During a stroke, every minute is critical. Patients and families rely on expert care teams for the latest treatments. We focus on providing endovascularthrombectomy (EVT), a key procedure for acute ischemic stroke.
EVT medical abbreviation stands for Endovascular Thrombectomy. It’s a minimally invasive method to treat acute ischemic stroke. It removes blood clots from blocked arteries in the brain. Studies show that combining EVT with medical treatment greatly improves patient outcomes if done quickly.
Key Takeaways
- EVT is a critical treatment for acute ischemic stroke, involving the removal of blood clots from blocked cerebral arteries.
- The procedure is minimally invasive and has been shown to improve patient outcomes when performed promptly.
- Combining EVT with standard medical treatment can significantly enhance recovery chances for stroke patients.
- Timely intervention is critical in stroke treatment, highlighting the need for quick and effective care.
- Our care teams are dedicated to delivering the most advanced treatment options, including EVT, to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Understanding EVT Medical Abbreviation and Its Significance
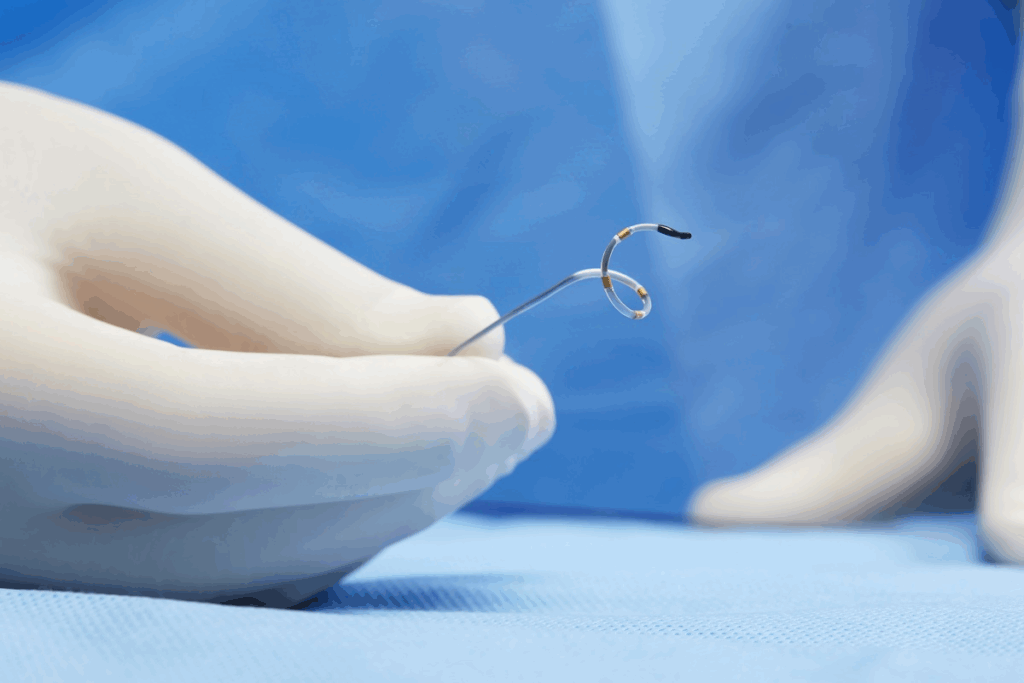
Knowing what EVT means is key for doctors and patients. EVT, or Endovascular Thrombectomy, is a big step forward in treating strokes. It helps patients with large blockages in their brain’s blood vessels. This treatment greatly improves their chances of survival and recovery.
Definition and Full Form of EVT
EVT stands for Endovascular Thrombectomy. It’s a procedure to remove blood clots from the brain’s blood vessels. The name tells us it’s done inside the blood vessels and aims to clear out clots.
This procedure is done without a big cut. Doctors use special tools to go through the blood vessels to find and remove the clot. By doing this, EVT helps keep the brain’s blood flowing, which can lessen the damage from a stroke.
Historical Development of Endovascular Thrombectomy
The idea of EVT has grown a lot over time. At first, treating strokes mainly involved medicine. But with new tech and understanding of strokes, EVT became a key treatment for acute ischemic strokes.
Big steps in EVT include the creation of mechanical devices to remove clots and better imaging tools. These changes have made it possible to help more people with this life-saving treatment.
