At Liv Hospital, we use fludeoxyglucose F 18 imaging to improve diagnosis. The F 18 FDG PET scan is a key tool in medical imaging. It helps find and manage many health issues.
This scan uses a glucose analog labeled with fluorine-18. It spots areas with high metabolic activity, like cancer or inflammation. The scan works by injecting 18f-fdg into the blood. This radiotracer builds up in the examined area.
We focus on patient care at Liv Hospital. The fluorodeoxyglucose PET scan helps us find cancer. It also checks if treatments are working and how likely recovery is.
Key Takeaways
- Advanced fludeoxyglucose F 18 imaging technology enhances diagnostic confidence.
- The F 18 FDG PET scan detects and manages various medical conditions.
- The procedure involves injecting the 18f-fdg radiotracer into the bloodstream.
- Our patient-centered care provides complete support during the diagnostic process.
- The fluorodeoxyglucose PET scan detects cancer and assesses treatment effectiveness.
Understanding F 18 FDG PET Scan Technology
F 18 FDG PET scan technology uses Fludeoxyglucose F 18, a substance that acts like glucose. It helps find areas in the body that are very active. This is key in finding and treating diseases, like cancer.
Definition and Basic Principles
F 18 FDG PET scan is a way to see how active tissues and organs are. It uses a tiny amount of Fludeoxyglucose F 18 that is injected into the blood. This substance goes to cells based on how much glucose they use.
Cells that use a lot of glucose, like cancer cells, take up more of this substance. The PET scan can then spot these active areas.
The Role of Fludeoxyglucose F 18 as a Radiotracer
Fludeoxyglucose F 18 is a great radiotracer because it acts like glucose. After it’s injected, it spreads through the body and gets taken up by cells. The PET scanner picks up the positrons from the fluorine-18, making detailed images of metabolic activity.
What makes Fludeoxyglucose F 18 a top choice for this role includes:
- It’s taken up by cells like glucose
- It emits positrons for PET imaging
- It has a half-life of about 110 minutes, which is long enough for imaging but short enough to keep radiation low
How FDG Mimics Glucose Metabolism
FDG acts like glucose by being phosphorylated by hexokinase to FDG-6-phosphate. But unlike glucose-6-phosphate, FDG-6-phosphate can’t be broken down further. This means it stays trapped in cells.
This trapping helps FDG build up in cells that use a lot of glucose, like cancer cells. This makes it a great tool for finding and tracking cancer. The amount of FDG taken up shows how active the cells are, helping doctors diagnose and monitor treatment.
The Science Behind Fluorodeoxyglucose (F-18)
Fluorodeoxyglucose (F-18), or FDG, is a key tool in medical imaging. It’s used in PET scans to see how the body uses energy. This helps doctors understand health issues better.
Production and Properties of F-18 Radiotracers
F-18 is made in a cyclotron by hitting oxygen-18 with protons. This creates fluorine-18, which is then attached to glucose. This makes FDG. Its short half-life and ability to bind to glucose make it perfect for PET scans.
Biochemical Pathway of FDG in Cells
After being given to a person, FDG is taken into cells. There, it’s changed into FDG-6-phosphate by an enzyme. This phosphate can’t be broken down further, so it stays in the cells. This lets doctors see how cells are using glucose.
Differences Between FDG and Natural Glucose
FDG and natural glucose are similar in how they enter cells. But they differ in what happens next. Natural glucose is broken down completely, while FDG gets stuck. This makes FDG great for showing where cells are most active.
| Characteristics | FDG | Natural Glucose |
| Uptake Mechanism | Glucose transporters | Glucose transporters |
| Metabolic Fate | Trapped after phosphorylation | Fully metabolized through glycolysis |
| Use in Diagnostics | PET scans for metabolic activity | Natural energy source |
Key Applications of F 18 FDG PET Scan in Oncology
The F 18 FDG PET scan has changed oncology by giving us key insights into cancer. It helps us diagnose, stage, and monitor cancer treatment better. This scan shows us where cancer is active, making it very useful in fighting cancer.
