At Liv Hospital, we know how vital Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR) is for treating abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA). EVAR is a new, less invasive way to fix AAA. It’s safer than old-school open surgery.
So, what is EVAR? It uses an EVAR graft to fix the aneurysm. This graft goes inside the aorta. It stops the aneurysm from getting bigger and bursting, saving lives.
We aim to give our patients the best care in a caring environment. We want them to get the best results possible with the EVAR graft procedure.
Key Takeaways
- EVAR stands for Endovascular Aneurysm Repair, a minimally invasive procedure.
- It is used to treat abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA).
- The EVAR graft is a key part of the EVAR procedure.
- EVAR is a safer choice than traditional open surgery.
- Liv Hospital offers advanced vascular surgery techniques like EVAR.
Understanding Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms (AAA)
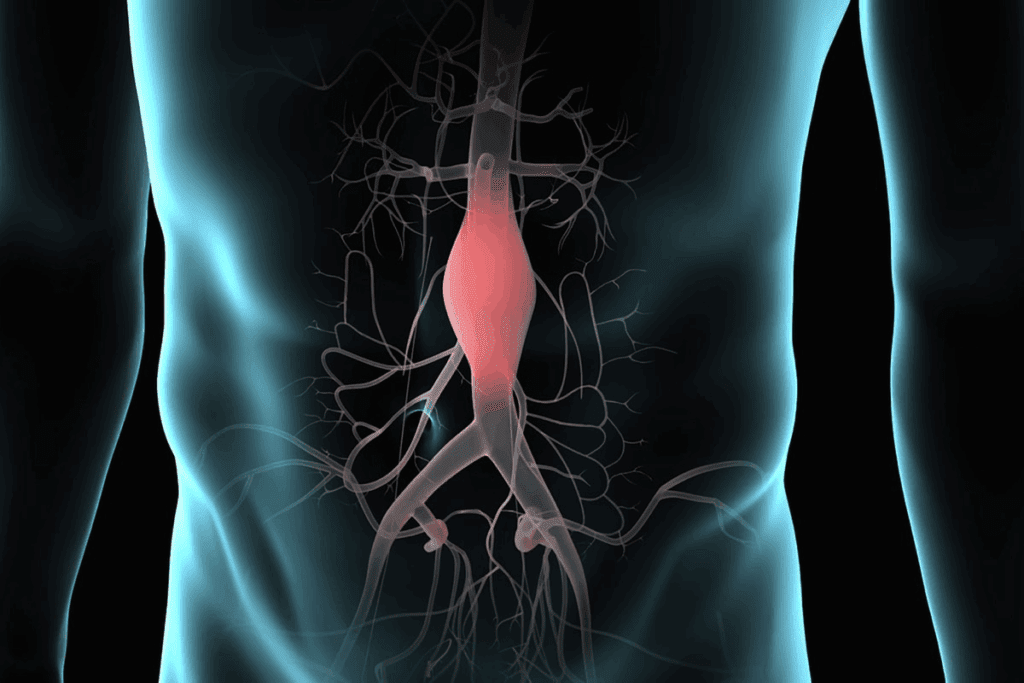
It’s key to know about abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA) to see why EVAR is important in vascular surgery. An AAA happens when the biggest artery in the belly gets too big. This artery is the main one that brings blood to the lower body.
Definition and Pathophysiology of AAA
An abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is when the belly’s main artery gets bigger than normal by more than 50%. This makes the artery weak, causing it to bulge like a balloon. The wall of the artery gets damaged, leading to this bulge.
The growth of AAA is linked to the loss of elastin and a drop in the artery’s strength. Inflammation is a big part of it, with certain proteins breaking down the artery’s wall.
Risk Factors and Prevalence
Many things can make AAA more likely, like age, smoking, high blood pressure, and family history. Men over 65 are more likely to get it. Smoking makes it even more likely, with smokers being 8 times more at risk than non-smokers.
| Risk Factor | Relative Risk |
| Smoking | Up to 8 times higher |
| Hypertension | 1.5-2 times higher |
| Family History | 2-3 times higher |
| Age (>65 years) | Significantly higher |
Knowing these risk factors helps find and treat AAA early. Many places have screening programs to catch it in people at high risk.
