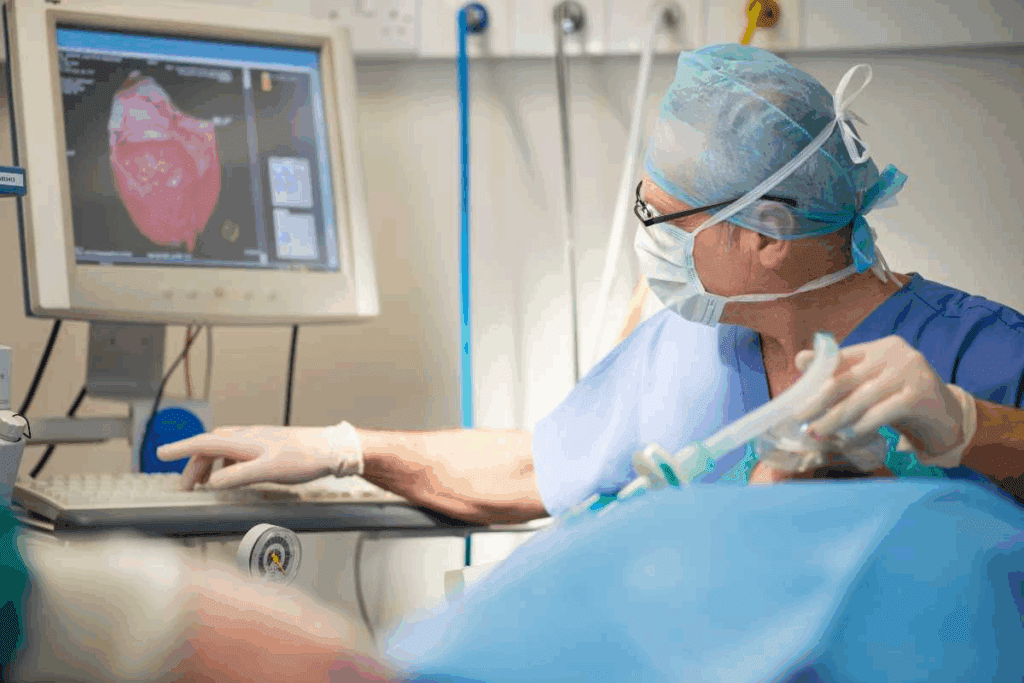
A brain aneurysm is a bulge in a blood vessel in the brain. It can be very dangerous if it bursts, causing bleeding. We at Liv Hospital use a special procedure called brain embolization to treat it. This method stops the aneurysm from bursting by cutting it off from blood flow.
Our team is skilled in using advanced techniques. We can successfully treat over 90% of brain aneurysms. This is a better option for many because it has a shorter recovery time and fewer risks than open surgery.
Key Takeaways
- Minimally invasive brain embolization procedure for treating cerebral aneurysms.
- Isolates the aneurysm from the bloodstream to prevent rupture and bleeding.
- Shorter recovery time compared to traditional open surgery.
- Advanced techniques used to exclude over 90% of cerebral aneurysms.
- Lower risk of complications for eligible patients.
