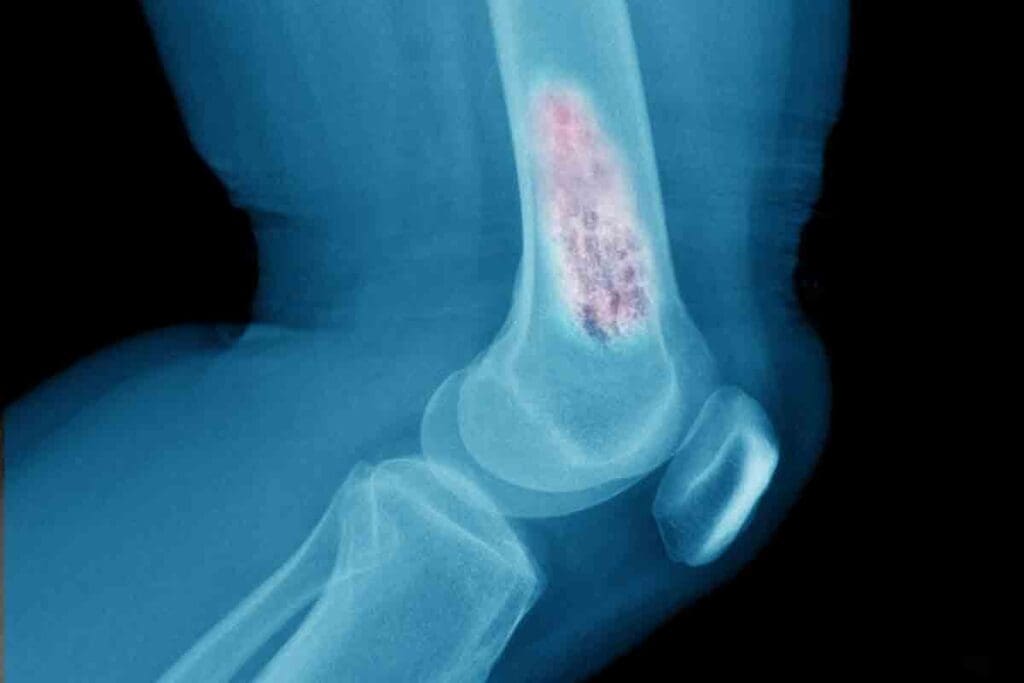
Ewing sarcoma is a rare and aggressive cancer that affects the bones and soft tissues, mostly in children and teenagers.
This fast-growing disease can seriously impact a person’s quality of life. Understanding the key Ewing sarcoma cancer symptoms and causes is essential for early detection and timely treatment.
Recognizing Ewing sarcoma cancer symptoms early — such as persistent bone pain, swelling, or unexplained fatigue — can make a big difference. Taking action quickly can greatly improve a patient’s chances of recovery and long-term health.
Key Takeaways
- Ewing sarcoma is a rare and aggressive cancer affecting bones and soft tissues.
- It mainly happens in children and teenagers, but can also affect adults.
- Early detection is key for effective treatment and better patient outcomes.
- Understanding the causes and symptoms is vital for timely medical intervention.
- The disease can cause a lot of pain and discomfort if not treated.
Understanding Ewing Sarcoma: A Rare and Aggressive Bone Cancer

Ewing sarcoma is a rare and aggressive bone cancer. It mainly affects bones and soft tissues. It grows fast and can spread, so early diagnosis and treatment are key.
Definition and Classification of Ewing Sarcoma
Ewing sarcoma is a malignant tumor in the Ewing’s sarcoma family of tumors (ESFT). It’s mostly a bone cancer but can also be in soft tissues. The World Health Organization (WHO) sees it as a unique type of bone tumor.
Doctors classify Ewing sarcoma by looking at its cells under a microscope. They use EWSR1-FLI1 gene fusion tests to confirm it.
Prevalence and Incidence Rates
Ewing sarcoma is rare, making up about 1% of all childhood cancers. In the United States, about 200 new cases are found each year. It’s more common in boys and young people.
| Age Group | Incidence Rate per Million |
| 0-14 years | 3.4 |
| 15-19 years | 4.6 |
| 20-24 years | 2.3 |
The table shows Ewing sarcoma’s incidence rates in different age groups. It’s most common in kids and young adults.
To sum up, knowing about Ewing sarcoma is important. It helps doctors and patients deal with this rare and aggressive bone cancer.
Who Is at Risk for Ewing Sarcoma?
It’s important to know who is most at risk for Ewing Sarcoma. This cancer mainly hits kids and teens. But, it can also affect young adults and, rarely, older adults.
