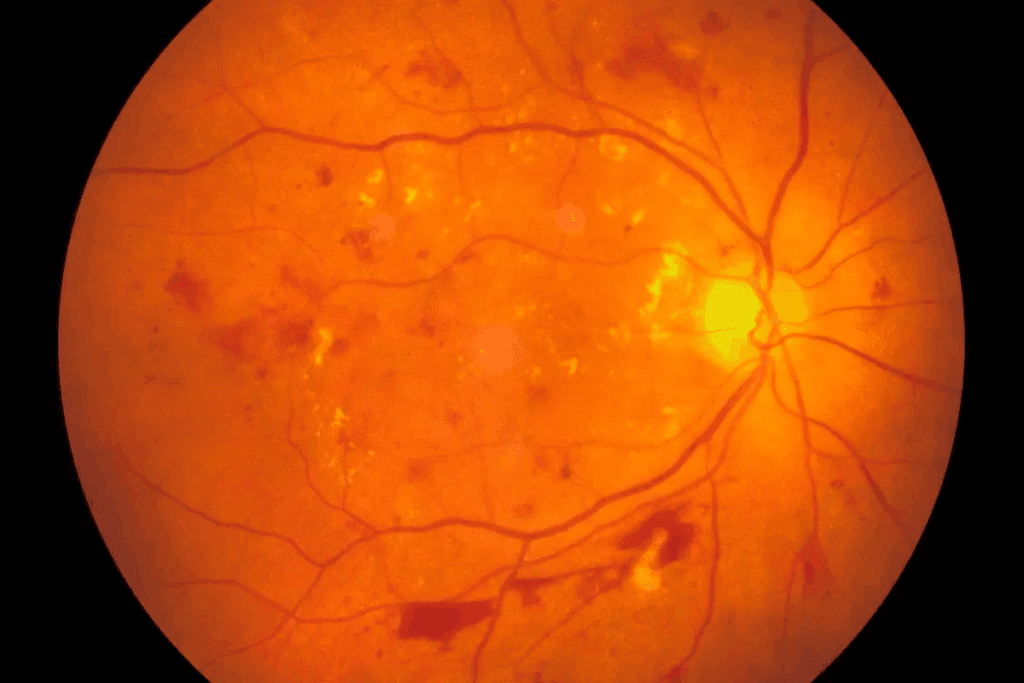
Epiretinal membrane (ERM) is a condition where a thin, semitranslucent layer forms on the retina’s inner surface. This pathologic fibrocellular tissue is created by the proliferation of myofibroblastic cells at the vitreoretinal interface.Learn about the epiretinal membrane eye condition. This essential guide explains ERM, its symptoms, and treatment options.
ERM affects millions worldwide, mostly those over 50. It can develop silently or cause distorted or blurred central vision. This can greatly affect a person’s quality of life.
At Liv Hospital, we focus on international medical excellence and patient care. We ensure proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plans for ERM. Knowing what ERM is and its impact on vision is key to managing it effectively.
Key Takeaways
- ERM is a condition characterized by the formation of a thin layer on the retina’s inner surface.
- It is a common condition among people over 50 years old.
- ERM can cause distorted or blurred central vision.
- Proper diagnosis is essential for effective management.
- Liv Hospital offers personalized treatment plans for ERM.
Understanding Epiretinal Membrane (ERM)
Epiretinal membrane (ERM) affects the retina, mainly the macula, and vision. We’ll look into what ERM is and how it changes the retina’s structure.
What Is an Epiretinal Membrane?
An epiretinal membrane is a thin layer of tissue on the retina’s surface, over the macula. It can cause visual disturbances, like blurry vision and distorted images.
ERM often comes with age. It can lead to macular pucker, where the membrane pulls the retina, causing wrinkles or bulges. Knowing about ERM’s causes and effects helps find the right treatment.
The Anatomy of the Retina and Macula
The retina is a key part of the eye, essential for seeing. The macula, at the retina’s center, handles central vision and fine details.
The retina has many layers, with ERM forming on the innermost one. The macula, full of photoreceptor cells, is most affected by ERM. This includes:
- Distorted vision
- Blurred central vision
- Difficulty with fine detail
Knowing the retina and macula’s details is key to understanding ERM’s impact on vision. It also helps find the best treatments.
