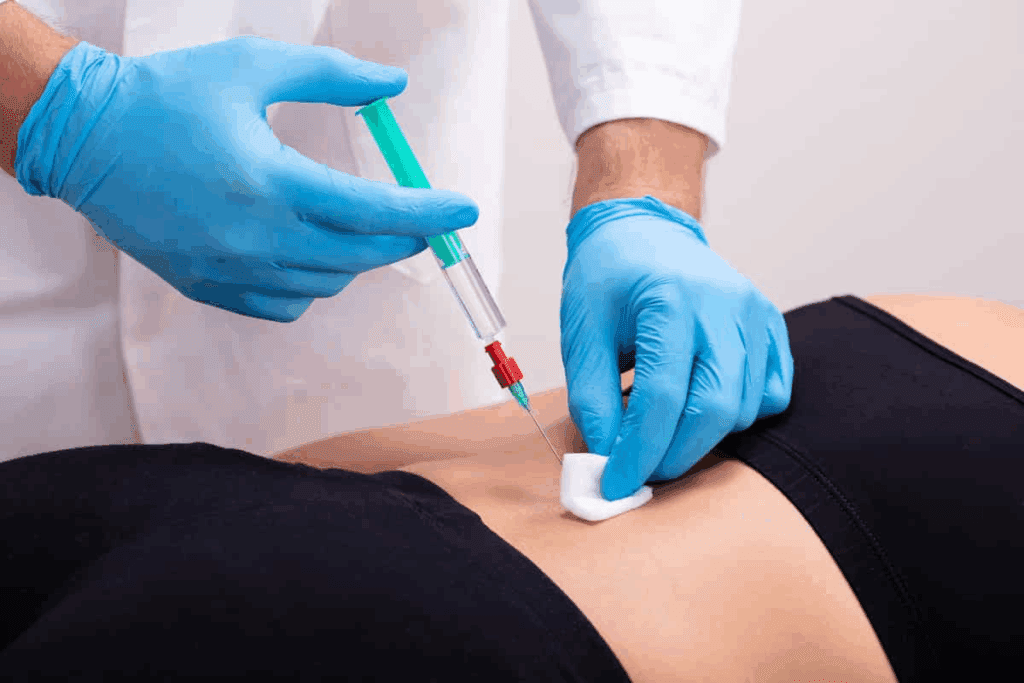
For those looking for relief from spine pain, a facet joint injection is a great option. We offer advanced intra-articular injections. These injections put pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory meds right where they’re needed.
Our team is here to help you understand the value of this procedure. It’s key in diagnosing and treating spine pain. In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about facet injections. This includes what they are, how they’re used, and how they’re done.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the definition and purpose of facet joint injections
- Learning about the clinical applications of facet joint shots
- Gaining insight into the step-by-step procedure of intra-articular facet injections
- Discovering the benefits of facet injections in diagnosing and treating spine pain
- Understanding the importance of seeking professional medical help for spine-related pain
What Are Facet Joint Injections and Their Clinical Applications
Facet joint injections are used for both finding and fixing spinal pain. They target the facet joints, small stabilizing spots between vertebrae. These joints are key for the spine’s flexibility and stability.
We’ll dive into what facet joint injections are, why they matter, and how they help with spinal pain. This will give you a full picture of their role in managing back pain.
Definition and Anatomical Relevance
Facet joint injections put medicine right into or around the facet joints. These joints have many pain sensors, making them a pain source. The mix of a numbing agent and a steroid is used.
The facet joints are important for the spine’s movement and stability. These injections help find or fix pain from these joints.
Diagnostic vs. Therapeutic Applications
Facet joint injections are used to figure out pain sources and to relieve pain. They can tell if the facet joints are causing pain. They also reduce inflammation and numb the area.
Whether to use facet joint injections depends on the patient’s situation and history. We’ll look at when to use them for each purpose later.
Common Terminology and Variations
Facet joint injections are also called facet injections or z-joint injections. Some call them paravertebral facet joint injections, highlighting their spot near the vertebrae. Knowing these names helps doctors talk clearly.
| Terminology | Description |
| Facet Joint Injections | Injections into or around the facet joints for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. |
| Facet Injections | A common abbreviation for facet joint injections. |
| Z-Joint Injections | Another term for facet joint injections, referencing the ‘z’ shape formed by the joints. |
| Paravertebral Facet Joint Injections | Emphasizes the location of the injections relative to the vertebrae. |
Knowing about facet joint injections helps doctors better treat spinal pain. This leads to better results for patients.