The Evolution of EVAR in Vascular Medicine
EVAR has changed vascular surgery by giving a new way to fix AAAs without open surgery. This change has made treating abdominal aortic aneurysms safer and faster.
Historical Development of Endovascular Techniques
The idea of endovascular repair started in the 1960s. But, it wasn’t until the 1990s that the first EVAR successes happened. Early innovations in endovascular techniques set the stage for today’s EVAR, thanks to better grafts and delivery systems.
“The introduction of endovascular aneurysm repair has been a game-changer in vascular surgery,” as noted by experts in the field.
“EVAR has transformed the treatment paradigm for AAA, making it safer and less invasive for patients.”
Transition from Open Surgery to Minimally Invasive Approaches
The move to less invasive methods is to lower risks and deaths from AAA repair. Studies show over 75 percent of elective AAA repairs in developed countries use EVAR now. This shows it’s becoming more popular.
There’s been a big move to EVAR because it’s minimally invasive. This means less damage to tissues and faster healing times than open repair. It’s appealing to both doctors and patients.
EVAR offers many benefits. These include shorter hospital stays, less pain after surgery, and treating patients who can’t have open surgery. This makes EVAR a great choice for many.
Decoding the EVAR Medical Abbreviation
In vascular medicine, abbreviations are common. EVAR is a key term, standing for Endovascular Aneurysm Repair. It’s vital to grasp its role in medical practice.
What EVAR Stands For: Endovascular Aneurysm Repair
EVAR means Endovascular Aneurysm Repair. It’s a new way to fix aneurysms, mainly in the abdominal aorta. This method cuts down recovery time and lowers surgery risks.
A study in the Journal of Vascular Surgery shows EVAR is a safer choice for many. It has lower death rates than traditional surgery. This makes it a good option for patients with the right anatomy.
Related Terminology in Vascular Surgery
Knowing EVAR also means understanding related terms. Words like endograft, stent-graft, and endoleak are key in EVAR. An endograft is a stent-graft device that blocks blood flow to the aneurysm.
- Endograft: A device used to repair the aneurysm from within the blood vessel.
- Stent-graft: A type of endograft that combines a stent with a graft to keep the artery open and exclude the aneurysm.
- Endoleak: A complication where blood leaks into the aneurysm sac after EVAR.
Common Usage of “AAA EVAR” in Clinical Settings
“AAA EVAR” is used in clinics for treating Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms (AAA). It’s a well-known term in vascular medicine, showing EVAR’s role in AAA treatment.
“The widespread adoption of EVAR for AAA has transformed the management of this condition, making it less invasive than open surgery.”
— Journal of Vascular Surgery
Experts say “AAA EVAR” is a key term in vascular surgery. It shows the importance of EVAR in treating abdominal aortic aneurysms.
The EVAR Graft: Components and Design
The EVAR graft is key in treating abdominal aortic aneurysms. It’s a less invasive way to stop the aneurysm from bursting. This medical device helps keep the blood flow away from the aneurysm.
Structure and Materials of Modern EVAR Grafts
Today’s EVAR grafts are made from strong, flexible materials. They use synthetic materials like polyester or PTFE. These are chosen for their ability to work well with the body and last long.
The design of EVAR grafts is complex. It includes the main body, limbs, and ways to secure it in place. These parts work together to fit well in the body. This helps prevent leaks and ensures the graft lasts a long time.
Types of EVAR Stents and Stent-Grafts
There are many types of EVAR stents and stent-grafts. Each has its own benefits and is suited for different needs. Some are for simple repairs, while others are for more complex cases.
We use evar stents that can shape to fit the body’s blood vessels. This is important for a good fit and to avoid problems.
Putting in evar vascular stent-grafts needs special tools. These include guidewires, catheters, balloons, and stents. Together, they help place the graft in the right spot and expand it to block the aneurysm.
Understanding EVAR grafts helps us see how complex and detailed endovascular aneurysm repair is. This knowledge is vital for giving the best care to patients having EVAR procedures.
