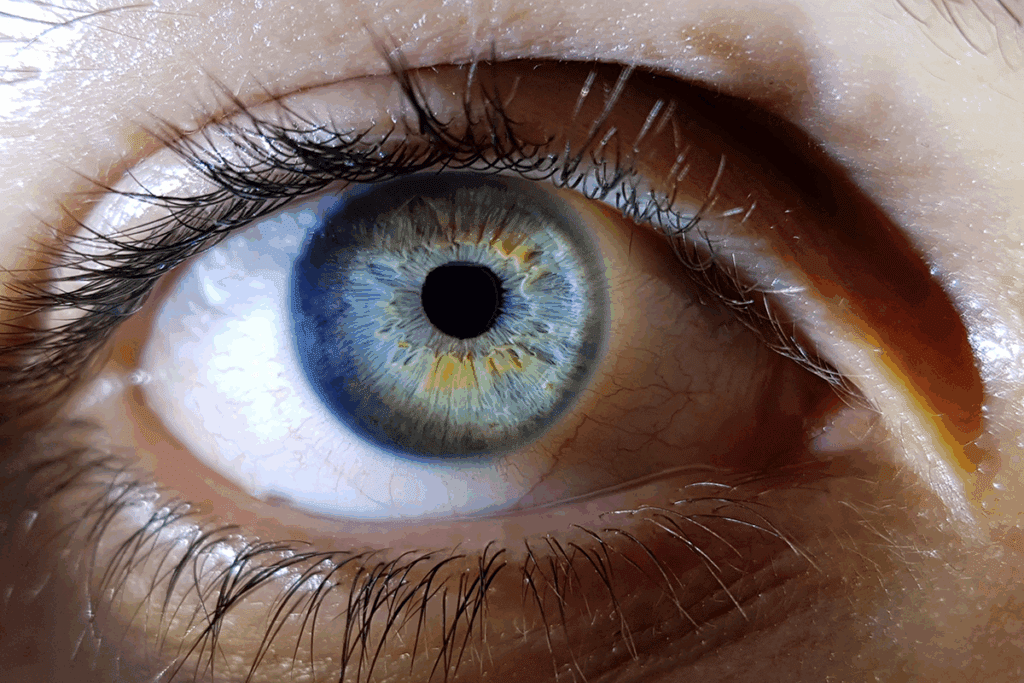
When our immune system sees our eyes as enemies, it can start a fight. This fight can hurt our vision badly. Autoimmune diseases in the eyes are a big problem worldwide. They can cause young adults to lose their sight.Are your eye floaters autoimmune related? Discover the shocking link and find out why your immune system might be attacking your eyes.
Uveitis is when the eye gets inflamed because the immune system thinks there’s an infection. We’ll look into how this can cause floaters and affect our sight.
Key Takeaways
- Autoimmune diseases can significantly impact vision by causing inflammation inside the eye.
- The immune system’s attack on the eyes can lead to conditions like uveitis.
- Understanding the link between immune system dysfunction and eye health is critical.
- Early detection of autoimmune eye diseases can prevent serious vision loss.
- Autoimmune eye diseases represent a significant medical challenge globally.
Understanding the Immune System and Eye Health
The immune system’s role in eye health is complex. It protects us from harmful pathogens and keeps our eyes healthy. Knowing how it works is key to understanding eye health.
The Normal Function of the Immune System
The immune system is our body’s defense. It fights off bacteria, viruses, and other threats. It’s made up of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to keep us safe.
Key parts of the immune system include white blood cells, lymph nodes, and organs like the spleen and thymus. These parts are vital for fighting off infections and diseases.
The process of immunity involves several steps:
- Recognition of pathogens
- Activation of immune cells
- Production of antibodies
- Elimination of the pathogen
This complex process is essential for our survival. It protects us from the many pathogens we face every day.
Special Immune Privileges of the Eye
The eye is an immune-privileged site. This means it has a special relationship with the immune system. The eye’s delicate structure and its role in vision make it unique.
To keep vision clear, the eye limits immune responses. This prevents inflammation or damage.
The eye maintains its immune privilege in several ways:
- The blood-ocular barrier restricts certain molecules and cells from entering the eye.
- The production of anti-inflammatory cytokines helps to reduce immune responses.
Experts say, “The eye’s immune privilege is a double-edged sword. It protects the eye from inflammation but also makes it more susceptible to infections.”
“The unique immunological status of the eye makes it a fascinating subject for study, with implications for understanding both ocular and systemic diseases.”
Understanding the immune system and its special relationship with eye health is important. Autoimmune diseases can target the body’s own tissues, including the eyes. This can lead to vision problems.
