Last Updated on November 26, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
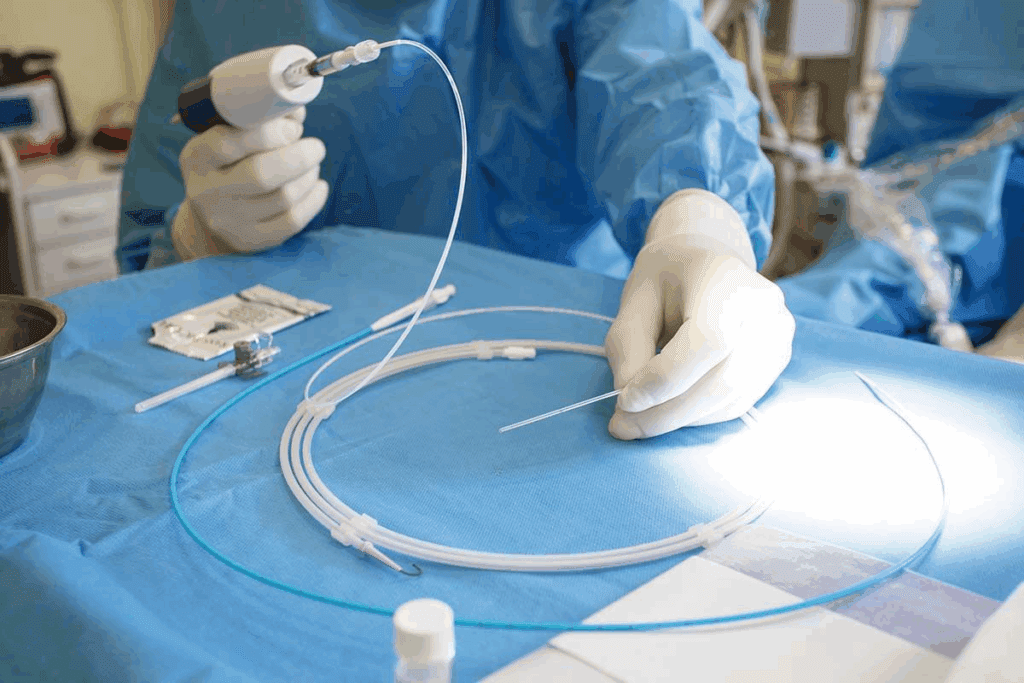
Dealing with an aortic aneurysm can be scary. But Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR) has changed how we treat it. EVAR is a minimally invasive procedure. It uses a stent-graft inserted through small incisions in the groin to fix the aortic wall.
At Liv Hospital, we use EVAR instead of open surgery. This makes recovery faster and reduces complications. As Cleveland Clinic explains, EVAR lines the aneurysm with a stent graft. This graft is made of fabric and metal, taking pressure off the aneurysm.
Key Takeaways
- EVAR is a minimally invasive procedure for treating aortic aneurysms.
- It involves inserting a stent-graft through small incisions in the groin.
- EVAR reduces recovery time and complications compared to open surgery.
- The procedure reinforces the weakened aortic wall to prevent rupture.
- EVAR is a viable treatment option for patients with large or rapidly growing aneurysms.
Understanding Aortic Aneurysms
It’s important to know about aortic aneurysms to see why treatments like Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR) are key. An aortic aneurysm happens when the aorta, the main artery, gets weak and bulges. This can be very dangerous if not treated.
To get why EVAR is important, we need to know about the different types of aortic aneurysms and their risks. Aortic aneurysms are divided by where they happen and what they look like.
Types of Aortic Aneurysms
There are a few types of aortic aneurysms:
- Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms (AAA): These are the most common, found in the belly area.
- Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms (TAA): These happen in the chest.
- Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysms (TAAA): These are in both the chest and belly.
Most often, EVAR is used to treat abdominal aortic aneurysms. Knowing the type of aneurysm helps decide the best treatment.
Risk Factors and Causes
Many things can lead to aortic aneurysms. These include:
| Risk Factor | Description |
| Age | Aneurysms are more common in people over 65 years old. |
| Smoking | Smoking greatly increases the risk of an aneurysm. |
| Family History | Having a family history of aneurysms raises your risk. |
| High Blood Pressure | Hypertension can make the aortic walls weak, leading to aneurysms. |
Knowing these risk factors helps in early detection and prevention. Understanding the causes and risks of aortic aneurysms shows why EVAR is vital in preventing rupture and improving patient outcomes.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s key to know the symptoms and how doctors check for aortic aneurysms. Many people with this condition don’t feel sick until it’s serious. Knowing the signs can help you get medical help fast.
