Ewing sarcoma is a rare cancer that often starts in the bones or soft tissue. It’s most common in teens and young adults, but Ewing sarcoma adults cases do occur and require special attention. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and survival chances is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment.
This cancer develops from specific cells in the bone or soft tissue and can behave differently in adults compared to younger patients. Awareness of Ewing sarcoma adults helps patients make informed health decisions and seek expert care early.
At Liv Hospital, specialists provide world-class treatment for Ewing sarcoma adults, combining advanced oncology techniques with compassionate, patient-centered care.
Key Takeaways
- Ewing sarcoma is a rare cancer that can occur in bones or soft tissue.
- It’s more common in adolescents and young adults, but can also occur in older adults.
- Understanding the causes, symptoms, and survival rates is key for adults.
- Liv Hospital offers advanced oncology care with a patient-focused approach.
- Timely and trustworthy information is vital for adults facing Ewing sarcoma.
Ewing Sarcoma in Adults: An Overview
Ewing sarcoma is not just for kids and teens; adults can get it too. It’s a rare cancer that can grow in bones or soft tissues. Knowing about it helps doctors diagnose and treat it better.
Definition and Characteristics
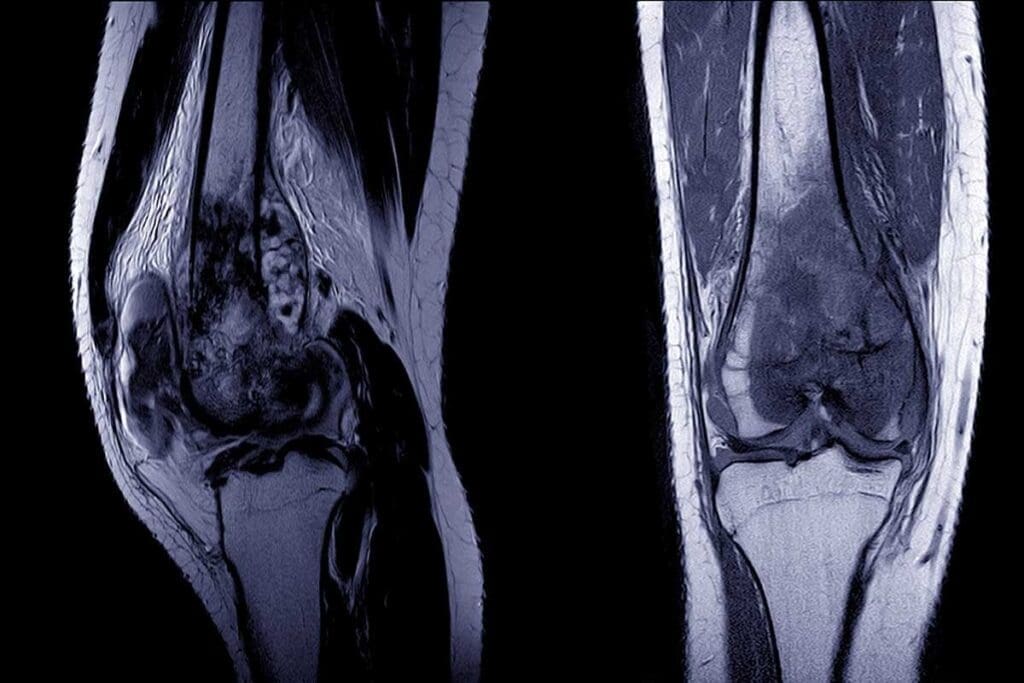
Ewing sarcoma is a fast-growing cancer. It can start in bones or soft tissues. In adults, it might show up in the legs, arms, chest, pelvis, spine, or skull. It can also appear in soft tissues near bones. Early detection is key because it can spread quickly.
Epidemiology and Age Distribution
Ewing sarcoma mostly affects the young, between 10 and 20 years old. But, adults can get it too, though it’s rarer. Adults face special challenges because it’s so uncommon in their age group.
It’s important to know about Ewing sarcoma in all age groups. Adults with this cancer often have a harder time getting diagnosed because it’s so rare in their age group.
The Unique Challenges of Adult Ewing Sarcoma Cases

Ewing sarcoma in adults comes with its own set of challenges. From finding out they have it to getting treatment, adults face unique hurdles. This is because the disease is rare in adults and they react differently to treatments.