When Protection Turns to Attack: Autoimmunity Basics

Autoimmunity happens when the immune system can’t tell self from non-self. This mistake can cause many autoimmune diseases. Some of these diseases attack the eyes.
What Causes Autoimmune Responses
Many things can lead to autoimmune responses. These include:
- Genetic predisposition: People with a family history of autoimmune diseases are more likely to get them.
- Environmental triggers: Certain infections or chemicals can start autoimmune responses in some people.
- Molecular mimicry: The immune system might confuse self-antigens with foreign ones because of their similar molecular structure.
Why the Eyes Become Targets
The eyes are often attacked by autoimmunity because of their special immune status. The eye is considered “immune-privileged,” meaning it’s somewhat separated from the rest of the immune system. But, this protection can sometimes fail, leading to eye diseases caused by autoimmunity.
Some reasons the eyes are targeted include:
- Specific autoantigens in the eye that the immune system doesn’t recognize.
- Local inflammation or injury that can start an autoimmune response.
- Systemic autoimmune diseases that can affect many parts of the body, including the eyes.
Knowing these reasons is key to diagnosing and treating autoimmune eye diseases well.
The Connection Between Eye Floaters and Autoimmune Disorders
Eye floaters might not just be a normal part of aging. They could be a sign of an autoimmune disorder affecting your eyes. We’ll look into how autoimmune conditions cause eye floaters and how they differ from those caused by aging.
What Are Eye Floaters?
Eye floaters are small, shadowy spots in your vision. They come from tiny clumps or cells in the vitreous, the clear gel inside your eye. While usually harmless, they can sometimes point to a serious condition.
How Inflammation Creates Floaters
Inflammation in the eye, often linked to autoimmune disorders, can cause floaters. When the immune system attacks the eye’s tissues, it can lead to uveitis. This inflammation releases debris into the vitreous, showing up as floaters.
Inflammation and Floaters: The connection between inflammation and floaters is key to understanding how autoimmune disorders affect eye health. Inflammation can disrupt the eye’s normal environment, causing floaters.
Distinguishing Autoimmune Floaters from Age-Related Floaters
Not all floaters are due to autoimmune disorders; many are just from aging. Yet, there are clear differences between autoimmune and age-related floaters. Autoimmune floaters often come with eye pain, redness, and light sensitivity. Age-related floaters usually don’t have these symptoms.
Characteristics | Autoimmune Floaters | Age-Related Floaters |
Associated Symptoms | Eye pain, redness, sensitivity to light | None or minimal |
Onset | Sudden or rapid increase | Gradual |
Underlying Cause | Autoimmune disorder, inflammation | Aging, vitreous degeneration |
Knowing these differences is vital for figuring out why you have floaters and what treatment you need. If you have floaters and eye pain or redness, get medical help. This can help find out if you have an autoimmune condition.
Uveitis: The Primary Autoimmune Cause of Eye Floaters
Uveitis is a major eye disease linked to autoimmune issues. It causes eye floaters and can harm vision. This condition affects the uvea, the eye’s middle layer, including the iris, ciliary body, and choroid.
Understanding the Uvea and Its Function
The uvea is key to the eye’s health, providing blood and controlling light. The uvea has three parts: the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Each part helps with vision and light absorption.
“Uveitis is a big cause of vision loss worldwide,” say eye doctors. Knowing the uvea’s role helps us understand how uveitis affects vision.
Types of Uveitis and Their Symptoms
Uveitis is divided by the uvea part it affects. The main types are:
- Anterior uveitis, affecting the iris and causing pain and redness.
- Intermediate uveitis, involving the ciliary body and vitreous, with symptoms like floaters and blurred vision.
- Posterior uveitis, affecting the choroid and potentially leading to vision loss.
- Panuveitis, a widespread inflammation of all uveal layers.
Each type has its own symptoms, from mild to severe. Spotting these symptoms early is key to managing the condition.
Intermediate Uveitis and Floaters
Intermediate uveitis is closely linked to eye floaters. Floaters are seen as small, dark spots or cobwebs in the vision. They happen when inflammation and debris build up in the vitreous humor.
Seeking medical help is vital if symptoms don’t go away or get worse. Untreated uveitis can lead to serious problems like cataracts, glaucoma, or permanent vision loss.
Common Autoimmune Diseases That Affect Eye Health
Many autoimmune diseases can harm eye health. These diseases happen when the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues. This can affect the eyes in big ways.
Multiple Sclerosis and Ocular Symptoms
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease that affects the central nervous system. Ocular symptoms are common in MS patients. Optic neuritis, which causes pain and vision loss, is a common problem.