Prevalence and Demographics

It’s important to know who is at risk for Epiretinal Membrane (ERM). This is key for managing the condition well. ERM is a big issue in eye care, mainly for older people.
Age-Related Prevalence
People over 50 are most likely to get ERM. The risk goes up a lot after 75. This shows that age plays a big role in getting ERM.
Age Group | Prevalence Rate
50-59 years |
20.8% |
This table shows how ERM gets more common with age. It’s why older adults need to get their eyes checked often.
Bilateral Occurrence
ERM can happen in one or both eyes. It’s more common for it to happen in both. If it’s in one eye, there’s a good chance it will happen in the other too.
Knowing about the chance of it happening in both eyes is key. We tell patients with ERM in one eye to watch the other closely. This helps catch any problems early.
Causes of Epiretinal Membrane Eye Conditions
Epiretinal Membrane (ERM) can be caused by different factors. These can be divided into idiopathic and secondary causes. Knowing these causes helps in managing and treating ERM.
Idiopathic Causes (Age-Related)
Idiopathic ERM is the most common type. It’s linked to aging. As we get older, the vitreous gel in our eyes changes. This can lead to ERM.
Age-related changes in the vitreous and retina cause idiopathic ERM. These changes can separate the vitreous gel from the retina. This separation can cause traction and lead to a membrane.
Secondary Causes
Secondary ERM is caused by other eye conditions. These include diabetic retinopathy, retinal detachment, and inflammatory eye diseases. These conditions can cause ERM as a complication.
The table below lists some secondary causes of ERM and their characteristics:
Secondary Cause | Description | Relation to ERM |
Diabetic Retinopathy | A complication of diabetes causing damage to the retina | Increased risk of ERM due to retinal damage |
Retinal Detachment | A condition where the retina separates from the underlying tissue | Can lead to ERM formation due to retinal trauma |
Inflammatory Eye Diseases | Conditions causing inflammation within the eye | May contribute to ERM development through inflammatory processes |
It’s important to understand the causes of ERM. This knowledge helps in creating effective treatment plans. By identifying the causes, healthcare providers can offer better care for ERM.
Symptoms and Visual Impact
An epiretinal membrane can change how we see the world. It can make everyday tasks harder. This affects how well we can do things we need to do every day.
Common Symptoms
People with this condition often see things differently. Metamorphopsia makes straight lines look wavy. It also makes objects seem off shape. Another symptom is blurred vision, which makes it hard to read or drive.
Other visual problems include:
- Difficulty with reading and other daily activities due to visual distortion
- Central vision loss or blind spots
- Changes in color perception
Impact on Daily Activities
ERM symptoms can really affect daily life. For example, it can make reading, cooking, or even walking hard. It can also make driving unsafe because of blurred vision or distortions.
Daily Activity | Impact of ERM Symptoms |
Reading | Difficulty due to blurred vision or distortion |
Driving | Compromised ability due to visual disturbances |
Cooking | Challenges in measuring ingredients or seeing cooking instructions clearly |
It’s important to understand how ERM symptoms affect daily life. Knowing these challenges helps people get the right medical care. It also helps them adjust their daily routines to deal with ERM’s effects.
Diagnosing Epiretinal Membrane
We use a detailed process to find Epiretinal Membrane. This helps us understand how serious it is and how it affects vision.
Clinical Examination
The first step is a thorough clinical check-up. An eye doctor checks how well you can see and looks for signs of ERM. This check is key to spotting symptoms of Epiretinal Membrane.
Key parts of the check-up are:
- Testing how sharp your vision is
- Looking closely at the retina and macula with a special tool
- Using an Amsler grid to check for vision distortions
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
OCT is a test that doesn’t hurt and is very important for finding ERM. It takes clear pictures of the retina. This lets doctors see the layers of the retina and any membranes on the surface.
OCT helps in:
- Seeing if there’s an Epiretinal Membrane
- Checking how thick and healthy the retina is
- Finding out how bad the retinal distortion or swelling is
Other Diagnostic Tests
Other tests might be used too. These help us learn more about your condition and make sure it’s not something else. For example, fluorescein angiography checks the blood vessels in the retina for any problems.