Cancer Detection and Metabolic Activity
The F 18 FDG PET scan is great at finding cancer because it spots where glucose is used more. Early detection is key for good treatment, and this scan helps us see how active tumors are.
Staging and Treatment Planning
Knowing how far cancer has spread is vital for treatment planning. The F 18 FDG PET scan helps us see if cancer has spread to lymph nodes or other parts of the body. This helps us plan treatment more accurately.
| Application | Description | Benefit |
| Cancer Detection | Identifies areas of high metabolic activity indicative of cancer | Early detection enables timely intervention |
| Staging | Determines the extent of cancer spread | Aids in precise treatment planning |
| Treatment Monitoring | Assesses response to therapy | Helps in adjusting treatment strategies |
Monitoring Therapy Response and Recurrence
It’s important to check how well treatment is working and if cancer comes back. The F 18 FDG PET scan shows us how tumors are doing after treatment. This helps us see if treatment is working and if cancer might come back.
In conclusion, the F 18 FDG PET scan is a powerful tool in fighting cancer. It helps us find cancer, understand how far it has spread, plan treatment, and check if treatment is working. Its detailed metabolic information is key in managing cancer.
Specific Cancer Types and 18F-FDG Imaging Effectiveness
18F-FDG imaging is very effective in managing different cancers. This includes lung, lymphoma, melanoma, and colorectal cancer. We will look at how it is used in these cancer types.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Evaluation
18F-FDG PET scans are key in checking non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). They show how active tumors are, which helps in planning treatment. Research shows 18F-FDG PET/CT helps find active tumors in NSCLC.
Lymphoma Staging and Management
In lymphoma, 18F-FDG PET scans help with staging, checking how well treatment works, and finding when cancer comes back. 18F-FDG PET/CT is very good at finding lymphoma. It helps us make treatment plans and watch how the disease changes.
Melanoma and Colorectal Cancer Applications
18F-FDG PET scans are also useful in melanoma and colorectal cancer. They help find where cancer has spread and check if treatment is working. In melanoma, they find distant cancer spots. In colorectal cancer, they help find cancer that has come back and see if treatment is working.
| Cancer Type | Application of 18F-FDG PET/CT | Benefits |
| Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | Evaluation and staging | Accurate assessment of tumor metabolic activity |
| Lymphoma | Staging, treatment response, and recurrence detection | High sensitivity in detecting lymphoma |
| Melanoma | Detecting metastatic disease | Identification of distant metastases |
| Colorectal Cancer | Detecting recurrent disease and assessing treatment response | Evaluation of therapy effectiveness |
Neurological Applications of 18F Fluorodeoxyglucose PET
The use of 18F fluorodeoxyglucose PET (FDG PET) has changed how we diagnose and treat brain disorders. It shows how the brain uses glucose, giving doctors important clues. This helps them make better choices for their patients.
Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia Diagnosis
FDG PET is key in spotting Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias. It finds where the brain uses less glucose, a sign of these diseases. Key features include:
- Reduced glucose metabolism in temporal and parietal lobes
- Characteristic patterns of hypometabolism that correlate with disease severity
- Ability to differentiate Alzheimer’s disease from other forms of dementia
Epilepsy Focus Localization
In epilepsy, FDG PET helps find where seizures start, which is hard in some cases. It spots areas where glucose use is off, helping plan surgery. The benefits include:
- Identification of hypometabolic regions corresponding to the seizure focus
- Improved surgical outcomes by accurately localizing the epileptogenic zone
- Reduced need for invasive diagnostic procedures
Brain Tumor Assessment and Differentiation
FDG PET is also great for checking brain tumors. It helps tell different tumors apart and their severity. Key applications include:
- Distinguishing between high-grade and low-grade tumors based on glucose metabolism
- Identifying tumor recurrence versus radiation necrosis
- Guiding biopsy and treatment planning
Thanks to 18F fluorodeoxyglucose PET, doctors can get better at diagnosing and treating brain problems. This leads to more effective treatments for patients.