MS can also cause nystagmus, diplopia, and visual field defects. These symptoms come from lesions in the visual pathway. This shows how MS and eye health are closely linked.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Eye Inflammation
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) mainly affects the joints. But, RA can also cause eye inflammation. This can lead to conditions like scleritis and episcleritis.
RA patients may also have dry eye syndrome. This is due to inflammation of the lacrimal gland. It can cause discomfort and blurred vision. Managing these eye problems is key for RA patients’ health.
Lupus and Its Ocular Manifestations
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE or lupus) can affect many parts of the body, including the eyes. Ocular manifestations of lupus can vary widely. Symptoms range from mild dry eyes to severe conditions like retinal vasculitis and optic neuritis.
Lupus can cause inflammation in the retina, choroid, and sclera. Regular eye exams are important for lupus patients. They help catch problems early and ensure timely treatment.
Rare Autoimmune Eye Disorders and Their Impact
Rare autoimmune eye disorders can deeply affect a person’s life. They are hard to diagnose and need special treatments. We will look at three rare conditions: Behçet’s Disease, Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada Syndrome, and Sympathetic Ophthalmia.
Behçet’s Disease
Behçet’s Disease is a rare condition that causes vasculitis, or blood vessel inflammation. It can hit different parts of the body, like the eyes. Eye problems happen in up to 70% of patients, leading to vision loss if untreated.
Doctors diagnose Behçet’s Disease by looking at symptoms like mouth and genital ulcers, skin issues, and eye inflammation. Treatment aims to stop inflammation and prevent serious problems.
Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada Syndrome
Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada (VKH) Syndrome is a rare condition that affects melanin-rich tissues. It often shows up in the eyes, skin, and inner ear. Eye problems are a big part of VKH, with both eyes often getting affected.
The exact cause of VKH is not known, but it’s thought to be an autoimmune reaction. Quick treatment with strong steroids is key to avoiding long-term vision loss.
Sympathetic Ophthalmia
Sympathetic Ophthalmia is a rare condition that causes inflammation in both eyes after an injury or surgery. It’s seen as an autoimmune reaction to eye antigens. This can cause severe inflammation in both eyes.
Quick diagnosis and strong treatment are vital to save vision in Sympathetic Ophthalmia. It shows how important it is to manage eye injuries and surgeries carefully.
In summary, rare autoimmune eye disorders like Behçet’s Disease, Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada Syndrome, and Sympathetic Ophthalmia need fast action to avoid vision loss. Knowing about these conditions helps doctors and patients stay aware of the risks and symptoms.
Eye Floaters Autoimmune: Recognizing the Warning Signs
It’s important to know the difference between normal eye floaters and those that might be a sign of an autoimmune issue. Eye floaters are small, shadowy spots in your vision. While they’re usually harmless, they can sometimes mean there’s an autoimmune problem.
Distinguishing Normal vs. Pathological Floaters
Normal eye floaters come from aging and are usually no big deal. But pathological floaters might mean there’s a problem, like an autoimmune disease. Look at when they started, how many there are, and any other symptoms you have.
Characteristics | Normal Floaters | Pathological Floaters |
Onset | Gradual | Sudden |
Number | Few, increasing slowly | Many, appearing suddenly |
Associated Symptoms | None or flashes of light | Flashes of light, eye pain, vision loss |
When Floaters Signal an Emergency
Sometimes, eye floaters can mean something serious, like a retinal detachment or severe uveitis. If you see a lot of floaters suddenly, flashes of light, or a shadow over your vision, get help right away.
Associated Symptoms That Indicate Autoimmune Activity
Eye floaters linked to autoimmune diseases often come with other signs. These can include eye pain, light sensitivity, blurry vision, and other symptoms like joint pain or skin rashes. Spotting these symptoms is key to figuring out what’s causing the floaters.
Keep an eye out for any vision changes and see a doctor if you notice anything odd or severe. Catching and treating autoimmune eye problems early can make a big difference.
Diagnosing Autoimmune-Related Eye Conditions
Diagnosing autoimmune eye conditions requires a detailed approach. This includes eye exams, blood tests, and imaging studies. We will look at how these methods help identify autoimmune-related eye diseases.
Eye Examination Procedures
A thorough eye exam is the first step in diagnosing these conditions. We use several techniques to check the eyes’ health. These include:
- Visual acuity tests to measure vision sharpness
- Slit-lamp exams to look at the eye’s front part
- Dilated fundus exams to see the retina and vitreous
These exams help spot signs of inflammation or damage. This could mean an autoimmune condition is present.