What Is an EVAR Procedure? Step-by-Step Explanation
The EVAR procedure is a big step forward in vascular surgery. It’s a less invasive way to fix abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA). This method is safer and more efficient for patients.
Pre-Operative Assessment and Planning
Before an EVAR procedure, patients get a thorough check-up. We use CT scans and angiograms to see the aneurysm’s size and location. We also look at the patient’s health and any other conditions that might affect the surgery or recovery.
Planning is key for a successful EVAR procedure. We create a 3D model of the aorta using advanced imaging software. This helps us place the stent graft perfectly to block blood flow to the aneurysm.
The EVAR Vascular Procedure Technique
The procedure starts with small incisions in the groin to reach the femoral arteries. We then use a catheter to deploy the stent graft under imaging. The stent graft is placed in the aneurysm, fitting tightly against the aortic walls.
EVAR uses advanced imaging and catheter technology. It’s a complex method that requires skill and precision. The EVAR procedure is a major innovation in treating aneurysms.
Post-Procedure Care and Recovery
After the procedure, patients are watched closely in a recovery unit. We check for any immediate issues and manage pain. Most patients can get back to normal in a few weeks, but they should avoid hard activities for longer.
Regular follow-ups are important for the EVAR procedure’s success. We schedule check-ups and imaging studies to keep an eye on the stent graft. This helps catch any problems early.
Advanced EVAR Techniques for Complex Anatomies
Complex aortic aneurysms need special EVAR techniques. These include fenestrated and branched grafts. These methods help treat cases that were once too risky or not possible.
Fenestrated EVAR (FEVAR) for Juxtarenal Aneurysms
Fenestrated EVAR is a complex method for aneurysms near the renal arteries. It customizes the EVAR graft with precise holes. These holes match the patient’s arteries, ensuring blood flow to important organs.
Key benefits of FEVAR include:
- Ability to treat aneurysms with short or no infrarenal neck
- Preservation of blood flow to renal and visceral arteries
- Reduced risk of type I endoleaks
Branched Endografts and Custom Solutions
Branched endografts are advanced EVAR techniques. They’re great for complex thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms (TAAAs). These grafts have branches that fit the patient’s arteries, ensuring a strong repair.
| Technique | Application | Key Features |
| Fenestrated EVAR | Juxtarenal aneurysms | Custom fenestrations for renal and visceral arteries |
| Branched Endografts | Thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms | Branches for visceral and renal arteries |
These advanced EVAR techniques have greatly improved treatment for complex aortic aneurysms. They offer customized solutions for effective and lasting repairs. This enhances patient care and improves their quality of life.
Benefits and Limitations of EVAR Vascular Surgery
EVAR vascular surgery has changed how we treat abdominal aortic aneurysms. It’s a less invasive option compared to traditional open repair. This has greatly improved patient outcomes and recovery times.
Advantages Over Traditional Open Repair
EVAR has many advantages over traditional open repair. It leads to fewer complications during and after surgery. This is because EVAR is less invasive, causing less damage to tissues and less blood loss.
Key benefits of EVAR include:
- Reduced risk of perioperative complications
- Faster recovery times
- Less invasive, resulting in smaller incisions
- Lower risk of infection compared to open surgery
A study in the Journal of Vascular Surgery found EVAR to be a safe and effective option. It’s a good alternative to open repair for treating abdominal aortic aneurysms.
“The endovascular approach has revolutionized the management of aortic aneurysms, providing a less invasive and potentially safer option for patients.”
| Aspect | EVAR | Open Repair |
| Invasiveness | Minimally invasive | Highly invasive |
| Recovery Time | Faster recovery | Longer recovery |
| Blood Loss | Less blood loss | More significant blood loss |
| Hospital Stay | Shorter hospital stay | Longer hospital stay |
Potential Complications and Considerations
EVAR has many benefits but also some risks. Complications like endoleaks, stent migration, and kidney injury are possible. We must consider these risks when deciding if EVAR is right for a patient.
Studies show EVAR reduces some risks of open surgery but introduces new ones. “The risk of endoleaks and stent migration necessitates long-term surveillance and follow-up care.”
