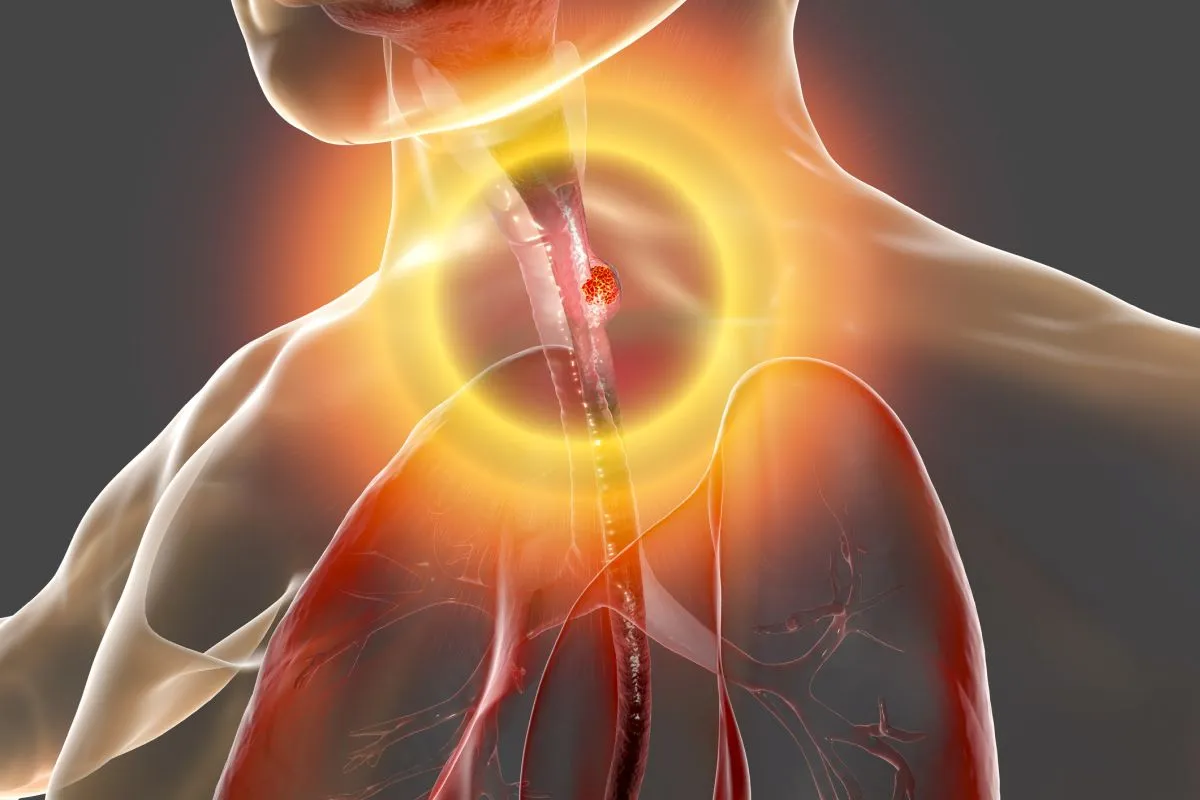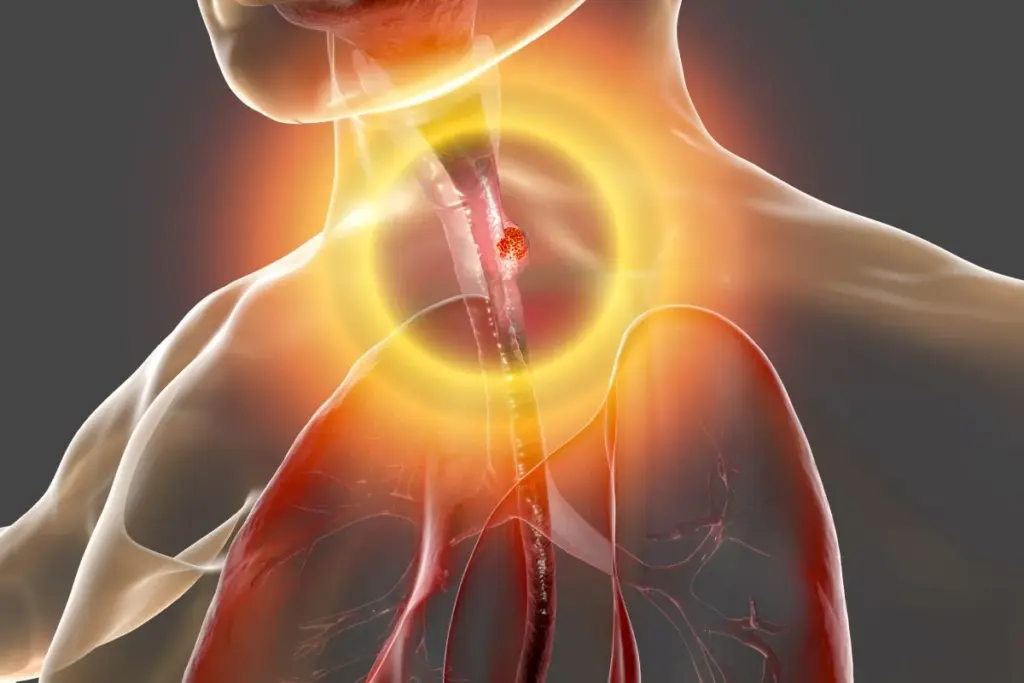
Esophagus Warning Signs: Early Cancer Alerts is a serious issue with a tough prognosis. It’s often not caught until it’s too late. Early detection is key to better outcomes and survival chances. The signs can be tricky to spot because they often seem like usual digestive problems.
Common symptoms include trouble swallowing, chest pain, and unexpected weight loss. For example, trouble swallowing (dysphagia) is a common first sign. It feels like food is stuck in your throat or chest. You can find more about these symptoms and their meaning on a page about signs and symptoms of esophageal cancer.
Key Takeaways
- Esophageal cancer often goes undetected until its later stages.
- Early detection is key for better patient outcomes.
- Common symptoms include trouble swallowing, chest pain, and unexplained weight loss.
- Trouble swallowing is often one of the first noticeable symptoms.
- Knowing these warning signs can help catch the disease early.
The Esophagus: Structure and Function
The esophagus is a muscular tube that helps us swallow food. It carries food from our throat to our stomach. This happens through a process called peristalsis.
Anatomy of the Esophagus
The esophagus is about 10 inches long. It has mucous membranes that make swallowing easier. Its muscles are made up of circular and longitudinal layers. These layers work together to push food down towards the stomach.
At each end, the esophagus has two sphincters. The upper esophageal sphincter (UES) is at the top. It connects the esophagus to the throat. The lower esophageal sphincter (LES) is at the bottom, linking it to the stomach. These sphincters help control food movement and prevent it from coming back up.
|
Layer |
Description |
Function |
|---|---|---|
|
Mucosa |
Lined with mucous membranes |
Lubricates food |
|
Submucosa |
Contains blood vessels and nerves |
Supports mucosa, aids in food passage |