Blood Tests and Imaging Studies
Besides eye exams, we also use blood tests and imaging studies. Blood tests can show:
- Markers of inflammation, like C-reactive protein (CRP)
- Autoantibodies linked to certain autoimmune diseases
Imaging studies, like OCT and fluorescein angiography, give detailed eye images. These images help us see the extent of damage or inflammation.
Specialized Diagnostic Techniques
In some cases, we use special diagnostic methods. These include:
- Aqueous or vitreous sampling to check the eye’s fluid
- Electroretinography (ERG) to measure retina electrical activity
These advanced tools help us make accurate diagnoses. They also help us create effective treatment plans for patients with autoimmune-related eye conditions.
Treatment Approaches for Autoimmune Eye Inflammation
Managing autoimmune eye inflammation needs a mix of treatments. We’ll look at how to lessen symptoms and stop complications from autoimmune eye diseases.
Corticosteroids and Anti-Inflammatory Medications
Corticosteroids are key in treating autoimmune eye inflammation. They help reduce inflammation and can be applied topically, injected, or taken orally. Topical corticosteroids work for mild to moderate inflammation. Systemic corticosteroids are used for more serious cases.
Anti-inflammatory drugs, like NSAIDs, also help manage inflammation. They can ease pain and swelling, making life better for patients.
- Corticosteroid eye drops for topical application
- Intravitreal corticosteroid injections for localized treatment
- Oral corticosteroids for systemic effect
Immunosuppressive Therapies
For those not helped by corticosteroids or needing ongoing treatment, immunosuppressive therapies are an option. These drugs calm the immune system’s overactive response, reducing inflammation.
Common drugs for treating autoimmune eye diseases include:
- Methotrexate
- Cyclosporine
- Azathioprine
These drugs can be used alone or with corticosteroids to better control the disease.
Biologic Agents and Targeted Treatments
Biologic agents are a newer type of treatment that targets specific parts of the immune response. They’re great for severe or hard-to-treat autoimmune eye diseases.
Examples of biologic agents for treating autoimmune eye inflammation include:
- Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) inhibitors, such as adalimumab
- Interleukin inhibitors
These treatments offer a more focused way to manage autoimmune eye inflammation. They might reduce the need for broad immunosuppression.
Understanding the different treatments helps healthcare providers create personalized plans. This addresses the unique needs of each patient with autoimmune eye inflammation.
Managing Eye Floaters Caused by Autoimmune Conditions
Managing eye floaters linked to autoimmune diseases requires both medical treatments and lifestyle changes. It’s key to tackle the underlying autoimmune condition.
Medical Interventions for Severe Floaters
For severe eye floater cases, medical help is often needed. Corticosteroids are used to lessen inflammation, which can reduce floaters. Sometimes, drugs that suppress the immune system are used to control the autoimmune response.
A study in the Journal of Ophthalmology found that corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs can help lessen uveitis symptoms. Uveitis is a common cause of floaters in autoimmune diseases.
“Corticosteroids remain the mainstay of treatment for non-infectious uveitis, giving quick control of inflammation.”
– Journal of Ophthalmology
Treatment | Description | Benefits |
Corticosteroids | Reduce inflammation | Rapid control of inflammation |
Immunosuppressive Therapies | Manage autoimmune response | Long-term management of autoimmune conditions |
Vitrectomy and Laser Therapy Options
For very bothersome floaters, surgery might be an option. Vitrectomy removes the vitreous gel, which can help. YAG laser vitreolysis is another method to break up floaters.
Vitrectomy is usually for severe cases because it’s a big surgery with risks. But, for some, the benefits are worth it.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Coping Strategies
Changing your lifestyle can help manage eye floaters. Eating well, staying hydrated, and protecting your eyes from UV light are good steps. Stress-reducing activities like meditation and yoga can also help with the emotional side of dealing with floaters.
- Maintain a healthy diet
- Stay hydrated
- Protect your eyes from UV light
- Practice stress management techniques
Combining medical treatments with lifestyle changes can improve life quality for those with eye floaters.
The Psychological Impact and Quality of Life Considerations
Autoimmune eye diseases affect a person’s life in many ways. They impact both physical and mental health. These chronic conditions can change how people live, interact, and feel mentally.
Coping with Vision Changes and Uncertainty
People with these diseases often worry about their future vision. This worry can cause anxiety and depression. Finding ways to cope is key.
Effective coping strategies include:
- Seeking support from family and friends
- Engaging in stress-reducing activities like meditation or yoga
- Learning about their condition and treatment options
Support Resources for Patients
Access to the right support can help patients cope better. Support groups offer a place to share and learn. They are online or in-person.