Common Alternative Terms: Cerebral Thrombectomy and Stroke Thrombectomy
EVT is also called cerebral thrombectomy or stroke thrombectomy. These names are used a lot in medicine. Cerebral thrombectomy points out the brain focus, while stroke thrombectomy shows its role in treating strokes.
| Term | Description | Usage |
| EVT | Endovascular Thrombectomy | General medical terminology |
| Cerebral Thrombectomy | Emphasizes the procedure’s focus on the brain | Neurological and stroke care contexts |
| Stroke Thrombectomy | Highlights its application in stroke treatment | Emergency and stroke care settings |
The Science Behind Ischemic Stroke and Blood Clots
It’s important to know how ischemic stroke and blood clots work. This helps us see why quick medical help is so vital. Ischemic stroke happens when blood flow to the brain is blocked. This blockage is usually caused by blood clots or hardened arteries.
How Cerebral Blood Clots Form
Blood clots in the brain form through a complex process. It involves many clotting factors coming together to make a fibrin clot. Things like atrial fibrillation, atherosclerosis, or blood vessel injury can start this process.
Many factors can affect how these clots form. These include blood flow, the health of the blood vessel walls, and blood disorders.
Impact of Blood Clots on Brain Tissue
When a blood clot blocks a brain blood vessel, it stops oxygen and nutrients from getting to brain cells. This can cause cell damage or death. The damage depends on where and how big the clot is, and how long the brain is without blood.
Brain tissue is very sensitive to lack of blood. The damage can start quickly, within minutes to hours after the stroke begins.
| Time After Stroke Onset | Effects on Brain Tissue |
| 0-4.5 hours | Potential for significant recovery with timely treatment like cerebral thrombectomy |
| 4.5-24 hours | Treatment window may be available depending on individual patient factors |
| Beyond 24 hours | Increasing likelihood of irreversible damage |
Time Sensitivity in Stroke Treatment
Treating ischemic stroke quickly is key. The sooner treatment starts, the less brain damage there will be. Endovascular thrombectomy is a key treatment for some patients. It can help restore blood flow and improve outcomes.
It’s vital for both doctors and patients to understand the urgency and treatment options.
When Is EVT Procedure Recommended?
Choosing to do an EVT procedure depends on several important factors. We look at the patient’s condition carefully. This helps us decide if EVT is right for someone with an acute ischemic stroke.
Patient Selection Criteria
Choosing the right patient for EVT is key. We check a few things. These include how severe the stroke is, how long it’s been happening, and what the scans show.
- Severity of stroke assessed using the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS)
- Time elapsed from when symptoms started
- What scans show, like if a big blood vessel is blocked
Time Window for Effective Treatment (6-24 Hours)
The time when EVT can be done is very important. Studies show EVT can work up to 24 hours after symptoms start. But, the sooner it’s done, the better the results.
Key Timeframes:
- 0-6 hours: Best time for EVT in most cases.
- 6-24 hours: EVT can help some patients, based on what scans show.
Imaging Requirements Before EVT
Imaging is very important before doing EVT. We use special scans to see how big the stroke is and if there’s brain tissue that can be saved.
Scans like CT, MRI, and angiography are used. They help us find out who will likely get better from EVT.
Emergency Assessment Process
The emergency process for EVT is fast. We quickly check the patient’s condition. This includes a neurological exam, scans, and lab tests. It’s important to start treatment quickly.
A team of doctors works together in this process. This way, we make sure we’re considering everything about the patient’s situation.
Step-by-Step Guide to the EVT Procedure
The EVT procedure is a detailed process to remove blood clots from the brain. It’s a minimally invasive surgery that needs a lot of precision and skill from the medical team.
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Before starting the EVT procedure, patients go through a thorough preparation. They receive local anesthesia to reduce pain. This makes sure they are comfortable and stable during the surgery.
We also review the patient’s imaging results one last time. This confirms the clot’s location and size.
Catheter Insertion and Navigation Through Blood Vessels
The next step is inserting a catheter into the femoral artery, usually in the groin. We use advanced imaging to guide the catheter through the blood vessels to the brain clot. This step requires a lot of attention to avoid damaging the blood vessels.
Clot Removal Techniques in Brain Thrombectomy
With the catheter in place, we use different techniques to remove the clot. We might use stent retrievers or aspiration catheters. Stent retrievers deploy a stent to trap the clot, then we retrieve it. Aspiration catheters use suction to remove the clot.
The choice of device depends on the clot’s location and size.
Procedure Duration: What to Expect
The time it takes for the EVT procedure varies. It can last from 30 minutes to 2 hours. This depends on the case’s complexity and the patient’s anatomy.