|
Muscularis |
Composed of circular and longitudinal muscles |
Facilitates peristalsis |
|
Adventitia |
Outermost layer, connects to surrounding tissues |
Anchors the esophagus |
Role in the Digestive System
The esophagus is key in the digestive system. It moves food from the mouth to the stomach. This is thanks to esophageal motility, which makes the muscles work together.
This ensures food is swallowed right and gets to the stomach easily. So, the esophagus is more than just a tube. It actively helps the digestive process work smoothly.
Types of Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer comes in several forms, each with its own traits. Knowing these differences is key for the right diagnosis and treatment. We’ll look at the main types, including adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, and the rare ones.
Adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma starts in the glandular cells of the esophagus. It’s the most common type in Western countries, like the U.S. It’s often linked to Barrett’s esophagus, where the esophagus lining changes to look like the intestine’s.
Factors that raise the risk of adenocarcinoma include GERD, obesity, and smoking. Its symptoms, like trouble swallowing and chest pain, can be similar to other cancers.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma comes from the squamous cells lining the esophagus. It’s more common worldwide and linked to tobacco and alcohol. It can happen anywhere in the esophagus, but often in the upper and middle parts.
Smoking, heavy drinking, and certain diets increase the risk of squamous cell carcinoma. Its symptoms are similar to adenocarcinoma, making diagnosis tough.
Rare Types of Esophageal Cancer
Adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the most common, but there are rarer types. These include small cell carcinoma, sarcomas, and lymphomas. Each rare type has unique features and may need different treatments.