Cardiac Viability Assessment Using Fludeoxyglucose 18F
In cardiology, fludeoxyglucose 18F PET scans are key for checking heart health. They help us see how active the heart is, which guides treatment. This advanced imaging is vital for patient care.
Identifying Viable Myocardium
Fludeoxyglucose 18F PET scans spot active heart areas. This is key for treating heart disease or after a heart attack. It shows which parts of the heart can recover.
We inject fludeoxyglucose 18F into the blood. It goes to the heart, showing which parts are working. High uptake means the heart tissue is alive. Low uptake might mean it’s damaged.
Differentiating Stunned from Scarred Tissue
Fludeoxyglucose 18F PET scans can tell stunned from scarred heart tissue. Stunned tissue is temporarily not working but can get better. Scarred tissue is permanently damaged.
| Tissue Type | Fludeoxyglucose 18F Uptake | Clinical Implication |
| Viable Myocardium | High | Potential for recovery with appropriate treatment |
| Stunned Myocardium | Moderate to High | May recover with restoration of blood flow |
| Scarred Myocardium | Low | Permanently damaged, limited recovery |
Cardiac Sarcoidosis and Inflammation Detection
Fludeoxyglucose 18F PET scans also find cardiac sarcoidosis and inflammation. Cardiac sarcoidosis is a serious condition. Finding it early is key to managing it.
These scans are very good at spotting heart inflammation. They help us target treatments, improving patient outcomes. This is very helpful for those with suspected cardiac sarcoidosis or unexplained heart failure.
Infection and Inflammation Detection with F-FDG
F-FDG PET scans are key in finding infections and inflammation. They spot areas with high activity, showing signs of infection or inflammation.
Fever of Unknown Origin Evaluation
Fever of Unknown Origin (FUO) is hard to solve. F-FDG PET scans help find the cause by showing where activity is high.
They help doctors focus on the right areas for more tests or treatment.
Vascular Inflammation Assessment
Vascular inflammation is key in diseases like atherosclerosis. F-FDG PET imaging spots this by seeing more glucose in artery walls.
This info is vital for spotting high-risk patients and checking if treatments work.
Orthopedic Infection Diagnosis
Diagnosing infections in joints or bones is tough. F-FDG PET scans are great because they can tell infection from other inflammation.
They help doctors know how big the infection is and what to do next, helping patients get better.
In summary, F-FDG PET scans are a big help in finding and treating infections and inflammation. They’re great for looking at FUO, checking for vascular inflammation, and finding infections in joints or bones.
Patient Preparation and Procedure for an F 18 FDG PET Scan
Knowing what to expect from an F 18 FDG PET scan can help reduce anxiety. We help our patients through every step to make the process smooth and successful.
Pre-Scan Dietary and Medication Guidelines
Before an F 18 FDG PET scan, patients need to follow certain dietary rules. They should fast for 4-6 hours, but water is okay. Avoiding strenuous exercise and sugary foods is also important.
Certain medications might need to be adjusted or stopped. Our medical team will give specific instructions based on each patient’s situation.
The Injection and Uptake Period
On the day of the scan, a small amount of 18F-FDG is injected into a vein. This fluorodeoxyglucose is absorbed by cells, like cancer cells, with high metabolic rates. There’s a 60-minute wait for the radiotracer to spread throughout the body.
During this time, patients should rest quietly. This helps avoid muscle activity that could affect the scan results.