Diagnostic Complexities in Adults
Finding out if an adult has Ewing sarcoma can be hard. Common signs include swelling, pain, fever, bone pain, and fractures. These symptoms can be confused with other conditions, causing delays in diagnosis.
To diagnose, doctors use imaging, biopsies, and genetic tests. These help find the EWSR1-FLI1 gene, a key sign of Ewing sarcoma.
| Diagnostic Tool | Purpose | Key Findings |
| Imaging Studies (MRI, CT) | To assess tumor size and location | Tumor extent and possible spread |
| Biopsy | To get tissue for examination | Small, round, blue cells found |
| Molecular Testing | To find specific genetic changes | EWSR1-FLI1 fusion gene found |
Treatment Response Differences
Adults with Ewing sarcoma may not react the same to treatments as kids. Treatments include chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation. But adults might face more severe side effects and long-term problems.
Psychosocial Impact on Adult Patients
Ewing sarcoma can deeply affect adults’ lives. It can impact their work, relationships, and overall well-being. Support from loved ones and mental health experts is key in helping them cope.
It’s vital to understand these challenges to give the best care to adult Ewing sarcoma patients. By recognizing the diagnostic hurdles, treatment differences, and emotional impacts, doctors can create better plans for adults with this rare cancer.
Common Locations of Ewing Sarcoma
Ewing sarcoma can show up in different parts of the body, mainly in bones and soft tissues. It often picks certain areas, which helps doctors figure out how to treat it.
Primary Bone Involvement
Ewing sarcoma usually starts in the long bones of the leg or arm. It also likes flat bones like the pelvic bone, scapula, or ribs. The pelvis is a big spot, often linked to hip sarcoma.
The long bones in the lower legs, like the femur and tibia, get hit a lot too.
When bones get involved, it can cause pain and swelling. Knowing where the cancer is helps doctors diagnose and plan treatment for ewing’s sarcoma bone cancer.
Extraosseous (Soft Tissue) Occurrence
Ewing sarcoma can also show up in soft tissues. These include muscles, fat, and other connective tissues. Soft tissue Ewing sarcoma is less common but just as serious.
It can pop up in many places, like the trunk, limbs, and head and neck. Getting a correct diagnosis is key to knowing how far the disease has spread.
To wrap it up, Ewing sarcoma can happen in bones like the pelvis and legs, or in soft tissues. Knowing where it often occurs is key for catching it early and treating it well.
What Causes Ewing Sarcoma?
Scientists have made big strides in studying Ewing sarcoma. But, they’re not sure what causes this bone and soft tissue cancer. They’ve found that certain genetic changes, like the EWSR1-FLI1 fusion gene, are linked to it.
The EWSR1-FLI1 Fusion Gene
The EWSR1-FLI1 fusion gene comes from a genetic swap. It combines the EWSR1 and FLI1 genes. This change is found in most Ewing sarcoma cases and is thought to be key in the disease’s development.
Risk Factors and Misconceptions
Even though we don’t know the exact cause of Ewing sarcoma, some risk factors and misconceptions have been found. Unlike some cancers, Ewing sarcoma isn’t directly caused by lifestyle or environmental factors.
- No clear evidence links Ewing sarcoma to inherited genetic syndromes.
- The role of radiation exposure in causing Ewing sarcoma is being researched.
- Ewing sarcoma is not caused by injuries or trauma to the affected area.
A study in the Journal of Clinical Oncology says, “The etiology of Ewing’s sarcoma remains largely unknown, with no established risk factors other than genetic predisposition in some cases.”
| Risk Factor | Association with Ewing Sarcoma |
| Genetic Predisposition | Possible, but rare |
| Environmental Exposures | No clear link |
| Radiation Exposure | Under investigation |
Understanding Ewing sarcoma’s causes is key to finding better treatments. More research into its genetics and molecular mechanisms is needed to help patients.
Recognizing Ewing Sarcoma Symptoms in Adults
It’s important for adults to know the signs of Ewing sarcoma to get help fast. This rare cancer can show up in different parts of the body. Its symptoms might look like other, less serious issues.