Rare types are often found late because their symptoms are not clear and getting a tissue sample is hard. Treatment plans are tailored based on the cancer type, stage, and the patient’s health.
Epidemiology of Esophagus Cancer in the United States
It’s important to understand the spread of esophagus cancer in the U.S. This cancer is not as common as others but is serious because it’s hard to treat and is getting more common.
Prevalence and Incidence Rates
Esophageal cancer makes up about 1% of all cancers in the U.S. The number of cases is going up, mainly for a type called adenocarcinoma. The latest numbers show about 4.5 cases per 100,000 people each year.
Incidence trends show a big jump in adenocarcinoma, mostly in white men. Rates for another type, squamous cell carcinoma, have stayed the same or gone down a bit.
Demographic Patterns
Esophageal cancer shows big differences in who gets it. Men are more likely to get it than women, with a 3:1 ratio for adenocarcinoma. African Americans have higher rates of squamous cell carcinoma.
Age is also key, as the risk goes up after 50.
Survival Statistics
Survival rates for esophageal cancer are low, mainly because it’s often caught late. The 5-year survival rate is about 20%. But, survival chances change a lot based on when it’s found.
Early detection and treatment are key to better survival rates. Knowing these trends helps us find better ways to help patients.
Risk Factors That Increase Likelihood of Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer risk comes from genetics, lifestyle, and environment. Knowing these factors helps spot who’s at higher risk. This can lead to better care and prevention.
Lifestyle Factors
Our lifestyle choices greatly affect esophageal cancer risk. Key factors include:
- Smoking: Tobacco is a big risk for squamous cell carcinoma.
- Diet: Eating less fruits and veggies and more processed meat can raise risk.
- Alcohol Consumption: Drinking too much alcohol increases squamous cell carcinoma risk.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese raises adenocarcinoma risk.
|
Lifestyle Factor |
Type of Esophageal Cancer |
Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
|
Smoking |
Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
High |
|
Diet (low in fruits and vegetables) |
Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
Moderate |
|
Alcohol Consumption |
Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
High |
|
Obesity |
Adenocarcinoma |
Moderate to High |
Medical Conditions
Some medical conditions raise esophageal cancer risk. These include:
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Chronic GERD is a big risk for adenocarcinoma.
- Barrett’s Esophagus: This condition can lead to adenocarcinoma.
- Esophageal Strictures: Narrowing of the esophagus increases risk.
Knowing these risk factors helps us lower our risk. If symptoms appear, seek medical help.
Dysphagia: The Most Common Warning Sign
Dysphagia, or trouble swallowing, is a key warning sign for esophageal cancer. It makes eating hard and affects daily life. We’ll look at how swallowing problems get worse, how eating habits change, and the impact on quality of life.
Progressive Nature of Swallowing Difficulties
Dysphagia in esophageal cancer gets worse slowly. At first, it’s hard to swallow solid foods. Later, it’s hard to swallow liquids too. This shows the disease is getting worse.
Changes in Swallowing Patterns
As cancer grows, swallowing patterns change. People might swallow more or food gets stuck. These signs start small but get bigger as the disease gets worse.
Impact on Eating Habits
Dysphagia makes eating hard. People might skip foods or eat alone. This can lead to not getting enough nutrients and losing weight, making health problems worse.
|
Stage of Dysphagia |
Symptoms |
Impact on Eating Habits |
|---|---|---|
|
Early |
Difficulty swallowing solid foods |
Avoiding certain solid foods |
|
Moderate |
Difficulty with softer foods, occasional food sticking |
Changing diet to softer foods, eating slowly |
|
Advanced |
Difficulty swallowing liquids, frequent food sticking |
Significant weight loss, nutritional deficiencies, avoiding eating in public |
Chest Pain and Heartburn Symptoms
Esophageal cancer can show up as chest pain and heartburn. These symptoms are often mistaken for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It’s important to know the difference to catch cancer early and treat it right.
Distinguishing Cancer Pain from GERD
Chest pain from esophageal cancer can feel like GERD. But, cancer pain lasts longer and doesn’t get better with usual GERD treatments. Knowing these differences helps spot warning signs.
Key differences between cancer pain and GERD:
- Pain that doesn’t go away with treatment
- Pain that gets worse over time
- Pain with other symptoms like trouble swallowing
Persistent Heartburn as a Warning Sign
Heartburn is common in GERD, but it can also mean esophageal cancer if it doesn’t go away. Stomach acid can cause long-term damage and lead to cancer.