Diagnostic Test | Purpose |
Clinical Examination | Check how well you can see and the health of your retina |
OCT Imaging | See the layers of the retina and find ERM |
Fluorescein Angiography | Look at the health of the blood vessels in the retina |
By looking at all these test results, we can accurately say if you have Epiretinal Membrane. Then, we can plan the best treatment for you.
Conservative Management Approaches
Not all cases of epiretinal membrane need surgery. Sometimes, just watching and waiting can help. This choice depends on how bad the symptoms are and how they affect your daily life.
Monitoring and When It’s Appropriate
Watching the condition closely is a first step in conservative management. This is best for those with mild symptoms or no symptoms at all. Regular eye exams are key to seeing if the condition is getting worse.
Your eye doctor might use tools like Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) during these exams. This helps check how thick the membrane is and its effect on the retina.
Managing Visual Symptoms Without Surgery
For those with vision problems from epiretinal membrane, there are ways to help without surgery. Correcting vision with glasses or contact lenses can sometimes make things better. Also, low vision aids can help those with big vision problems.
Living a healthy lifestyle is also important. Eating foods full of antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids helps your eyes. Wearing sunglasses with UV protection is also good for eye health.
By following these steps, many people with epiretinal membrane can manage their symptoms well. They can keep their quality of life high without needing surgery right away.
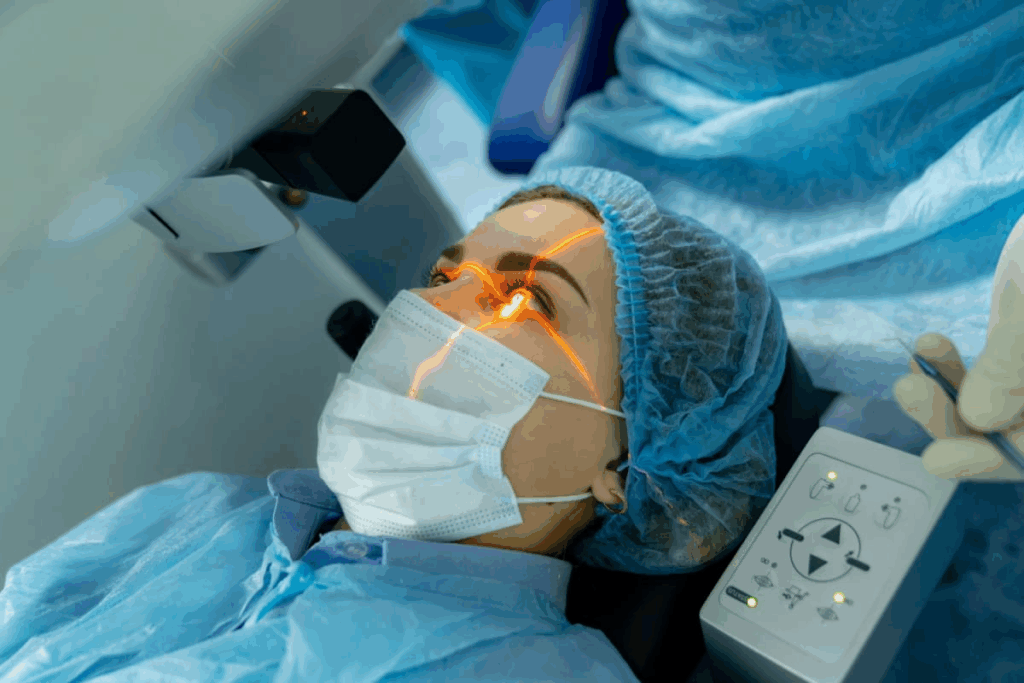
Surgical Treatment Options
When other treatments don’t work, surgery might be needed for Epiretinal Membrane. Choosing surgery is a big decision. It’s important to know about the different surgical options.
Vitrectomy with Membrane Peeling
The main surgery for Epiretinal Membrane is vitrectomy with membrane peeling. This surgery removes the vitreous gel and the membrane causing the problem. It aims to reduce the pressure on the retina and improve vision.