Age Distribution and Demographics
Ewing Sarcoma is most common in teens, with many cases in those 10 to 19 years old. It can also strike younger kids and adults in their 20s and 30s. Studies show it’s more common in males than females.
Ewing Sarcoma is mainly a cancer of kids and teens. But, it’s important to remember it can happen in other age groups too.
Ewing Sarcoma Age Range: Children vs. Adults
Ewing Sarcoma is more common in kids and teens. But, adults can get it too. The symptoms and treatment can differ between these groups. This is because of health differences and the cancer’s specifics.
| Age Group | Incidence Rate | Common Characteristics |
| Children (0-9 years) | Less common | Often presents with systemic symptoms like fever |
| Adolescents (10-19 years) | Most common | Typically presents with localized pain and swelling |
| Young Adults (20-30 years) | Less common than in adolescents | May have delayed diagnosis due to lower suspicion |
Ewing Sarcoma’s age distribution shows we need to be aware across all ages. Spotting the signs early can greatly improve treatment results.
The 7 Key Ewing Sarcoma Cancer Symptoms to Watch For
Ewing sarcoma is a rare and aggressive bone cancer. It has distinct symptoms that need quick attention. Spotting these symptoms early is key for a timely diagnosis and effective treatment.
1. Persistent Bone Pain
Persistent bone pain is a common symptom of Ewing sarcoma. This pain can be severe and gets worse over time. It usually happens in the area where the tumor grows. Unlike regular bone pain, this pain doesn’t go away and is a big sign of the disease.
2. Swelling Near Affected Area
Swelling near the affected bone or soft tissue is another symptom. This swelling happens because the tumor grows. It makes the area around it inflamed and tender.
3. Visible Lump Formation
A visible or palpable lump is a significant symptom of Ewing sarcoma. As the tumor grows, it can form a noticeable mass under the skin. This is more common when the tumor is close to the surface.
4. Unexplained Fever
Unexplained fever can be a systemic symptom of Ewing sarcoma. Patients might have recurrent or persistent fevers without a clear cause. This can be a sign of the body’s response to the cancer.
Patients with Ewing sarcoma may also feel tired, lose weight without trying, and have fractures without any trauma. The symptoms can vary in how they appear and how severe they are for each person.
| Symptom | Description |
| Persistent Bone Pain | Severe pain localized to the tumor area |
| Swelling | Inflammation near the affected bone or tissue |
| Visible Lump | Noticeable mass under the skin |
| Unexplained Fever | Recurrent fevers without apparent cause |
| Fatigue | General feeling of tiredness and weakness |
| Unexplained Weight Loss | Significant weight loss without known reason |
| Unexplained Fractures | Fractures occurring without significant trauma |
Understanding these symptoms is key for early detection and treatment of Ewing sarcoma. If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to see a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and care.
Common Locations Where Ewing Sarcoma Develops
Ewing sarcoma often starts in specific bones. It most commonly occurs in the long bones of the arms and legs, the pelvis, and the chest wall. Knowing these common areas helps in catching the disease early.
Pelvis and Hip Sarcoma
The pelvis is a common spot for Ewing sarcoma, often showing up as hip sarcoma. This can cause a lot of problems because of the pelvis’s complex structure. Symptoms like hip pain and swelling might be mistaken for other issues, which can delay finding out what’s wrong.
“Ewing’s sarcoma in the pelvis is tough because of where it is and how big it can be at diagnosis,” notes a top oncologist. Finding it early is key to better results.
Limbs and Extremities
Ewing sarcoma also happens in the long bones of the limbs, like the thigh bone, tibia, and fibula. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and sometimes a lump that can be seen. Because it can grow fast, it needs quick treatment.
- Pain and swelling in the affected limb
- Visible lump or mass
- Reduced mobility or function
Other Possible Sites
Though rare, Ewing sarcoma can also show up in bones like the ribs, spine, and skull. It can act differently based on where it is, so a detailed check is needed for the right diagnosis.
To wrap it up, Ewing sarcoma can pop up in many places, but it’s most common in the pelvis, limbs, and chest wall. Knowing where it can happen and what symptoms to look for is important for catching it early and treating it well.
Ewing Sarcoma in Adults: Special Considerations
Ewing sarcoma is a cancer mostly seen in kids and teens. But it can also happen in adults, making diagnosis tricky. Symptoms and how doctors check for it need careful thought.
Symptoms in Adults
Adults with Ewing sarcoma might feel bone pain and swelling. Chronic pain is a big issue, sometimes making it hard to find the cause.
Diagnostic Challenges
Finding Ewing sarcoma in adults is hard because it’s rare and symptoms are not specific. Adults might have other health issues that seem like Ewing sarcoma at first.