Understanding Cerebral Aneurysms: Causes and Symptoms
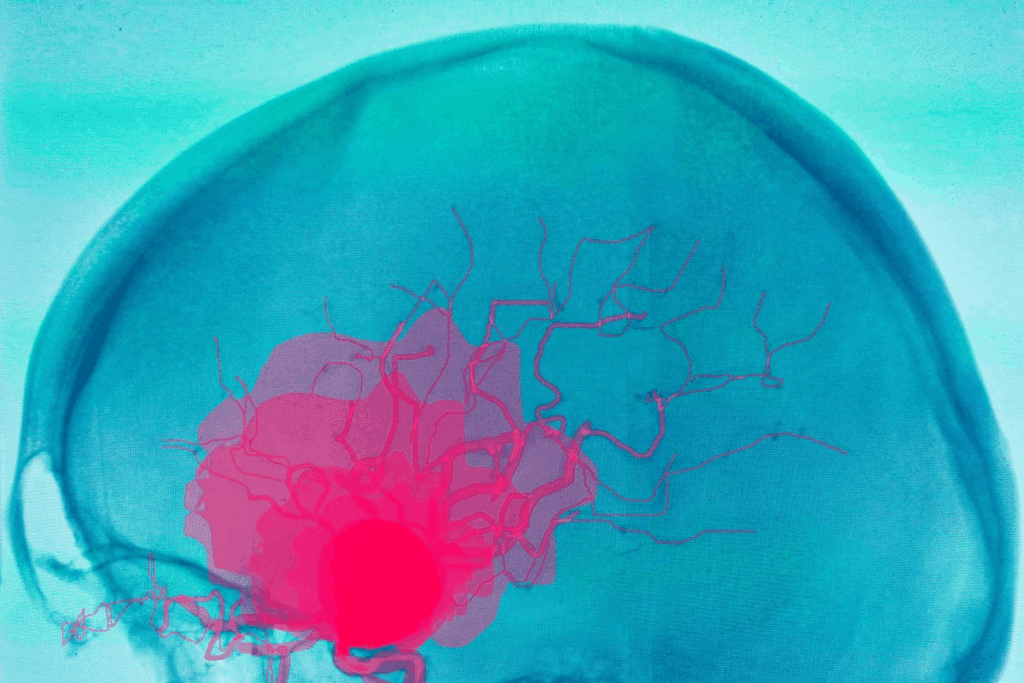
Learning about cerebral aneurysms can really help patients. These are abnormal bulges in brain blood vessels. They can burst, causing serious problems.
Causes of Brain Aneurysms
Brain aneurysms can be caused by genetics, environment, and lifestyle. Genetics are a big factor, with a family history increasing risk. Other causes include high blood pressure, smoking, and atherosclerosis.
It’s important to know these risk factors. This helps us understand why an aneurysm might form. It also helps in preventing and catching them early.
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact on Aneurysm Development |
| Genetics | Family history of aneurysms | High |
| High Blood Pressure | Hypertension | Moderate to High |
| Smoking | Lifestyle factor | Moderate to High |
| Atherosclerosis | Build-up of plaque in arteries | Moderate |
Warning Signs and Symptoms
Cerebral aneurysms often don’t show symptoms until they burst. But, some people might feel headaches, numbness, or vision changes. It’s key to notice these signs for quick medical help.
Symptoms can differ based on the aneurysm’s location and size. Common signs include:
- Severe headache
- Numbness or weakness in the face or limbs
- Vision problems
- Nausea and vomiting
Diagnosis Methods
Diagnosing cerebral aneurysms uses imaging techniques like CT scans, MRI, and angiography. These tools help doctors see the aneurysm and plan treatment.
These methods help us understand the aneurysm’s size, location, and shape. This information is key for choosing the right treatment.
The Embolisation of Aneurysm: Key Fact #1 – Definition and Purpose
Embolisation of an aneurysm is a safe way to stop it from bursting. It works by cutting off the aneurysm from the blood flow. This is very important for people with brain aneurysms because it lowers the chance of bleeding and serious problems.
How Embolisation Prevents Rupture
Embolisation stops an aneurysm from bursting by filling it with coils or liquid. This blocks blood from getting in. It keeps the aneurysm from getting bigger and lowers the pressure on its walls, making it less likely to burst.
We use special imaging during the procedure to place the embolic material exactly right. This is key to making sure the treatment works and avoiding problems.
History and Development of the Technique
The idea of embolisation has been around for decades. But, new technology and methods have made it much better. Now, we use advanced tools like microcatheters, coils, and liquid agents.
Doctors have worked hard to make treatments for brain aneurysms safer and more effective. Thanks to new technology, embolisation is now a top choice for many patients.