We keep a close eye on the patient’s condition. This ensures the procedure is done as quickly and safely as possible.
Medical Equipment and Technology Used in Cerebral Thrombectomy
Advanced medical equipment is key to the success of EVT procedures. The field of cerebral thrombectomy has seen big improvements. New technologies aim to better patient outcomes.
Catheter Types and Selection
Catheters are essential in EVT procedures. We use different catheter types for various tasks. These include navigating through complex blood vessels or delivering treatments to clots.
Choosing the right catheter is very important. It depends on the clot’s location, size, and the patient’s blood vessels.
Stent Retrievers and Their Mechanism
Stent retrievers are a major tool in cerebral thrombectomy. They work by opening the blocked vessel with a stent-like device. This allows them to pull out the clot. New stent retrievers are better at navigating and removing clots.
A leading researcher said, “Stent retrievers have changed EVT. They help us get better at removing clots.”
“Stent retrievers have been a big change in treating acute ischemic stroke. They help us get blood flowing to the brain better.”
Aspiration Devices and Systems
Aspiration devices are also important in EVT. They use suction to remove clots from blocked vessels. New technology in aspiration has made EVT safer and more effective.
- Aspiration catheters with advanced tips for better clot capture
- Systems that use suction and stent retrievers together for better clot removal
Advanced Imaging Technology During EVT
Advanced imaging technology is vital for EVT success. It lets us see the procedure in real-time. Tools like digital subtraction angiography and flat-panel detector CT scans help us understand the blood vessels and where the blockage is.
These imaging tools help us navigate the brain’s blood vessels accurately. This ensures we place devices correctly and remove clots effectively.
Recovery and Outcomes After Thrombectomy for Stroke
After a stroke, patients start a critical recovery phase. This phase is key for checking the procedure’s success and managing any issues.
Immediate Post-Procedure Recovery Timeline
Right after thrombectomy, patients are closely watched in a specialized unit. Close monitoring of their health and brain function is vital. We usually keep them for at least 24 hours to watch for any problems.
The medical team checks the patient’s brain function closely. Early mobilization is encouraged to avoid bed rest issues.
Hospital Stay Duration
The time in the hospital after thrombectomy varies. It depends on the stroke’s severity, the patient’s health, and any complications. On average, patients stay 3 to 7 days.
In the hospital, a team of experts provides care. This team includes neurologists, nurses, and more. They work together to help the patient recover and get ready for going home.
Long-term Rehabilitation Process
Rehabilitation after thrombectomy is a big part of recovery. Most patients need therapy to regain lost functions. This includes physical, occupational, speech, and cognitive therapy.
The length and intensity of rehab depend on the patient’s needs. Some need inpatient rehab, while others can do it on an outpatient basis.
Success Rates and Functional Outcome Measures
Studies show EVT greatly improves outcomes for stroke patients. Success is measured with scales like the modified Rankin Scale (mRS). It checks how well patients can do daily activities.
Research shows thrombectomy leads to better outcomes than just medical treatment. Early intervention and choosing the right patients are key to success.
Understanding the recovery and outcomes after thrombectomy helps us support patients and their families. Our goal is to provide care that meets both immediate and long-term needs. This improves the lives of stroke survivors.
Potential Risks and Complications of EVT
The EVT procedure is a lifesaver for many stroke patients. Yet, it comes with risks and complications. It’s vital to know these risks to make informed treatment choices.
Procedural Complications
During EVT, several complications can happen. These include:
- Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage, a potentially life-threatening condition.
- Vascular complications such as dissection or perforation of blood vessels.
- Emboli or clots forming in other parts of the body during the procedure.
Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage is a severe complication. It’s when there’s bleeding in the brain. This risk is very concerning because it can greatly affect patient outcomes.
Post-Procedure Risks
After EVT, patients face various risks. These include:
- Infection at the catheter site or elsewhere.
- Re-occlusion of the treated blood vessel.
- Neurological deterioration due to various factors.
Close monitoring and post-procedure care are key. They help reduce these risks and ensure the best outcomes.
Risk Factors That May Affect Outcomes
Several factors can impact EVT outcomes. These include:
- Time elapsed before the procedure is performed.
- The patient’s overall health and presence of comorbidities.
- The size and location of the clot.
Knowing these risk factors helps healthcare providers create personalized treatment plans.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
To lessen EVT risks, several strategies are used:
- Careful patient selection based on imaging and clinical criteria.