Watching how often and how bad heartburn is can tell us if it’s serious.
Pain Characteristics and Patterns
The way chest pain and heartburn feel and when they happen can tell us a lot. Pain after eating or when lying down might be GERD. But, if you also lose weight or have trouble swallowing, it could be cancer.
Looking at these signs can help figure out what’s wrong:
- When and why pain happens
- How bad and long-lasting symptoms are
- Changes in swallowing or appetite
Unexplained Weight Loss in Esophageal Cancer
Weight loss without a clear reason is a common and concerning symptom among patients with esophageal cancer. This symptom not only affects the patient’s quality of life but also complicates the management of the disease.
Mechanisms Behind Cancer-Related Weight Loss
Cancer-related weight loss, also known as cachexia, is a multifactorial syndrome characterized by the loss of muscle and fat mass. In esophageal cancer, several mechanisms contribute to this condition, including reduced oral intake due to dysphagia, metabolic changes induced by the tumor, and systemic inflammation.
The tumor can alter the body’s metabolism, increasing the resting energy expenditure and changing the way the body uses nutrients. This metabolic shift can lead to the breakdown of muscle and fat tissues, even when the patient’s caloric intake is adequate.
Quantifying Significant Weight Loss
Significant weight loss is typically defined as a loss of more than 5% of body weight over the past 6-12 months. In the context of esophageal cancer, quantifying weight loss is critical for assessing the severity of the condition and planning appropriate nutritional interventions.
Healthcare providers use various tools, including patient history and anthropometric measurements, to monitor weight changes. Early detection of significant weight loss allows for timely intervention, which can improve patient outcomes.
Nutritional Challenges
Patients with esophageal cancer often face significant nutritional challenges due to the symptoms of their disease and the side effects of treatment. Dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, is a common symptom that can limit oral intake, making it difficult for patients to consume enough calories and nutrients.
Nutritional support is a critical component of esophageal cancer care. We work with patients to develop personalized nutrition plans that may include dietary modifications, nutritional supplements, or alternative feeding methods, such as enteral nutrition, to ensure they receive the necessary nutrients.
Addressing nutritional challenges is essential for maintaining the patient’s strength, supporting their overall health, and optimizing their response to treatment.
Respiratory and Voice Changes
Changes in breathing and voice can hint at esophageal cancer. As the disease grows, it can harm nearby areas, causing problems.
Chronic Cough Development
A long-lasting cough might mean esophageal cancer is advanced. This cough could be from the tumor irritating nearby tissues or from food or liquids getting into the airway.
“A persistent cough is not just a minor issue; it can be a sign of a more serious underlying condition,” says highlighting the importance of medical evaluation for persistent respiratory symptoms.
Hoarseness and Voice Alterations
Hoarseness or voice changes can happen if the cancer hits the nerves controlling the vocal cords. This symptom is worrying if it lasts or comes with other signs.
Changes in voice can really affect someone’s life. So, finding and treating it early is key.
Aspiration Concerns
Aspiration, or breathing in food or liquids, is a big worry with esophageal cancer. It can cause pneumonia or other lung infections, making the disease worse.
- Aspiration can happen if the tumor blocks the esophagus.
- It might also come from the cancer messing with the swallowing process.
Knowing these risks shows why quick medical help is needed if symptoms don’t go away or get worse.
Gastrointestinal Disturbances as Warning Signs
It’s important to know about gastrointestinal disturbances. They can be early signs of esophageal cancer. These issues can really affect a person’s life quality. If caught early, they can lead to better treatment and diagnosis.
Vomiting After Meals
Vomiting after meals is a symptom that needs attention. In esophageal cancer, it’s because a tumor blocks food from moving down. This makes it hard for food to pass through.
Characteristics of vomiting associated with esophageal cancer include:
- Occurring shortly after eating
- Presence of undigested food
- Possible presence of blood
Food Regurgitation
Food regurgitation is when food comes back up without nausea or force. This happens when a tumor narrows the esophagus. It makes it hard for food to go down.
The impact of food regurgitation includes:
- Difficulty swallowing
- Sensation of food being stuck
- Potential for aspiration
Changes in Appetite
Changes in appetite, like eating less, can be a sign of esophageal cancer. It might be because eating hurts or the body reacts to the cancer.