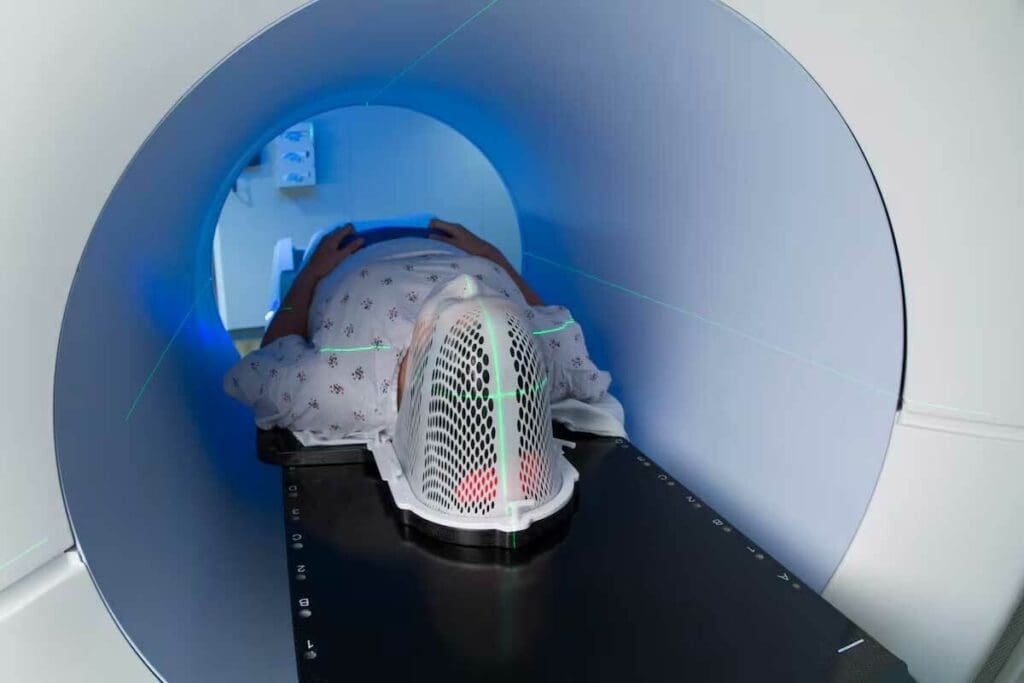
The Scanning Process and Patient Experience
After the uptake period, patients lie on a scanning table for the F 18 FDG PET scan. The scan lasts 30 to 60 minutes, and patients must stay very quiet. Our PET/CT scanners combine functional and anatomical imaging for detailed information.
We aim to make the experience as comfortable as possible. We address any concerns or questions patients have before, during, or after the scan.
Interpreting PET-CT Results and Standardized Uptake Values
Understanding PET-CT scans is key. It involves knowing SUV measurements and spotting uptake patterns in diseases. We use 18F-FDG SUVs to measure the uptake in tissues.
Understanding SUV Measurements
SUVs give us a semi-quantitative look at FDG uptake. They help us see which tissues are more active. An SUV of 2.5 is a common cut-off for cancer, but it can change based on the case.
Many things affect SUVs, like how the patient is prepared and the scanner used. So, we look at SUVs along with the images and patient history.
Common Uptake Patterns in Different Diseases
Different diseases show unique FDG uptake patterns. For example:
- Cancer cells often take up a lot of FDG because they use more glucose.
- Infections and inflammation show up because immune cells take up FDG.
- Neurological diseases like Alzheimer’s show decreased glucose use in certain brain areas.
Spotting these patterns helps us diagnose and track diseases more accurately.
Potential False Positives and Negatives
FDG PET-CT is very useful but has its limits. False positives can happen due to inflammation, infection, or normal tissue uptake. False negatives might occur with small tumors, low-grade cancers, or tumors that don’t take up much FDG.
Knowing these issues helps us interpret PET-CT scans better. We must look at the whole picture, including other scans and sometimes more tests, to confirm our findings.
By grasping SUVs, recognizing patterns, and being aware of false positives and negatives, we can better understand PET-CT scans. This helps us manage patient care more effectively.
Safety Considerations and Limitations of F 18 FDG Imaging
F 18 FDG PET scans use radioactive materials. This means we need to handle them carefully and manage patient safety. It’s important to think about the good and bad sides of using this tool.
Radiation Exposure Compared to Other Modalities
F 18 FDG PET scans give patients a small amount of radiation. The dose is about 7-10 mSv. For comparison, a chest CT scan has a similar dose, around 7-8 mSv according to the National Cancer Institute.