Early Warning Signs
Adults should watch for early signs of Ewing sarcoma. These include:
- Persistent bone pain that doesn’t go away with rest.
- A growing lump or swelling near the bone or soft tissue, feeling soft or warm.
- Pain, swelling, or tenderness at the tumor site.
Advanced Symptoms
As Ewing sarcoma gets worse, symptoms can get more serious. These include:
- Pain that gets worse and can make daily tasks hard.
- Visible swelling or a growing mass.
- Systemic symptoms like fever, fatigue, or weight loss.
Adults should see a doctor if they have these advanced symptoms.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Adults should get medical help right away if they notice unusual or lasting symptoms. Early diagnosis is key for better treatment and survival chances.
Prompt medical evaluation can greatly improve outcomes for adults with Ewing sarcoma.
Diagnostic Journey for Adult Patients
The journey to diagnose Ewing sarcoma in adults is complex. It includes initial checks, imaging tests, and genetic tests. Accurate diagnosis is key to creating a good treatment plan.
Initial Assessment and Physical Examination
The first step is a detailed check-up and physical exam. Doctors look for signs like pain, swelling, or a lump. They also ask about your medical history to find any risk factors.
Key components of the initial assessment include:
- Patient history
- Physical examination
- Initial laboratory tests
Imaging Studies
Imaging tests are vital for diagnosing Ewing sarcoma. They show where, how big, and how far the tumor is.
Common imaging studies used include:
- X-rays
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scans
- CT (Computed Tomography) scans
- PET (Positron Emission Tomography) scans
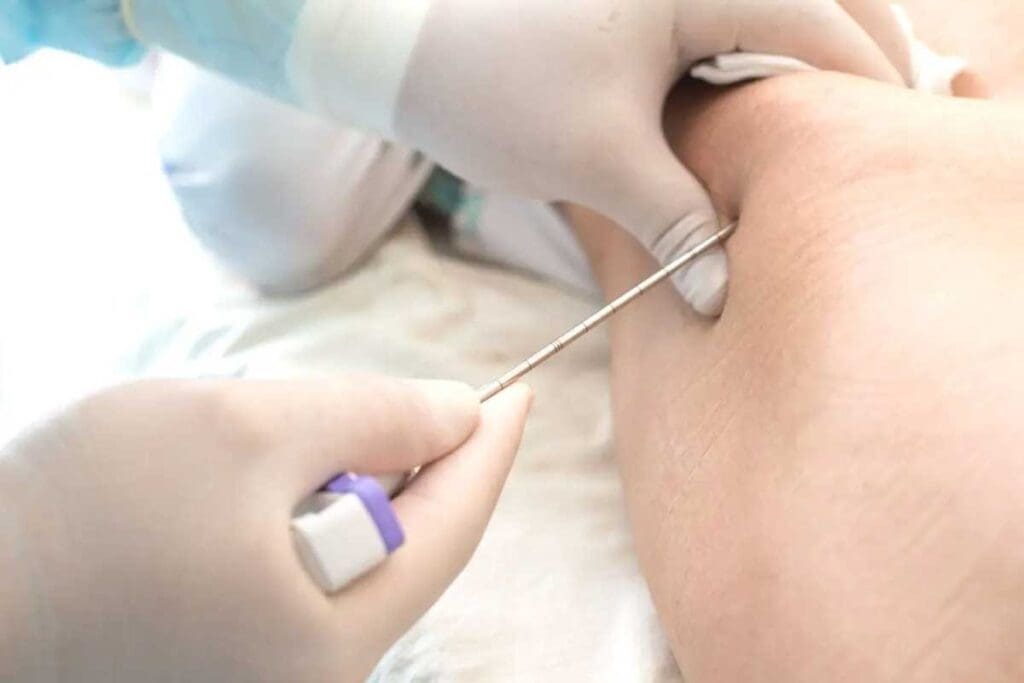
Biopsy Procedures
A biopsy is key to confirming Ewing sarcoma. It involves taking a tumor sample for microscopic examination.
| Biopsy Type | Description |
| Needle Biopsy | A minimally invasive procedure using a needle to collect tissue samples. |
| Surgical Biopsy | A surgical procedure to remove a larger tissue sample for examination. |
Molecular and Genetic Testing
Molecular and genetic tests are vital for Ewing sarcoma diagnosis. They look for specific genetic changes, like the EWSR1-FLI1 gene fusion.