The surgery is done under local anesthesia. The goal is to remove the membrane that’s causing the vision issues.
During the surgery, we use special tools to carefully remove the membrane from the retina. This process needs a lot of skill to avoid harming the retina. The success of the surgery depends on how severe the membrane is and the eye’s health.
Potential Complications
While vitrectomy with membrane peeling is usually safe, there are risks. These include retinal detachment, cataract, and endophthalmitis. We take many precautions to lower these risks. Our experienced surgeons will talk about these risks before the surgery.
It’s important to know that, like any surgery, ERM surgery has risks. But for many, the benefits of better vision are worth it. We make sure our patients are well-informed and comfortable with their choice.
Newer Surgical Approaches
New techniques are being developed for treating Epiretinal Membrane. These include using intraoperative OCT for better vision during surgery and minimally invasive vitrectomy for faster recovery. We keep up with these new methods to offer the best treatments.
We are always working to improve our surgical techniques. Our goal is to give our patients the best results. Whether it’s traditional vitrectomy or new methods, we aim to improve vision and quality of life for those with Epiretinal Membrane.
Living with Epiretinal Membrane
Living with ERM means adjusting to how it affects your daily life and vision. It’s important to understand its impact.
Adapting to Visual Changes
ERM can make your vision blurry and images distorted. To cope, check your vision regularly and change your daily habits. Small changes, like better lighting or magnifying glasses, can help a lot.
A top eye doctor says, “People with ERM can get help from low vision programs. These programs teach them to use their vision better.”
“Rehabilitation programs can greatly improve life for those with ERM. They teach how to use what vision they have left.”
Follow-up Care and Monitoring
Seeing your eye doctor regularly is key to managing ERM. This means going for scheduled check-ups to watch how the condition changes. Your doctor will use OCT scans to check your retina and look for fluid or distortion.
To get the best care, follow these steps:
- Write down your symptoms and any vision changes to talk about at your visits.
- Follow your doctor’s advice on when to come back and what treatments you need.
- Ask about your condition and treatment options to stay up to date.
By being proactive in your care and staying informed, you can handle ERM’s challenges. This helps keep your eyes healthy.
Conclusion
Understanding epiretinal membrane eye conditions is key to managing them. Knowing the causes, symptoms, and how they affect vision helps people make better choices for their care.
There are different ways to handle ERM. Some methods involve watching the condition and treating symptoms without surgery. Others, like vitrectomy with membrane peeling, aim to improve vision and reduce symptoms.
At our institution, we offer caring and expert care for those with ERM. Our team works with patients to create treatment plans that meet their specific needs. This approach helps ensure the best possible outcomes.
In summary, managing ERM needs a complete approach that includes understanding, diagnosis, and treatment. By giving people the knowledge and support they need, we help them deal with ERM’s challenges. This is important for keeping vision sharp and maintaining eye health.
FAQ
What is an epiretinal membrane (ERM) in ophthalmology?
An epiretinal membrane is a condition where a layer of fibrous tissue forms on the retina’s surface. It often affects the macula. This can cause visual distortion and blurred vision.
How serious is epiretinal membrane?
The severity of ERM varies. Some people may have mild symptoms, while others face significant visual impairment. Untreated ERM can lead to severe vision problems.
What are the causes of epiretinal membrane?
ERM can be caused by age-related changes or secondary to other ocular conditions. This includes retinal detachment, trauma, or inflammation.
What are the symptoms of epiretinal membrane?
Common symptoms include visual distortion, blurred vision, and difficulty with daily activities. This includes reading or driving.
How is epiretinal membrane diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a clinical examination and Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT). Other diagnostic tests confirm the presence and severity of ERM.
What are the treatment options for epiretinal membrane?
Treatment options include conservative management and surgical intervention. Surgical options include vitrectomy with membrane peeling.
What is vitrectomy with membrane peeling?
Vitrectomy with membrane peeling is a surgical procedure. It removes the vitreous gel and peels away the epiretinal membrane from the retina. This aims to restore vision.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6643061/)