- Use of advanced imaging techniques to guide the procedure.
- Continuous monitoring during and after the procedure.
By using these risk mitigation strategies, healthcare providers can greatly improve patient outcomes.
Recent Advancements in EVT Research and Techniques
Recent years have brought big changes to EVT research, changing how we treat strokes. We’re seeing a big shift in how EVT is done, leading to better results for patients.
Evolution of Devices and Approaches
The tools and methods in EVT have changed a lot. New stent retrievers and aspiration catheters can remove clots better and cause fewer problems. A study onPubMed Central shows these new devices are making a big difference.
Expanding Treatment Windows
One big leap in EVT research is the longer treatment windows. Studies show EVT can work even when time is running out. This is thanks to better imaging that spots the right patients, no matter how long it’s been.
Improved Patient Selection Methods
Choosing the right patients for EVT is key. New research is working on better ways to pick who will benefit most. Techniques like perfusion imaging and CT angiography help see how much brain can be saved.
EVT’s Establishment as the Gold Standard Treatment
EVT is now the top choice for treating acute ischemic stroke. Many clinical trials have proven its effectiveness. As research keeps improving, we’ll see even better results for stroke patients.
Conclusion: The Future of EVT in Stroke Management
EVT has changed how we treat acute ischemic stroke, making a big difference for patients. As research keeps going, EVT’s role in stroke care will grow. New tech and research are leading to a bright future for EVT.
The outlook for EVT in stroke care is very positive. New tools and methods are being created to make the procedure better. We’re also looking at ways to treat more patients and choose the right ones for EVT.
With EVT, patients get quick and effective treatment, leading to better results. We’re dedicated to top-notch healthcare and helping international patients. EVT will keep being key in stroke care, and we’re excited for what’s next.
FAQ
What does EVT stand for in medical terms?
EVT stands for Endovascular Thrombectomy. It’s a procedure to remove blood clots from blocked arteries in the brain. This is for patients with acute ischemic stroke.
What is the significance of EVT in stroke treatment?
EVT is a key treatment for acute ischemic stroke. It greatly improves patient outcomes. This is because it restores blood flow to the brain tissue quickly.
How is EVT performed?
To perform EVT, a catheter is inserted into the blocked artery. Then, devices like stent retrievers or aspiration systems are used to remove the clot. This helps restore blood flow.
What are the criteria for recommending EVT?
Doctors decide on EVT based on several factors. These include how long symptoms have lasted, imaging findings, and the patient’s overall health.
What is the optimal time window for EVT?
The best time for EVT is within 6 hours of symptoms starting. But, it can go up to 24 hours for some patients based on imaging.
What imaging requirements are necessary before EVT?
Before EVT, imaging tests are needed. These include non-contrast CT, CT angiography, and CT perfusion scans. They help see the extent of ischemia and large vessel occlusions.
What are the possible risks and complications of EVT?
EVT can have risks like vessel perforation or dissection. There are also post-procedure risks like re-occlusion or hemorrhage. The patient’s condition also plays a role.
What is the recovery process like after EVT?
After EVT, patients are closely monitored. They stay in the hospital for observation and management of complications. Long-term rehabilitation helps regain lost functions.
How long does a thrombectomy procedure take?
A thrombectomy procedure can take anywhere from 30 minutes to several hours. It depends on the case’s complexity and the techniques used.
What is the success rate of EVT in treating ischemic stroke?
EVT has a high success rate. Many patients see improved outcomes. But, results can vary based on stroke severity and how quickly treatment is given.
Are there any recent advancements in EVT research and techniques?
Yes, EVT research and techniques are constantly improving. New devices, better patient selection, and longer treatment windows are being explored. All aim to improve stroke patient outcomes.
References
- Saver, J. L., Goyal, M., van der Lugt, A., Menon, B. K., Majoie, C. B., Dippel, D. W., Campbell, B. C., Nogueira, R. G., Demchuk, A. M., Tomasello, A., Cardona, P., Devlin, T. G., Frei, D. F., du Mesnil de Rochemont, R., Berkhemer, O. A., Jovin, T. G., Siddiqui, A. H., van Zwam, W. H., Davis, S. M., … HERMES Collaborators. (2016). Time to treatment with endovascular thrombectomy and outcomes from ischemic stroke: A meta-analysis. JAMA, *316*(12), 1279-1288. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27673305/



