It’s key to compare radiation doses from different scans. For example, a PET/CT scan might give more radiation. But, it often helps doctors see more clearly, which is worth it for many patients.
Patient Selection and Contraindications
Choosing the right patients for F 18 FDG PET scans is very important. Conditions like diabetes can change how scans are read. We must manage diabetes carefully to get accurate results.
Diabetic patients might need to change their diet or insulin before the scan. This helps make sure the scan works right.
Managing Diabetic Patients
Preparing diabetic patients for F 18 FDG PET scans is a big job. We tell them to follow a special diet and adjust their meds if needed. This keeps their blood sugar right for the scan.
Pregnancy and Pediatric Considerations
Using F 18 FDG PET scans on pregnant women and kids is tricky because of radiation risks. We have to think hard about the benefits and risks for these groups. Pregnant women might get other scans instead. For kids, we decide on a case-by-case basis, looking at the benefits and risks.
Conclusion: Advances and Future Directions in FDG PET Technology
The F 18 FDG PET scan is key in diagnosing and managing diseases. It has changed how we look at cancer, brain, and heart health. Thanks to F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose, doctors can now see more clearly and make better diagnoses.
The future of FDG PET looks bright, with new uses in personalized medicine and theranostics. Fluoro deoxy glucose will keep being a critical part of these scans. We can look forward to even better images and more precise measurements.
By keeping up with these advancements, we can make the most of F 18 FDG PET scans. This will help patients get better care. As research goes on, FDG PET will keep being a vital tool in healthcare, leading to new discoveries and better treatments.
FAQ
What is F 18 FDG PET scan technology?
F 18 FDG PET scan technology uses a special sugar labeled with a radioactive isotope. It helps find and manage health issues by spotting areas that use a lot of energy.
How is fluorodeoxyglucose (F-18) produced?
F-18 is made in a special machine called a cyclotron. Oxygen-18 is hit with protons to make fluorine-18. Then, it’s mixed with glucose to create FDG.
What are the applications of F 18 FDG PET scan in oncology?
In oncology, the F 18 FDG PET scan helps find, stage, and plan treatment for cancer. It’s great for lung, lymphoma, melanoma, and colorectal cancers.
How does 18F-FDG PET scan help in neurological conditions?
The 18F-FDG PET scan helps diagnose Alzheimer’s and other brain diseases. It also finds epilepsy and brain tumors by looking at how the brain uses sugar.
What is the role of F-FDG PET scan in cardiology?
In cardiology, the F-FDG PET scan checks if the heart is working right. It tells the difference between damaged and scarred heart tissue. It also finds inflammation in the heart.
How is F-FDG PET scan used in detecting infection and inflammation?
The F-FDG PET scan finds infections and inflammation. It’s useful for unknown fevers, heart inflammation, and bone infections. It spots areas that are very active.
What are the guidelines for patient preparation before an F 18 FDG PET scan?
Before the scan, patients must follow a special diet and adjust their medicines. This ensures the scan works well.
How are PET-CT results interpreted?
To understand PET-CT results, look at SUV values and know what different patterns mean. Be aware of false positives and negatives too.
What are the safety considerations for F 18 FDG PET imaging?
Safety first includes watching out for radiation and choosing the right patients. Diabetic patients, pregnant women, and kids need special care for safe scans.
What is the significance of Standardized Uptake Values (SUV) in PET-CT scans?
SUV values measure how much the tracer is taken up. They help see how severe a disease is and if treatment is working.
Can F 18 FDG PET scan be used for all types of cancer?
F 18 FDG PET scan works well for many cancers. But, it’s not perfect for all types. It depends on the cancer.
References
- Anand, S. S., & Minarik, D. (2011). Clinical applications of PET and PET/CT: Oncology, neurology, and cardiology. The Indian Journal of Radiology & Imaging, 21(3), 160-168. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4921358/




