Notable aspects of appetite changes include:
- Unintended weight loss
- Early satiety
- Aversion to certain foods
Seeing these signs as warnings for esophageal cancer is key. If you or someone you know has these symptoms, see a doctor. It’s very important.
Fatigue and Systemic Symptoms
Patients with esophageal cancer often feel extremely tired. This is called cancer-related fatigue. It can really affect their life, making them feel both physically and emotionally drained.
Cancer-Related Fatigue Mechanisms
Cancer-related fatigue is a complex issue. It comes from many factors linked to cancer and its treatment. These include the cancer itself, inflammation, metabolic changes, and treatments like chemotherapy and radiation.
The body’s energy balance is disrupted by cancer. This imbalance can make people feel tired. Also, the emotional stress of having cancer can add to feelings of exhaustion.
Anemia and Its Connection to Esophageal Cancer
Anemia is common in esophageal cancer patients. It can be caused by chronic blood loss, poor nutrition, or the cancer’s effect on red blood cell production. Anemia makes fatigue worse because the body doesn’t get enough oxygen.
|
Condition |
Effect on Red Blood Cells |
Impact on Fatigue |
|---|---|---|
|
Anemia |
Reduced red blood cell count or function |
Increased fatigue due to decreased oxygen delivery |
|
Chronic Blood Loss |
Gradual decrease in red blood cells |
Contributes to anemia and increased fatigue |
|
Nutritional Deficiencies |
Insufficient nutrients for red blood cell production |
Can lead to anemia and exacerbate fatigue |
Impact on Daily Functioning
Fatigue from esophageal cancer can make everyday tasks hard. It can also make it hard to do things they enjoy. This affects not just the patients but also their families and caregivers, who may have to change their roles to help.
It’s important to understand and tackle cancer-related fatigue. Healthcare providers can help with this. They can offer advice on nutrition, exercise, and emotional support.
Bleeding Manifestations in Esophagus Cancer
Bleeding is a scary sign of esophageal cancer. It can show up in different ways. Knowing these signs is key to getting help fast.
Hematemesis (Blood in Vomit)
Hematemesis means blood in your vomit. It’s a big warning sign. The blood might look bright red or like coffee grounds. Vomiting blood is a medical emergency that needs quick action.
When cancer in the esophagus bleeds, it can cause hematemesis. The tumor can damage blood vessels, leading to a lot of bleeding. Anyone with hematemesis should get medical help right away.
Melena (Black, Tarry Stools)
Melena is when you have black, tarry stools. It’s a sign of bleeding in the upper GI tract, possibly from esophageal cancer. The blood turns black because it’s digested a bit.
Melena can mean slow bleeding from the esophagus. It’s a sign that the tumor is bleeding. It’s important to find out why you have melena to get the right treatment.
|
Symptom |
Description |
Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|
|
Hematemesis |
Vomiting blood, which may appear bright red or like coffee grounds |
Indicates active bleeding, potentially from esophageal cancer |
|
Melena |
Passage of black, tarry stools |
Suggests upper GI bleeding, possibly due to esophageal cancer |
|
Occult Bleeding |
Hidden bleeding not visible to the naked eye |
Can lead to anemia and other complications if not addressed |
Occult Bleeding and Anemia
Occult bleeding is hidden and not seen easily. In esophageal cancer, it happens when the tumor slowly bleeds. This can cause iron deficiency anemia over time.
Anemia from occult bleeding can make you feel tired, weak, and short of breath. Finding the cause of anemia is important. In esophageal cancer patients, anemia can really affect their health and treatment.
It’s important to know about bleeding signs in esophageal cancer for early detection and treatment. If you or someone you know has symptoms like hematemesis, melena, or anemia signs, getting medical help is key.
Symptom Overlap with Other Conditions
Diagnosing esophageal cancer can be tricky because its symptoms are similar to other conditions. This makes it important to know the unique signs of esophageal cancer.
We will look at how esophageal cancer symptoms can be confused with GERD and esophagitis. We will also talk about what makes them different.
GERD and Esophagitis
GERD and esophagitis share symptoms with esophageal cancer, making diagnosis harder. GERD causes chronic acid reflux, leading to esophagitis. Both can cause heartburn, difficulty swallowing, and chest pain, just like esophageal cancer.
The main difference is in how long symptoms last and get worse. For example, GERD can cause swallowing trouble, but esophageal cancer’s trouble gets worse and lasts longer. A study shows how important it is to check symptoms carefully.