- Persistent bone pain
- Swelling or lump formation
- Systemic symptoms like fever
Why Adult Cases Often Have Delayed Diagnosis
Adults often get diagnosed late because Ewing sarcoma is seen as a kid’s disease. They might also wait longer to see a doctor, adding to the delay.
Doctors need to remember that Ewing sarcoma can happen in adults. They should look out for signs like ongoing bone pain or swelling.
What Causes Ewing Sarcoma? The Genetic Basis
Ewing Sarcoma is mainly caused by genetic changes, not by outside factors. This rare bone cancer is driven by specific genetic changes. These changes lead to its aggressive growth.
The EWSR1-FLI1 Gene Fusion
The EWSR1-FLI1 gene fusion is a key feature of Ewing Sarcoma. It comes from a chromosomal swap t(11;22). This genetic mix-up is seen in about 85% of cases and is a key sign of the disease.
The EWSR1-FLI1 fusion gene is an oncogene. It makes cancer cells grow uncontrollably. It messes with normal cell functions. It creates a new factor that boosts tumor growth.
| Genetic Alteration | Frequency in Ewing Sarcoma | Impact on Tumor |
| EWSR1-FLI1 fusion | 85% | Drives cell proliferation |
| Other EWSR1 fusions | 10% | Similar oncogenic effect |
| Unknown/other alterations | 5% | Varying effects |
Other Genetic Alterations
While the EWSR1-FLI1 fusion is common, other EWSR1 fusions also play a role. These different fusions help the disease grow and spread.
“The genetic landscape of Ewing Sarcoma is characterized by a limited number of driving mutations, mainly involving the EWSR1 gene.”
Why Ewing’s Sarcoma Is Not Hereditary
Ewing Sarcoma is not passed down through families. The genetic changes that cause it happen in the tumor cells, not in the cells that pass on traits.
Because it’s not inherited, Ewing Sarcoma doesn’t follow a family pattern. It happens randomly, not through family history.
Diagnosis: From Symptoms to Confirmation
Diagnosing Ewing Sarcoma is a detailed process. It involves physical checks, imaging tests, and genetic tests. This ensures a correct diagnosis and the right treatment plan.
Initial Evaluation and Physical Examination
The first step is a detailed physical check and medical history. Doctors look for signs like swelling, pain, or a mass. This initial check is key to moving forward.
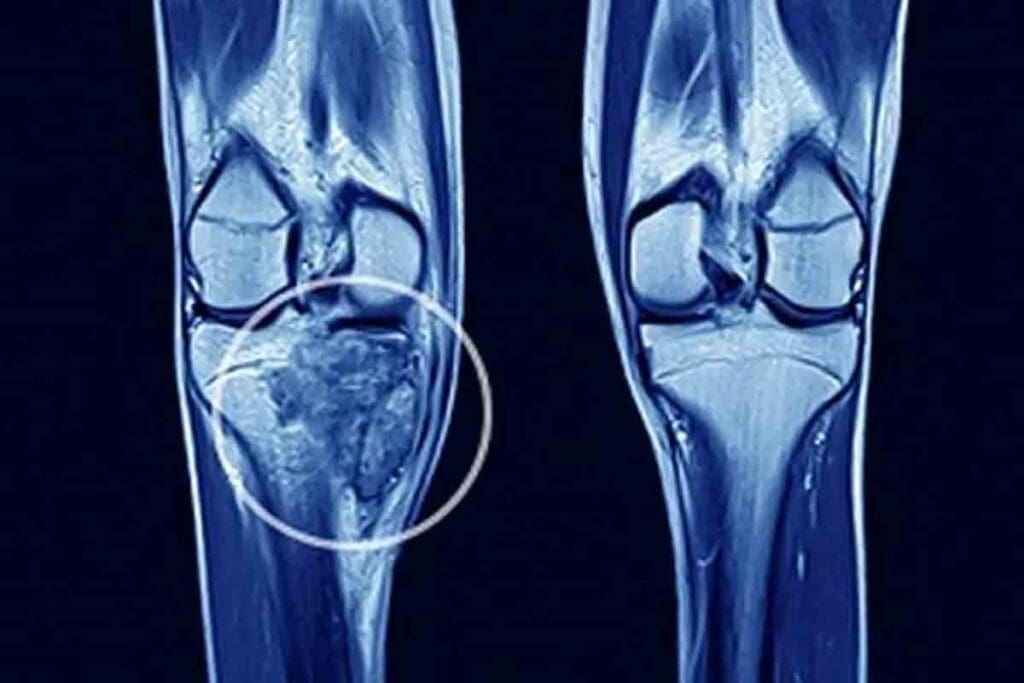
Imaging Studies
Imaging tests are essential for diagnosing Ewing Sarcoma. X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, and PET scans help find the tumor’s location and size. These images guide further tests and treatment.