Symptoms of Aortic Aneurysms
Some people might feel pain in their belly or back. They might also feel a pulsing near their navel. These signs can mean you have an aortic aneurysm, which is more common in older folks or those with heart disease in their family. It’s very important to notice these signs and get medical help right away.
The symptoms can differ based on where and how big the aneurysm is. For example, a chest aneurysm might cause pain or trouble swallowing. An aneurysm in the belly might cause pain or a noticeable lump.
Diagnostic Procedures
Tests are very important to find aneurysms and see how they’re growing. Here are some common tests:
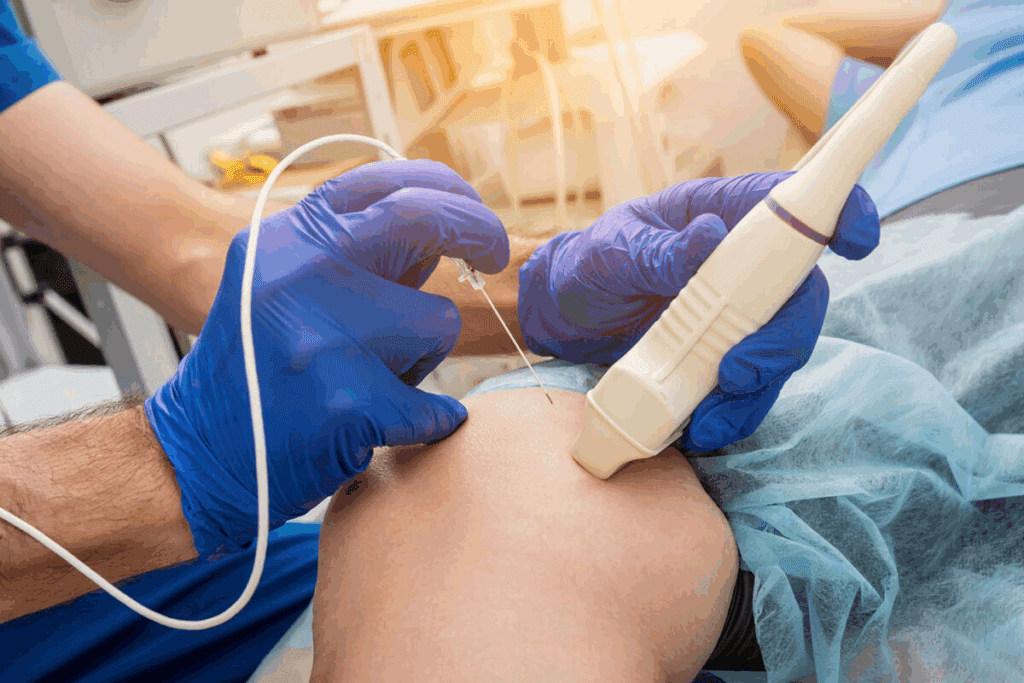
- Ultrasound: A test that uses sound waves to see the aorta.
- CT scans: Give detailed pictures of the aorta to check the aneurysm’s size and shape.
- MRI: Makes detailed pictures of the aorta without using harmful radiation.
Regular check-ups are very important for people at high risk. Knowing about symptoms and tests helps get the right treatment. This could include Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR) or other treatments.
| Diagnostic Method | Description | Benefits |
| Ultrasound | Non-invasive imaging using sound waves | No radiation, quick results |
| CT Scan | Detailed cross-sectional images | High accuracy, assesses size and shape |
| MRI | Detailed images without radiation | No radiation, excellent soft tissue detail |
Treatment Options for Aortic Aneurysms
Managing aortic aneurysms involves different methods, from watching them closely to surgery. The right treatment depends on the aneurysm’s size, how fast it grows, and the patient’s health.
Conservative Management
For smaller aneurysms, conservative management is often the best choice. This means regular checks with tests like ultrasound or CT scans. We also work on controlling risk factors like high blood pressure through lifestyle changes and medicine.
Traditional Open Surgery
Traditional open surgery is a more serious option. It involves replacing the weak part of the aorta with a graft. This method needs a big cut and takes longer to recover from. A study in the Journal of Vascular Surgery says it’s a reliable and effective treatment, even with newer methods.
“Open surgical repair remains a durable and effective treatment for abdominal aortic aneurysms, despite the advent of endovascular techniques.”
Journal of Vascular Surgery
Minimally Invasive Approaches
Minimally invasive approaches, like Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR), are alternatives to open surgery. EVAR uses a stent-graft inserted through small cuts in the groin, guided by imaging. It’s great for those at high risk for open surgery or wanting a quicker recovery.
Understanding the various treatments for aortic aneurysms is key to making good choices. By looking at the pros and cons of each, patients and doctors can pick the best option.
What Is Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR)?
EVAR, or Endovascular Aneurysm Repair, is a new way to treat aortic aneurysms without open surgery. This method is less invasive and safer, with fewer complications. It’s a big change in how aortic aneurysms are managed.
Definition and Basic Principles
EVAR is a procedure that uses a stent-graft to treat aortic aneurysms. It’s done through small cuts in the groin. The stent-graft is placed under imaging guidance to support the aortic wall.
This method stops the aneurysm from getting bigger or bursting. It does this by creating a new path for blood flow. This path goes around the weak part of the aorta.
Comparison to Traditional Open Surgery
EVAR has big advantages over traditional open surgery. The main one is the shorter recovery time. EVAR is less invasive, leading to less damage and fewer problems. This means patients can get back to their lives sooner.
Another big plus is the lower risk of complications. Open surgery needs a big cut and can cause a lot of blood loss. EVAR, on the other hand, uses small cuts. This lowers the chance of infection and other issues after surgery.
Knowing the differences between EVAR and open surgery helps patients make better choices. EVAR offers a safer, less invasive option. It leads to quicker recovery and better results.
Candidates for EVAR Procedure
EVAR is not for everyone. Finding the right candidates is key to its success. Doctors look at many things to decide if EVAR is right, like the aneurysm’s size and shape, the patient’s health, and their blood vessel anatomy.
Ideal Patient Profiles
People with big aneurysms that haven’t burst are often good candidates for EVAR. The size and shape of the aneurysm matter a lot. Also, those with complex blood vessel anatomy or health issues might choose EVAR over open surgery.
Contraindications and Limitations
Even though EVAR is helpful, it’s not for everyone. Some contraindications and limitations exist. For example, those with complex aneurysm shapes or big health problems might not qualify. Special stent-grafts are sometimes needed.
Doctors carefully check these factors to find the best fit for EVAR. This way, patients get the right treatment for their needs.
The EVAR Procedure Step by Step
The EVAR procedure is done in a controlled setting with advanced imaging. It’s a detailed treatment for aortic aneurysms. It includes several steps, from getting ready to placing the stent-graft.
Pre-Operative Preparation
Before starting the EVAR procedure, a lot of preparation is needed. This includes CT scans to plan where the stent-graft will go. We look at the aneurysm’s size, shape, and where it is, and the nearby vessels.
Patients also have to do various tests to check their health. These tests might include blood work, electrocardiograms, and more.
Anesthesia Options
The EVAR procedure can be done under different anesthetics. General anesthesia is common, making sure the patient is comfortable and pain-free.
In some cases, regional anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation might be used. The choice depends on the patient’s needs and medical history.
Stent-Graft Insertion and Deployment
The main part of the EVAR procedure is putting in and expanding the stent-graft. This is done through small cuts in the groin. The stent-graft is guided to the aneurysm using real-time imaging.
Once in place, the stent-graft is expanded to strengthen the aortic wall. We then check its position and function using imaging.
| Step | Description | Key Considerations |
| 1. Pre-Operative Preparation | Imaging studies and patient evaluation | Accurate sizing and planning |
| 2. Anesthesia Administration | General, regional, or local anesthesia | Patient comfort and safety |
| 3. Stent-Graft Insertion | Guiding the stent-graft to the aneurysm site | Precision and real-time imaging |
| 4. Stent-Graft Deployment | Expanding the stent-graft to reinforce the aortic wall | Correct positioning and function |
Understanding the EVAR procedure helps patients see its complexity and precision. It’s a key treatment for aortic aneurysms.
Advanced EVAR Technologies and Techniques
The field of Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR) is seeing big changes. New technologies and techniques are coming out. These changes help improve patient care and make EVAR available to more people with complex aortic aneurysms.
Fenestrated and Branched Stent-Grafts
Fenestrated and branched stent-grafts are big steps forward in EVAR. They help treat aneurysms near important blood vessels. These vessels were once hard to reach with standard EVAR.
Fenestrated stent-grafts have special openings that match up with the blood vessels. This lets blood flow through while treating the aneurysm.
Branched stent-grafts go even further. They have branches that fit into the blood vessels. This creates a strong seal and keeps blood flowing to vital organs.
| Feature | Fenestrated Stent-Grafts | Branched Stent-Grafts |
| Design Purpose | To treat aneurysms near critical branches | To treat complex aneurysms involving multiple branches |
| Key Benefit | Preserves blood flow to critical branches | Provides a secure seal and maintains organ perfusion |
Endologix Nellix System
The Endologix Nellix System is another new idea in EVAR. It uses polymer-filled bags to seal the aneurysm. This might lower the chance of leaks and make the treatment more effective.
This system aims to create a more lasting repair. It fills the aneurysm with a safe material. This could reduce the risk of future problems.
Other Innovative Approaches
There are more new ideas in EVAR too. These include better stent-graft materials, ways to deploy them, and new imaging tools. These advancements could lead to even better treatments for aortic aneurysms.
As these technologies get better, we’ll see safer and more effective treatments. This means better care and results for patients with aortic aneurysms.
Benefits of Endovascular Aneurysm Repair
EVAR has changed how we treat aortic aneurysms. It brings many benefits to patients. These advantages improve patient outcomes in several ways.
Reduced Recovery Time
One big plus of EVAR is the reduced recovery time. It’s a less invasive method than open surgery. This means patients can leave the hospital sooner and get back to their lives faster.
They often feel less pain and can start doing things they love again sooner.
Lower Complication Rates
EVAR has lower complication rates than open surgery. It doesn’t require big cuts or clamping the aorta. This makes it safer for many patients, including those with health issues.
Quality of Life Improvements
After EVAR, patients see big improvements in their quality of life. They can get back to their normal life quickly with less pain. This lets them stay independent and keep up with their daily activities without a long break.
Knowing these benefits helps patients and doctors choose the best treatment for aortic aneurysms. EVAR is a great option for many patients because of its advantages.
Potential Risks and Complications
EVAR is a groundbreaking treatment for aortic aneurysms. Yet, it’s important to know the risks and complications it may have. Every medical treatment has its challenges, and EVAR is no exception.
Short-Term Complications
Short-term issues after EVAR might include:
- Bleeding or hematoma at the access site
- Infection at the incision sites
- Reactions to the contrast dye used during imaging
- Cardiovascular events such as myocardial infarction or stroke
These problems, though rare, need careful watching and handling. We stress the need for close post-procedure care to reduce these risks.
Long-Term Concerns
Long-term worries with EVAR focus on the stent-graft’s durability and changes in the aneurysm. Key issues include:
- Stent-graft migration or component separation
- Aneurysm growth or rupture despite the stent-graft
- The need for ongoing surveillance to monitor the stent-graft and aneurysm sac
It’s vital for both patients and healthcare providers to understand these long-term concerns. This ensures proper follow-up and management.
Endoleaks and Other EVAR-Specific Issues
Endoleaks are a major complication of EVAR. They occur when blood leaks into the aneurysm sac despite the stent-graft. There are different types, each needing specific management.
- Type I endoleak: Perigraft leakage at the proximal or distal attachment sites.
- Type II endoleak: Retrograde flow from branches of the aorta.
- Type III endoleak: Leakage through tears or holes in the graft.
We emphasize the need for regular follow-up imaging to catch and manage these issues quickly.
In summary, EVAR is a highly effective treatment for aortic aneurysms. Yet, it comes with risks. By understanding these complications, we can manage and reduce them. This ensures the best outcomes for our patients.
Recovery and Post-Procedure Care
Recovery after EVAR is a series of steps to help you heal well and avoid problems. We’ll guide you through this important time. It’s key to know about post-procedure care for a good outcome.
Hospital Stay Duration
Most patients start moving around within 24 hours after EVAR. You’ll usually stay in the hospital for 2 to 3 days. During this time, doctors watch your health closely and handle any immediate issues.
The time you stay in the hospital can change based on your needs and any complications. Our team checks if you’re ready to go home based on your health, any side effects, and if you can follow care instructions.
Activity Restrictions
It’s important to avoid heavy lifting, bending, and hard work for weeks after EVAR. This helps your body heal and lowers the risk of problems with the stent-graft or the aneurysm.
We suggest you start with light activities a few days to a week after EVAR. Then, you can slowly do more as your doctor advises.
Follow-Up Imaging and Monitoring
Follow-up care is key after EVAR. Tests like CT scans are used to check the stent-graft, look for leaks, and see how well the procedure worked.
The timing of these tests depends on your health and your doctor’s plan. Usually, you’ll have tests at 1, 6, and 12 months after the procedure, and then every year.
| Follow-Up Timeline | Imaging Test | Purpose |
| 1 Month | CT Scan | Initial assessment of stent-graft position and detection of any complications |
| 6 Months | CT Scan | Monitoring for leaks and stent-graft movement |
| 12 Months | CT Scan | Annual check-up of stent-graft performance and aneurysm size |
Following the recommended follow-up schedule and care instructions helps you recover well after EVAR. This reduces the chance of complications.
Conclusion
We’ve looked into Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR), a new way to treat aortic aneurysms. This method is less invasive and has changed how we treat these conditions. It shows how EVAR improves patient care.
EVAR is a big step forward in treating aortic aneurysms. It’s a safer choice than open surgery. Patients recover faster and face fewer complications. As technology gets better, EVAR will keep getting safer and more effective.
In short, EVAR is a game-changer for treating aortic aneurysms. It’s important for doctors to know about EVAR’s benefits and risks. With ongoing research, EVAR’s future looks bright, with better devices and techniques on the horizon.
The evar conclusion is clear: it’s a key treatment for aortic aneurysms. It’s a safe, effective option that’s changing the game. An endovascular aneurysm repair summary shows its value in saving lives and reducing serious health issues.
FAQ
What is Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR)?
EVAR is a minimally invasive surgery for aortic aneurysms. It uses a stent-graft inserted through small incisions, usually in the groin.
How does EVAR compare to traditional open surgery?
EVAR is better than open surgery in many ways. It means less pain, quicker recovery, and fewer complications.
Who is a suitable candidate for EVAR?
The best candidates for EVAR have large aneurysms that need treatment but haven’t ruptured yet. They also need to have the right blood vessel anatomy.
What are the risks and possible complications of EVAR?
Short-term risks include bleeding, infection, and reactions to dye. Long-term, there’s worry about the stent-graft’s durability and endoleaks.
What is the recovery process like after EVAR?
Recovery from EVAR is faster than open surgery. Most patients go home in a few days. They’re told to avoid heavy lifting and hard activities for weeks.
What are the benefits of EVAR in treating aortic aneurysms?
EVAR has big advantages. It leads to quicker recovery, fewer complications, and a better quality of life.
How is EVAR performed?
EVAR involves several steps. First, there’s preparation before surgery. Then, the stent-graft is inserted and deployed under imaging guidance.
What advancements have been made in EVAR technology?
New EVAR tech includes fenestrated and branched stent-grafts. The Endologix Nellix System is also a recent innovation, improving outcomes and making EVAR available to more people.
What is an endoleak, and how is it related to EVAR?
An endoleak is a complication of EVAR. It happens when blood leaks into the aneurysm sac around the stent-graft. It needs monitoring and might need further treatment.
How does EVAR impact the quality of life for patients with aortic aneurysms?
EVAR greatly improves life for those with aortic aneurysms. It reduces rupture risk, lowers pain, and allows for a quicker return to daily activities.
What diagnostic procedures are used to detect aortic aneurysms?
Ultrasound and CT scans are key in finding aneurysms. They help determine the size and growth rate of the aneurysm.
What are the symptoms of an aortic aneurysm?
Many aneurysms don’t show symptoms until they rupture. Some people might feel abdominal or back pain.
Reference
- Saratzis, A., Patel, S. R., & Powell, J. T. (2022). Management of abdominal aortic aneurysm. BMJ, 376, e069958. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35172936