The importance of molecular testing includes:
- Confirming the diagnosis
- Identifying genetic mutations
- Guiding treatment decisions
By using initial checks, imaging, biopsies, and genetic tests, doctors can accurately diagnose Ewing sarcoma. This helps in creating a personalized treatment plan.
Staging and Classification of Ewing Sarcoma
Staging and classification of Ewing sarcoma are key to understanding the disease’s spread. They help doctors decide on the best treatment. Knowing the stage and type of Ewing sarcoma is vital for a good prognosis and treatment plan.
TNM Staging System
The TNM staging system is a common method used. It looks at the tumor’s size and spread (T), nearby lymph nodes (N), and if it has spread (M). This system helps sort Ewing sarcoma into stages, which is important for treatment planning.
Key components of the TNM staging system include:
- Tumor size and extent
- Lymph node involvement
- Presence of metastasis
Localized Disease Characteristics
Localized Ewing sarcoma means the cancer is only in the original site. It hasn’t spread to other parts of the body. Key features of localized disease are:
- The tumor is only in the bone or soft tissue where it started
- No distant metastasis
- The tumor can possibly be surgically removed
Metastatic Disease Identification
Metastatic Ewing sarcoma happens when cancer spreads to other parts of the body. Common places for it to spread include the lungs, bones, and bone marrow. Finding metastatic disease is important for understanding the prognosis and treatment.
Signs of metastatic disease may include:
- Pain or swelling in the affected area
- Systemic symptoms such as fever or weight loss
- Abnormal imaging findings on X-rays, CT scans, or PET scans
Prognostic Grouping
Prognostic grouping sorts patients based on factors that affect their outlook. For Ewing sarcoma, these factors include the disease stage, tumor size, and how well it responds to treatment. Patients with localized disease usually have a better outlook than those with metastatic disease.
Understanding prognostic grouping helps healthcare providers to:
- Estimate the likelihood of recovery
- Plan appropriate treatment strategies
- Provide patients with realistic expectations about their disease outcome
Comprehensive Treatment Approaches
Effective treatment for Ewing sarcoma is key to better patient outcomes. It needs a mix of treatments to manage the disease well.
Multidisciplinary Treatment Teams
A multidisciplinary treatment team is vital for Ewing sarcoma care. This team includes doctors, surgeons, and radiologists. They work together to create a treatment plan tailored for each patient.
Neoadjuvant Therapy
Neoadjuvant therapy is given before the main treatment. It aims to shrink tumors, making them easier to remove. Chemotherapy is often used to reduce tumor size and treat any hidden cancer cells.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical interventions are key for treating Ewing sarcoma, mainly for localized cases. Surgery aims to remove the tumor and some healthy tissue around it. This ensures all cancer cells are gone. The decision to have surgery depends on the tumor’s size and location.
Adjuvant Therapy
Adjuvant therapy is given after the main treatment to lower cancer return risk. For Ewing sarcoma, this might include chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy. It depends on how well the patient responds to initial treatment and other factors.
| Treatment Modality | Purpose | Common Applications |
| Neoadjuvant Therapy | Shrink tumors before main treatment | Chemotherapy |
| Surgical Interventions | Remove tumors and affected tissue | Localized Ewing Sarcoma |
| Adjuvant Therapy | Reduce risk of recurrence | Chemotherapy, Radiation Therapy |
Ewing’s Sarcoma Metastasis: Understanding the Spread
Ewing’s sarcoma metastasis is a complex process that affects survival rates and treatment strategies. This rare cancer usually affects bones or soft tissue around bones. It can spread to other parts of the body, making treatment harder and impacting patient outcomes.
Common Sites of Metastatic Disease
Ewing’s sarcoma often spreads to the lungs, other bones, and bone marrow. Knowing these common sites is key for diagnosis and treatment planning.
- The lungs are a primary site for metastasis, and pulmonary metastases can significantly affect patient prognosis.
- Bone metastases indicate a more advanced stage of the disease and are associated with a poorer prognosis.
- Bone marrow metastasis is also a serious development, as it suggests the cancer has spread beyond its initial location.