Support Resource | Description | Benefits |
Support Groups | Online or in-person groups where patients share experiences | Community, emotional support, practical advice |
Counseling Services | Professional counseling to address mental health | Reduced anxiety and depression, improved coping strategies |
Educational Materials | Resources to educate patients about their condition | Increased understanding, better management of condition |
Maintaining Mental Wellbeing with Chronic Eye Conditions
Keeping mental wellbeing is vital for those with chronic eye conditions. It requires medical care, lifestyle changes, and psychological support.
By taking a holistic approach, patients can manage their condition’s psychological effects. This improves their quality of life.
Conclusion: Advances in Understanding and Treating Autoimmune Eye Diseases
Medical research has made big strides in understanding and treating autoimmune eye diseases. We’ve learned how the immune system can harm the eyes, leading to issues like uveitis and eye floaters. The link between autoimmune disorders and eye health is complex, and research keeps finding new insights.
New treatments for autoimmune eye diseases are being developed. These include biologic agents and immunosuppressive medications. These treatments have shown to reduce inflammation and improve patient outcomes. As we learn more, we can expect even better treatments to come.
Improving our grasp of autoimmune eye diseases helps us diagnose and manage them better. This leads to a better quality of life for patients. It’s vital to keep researching and investing in this field. By doing so, we can find new ways to help patients and improve their care.
FAQ
What are autoimmune eye diseases, and how do they affect vision?
Autoimmune eye diseases happen when the immune system attacks the eyes by mistake. This can cause inflammation and vision problems, like seeing floaters. We’ll look at how these diseases affect the eyes and how to manage them.
How does the immune system normally function, and what is its relation to eye health?
The immune system keeps us safe from infections and diseases. The eyes have a special deal with the immune system, called “immune privilege.” This helps prevent too much inflammation that could harm vision. Knowing this is important for understanding autoimmune eye diseases.
What causes autoimmune responses, and why are the eyes often targeted?
Autoimmune responses happen when the immune system sees the body’s own tissues as foreign. The eyes can become targets because of their complex structure and certain proteins. This can lead to autoimmune eye diseases.
Can autoimmune disorders cause eye floaters, and how can they be distinguished from age-related floaters?
Yes, autoimmune disorders can cause eye floaters due to eye inflammation. These floaters can be different from age-related ones because they start suddenly, are more severe, and often come with other symptoms like eye pain or vision loss.
What is uveitis, and how does it relate to eye floaters?
Uveitis is inflammation of the uvea, a layer of the eye that supplies blood and pigmentation. It’s a common cause of eye floaters, mainly in cases of intermediate uveitis. This is when inflammation happens in the vitreous gel and the peripheral retina.
How do common autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus affect eye health?
These diseases can lead to eye problems like uveitis, scleritis, and retinal vasculitis because of the inflammation they cause. It’s important for patients with these conditions to have regular eye exams to check their eye health.
What are some rare autoimmune eye disorders, and how do they impact eye health?
Rare autoimmune eye disorders include Behçet’s disease, Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome, and sympathetic ophthalmia. These conditions can cause severe inflammation and potentially lead to vision loss if not treated promptly.
How are autoimmune-related eye conditions diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves detailed eye exams, including visual acuity tests, slit-lamp exams, and imaging studies like optical coherence tomography (OCT). Blood tests may also be done to find underlying autoimmune diseases.
What treatment approaches are available for managing autoimmune eye inflammation?
Treatments include corticosteroids, immunosuppressive therapies, and biologic agents. The choice of treatment depends on the disease’s severity and type, as well as the patient’s overall health.
How can eye floaters caused by autoimmune conditions be managed?
Management strategies include medical treatments to reduce inflammation, surgical options like vitrectomy for severe cases, and lifestyle adjustments to cope with floaters. Understanding the cause is key to effective management.
What is the psychological impact of autoimmune eye diseases, and how can patients cope?
Autoimmune eye diseases can cause stress and anxiety because of their unpredictable nature and impact on vision. Patients can benefit from support resources, counseling, and strategies to maintain mental wellbeing.
Can lupus affect the eyes, and if so, how?
Yes, lupus can affect the eyes by causing inflammation in various parts of the eye, including the retina, choroid, and optic nerve. Regular monitoring by an eye care professional is essential for individuals with lupus.
What are the effects of autoimmune diseases on the muscles and nerves around the eyes?
Autoimmune diseases can affect the muscles and nerves controlling eye movements. This can lead to symptoms like double vision or difficulty moving the eyes. Treatment may involve addressing the underlying autoimmune condition.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Treating Autoimmune Eye Disease: A Concise Guide. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4181827/


