Patient Selection Criteria
Not every patient with a brain aneurysm can have embolisation. We look at things like the size and location of the aneurysm, and the patient’s health and past medical history.
We think about many things when deciding if embolisation is right for a patient. This includes if they have symptoms, the risk of the aneurysm bursting, and the benefits and risks of the treatment. This careful process helps make sure patients get the best treatment for their needs.
| Criteria | Description | Importance |
| Aneurysm Size | Size of the aneurysm sac | High |
| Aneurysm Location | Location of the aneurysm in the cerebral vasculature | High |
| Patient Health | Overall health and medical history of the patient | High |
Brain Embolization Procedure: Key Fact #2 – How It Works
The brain embolization procedure is a detailed treatment that needs careful steps for success. It’s a minimally invasive method. We navigate through blood vessels to the aneurysm. There, we deploy a material to stop blood flow.
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Before the procedure, patients get diagnostic tests. These tests check the aneurysm’s size, location, and shape. We also look at the patient’s health and medical history for risks.
Preparation includes:
- Stopping certain medications that could interfere with the procedure
- Avoiding food and drink for a specified period before the procedure
- Arranging for transportation home after the procedure, as patients may be groggy or sedated
The Endovascular Approach
The endovascular approach is key in the brain embolization procedure. It starts with a small incision in the groin to access the femoral artery. Then, a microcatheter is guided to the aneurysm under imaging.
Key steps in the endovascular approach include:
- Navigating the microcatheter through the blood vessels to the aneurysm
- Deploying coils or liquid agents into the aneurysm to prevent further blood flow
- Monitoring the procedure in real-time using imaging technologies
Microcatheter Navigation Techniques
Microcatheter navigation is a critical part of the procedure. It needs skill and precision to navigate through blood vessels to the aneurysm.
| Technique | Description | Advantages |
| Roadmapping | Uses imaging to create a roadmap of the blood vessels | Enhances navigation accuracy |
| Real-time Imaging | Provides live feedback during the procedure | Allows for immediate adjustments |
| Microcatheter Design | Advanced design for flexibility and maneuverability | Improves navigation through complex vessels |
By using advanced microcatheter navigation and the endovascular approach, we can treat aneurysms effectively. This minimizes risks and complications.
Coil Embolization for Aneurysm: Key Fact #3 – Success Rates
Coil embolization for aneurysms is a promising solution with a high success rate. This minimally invasive procedure has seen significant advancements. It’s now a preferred treatment for many patients.
Types of Coils and Materials Used
The success of coil embolization depends on the coils and materials used. We use platinum coils, hydrogel-coated coils, and bioactive coils. These materials help in effectively closing the aneurysm.
We choose the right coil type for each patient. The choice depends on the aneurysm’s size, location, and the patient’s health.
The 90% Success Rate Explained
Studies show that coil embolization has a success rate over 90% in treating aneurysms. This high success rate comes from better coil technology and skilled medical professionals.
The success rate is confirmed by imaging after the procedure. A successful outcome greatly lowers the risk of aneurysm rupture.
Factors Affecting Successful Outcomes
Several factors can affect the success of coil embolization. These include the aneurysm’s size and location, the patient’s health, and the medical team’s expertise.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Success |
| Aneurysm Size | Smaller aneurysms are generally easier to treat. | Higher success rate for smaller aneurysms. |
| Aneurysm Location | Location affects accessibility and coil placement. | More challenging locations may reduce success. |
| Patient Health | Overall health influences recovery and outcome. | Better health correlates with higher success. |
By carefully evaluating these factors, we can improve the chances of a successful outcome for patients undergoing coil embolization for aneurysm treatment.
Brain Embolization Surgery vs. Open Surgery: Key Fact #4 – Benefits
Brain embolization has changed how we treat cerebral aneurysms. It’s a less invasive option compared to open surgery. We’ll look at the benefits of brain embolization, like faster recovery and less invasive procedures. We’ll also talk about when open surgery might be needed.