Biopsy and Genetic Testing
A biopsy confirms Ewing Sarcoma cells. A tissue sample is taken and checked under a microscope. Genetic tests look for specific changes, like the EWSR1-FLI1 gene fusion. This confirms the diagnosis and helps plan treatment.
The process to diagnose Ewing Sarcoma includes:
- Physical examination and medical history
- Imaging studies (X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, PET scans)
- Biopsy to confirm Ewing Sarcoma cells
- Genetic testing to find specific genetic changes
By using these methods, doctors can accurately diagnose Ewing Sarcoma. They then create a treatment plan that meets each patient’s needs.
Understanding Ewing’s Sarcoma Metastasis
It’s key to know how Ewing’s sarcoma spreads to other parts of the body. This rare and aggressive bone cancer mainly hits kids and young adults. When it spreads, it makes treatment harder.
Common Sites of Spread
The cancer often goes to the lungs, bones, and bone marrow. The lungs are a common spot because of their blood flow. Bones like the spine, pelvis, and ribs also get affected. Bone marrow spread is scary because it can spread cancer cells everywhere.
Common metastatic sites include:
- Lungs
- Bones (spine, pelvis, ribs)
- Bone marrow
When cancer reaches these places, it can really hurt a patient’s life and treatment choices. For example, bone cancer can cause a lot of pain and breakage. Lung cancer can mess with breathing.
Signs of Metastatic Disease
Spotting metastatic Ewing’s sarcoma early is very important. Symptoms depend on where the cancer spreads. For instance, bone cancer might hurt, while lung cancer can cause coughing or trouble breathing.
Signs that may indicate metastatic disease include:
- Unexplained pain in bones or joints
- Respiratory symptoms like coughing or difficulty breathing
- Neurological symptoms if the cancer spreads to the brain or spinal cord
It’s vital for patients and doctors to watch for these signs and act fast. This helps manage the disease better.
About 20% of Ewing’s sarcoma patients have metastasis. This shows the importance of catching it early and treating it strongly. Knowing where and how it spreads helps doctors create better treatment plans for each patient.
Treatment Approaches for Ewing Sarcoma
Effective treatment of Ewing sarcoma needs a team effort from many medical fields. This disease is aggressive and can spread, so a strong treatment plan is needed. A multidisciplinary team is key, combining specialists for a full care approach.
Multidisciplinary Team Approach
Healthcare pros like oncologists, surgeons, and radiologists work together. They create a treatment plan that fits each patient’s needs. This collaborative approach manages the disease from start to spread.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is vital for Ewing sarcoma, aiming to remove the tumor and healthy tissue around it. Sometimes, surgery is paired with chemotherapy and radiation to boost treatment success.
Chemotherapy Protocols
Chemotherapy is a mainstay in Ewing sarcoma treatment, targeting cancer cells that have spread. The treatment plan varies based on the disease’s stage and the patient’s health. Chemotherapy regimens use a mix of drugs over several cycles to reduce tumors.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is also key, aiming to kill cancer cells. It’s used alone or with surgery and chemotherapy. The choice depends on the tumor’s location, size, and response to other treatments. Advanced radiation techniques focus on the tumor, protecting healthy tissues.
Combining these treatments has greatly improved Ewing sarcoma outcomes. Knowing the treatment options helps patients and families make informed decisions.
Ewing’s Sarcoma Survival Rates and Prognosis Factors
It’s important to know about survival rates and prognosis factors for Ewing’s sarcoma. This rare and aggressive bone cancer has seen better survival rates thanks to new treatments.
Age-Related Differences in Outcomes
Age is a big factor in Ewing’s sarcoma prognosis. Kids and teens usually do better than adults. Younger patients can handle tough treatments better and often have fewer health problems.
Key age-related factors influencing Ewing’s sarcoma outcomes include:
- The patient’s overall health and ability to withstand intensive therapy
- The presence of metastasis at diagnosis
- The tumor’s location and size
Impact of Tumor Location and Stage
The tumor’s location and stage at diagnosis matter a lot. Tumors in the pelvis or spine are harder to treat because of their location. Tumors that are caught early and haven’t spread tend to have better outcomes.
The 5-year relative survival rate for Ewing’s sarcoma varies based on the stage at diagnosis:
- Localized tumors: 82%
- Regional spread: 71%
- Distant metastasis: 39%
Metastasis and Survival Expectations
Having metastasis at diagnosis makes survival harder. But, new treatments like chemotherapy and targeted therapy have helped even those with advanced disease.