- Persistent heartburn that doesn’t get better with treatment
- Difficulty swallowing that gets worse over time
- Unexplained weight loss
Esophageal Strictures
Esophageal strictures are narrowings of the esophagus, often caused by GERD or cancer. They can cause swallowing trouble. But, the type of stricture and symptoms can tell if it’s caused by cancer or not.
Differentiating Features of Cancer
Esophageal cancer symptoms can look like other conditions, but there are clues to tell them apart. These include symptoms that get worse over time, significant weight loss, and feeling very tired.
- Progressive dysphagia
- Significant unintentional weight loss
- Persistent pain or discomfort
Knowing these clues is key to catching cancer early. We stress the need for a detailed medical check-up for anyone with ongoing or worsening symptoms.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Knowing the red flag symptoms of esophageal cancer is key to better treatment. It’s vital to spot these signs early to get medical help fast.
Red Flag Symptoms Requiring Urgent Care
Some symptoms mean you need to see a doctor right away. These include severe trouble swallowing and signs of bleeding like blood in vomit or dark stools.
Persistent Symptoms That Warrant Evaluation
Not all symptoms need urgent care, but some should not be ignored. Unexplained weight loss, a chronic cough, or hoarseness are signs to see a doctor. They could mean esophageal cancer or another serious issue.
Communicating Effectively with Healthcare Providers
Talking clearly about your symptoms is important when you see a doctor. Keeping a journal of your symptoms can help doctors understand your situation better.
|
Symptom |
Description |
Action |
|---|---|---|
|
Severe Dysphagia |
Difficulty swallowing that worsens over time |
Seek urgent medical care |
|
Bleeding Manifestations |
Blood in vomit or black, tarry stools |
Seek immediate medical attention |
|
Unexplained Weight Loss |
Significant weight loss without a clear reason |
Schedule a medical evaluation |
Knowing when to go to the doctor can save lives. Spotting red flag symptoms and talking well with doctors can lead to quick diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnostic Pathway for Suspected Esophageal Cancer
Diagnosing esophageal cancer involves several steps. It starts with an initial check and moves to more detailed tests. We’ll explain each step and why they’re important in finding out if you have esophageal cancer.
Initial Evaluation and Physical Examination
The first step is a detailed medical history and physical check. We look for symptoms like trouble swallowing, weight loss, and chest pain. These signs might point to esophageal cancer.
During the physical exam, we search for any signs that could mean esophageal cancer. While this exam can’t confirm cancer, it helps us decide what tests to do next.
Imaging Studies
Imaging tests are key in finding and understanding esophageal cancer. We use different methods to see the esophagus and nearby areas.
- Endoscopy: This lets us see inside the esophagus and take tissue samples for tests.
- Barium Swallow: An X-ray that uses barium to show the esophagus’s shape and find any problems.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: Gives detailed pictures of the esophagus and nearby areas, helping us see the tumor’s size and spread.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan: Shows where cancer might have spread by looking at metabolic activity.
|
Imaging Modality |
Purpose |
Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
|
Endoscopy |
Direct visualization and biopsy |
Tumor presence, mucosal abnormalities |
|
Barium Swallow |
Structural assessment |
Strictures, filling defects |
|
CT Scan |
Tumor sizing and spread assessment |
Tumor size, lymph node involvement |
|
PET Scan |
Metabolic activity assessment |
Cancer spread to lymph nodes or distant sites |
Staging Process
After finding esophageal cancer, we stage it to know how far it has spread. Staging looks at the tumor’s size, where it is, and if it has spread to lymph nodes or other parts of the body. The TNM system is often used for this.
Knowing the cancer’s stage is vital for choosing the right treatment and understanding your outlook. We use imaging, endoscopy, and biopsy results to accurately stage the cancer.
Multidisciplinary Treatment Approaches
Managing esophageal cancer needs a team effort. This includes surgery, radiation, and other treatments. A detailed plan that brings together different medical fields is key. It aims to give patients the best care possible.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is a main way to treat esophageal cancer. It tries to remove the tumor and parts of the esophagus. Surgical interventions depend on the cancer’s stage, location, and the patient’s health.
- Esophagectomy: Surgical removal of part or all of the esophagus.
- Minimally invasive surgery: Techniques that reduce recovery time and scarring.