Recovery Time Comparison
Brain embolization surgery has a shorter recovery time than open surgery. Open surgery means a longer hospital stay and recovery. But, brain embolization lets patients get back to their lives sooner.
- Faster Recovery: This surgery causes less damage and trauma, leading to a quicker recovery.
- Shorter Hospital Stay: Patients have shorter hospital stays, lowering the risk of infections and complications.
Minimally Invasive Advantages
Brain embolization is a minimally invasive procedure. It has many benefits, like less risk of complications and less pain after surgery. It’s great for patients at high risk for open surgery complications.
“The minimally invasive nature of brain embolization surgery makes it an attractive option for patients with complex aneurysms or those who are poor candidates for open surgery.”
When Traditional Surgery May Be Necessary
Even though brain embolization is preferred, open surgery is sometimes needed. The choice depends on the aneurysm’s size and location, the patient’s health, and other medical conditions.
- Complex Aneurysms: Large or complex aneurysms often need open surgery for treatment.
- Patient Health: Certain health conditions may make open surgery a better option for some patients.
The decision between brain embolization and open surgery should be made with a neurosurgeon. They consider the patient’s specific needs and situation.
Brain Embolization Side Effects: Key Fact #5 – Risks and Complications
Brain embolization, like any medical procedure, has its risks. It’s important for patients to know these to make informed choices.
Common Side Effects
Side effects like headaches, nausea, and neurological issues are common. These usually go away in a few days. But sometimes, they can last longer or get worse, needing more medical help.
Some might face vasospasm, a temporary blood vessel narrowing. We watch for this closely to act quickly.
Serious Complications
Though rare, serious issues like stroke, cerebral hemorrhage, or coil migration can happen. We do everything we can to avoid these, like choosing patients carefully and using precise techniques.
Some might have an allergic reaction to the materials used. We check for allergies before starting treatment.
Long-term Monitoring Requirements
After the procedure, we keep a close eye on patients. Regular check-ups help us see how well the treatment is working and catch any long-term problems early.
We ask patients to tell us about any new or worsening symptoms right away. This helps us catch and treat problems quickly, ensuring the best results.
| Complication | Frequency | Management |
| Headaches | Common | Symptom management with medication |
| Vasospasm | Occasional | Monitoring and medical therapy |
| Stroke | Rare | Emergency medical intervention |
Knowing about the possible side effects and complications helps patients understand their treatment better. Our team is dedicated to giving full care and support every step of the way.
Aneurysm and Embolism: Key Fact #6 – Understanding the Difference
In vascular medicine, it’s key to tell aneurysms from embolisms for right diagnosis and treatment. These terms are often used in talking about vascular health. But they mean different things for patient care.
Vessel Wall Bulges: Aneurysms
An aneurysm is a bulge in a blood vessel’s wall. It happens when the wall weakens. This weakness can come from genetics, high blood pressure, or atherosclerosis. Aneurysms mostly show up in the aorta and brain.
An aneurysm can burst, leading to severe bleeding. This is very dangerous. So, finding and treating aneurysms before they burst is very important.
Vessel Obstructions: Embolisms
An embolism is when something blocks a blood vessel. This blockage is usually a blood clot that moved from somewhere else. Symptoms vary based on where and how bad the blockage is.
For example, a pulmonary embolism blocks a lung artery, and a cerebral embolism can cause a stroke by blocking a brain blood vessel. Embolisms often come from DVT or atrial fibrillation.
How They Relate to Each Other
Even though aneurysms and embolisms are different, they can be linked. An aneurysm might make blood clots form inside it, which can then travel to other places. On the other hand, an embolism can happen on its own, without an aneurysm.
Knowing the difference is key for the right treatment. Endovascular embolization is used to treat aneurysms by filling them with coils. For embolisms, treatments like anticoagulation therapy or mechanical thrombectomy might be used.