Indications and Patient Selection Criteria

It’s important to know when and who should get facet joint injections. These injections help those with chronic back or neck pain who haven’t found relief with other treatments. Medical Conditions Suitable for Treatment
Facet joint injections are good for certain health issues. These include facet joint arthritis, degenerative spondylolisthesis, and rheumatoid arthritis. “Facet joint injections can provide significant relief for patients suffering from these conditions,” say doctors.
Patient History Considerations
Looking at a patient’s medical history is key when considering facet joint injections. We check their past treatments, how long they’ve had pain, and how they reacted to injections before. This helps us guess how well they might do with facet joint injections.
Contraindications and Precautions
Even though facet joint injections are mostly safe, there are some who shouldn’t get them. People with bleeding disorders, infections, or on certain meds might not be good candidates. “Careful patient selection is key to minimizing risks and maximizing benefits,” say clinical guidelines.
Pre-Procedure Assessment and Planning
The first step in facet joint interventions is a detailed evaluation and planning. We start by checking the patient’s condition and looking for any risks. This ensures the best results for the patient.
Clinical Evaluation and Physical Examination
We look closely at the patient’s medical history and symptoms. This helps us decide if the procedure is right for them. We also check for any special precautions needed.
During the physical exam, we check the patient’s spinal movement and pain. We also check their nerves. This helps us confirm the diagnosis and plan the best treatment.
Imaging Studies and Diagnostic Workup
We use X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans to confirm the diagnosis. These images show us the facet joints’ condition. They help us see any problems that might affect the procedure.
We also review the patient’s medical records and lab results. This gives us a full picture of their health.
Procedure Scheduling and Patient Preparation
After the assessment, we schedule the procedure. We give the patient instructions on how to prepare. This includes what to eat and any medication changes.
Teaching the patient about the procedure is key. We explain its benefits and risks. We also tell them what to expect during recovery.
| Pre-Procedure Assessment Component | Description | Importance |
| Clinical Evaluation | Assessment of medical history and current symptoms | High |
| Physical Examination | Evaluation of spinal mobility, pain levels, and neurological status | High |
| Imaging Studies | X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans to confirm diagnosis | High |
| Procedure Scheduling | Coordination of procedure timing and patient preparation | High |
| Patient Education | Informing patients about the procedure and recovery | High |
Essential Equipment and Materials for Facet Joint Injection
Facet joint injections need special equipment for safe and accurate administration. The right tools and materials are key for skilled practitioners to do their job well.
Needles and Injection Materials
The right needle is vital for a successful facet joint injection. Spinal needles are often used because they fit well in the facet joint. The needle’s length and thickness depend on the patient’s body and the joint being treated.
The materials used for the injection are also important. This includes steroid medication to reduce swelling and local anesthetic for pain relief. Choosing these materials carefully is based on the patient’s health, the condition being treated, and any allergies.
Fluoroscopy and Imaging Equipment
Fluoroscopy is key for facet joint injections. It gives real-time images to help place the needle correctly. The fluoroscope lets doctors see where the needle is going and where it should be. Sometimes, ultrasound is used too, but fluoroscopy is the best for these injections.
Sterilization Supplies and Personal Protective Equipment
Keeping everything clean is very important for facet joint injections. Sterilization supplies like antiseptic solutions and gloves are needed. Doctors also wear personal protective equipment (PPE) like masks and gowns to stay safe.
Having all the right equipment and using it correctly helps doctors do facet joint injections safely. This helps patients with facet joint syndrome find relief.
Patient Positioning and Preparation
Getting the patient in the right position is key for a successful facet joint injection. This ensures the injection is done right, reducing risks and improving treatment results.
Informed Consent Process
We get the patient’s consent before the injection. We talk about the procedure, its benefits, risks, and other options. We make sure the patient understands and can ask questions.
Positioning for Cervical Injections
For cervical injections, the patient lies on their stomach or back. We use pillows to support the neck for comfort and stability. The head is positioned for easy access to the facet joint.
Positioning for Thoracic Injections
Thoracic injections are done with the patient on their stomach. A pillow may be used to flex the spine for better access. Arms are placed for comfort.
Positioning for Lumbar Injections
Lumbar injections are done with the patient on their stomach. A pillow may be used to reduce the spine’s curve. Legs are relaxed, and feet are free to rotate.
The table below shows the typical positions for different facet joint injections:
| Injection Type | Patient Position | Additional Support |
| Cervical | Stomach or Back | Pillows or wedges under the neck |
| Thoracic | Stomach | Pillow under the abdomen |
| