Discovering that your ovary is enlarged can be worrying. But, most causes are not serious. At Liv Hospital, we focus on detailed checks and care tailored to your needs.enlarged ovary treatmentPolycystic Ovary Syndrome Infertility Treatment
Conditions like PCOS, ovarian cysts, and endometriosis can cause ovarian enlargement. Knowing the reasons and treatment choices is key to managing it well.
We combine top-notch skills and care that puts you first. This way, we offer the right diagnosis and treatment plans for your ovarian health.
Key Takeaways
- Ovarian enlargement can be caused by various conditions, including PCOS and ovarian cysts.
- Understanding the underlying cause is critical for effective treatment.
- Liv Hospital offers thorough evaluation and care tailored to your needs for ovarian health concerns.
- Treatment options depend on the cause and how severe the symptoms are.
- Getting an accurate diagnosis is vital for managing ovarian enlargement.
Understanding Ovarian Enlargement
Ovarian enlargement is a topic that needs a closer look. The ovaries are key to the female body, making eggs and hormones. These hormones control the menstrual cycle and help with pregnancy.
Normal Ovary Size and Function
The ovaries are about the size of an almond. They sit on either side of the uterus and are vital for reproductive health. Inside the ovaries, follicles hold eggs. Each month, one follicle releases an egg in a process called ovulation.
The ovaries also make important hormones like estrogen and progesterone. These hormones manage the menstrual cycle, support pregnancy, and keep reproductive health in check. Normal ovary size is typically between 2.5 to 5 cm in length, 1.5 to 3 cm in width, and 0.6 to 1.5 cm in thickness.
When Is an Ovary Considered Enlarged?
An ovary is considered enlarged if it’s bigger than usual. This can happen for many reasons, like cysts, tumors, or hormonal imbalances. Ovarian enlargement is often detected during a pelvic examination or through imaging tests like ultrasound.
To understand ovarian enlargement better, let’s look at some key factors:
Cause | Description | Common Symptoms |
Functional Ovarian Cysts | Fluid-filled sacs on the ovary, often resolving on their own | Pelvic pain, bloating |
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) | Hormonal disorder causing multiple cysts on the ovaries | Irregular periods, excess hair growth |
Endometriosis | Tissue similar to uterine lining growing outside the uterus | Pelvic pain, heavy bleeding |
Research shows that PCOS is a common cause of ovarian enlargement. According to Zuliani et al. (2020), women with PCOS are more likely to have enlarged ovaries. This highlights the need to understand the causes and effects of ovarian enlargement.
Common Causes of Enlarged Ovaries
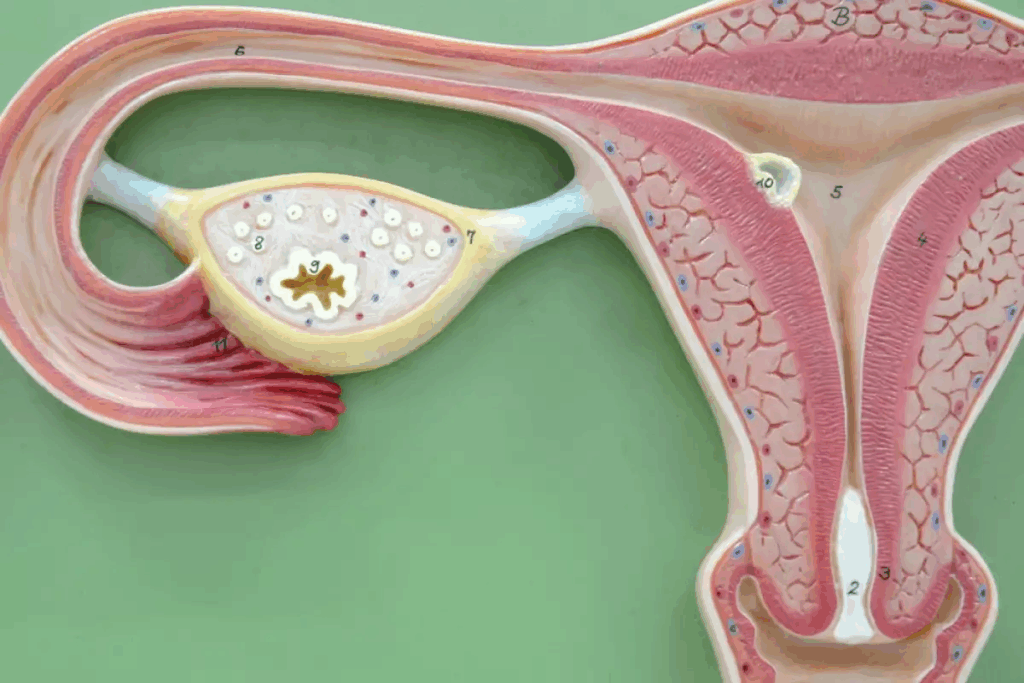
Enlarged ovaries can come from many conditions. Each has its own signs and health effects. Knowing these causes helps in managing and treating them.
Functional Ovarian Cysts
Functional ovarian cysts are a common reason for enlarged ovaries. These cysts appear during the menstrual cycle and are usually harmless. They can make the ovary bigger, causing pain and other symptoms.
- Characteristics: Typically fluid-filled sacs within the ovary.
- Symptoms: Pelvic pain, bloating, and menstrual irregularities.
- Treatment: Often resolve on their own; hormonal contraceptives may be prescribed to prevent new cysts.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a hormonal disorder that can cause ovarian enlargement. It is marked by multiple cysts on the ovaries, irregular menstrual cycles, and hormonal imbalance.
Key Features of PCOS:
- Hormonal imbalance, with too much androgen.
- Irregular or absent menstrual periods.
- Multiple small cysts on the ovaries.
Endometriosis and Endometriomas
Endometriosis is a condition where tissue like the uterus lining grows outside of it. This leads to inflammation and scarring. Endometriomas, or chocolate cysts, are a type of ovarian cyst linked to endometriosis.
Characteristics and Symptoms:
- Painful periods and pelvic pain.
- Infertility and ovarian enlargement.
- Cysts filled with old blood, giving them a characteristic appearance.
Ovarian Tumors (Benign and Malignant)
Ovarian tumors can also cause ovarian enlargement. These tumors can be benign or malignant and vary in their characteristics and impact on health.
Types and Considerations:
- Benign Tumors: Often removable with surgery, with a good prognosis.
- Malignant Tumors: Require prompt treatment, often involving surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy.
Why Is One Ovary Bigger Than the Other?
Differences in ovary size can come from many reasons. These include normal variations and serious health issues. If one ovary is bigger, it’s important to know why.
Normal Anatomical Variations
Often, one ovary being slightly larger is just normal. Ovaries can vary in size due to their function and cycle. For example:
- The dominant ovary, which releases an egg, might be a bit bigger.
- Hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle can also affect size.
These differences are usually not a worry. They might be found during a pelvic exam or imaging for other reasons.
Pathological Causes of Asymmetrical Ovaries
But, some cases of uneven ovaries can be serious. It’s key to find out why to get the right treatment. Some possible serious reasons include:
- Ovarian Cysts: These cysts can make one ovary bigger.
- Endometriosis: Cysts related to endometriosis can also cause uneven sizes.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS can sometimes make one ovary bigger.
- Ovarian Tumors: Both good and bad tumors can make an ovary larger.
If you’re worried about your ovaries or have symptoms like pelvic pain, see a doctor. They can check you out and help.
Recognizing Symptoms of Enlarged Ovaries
It’s important to know the signs of an enlarged ovary to get help quickly. Enlarged ovaries can cause different symptoms. Some symptoms mean you should see a doctor right away.
Common Physical Symptoms
Women with enlarged ovaries might feel a few things. These include:
- Pelvic pain or discomfort, which can range from mild to severe
- Bloating or swelling in the abdominal area
- Abdominal tenderness or pain during physical activity
- Frequent urination due to pressure on the bladder
- Discomfort during intercourse
These symptoms can really affect your daily life. It’s key to see them as signs of ovarian enlargement.
Menstrual Irregularities
Enlarged ovaries can also cause changes in your menstrual cycle. These changes might include:
- Irregular periods or amenorrhea (absence of menstruation)
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Intermenstrual bleeding or spotting
These changes can be upsetting. They might show hormonal imbalances linked to ovarian enlargement.
When Symptoms Indicate an Emergency
Some symptoms mean you need to get help fast, like ovarian torsion. Look out for:
- Severe, sudden pelvic pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
- Rapid heartbeat
If you see these signs, get medical help right away.
Symptom | Possible Indication |
Pelvic pain | Ovarian enlargement or torsion |
Menstrual irregularities | Hormonal imbalance or ovarian cysts |
Bloating and swelling | Fluid retention or ovarian cysts |
Knowing these symptoms and what they might mean can help you get diagnosed and treated sooner. This can improve your health if you have enlarged ovaries.
Should I Be Worried About an Enlarged Ovary?
Feeling worried about an enlarged ovary is normal. It can be caused by many things, from simple to serious health issues. Knowing the risks and when to see a doctor is important for your health.
Risk Factors for Serious Conditions
Some things can make an enlarged ovary more serious. These include:
- Family history of ovarian cancer or other reproductive health issues
- Age, with risks increasing after the age of 50
- Previous history of ovarian cysts or tumors
- Genetic predisposition, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations
Knowing these risk factors helps you and your doctor make better decisions about your care.
Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Enlargement
Not all enlarged ovaries are a problem. Sometimes, it’s just a normal change, like during ovulation. But, if it keeps getting bigger or is really big, you should see a doctor.
Cause | Characteristics | Concern Level |
Functional Ovarian Cysts | Typically resolve on their own, may cause pelvic pain | Low to Moderate |
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) | Associated with hormonal imbalance, multiple small cysts | Moderate |
Ovarian Tumors | Can be benign or malignant, may cause persistent pain or discomfort | High |
Knowing why your ovary is enlarged helps figure out what to do next.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Some symptoms need quick doctor visits. If you have any of these, go to the doctor right away:
- Severe pelvic pain that comes on suddenly
- Vaginal bleeding that is heavy or accompanied by other symptoms
- Dizziness or fainting
- Abdominal swelling or distension
These signs might mean something serious like ovarian torsion, which is an emergency.
Staying informed about your reproductive health is key. If you’re worried about an enlarged ovary, talk to your doctor to find out what to do next.
Diagnostic Procedures for Ovarian Enlargement
To find out why an ovary is enlarged, we need to do a detailed check. We use different tools to see why the ovary is big and what’s causing it.
Pelvic Examination
A pelvic exam is the first thing we do to check for big ovaries. A doctor will look at the ovaries and see if they’re tender or have any problems.
Ultrasound Imaging of Enlarged Ovaries
Ultrasound imaging is key for looking at big ovaries. It shows how big the ovaries are, if there are cysts or tumors, and how much blood they get.
Blood Tests and Hormone Panels
Blood tests, like hormone panels, help find out if hormones are out of balance. This can help figure out if the ovaries are big because of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).
Advanced Imaging Techniques
Sometimes, we need advanced imaging techniques like MRI or CT scans. These give us clear pictures of the ovaries and the area around them.
Diagnostic Procedure | Purpose |
Pelvic Examination | Assess ovary size and tenderness |
Ultrasound Imaging | Evaluate ovary size, cysts, and blood flow |
Blood Tests | Check for hormonal imbalances |
Advanced Imaging | Detailed evaluation of ovaries and surrounding tissues |
Enlarged Ovary Treatment: Comprehensives Approaches
Treating an enlarged ovary requires a detailed plan based on the latest research and care for the patient. The right treatment varies by the cause, how severe the symptoms are, and the patient’s health. It’s not a one-size-fits-all solution.
Watchful Waiting Approach
For some, a watchful waiting approach is suggested if the enlarged ovary is due to a functional cyst. This means keeping an eye on it with regular ultrasounds. We tell patients to come back in 6-12 weeks for another ultrasound to see if the cyst has gone away.
Medical Interventions
Many women need medical interventions to manage symptoms and find the cause of ovarian enlargement. Hormonal birth control pills can help control menstrual cycles and prevent new cysts. For Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), medications like metformin can help with insulin resistance and hormone balance.
Pain management is key. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help with the pain from ovarian cysts or other enlargement causes.
Surgical Options
If other treatments don’t work or the diagnosis is unclear, surgical options might be needed. Laparoscopic surgery is a less invasive way to remove cysts or other issues while keeping as much of the ovary as possible. In serious cases, like ovarian torsion or big cysts, more surgery might be required.
Dealing with an enlarged ovary can be tough. Our healthcare team is dedicated to giving personalized care and support. We make sure patients get the best treatment for their specific situation.
Managing PCOS-Related Ovarian Enlargement
Managing PCOS-related ovarian enlargement needs a mix of medical treatments and lifestyle changes. PCOS is a complex disorder that affects women differently. So, personalized care is key.
Regulating Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal birth control is often used to manage PCOS symptoms. Birth control pills can help regulate menstrual cycles and lower androgen levels. This can reduce the size of ovarian cysts. It’s important to talk to a healthcare provider about the best hormonal contraceptive.
For women who can’t or don’t want to use hormonal birth control, anti-androgen medications might be an option. These can help with symptoms like hirsutism and acne, which are common in PCOS.
Improving Insulin Sensitivity
Insulin-sensitizing medications, like metformin, are used to treat insulin resistance in PCOS. These medications improve insulin sensitivity, which can lower androgen production and help with ovulation. It’s important to monitor and adjust the dosage with a healthcare provider’s guidance.
Lifestyle Changes for PCOS Management
Lifestyle changes are important for managing PCOS symptoms, including ovarian enlargement. Dietary changes and regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity, reduce weight, and regulate menstrual cycles. A balanced diet low in processed foods and sugars and high in fiber and nutrients is recommended.
- Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce the risk of complications
- Limiting processed foods and sugars
By combining lifestyle changes with medical treatments, women with PCOS can manage their symptoms better. This can improve their quality of life. We encourage women to work with their healthcare providers to create a personalized treatment plan.
Treating Functional Ovarian Cysts
Functional ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs on the ovaries. They can cause discomfort but usually don’t need aggressive treatment. These cysts are common and often go away in a few menstrual cycles.
Natural Resolution Timeline
Most of these cysts are benign and will go away on their own. They usually disappear in 2-3 menstrual cycles. It’s important to watch your symptoms and tell your healthcare provider about any changes.
Pain Management Strategies
Women with pain from these cysts have several options. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help. Sometimes, stronger pain meds are needed.
Hormonal Contraceptives for Prevention
Hormonal contraceptives can prevent new cysts and reduce the chance of them coming back. Birth control pills, patches, or hormonal IUDs help control hormones that lead to cysts.
Follow-up Ultrasound Monitoring
Regular ultrasounds are key to watching the cysts. They help doctors see if the cyst is getting smaller or if more action is needed. How often you need an ultrasound depends on the cyst’s size and your health.
Here’s a quick look at how to manage functional ovarian cysts:
Management Strategy | Description | Benefits |
Watchful Waiting | Monitoring the cyst for resolution without immediate intervention | Avoids unnecessary medical procedures |
Pain Management | Using medication to alleviate discomfort associated with the cyst | Improves quality of life during cyst resolution |
Hormonal Contraceptives | Using birth control to prevent new cysts and regulate hormones | Reduces recurrence risk and regulates menstrual cycle |
Addressing Endometriosis-Related Ovarian Enlargement
Ovarian enlargement due to endometriosis is a complex issue. It needs a detailed approach to manage and treat. Endometriosis is a chronic condition where endometrial tissue grows outside the uterus. This leads to inflammation, scarring, and adhesions.
When endometriosis affects the ovaries, it can cause endometriomas, or chocolate cysts. These cysts can make the ovaries enlarge significantly.
Hormonal Suppression Therapies
Hormonal suppression therapies are key in managing ovarian enlargement due to endometriosis. These therapies aim to reduce endometrial tissue growth by changing hormonal balances. Common therapies include:
- Combined Oral Contraceptives (COCs): COCs are used to manage symptoms by stopping ovulation and reducing menstrual flow.
- Progestins: Progestins, like dienogest, can shrink endometriomas and ease symptoms.
- Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) Agonists: GnRH agonists lower estrogen levels, reducing endometrioma size and symptoms.
These hormonal therapies can help manage symptoms and shrink ovarian enlargement. But, they may have side effects and aren’t right for everyone.
Surgical Management of Endometriomas
Surgery is often needed for large endometriomas or when cancer is suspected. The main surgery is:
- Laparoscopic Ovarian Cystectomy: This surgery removes the endometrioma while keeping as much ovarian tissue as possible.
Surgery can relieve symptoms and is needed for diagnosis and treatment. But, it carries risks, like damage to ovarian reserve.
Long-term Management Strategies
Managing endometriosis-related ovarian enlargement long-term involves medical therapy, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgery. Important strategies include:
Management Strategy | Description | Benefits |
Hormonal Therapy | Use of hormonal contraceptives or GnRH agonists to suppress endometriosis activity | Reduces symptoms, can decrease size of endometriomas |
Lifestyle Modifications | Dietary changes, exercise, stress management | Improves overall well-being, may reduce symptoms |
Surgical Intervention | Laparoscopic surgery to remove endometriomas | Provides symptom relief, can be diagnostic |
Effective management of endometriosis-related ovarian enlargement needs a personalized approach. It should consider the individual’s symptoms, reproductive goals, and health. By combining medical therapies, lifestyle changes, and, when needed, surgery, we can improve life quality for those with this condition.
Emergency Treatment for Ovarian Torsion
Ovarian torsion is a serious condition where the ovary twists. This can cut off blood supply, causing severe pain. If not treated quickly, it can lead to permanent damage.
Recognizing Torsion Symptoms
Symptoms of ovarian torsion include sudden, severe pelvic pain and nausea. Vomiting and fever can also occur. The pain may feel constant or come and go, sometimes spreading to the back or thigh.
Key symptoms to watch for:
- Sudden onset of severe pelvic pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
- Abdominal tenderness
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is the main treatment for ovarian torsion. The goal is to untwist the ovary and restore blood flow. Sometimes, if the ovary is too damaged, it must be removed. Laparoscopic surgery is often chosen because it’s less invasive and allows for faster recovery.
It’s vital to get surgery quickly to avoid long-term damage and protect fertility.
Recovery and Follow-up Care
After surgery, patients usually stay in the hospital for a short time. Managing pain is key during recovery. Follow-up visits are important to check on healing and discuss any needed treatments.
Post-surgery care includes:
- Pain management through medication
- Monitoring for complications
- Follow-up ultrasound to check ovarian health
Knowing the symptoms of ovarian torsion and seeking immediate medical help can save ovaries. This can also help preserve reproductive health.
Conclusion: Living with and Managing Ovarian Health
Understanding and managing ovarian health is key for overall well-being. We’ve looked at causes, symptoms, and treatment options for enlarged ovaries. Recognizing signs and getting medical help is important.
Managing ovarian health needs a full approach. This includes medical care, lifestyle changes, and regular checks. It’s vital to follow treatment plans and talk openly with doctors.
By actively managing ovarian health, people can lower the risk of problems. We urge readers to focus on their health and get medical help if needed.
Good ovarian health management needs teamwork between individuals and doctors. Together, we can achieve better health outcomes and support well-being.
FAQ
What is considered a normal ovary size, and when is it considered enlarged?
A normal ovary is about 3-4 cm long, 2-3 cm wide, and 1-2 cm thick. If it’s bigger, it might be due to cysts, PCOS, or tumors.
What are the common causes of ovarian enlargement?
Causes include cysts, PCOS, endometriosis, and tumors. Each has its own signs and treatment.
Why is one ovary sometimes bigger than the other?
It could be due to normal differences or problems like cysts or tumors. Always check with a doctor.
What are the symptoms of an enlarged ovary?
Symptoms include pelvic pain, bloating, and irregular periods. Severe cases might have sudden pain, nausea, and vomiting.
Should I be worried about an enlarged ovary?
While it might be okay, it could also mean serious issues like cancer or torsion. Getting checked is key.
How is ovarian enlargement diagnosed?
Diagnosis includes a pelvic exam, ultrasound, blood tests, and sometimes MRI or CT scans. These tools find the cause.
What are the treatment options for an enlarged ovary?
Treatment varies by cause. It can be waiting for cysts, medical help for PCOS, or surgery for tumors. The goal is to fix the problem and ease symptoms.
How is PCOS-related ovarian enlargement managed?
Management includes birth control, medications for insulin resistance, and lifestyle changes. These help symptoms and improve health.
What is the treatment approach for functional ovarian cysts?
For most, waiting is best. Pain relief and birth control might be needed. Ultrasound checks ensure the cyst goes away.
How is endometriosis-related ovarian enlargement treated?
Treatment includes hormones to reduce symptoms, surgery for cysts, and long-term plans to control symptoms and prevent recurrence.
What is the emergency treatment for ovarian torsion?
Ovarian torsion needs immediate surgery to save the ovary. Quick action is vital to avoid damage.
Can lifestyle changes help manage ovarian health?
Yes, a healthy weight, balanced diet, and exercise can help with conditions like PCOS and improve health.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Enlarged Ovary: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10047373/



