Healthcare providers need to accurately diagnose aneurysms, embolisms, or both. This way, they can give the best treatment, improving patient outcomes and lowering risks.
Beyond Aneurysms: Key Fact #7 – Other Applications
Cerebral embolization is not just for aneurysms. It helps treat many neurovascular conditions. This makes it a key part of improving patient care.
Arteriovenous Malformation Embolization
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are bad connections between arteries and veins. They can cause serious problems if not treated. Cerebral embolization is a good treatment for many AVMs. It’s a way to fix these problems without big surgery.
Our team has helped many patients with AVMs. We use embolization to make their lives better.
Acute Stroke Treatment
When someone has a stroke, acting fast is key. Embolization techniques can help. They can remove clots or put in medicine to help blood flow again.
Our advanced care at specialized centers is making a big difference. Many stroke patients are getting better fast.
Advanced Protocols at Specialized Centers
Places like ours have new ways to use cerebral embolization. We use the latest tech and methods. This helps us care for patients better, from start to finish.
| Condition | Treatment Approach | Benefits |
| Arteriovenous Malformations | Embolization | Reduced risk of rupture, symptom alleviation |
| Acute Ischemic Stroke | Embolization, Thrombolysis | Restored blood flow, improved outcomes |
We use the latest tech and work together to help our patients. The table shows some conditions we treat and how they benefit.
Conclusion: Advances in Brain Aneurysm Treatment
We’ve seen big steps forward in treating brain aneurysms, thanks to new embolization methods. Brain aneurysm embolization is now key in stopping ruptures and helping patients get better. Coil embolization has shown great success, making treatment less invasive for patients.
Medical tech keeps getting better, and so will brain aneurysm treatment. New embolization methods and materials will likely lead to even better results for patients. Our team is always learning about these new developments to give our patients the best care.
The future of treating brain aneurysms is bright, with new coil embolization and other techniques coming. We’re committed to top-notch healthcare and keeping up with the latest in brain aneurysm treatment. This will help patients get the advanced care they need.
FAQ
What is brain embolization, and how does it treat aneurysms?
Brain embolization is a procedure that treats aneurysms without surgery. It blocks blood flow into the aneurysm, stopping it from rupturing. Our team uses advanced methods to treat over 90% of cerebral aneurysms.
What are the causes and symptoms of cerebral aneurysms?
Cerebral aneurysms are caused by genetics and environment. Symptoms include severe headaches, nausea, and vomiting. Knowing these helps us identify and treat at-risk individuals.
How is brain embolization performed?
The procedure starts with preparation and uses a minimally invasive approach. Our team guides a tiny catheter to the aneurysm. This method is less invasive than traditional surgery.
What are the success rates of coil embolization for aneurysm?
Coil embolization is very successful, with over 90% of cases treated successfully. The type of coil and patient selection play key roles in this success.
What is the difference between brain embolization surgery and open surgery?
Brain embolization is less invasive and has a shorter recovery time. Open surgery is needed in some cases. Both methods have their benefits and risks.
What are the possible side effects and complications of brain embolization?
Side effects and complications can happen. Long-term monitoring is key. Our team stresses the importance of follow-up care.
What is the difference between an aneurysm and an embolism?
An aneurysm is a blood vessel bulge, while an embolism is a blockage. Knowing the difference is vital for patient care.
What are the other applications of cerebral embolization?
Cerebral embolization treats arteriovenous malformations and acute strokes. It’s also used in advanced treatments at places like Liv Hospital.
What are the benefits of endovascular embolization?
Endovascular embolization is less invasive, with quicker recovery and lower risk. It’s a preferred option for many patients.
How does coil embolization prevent aneurysm rupture?
Coil embolization blocks blood flow into the aneurysm. This reduces the risk of rupture and helps the aneurysm stabilize.
References:
- StatPearls. (2023). Cerebral Aneurysm. StatPearls Publishing.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507902




