Radiation and Chemotherapy
Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are often used with surgery or as main treatments. Radiation kills cancer cells with high-energy rays. Chemotherapy uses drugs to target cancer cells in the body.
|
Treatment Modality |
Description |
Application |
|---|---|---|
|
External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT) |
Delivers radiation from outside the body |
Used to treat tumors and relieve symptoms |
|
Chemotherapy |
Uses drugs to kill cancer cells |
Can be used before or after surgery, or as a primary treatment |
|
Brachytherapy |
Places radioactive material directly into or near the tumor |
Used for localized treatment, often in combination with EBRT |
Targeted Therapies
Targeted therapies aim to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. For esophageal cancer, these treatments are used in advanced cases or with other treatments.
Palliative Care Options
Palliative care helps with symptoms and stress of serious illnesses like esophageal cancer. It aims to improve life quality for patients and their families.
- Symptom management: Controlling pain, nausea, and other symptoms.
- Nutritional support: Ensuring adequate nutrition despite swallowing difficulties.
- Emotional and psychological support: Addressing the mental health impacts of cancer.
By using these treatments together, healthcare teams can offer care that meets each patient’s needs.
Conclusion
It’s important to know the warning signs of esophageal cancer early. We talked about symptoms like trouble swallowing, chest pain, unexpected weight loss, and stomach issues. These signs might mean you have esophageal cancer.
Spotting these signs early can really help. If you notice any of these symptoms, see a doctor right away. This can greatly improve your treatment options.
We all need to stay informed about esophageal cancer. Talking openly with doctors is key to getting the right care. Let’s all take care of our health and watch out for any risks.
FAQ
What are the most common warning signs of esophageal cancer?
Warning signs include trouble swallowing, chest pain, and heartburn. Also, unexplained weight loss and vomiting after meals are signs.
What is dysphagia, and how is it related to esophageal cancer?
Dysphagia is trouble swallowing. In esophageal cancer, it gets worse, making it hard to swallow food or liquids.
How does esophageal cancer affect a person’s eating habits?
It changes how you swallow. Patients might avoid certain foods or feel pain while eating. This affects their nutrition.
What is the difference between adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma?
Adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are two types of esophageal cancer. They start in different parts of the esophagus and have different risk factors.
What are the risk factors for developing esophageal cancer?
Risk factors include smoking and drinking alcohol. Also, GERD and some genetic conditions can increase your risk.
How is esophageal cancer diagnosed?
Diagnosis starts with an initial evaluation and physical exam. Imaging like endoscopy and CT scans are used. Staging shows how far the cancer has spread.
What are the treatment options for esophageal cancer?
Treatments include surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Targeted therapies and palliative care are also options, based on the cancer’s stage and type.
Can esophageal cancer be prevented?
While not fully preventable, you can lower your risk. Quit smoking and manage GERD to reduce your risk.
How does esophageal cancer impact daily functioning?
It causes fatigue and nutritional deficiencies. These symptoms affect your daily life and quality of life.
What is the significance of unexplained weight loss in esophageal cancer?
Unexplained weight loss is a warning sign. It shows the cancer is affecting your body’s ability to maintain weight.
How does esophageal cancer cause bleeding manifestations?
Bleeding can happen when the tumor erodes into blood vessels. This leads to blood in vomit or black stools, causing anemia.
What is the role of the esophageal sphincter in swallowing?
The esophageal sphincter controls food passage into the esophagus. It prevents reflux, which is key for normal swallowing.
How does esophageal stricture relate to esophageal cancer?
An esophageal stricture is a narrowing caused by cancer or treatment. It leads to swallowing troubles and dysphagia.
When should someone seek medical attention for symptoms that could indicate esophageal cancer?
Seek medical help for persistent or severe symptoms like dysphagia, chest pain, or unexplained weight loss.
References
• American Cancer Society. Signs and Symptoms of Esophageal Cancer. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/esophagus-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/signs-and-symptoms.html
• Medical News Today. Esophageal Cancer: Be Aware of the Early Warning Signs. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/releases/129014
• SEER Training. Signs & Symptoms of Esophageal Cancer. https://training.seer.cancer.gov/ugi/intro/symptoms.html
• National Cancer Institute. Esophageal Cancer. https://www.cancer.gov/pediatric-adult-rare-tumor/rare-tumors/rare-digestive-system-tumors/esophageal
Nature. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.nature.com/articles/6605219