Detection Methods for Metastatic Disease
Detecting metastasis early is critical for managing Ewing’s sarcoma effectively. Various diagnostic tools are used to identify metastatic disease.
- Imaging Studies: Techniques such as MRI, CT scans, and PET scans are key for spotting metastases in the lungs, bones, and other organs.
- Bone Marrow Biopsy: This procedure examines bone marrow samples for cancer cells, helping to determine if the disease has spread.
Treatment Strategies for Metastatic Cases
Treating Ewing’s sarcoma that has metastasized requires a detailed and multi-faceted approach. Treatment plans are tailored to the individual patient based on the extent and location of the metastatic disease.
Multidisciplinary Treatment Teams are essential in managing metastatic Ewing’s sarcoma. They use chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery as needed.
- Chemotherapy is a cornerstone in treating metastatic disease, aiming to control the spread of cancer.
- Radiation therapy can target specific metastatic sites, such as in the bones or lungs.
- Surgery may be considered for removing isolated metastases, if they cause significant symptoms or are in critical areas.
Understanding Ewing’s sarcoma metastasis is vital for improving patient outcomes. By recognizing common metastasis sites, using effective detection methods, and employing detailed treatment strategies, healthcare providers can offer the best care for patients with metastatic Ewing’s sarcoma.
Ewing’s Sarcoma Survival and Prognosis Factors
Ewing’s sarcoma survival rates in adults depend on several key factors. These include the tumor stage and how well the treatment works. Knowing these factors helps both patients and doctors make better treatment plans.
Five-Year Survival Statistics for Adults
Adults with Ewing’s sarcoma have a lower five-year survival rate than children. About 77% of patients without cancer spread will live at least 5 years after diagnosis. But, survival rates can change a lot based on the disease stage and treatment response.
Adults face a tougher prognosis because of delayed diagnosis and treatment differences. It’s vital for adults with Ewing’s sarcoma to get care from a team experienced in treating this rare cancer.
Key Prognostic Indicators
Several factors affect the prognosis for adults with Ewing’s sarcoma. These include:
- The stage of the disease at diagnosis
- The location and size of the tumor
- The presence of metastasis
- The patient’s overall health and age
- The tumor’s response to initial treatment
Long-term Survival Considerations
Adults with Ewing’s sarcoma need careful planning and follow-up care for long-term survival. Survivors may face late effects from treatment, such as secondary cancers, heart problems, or fertility issues. Regular monitoring and a detailed care plan can help manage these risks.
Survivors should also focus on a healthy lifestyle. This includes eating well and exercising regularly to improve overall health and reduce late effects.
Recurrence Risks and Management
The risk of recurrence is a big concern for Ewing’s sarcoma patients. Recurrence can happen locally or in distant parts of the body. Regular follow-up appointments and imaging studies are key for catching recurrence early.
Managing recurrence often involves a mix of treatments, like chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation therapy. The treatment choice depends on the recurrence location, extent, and the patient’s past treatments.
Living with Ewing Sarcoma: Support and Recovery
Dealing with Ewing sarcoma means getting treatment and care in many ways. It’s important to keep an eye on late effects and any tumor return. This is true for survivors.
Physical Rehabilitation
Physical therapy is key for Ewing sarcoma patients. It helps them get stronger, move better, and deal with side effects. A custom rehab plan can really improve life quality.
Components of Physical Rehabilitation:
- Physical therapy to improve mobility and strength
- Occupational therapy to assist with daily activities
- Pain management strategies
Psychological Support Resources
The mind also feels the effects of Ewing sarcoma. Patients and families need support to handle the diagnosis, treatment, and recovery. Counseling, support groups, and mental health experts are essential.
Benefits of Psychological Support:
- Reduces anxiety and depression
- Enhances coping mechanisms
- Improves overall well-being
Long-term Monitoring Protocols
Keeping an eye on health long-term is critical. Regular check-ups, imaging, and tests help catch any issues early. This is part of the monitoring plan.
| Monitoring Activity | Frequency | Purpose |
| Follow-up appointments | Every 3-6 months | Assess overall health, detect recurrence |
| Imaging studies (e.g., MRI, CT scans) | As recommended by healthcare provider | Monitor for signs of recurrence or metastasis |
| Blood tests | Regularly as advised | Check for late effects of treatment |
Support Groups and Community Resources
Support groups and resources are a big help for Ewing sarcoma patients and their families. They offer emotional support, advice, and a sense of community.