Survival expectations are influenced by:
- The extent of metastasis
- Response to initial treatment
- Patient’s age and overall health
In conclusion, survival rates and prognosis for Ewing’s sarcoma depend on many factors. These include age, tumor characteristics, and metastasis. Knowing these factors helps in creating better treatment plans and improving patient outcomes.
Advanced Care Options for Ewing Sarcoma Patients
Advanced care for Ewing sarcoma uses the latest treatments and follows international standards. This approach is key to better patient outcomes and quality of life.
Liv Hospital’s Multidisciplinary Approach
Liv Hospital is known for its team-based treatment of Ewing sarcoma. The team includes oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, and rehabilitation specialists. They work together to make treatment plans that fit each patient’s needs.
Key components of Liv Hospital’s approach include:
- Advanced diagnostic techniques to accurately stage the disease
- State-of-the-art surgical interventions to remove tumors
- Intensive chemotherapy protocols to target cancer cells
- Precision radiation therapy to minimize damage to healthy tissues
International Treatment Standards
Liv Hospital follows international standards for Ewing sarcoma treatment. This means patients get care that meets global best practices. The hospital also takes part in international clinical trials and follows guidelines from top oncology organizations.
| Treatment Aspect | Description | Benefit |
| Multidisciplinary Team | Collaboration among various specialists | Comprehensive care |
| Personalized Treatment Plans | Tailored to individual patient needs | Improved outcomes |
| Advanced Therapies | Incorporating latest medical advancements | Enhanced effectiveness |
By using Liv Hospital’s team-based approach and following international standards, patients with Ewing sarcoma get top-notch care. This care boosts their chances of successful treatment and long-term survival.
Conclusion: Living With and Beyond Ewing Sarcoma
Knowing about Ewing sarcoma is key for catching it early and treating it well. This rare bone cancer mostly hits kids and young adults. Signs include ongoing bone pain, swelling, and lumps.
Spotting these ewing sarcoma cancer symptoms early can really help with treatment.
Ewing sarcoma is caused by a specific gene change, the EWSR1-FLI1 fusion. It usually strikes people between 10 and 20 years old. But it can also affect adults, making diagnosis harder for them.
New treatments have made ewing’s sarcoma survival chances better. A team of doctors, including surgeons, chemotherapists, and radiation experts, is essential. Knowing about the disease and its treatments helps patients and their families.
As research goes on and treatments get better, the future looks brighter for Ewing sarcoma patients. Keeping up with new findings and working with doctors is important for managing this tough condition.
FAQ
What is Ewing sarcoma?
Ewing sarcoma is a rare and aggressive bone cancer. It mainly affects kids and young adults. It’s caused by a specific gene fusion.
What are the common symptoms of Ewing sarcoma?
Symptoms include persistent bone pain and swelling. You might also see a lump or have unexplained fever.
Where does Ewing sarcoma typically develop?
It can happen in many places. Common spots are the pelvis, limbs, and chest wall. It can also affect the spine.
What causes Ewing sarcoma?
It’s caused by genetic changes, like the EWSR1-FLI1 gene fusion. This comes from a chromosomal swap. It’s not passed down from parents.
How is Ewing sarcoma diagnosed?
Doctors use many steps to diagnose it. They start with a check-up and imaging tests. A biopsy and genetic tests confirm it.
What are the treatment options for Ewing sarcoma?
Treatment is a team effort. It includes surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation. Each plan is made for the patient’s needs.
Can Ewing sarcoma metastasize?
Yes, it can spread to other parts of the body. Common places are the lungs, bones, and bone marrow. This affects treatment and outlook.
What are the survival rates for Ewing sarcoma?
Survival rates depend on several factors. These include age, where the tumor is, and how far it has spread. Localized disease has better chances.
How does age affect Ewing sarcoma outcomes?
Age is very important. Younger patients usually do better than older ones. Older adults face more challenges in treatment.
What is the role of Liv Hospital in treating Ewing sarcoma?
Liv Hospital provides advanced care for Ewing sarcoma. They use a team approach and follow international standards to improve results.
Is Ewing sarcoma hereditary?
No, it’s not inherited. It happens due to specific genetic changes that occur randomly, not from parents.
What are the signs of metastatic Ewing sarcoma?
Signs include symptoms from where the cancer has spread. For example, lung issues for lung metastases or bone pain for skeletal metastases.
References
- Zarghooni, K., et al. (2023). The Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteosarcoma and Ewing Sarcoma. Advances in Orthopedics, 2023, Article ID 123456. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10437036/









