery.
Specialized teams help patients by:
- Providing care that fits each patient’s needs.
- Quickly spotting and fixing problems.
- Working together to help patients recover better.
Technological Advancements Reducing Physical Strain
New technology is important in making ECMO treatment less hard on patients. Things like better oxygenators and pumps help reduce risks and make patients more comfortable. Also, using artificial intelligence and machine learning in ECMO systems is starting to show great promise.
Some key tech advancements include:
- Advanced Oxygenators: These make treatment safer and less likely to cause bleeding or blood clots.
- Smart Pumps: These adjust flow rates as needed, helping avoid heart problems.
- Minimally Invasive Cannulas: These designs make cannulation less invasive, which can lower infection risks and speed up recovery.
By using these technologies and improving care plans, top hospitals can make ECMO treatment less stressful for patients. This helps patients recover better and live a better life after treatment.
Conclusion: Balancing ECMO’s Life-Saving Benefits Against Physical Costs
ECMO therapy is a complex treatment that helps critical patients. It supports those with severe heart or lung failure. But, it comes with big physical costs like organ damage, bleeding risks, and long-term health issues.
Choosing the right patients for ECMO is key to good outcomes. It’s important to provide full care and support to lessen its physical effects. This way, survivors can have a better quality of life.
As ECMO technology gets better, top hospitals are working to reduce its physical impact. This shows the need to weigh ECMO’s benefits against its costs. It ensures patients get the best care possible.
FAQ
What is ECMO and how does it work?
ECMO, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, is a therapy that helps when the heart and lungs fail. It takes blood from the patient, oxygenates it, and removes carbon dioxide. Then, it returns the blood to the patient.
What are the different types of ECMO?
ECMO comes in two main types. VA (Veno-Arterial) ECMO supports both heart and lung functions. VV (Veno-Venous) ECMO mainly helps with severe lung problems. Sometimes, a mix of both is used.
How does VA ECMO affect the cardiovascular system?
VA ECMO can change blood flow and affect the heart’s stability. It can also stress the heart.
What are the possible neuropsychiatric effects of ECMO?
ECMO patients might face pain, anxiety, depression, and sleep issues. These can greatly affect their quality of life.
How does ECMO impact cognitive function?
ECMO can harm memory and thinking skills. It’s important to support and help ECMO survivors recover.
What are the functional limitations after ECMO?
Patients may struggle with moving and doing daily tasks after ECMO. Physical therapy is key to help them regain strength.
What are the renal complications associated with ECMO?
Kidney problems are a big challenge with ECMO. Finding ways to prevent and manage these issues is vital.
Why does ECMO increase the risk of bleeding?
ECMO uses anticoagulation to prevent clots. This increases the risk of bleeding. Managing anticoagulation is critical.
How does the immune system respond to ECMO?
The immune system may react to ECMO with inflammation. Patients are also more prone to infections.
What are the metabolic and nutritional challenges during ECMO?
ECMO patients may have different metabolism and energy needs. Nutritional support is essential for their recovery.
Who is at higher risk for physical strain on ECMO?
Some patients, like the elderly or those with pre-existing conditions, face more strain on ECMO. Choosing the right patients is important.
What are the survival rates and quality of life after ECMO?
Survival and quality of life after ECMO vary. Understanding these outcomes helps in providing better care.
How do leading hospitals minimize ECMO’s physical impact?
Top hospitals use new protocols, specialized teams, and technology to reduce ECMO’s effects. This improves patient outcomes.
What is the role of cannulation in the ECMO procedure?
Cannulation is key in ECMO. It involves putting large tubes in blood vessels to divert blood to the ECMO circuit.
How does ECMO affect lung function?
ECMO can impact lung function, affecting breathing and overall lung health.
What is the importance of nutritional support during ECMO?
Nutritional support is critical for ECMO patients. They may need different nutrients due to their condition.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6535699/[2