Types of Support Groups:
- In-person support groups
- Online forums and social media groups
- Specialized support for specific needs (e.g., young adults, families)
Using these resources, people with Ewing sarcoma can get the support they need on their journey.
Excellence in Ewing Sarcoma Treatment: The Liv Hospital Approach
Liv Hospital’s Ewing sarcoma treatment combines academic rigor and personalized care. This approach sets a new standard in oncology. It ensures patients get the best treatment with compassion.
Multidisciplinary Oncology Teams
Liv Hospital’s Ewing sarcoma treatment program is led by expert teams. These teams include doctors from various fields. They work together to create a treatment plan that fits each patient’s needs.
Advanced Diagnostic and Treatment Technologies
Liv Hospital uses the latest technologies for diagnosis and treatment. Techniques like PET-CT scans and proton therapy improve treatment results. This keeps Liv Hospital at the forefront of care.
Patient-Centered Care Pathways
Liv Hospital puts patients first in their care. They offer psychological support, nutritional guidance, and rehabilitation to help patients. This approach improves care quality and outcomes.
Research and Innovation Initiatives
Liv Hospital is dedicated to oncology research and innovation. They join international trials and conduct studies. This research helps understand Ewing sarcoma better and offers new treatments.
Liv Hospital stands out in Ewing sarcoma treatment. They use teams, technology, patient focus, and research. Patients and families can trust they’re getting top-notch care.
Conclusion: Navigating Ewing Sarcoma as an Adult
Ewing sarcoma in adults is rare and complex. It needs a team of experts for care. Knowing about Ewing sarcoma is key for adults to deal with it.
Early detection and new treatments help save lives. A team of doctors, including oncologists and surgeons, is vital. They help create a good treatment plan. Adults should know about the latest treatments and trials.
Liv Hospital shows how important patient care is. They use the latest technology for Ewing sarcoma treatment. Raising awareness about Ewing sarcoma in adults can help improve their outcomes.
Adults with Ewing sarcoma should see a specialized center. The right care and support can help them survive. It’s all about navigating the disease and treatment well.
FAQ
What is Ewing sarcoma?
Ewing sarcoma is a rare cancer that affects bones or soft tissue. It mostly hits children and young adults. But it can also happen in adults.
What are the causes of Ewing sarcoma?
We don’t know the exact cause of Ewing sarcoma. But it’s linked to a genetic mutation. This mutation comes from a chromosomal translocation.
What are the symptoms of Ewing sarcoma in adults?
Adults with Ewing sarcoma might feel pain, swelling, or a lump. They might also have fever and lose weight if the cancer is advanced.
How is Ewing sarcoma diagnosed?
Doctors use X-rays, CT scans, and MRI to find the cancer. They also do biopsies and genetic tests. These tests look for the genetic mutations.
What are the treatment options for Ewing sarcoma?
Treatment includes chemotherapy, surgery, and more chemotherapy or radiation. This approach helps fight the cancer.
Can Ewing sarcoma metastasize?
Yes, it can spread to other parts of the body. This usually happens to the lungs, bones, and bone marrow. Treatment needs to be thorough.
What is the prognosis for adults with Ewing sarcoma?
The outlook depends on the disease’s stage, if it has spread, and the patient’s health. Survival rates vary a lot based on these factors.
How does Ewing sarcoma affect adults differently than children?
Adults face unique challenges. These include harder diagnosis, different treatment responses, and a unique psychosocial impact. This is different from younger patients.
What support is available for adults living with Ewing sarcoma?
Support includes physical therapy, mental health help, and ongoing care. There are also support groups and community resources to help with recovery and coping.
What advancements are being made in Ewing sarcoma treatment?
New treatments are coming from research and innovation. This includes targeted therapies and better diagnostic tools. These advancements improve care and outcomes for patients.
References
- Baldini, E. H., et al. (1999). Adults with Ewing’s Sarcoma/Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor: Outcome and Prognostic Factors. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 17(1), 12-23.https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1420848/