Potential complications of EVAR include:
- Endoleaks
- Stent migration or failure
- Kidney injury or renal complications
- Access site complications
In conclusion, EVAR vascular surgery is a big step forward in treating abdominal aortic aneurysms. It offers benefits and risks that need careful consideration for each patient.
Long-Term Outcomes and Follow-Up After EVAR
Success with EVAR depends on good follow-up care. We stress the need for a detailed plan to watch for problems. This ensures the stent graft works well.
Surveillance Protocols and Imaging
Regular imaging is key to catch issues early. Our plan includes:
- CT scans to check the stent graft and spot endoleaks or migration.
- Duplex ultrasound to check blood flow and look for problems.
- Regular checks to watch for symptoms or signs of trouble.
Imaging is vital for managing EVAR patients long-term. We use the latest imaging to make sure the stent graft is working right. We also catch any issues early.
Managing Endoleaks and Other Long-Term Complications
Endoleaks are a common problem after EVAR. They happen when blood leaks into the aneurysm sac. We sort them into types based on where they come from and handle them differently.
Managing endoleaks and other issues might involve:
- Watching small, symptom-free endoleaks.
- Fixing big or symptom-causing endoleaks with more stenting or embolization.
- Keeping a close eye on stent graft movement or other problems.
Good management of long-term issues needs a team effort. Vascular surgeons, radiologists, and others work together. This ensures our patients get the best care.
Conclusion
We’ve looked into how EVAR changes vascular surgery, mainly for treating abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA). Knowing about EVAR helps patients choose the right treatment.
EVAR has made treating AAA safer and less invasive than open surgery. It uses grafts and stent-grafts to improve results. This means patients recover faster and face fewer complications.
As vascular medicine advances, EVAR’s role in treating complex aneurysms grows. Keeping up with EVAR and AAA treatment news helps patients and doctors get the best results.
The future of EVAR is bright, with new research and ideas to make it better. This means better care and more treatment options for vascular conditions.
FAQ
What does EVAR stand for in vascular surgery?
EVAR stands for Endovascular Aneurysm Repair. It’s a minimally invasive way to treat abdominal aortic aneurysms.
What is an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)?
An abdominal aortic aneurysm is a swelling of the main blood vessel leading from the heart to the abdomen. It can rupture and cause severe bleeding if not treated.
How is EVAR different from open surgery for AAA?
EVAR is a minimally invasive procedure. It uses small incisions in the groin to introduce a graft. Open surgery, on the other hand, requires a large incision in the abdomen.
What is an EVAR graft, and what is its purpose?
An EVAR graft is a stent-graft placed in the aorta. It excludes the aneurysm from blood flow, preventing further expansion and rupture.
What are the benefits of EVAR compared to traditional open repair?
EVAR has several benefits. It offers reduced recovery time, less post-operative pain, and lower risk of complications. These make it a preferred option for many patients.
What are the possible complications of EVAR?
EVAR complications include endoleaks, graft migration, and vascular access issues. These require close surveillance and follow-up.
What is fenestrated EVAR (FEVAR), and when is it used?
Fenestrated EVAR is used for complex aneurysms involving the renal or visceral arteries. It requires a customized graft with fenestrations to accommodate these branches.
How is EVAR performed, and what are the steps involved?
The EVAR procedure starts with a pre-operative assessment. Then, the graft is introduced through the femoral arteries. The stent-graft is deployed, and post-procedure care and recovery follow.
What is the role of surveillance after EVAR?
Surveillance after EVAR is key. It monitors for complications like endoleaks, graft migration, or aneurysm expansion. It ensures the long-term success of the procedure.
Can EVAR be used for all types of abdominal aortic aneurysms?
EVAR is suitable for many patients with AAA. Its applicability depends on the aneurysm’s anatomy. Some cases may need advanced techniques or open surgery.
What is the significance of EVAR in modern vascular surgery?
EVAR has revolutionized treating abdominal aortic aneurysms. It offers a minimally invasive and effective solution. This has improved patient outcomes and reduced morbidity and mortality.
References
- Paravastu, S. C., Jayarajasingam, R., Cottam, R., Palfreyman, S. J., Michaels, J. A., & Thomas, S. M. (2014). Endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, *2014*(1), CD004178. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10799965/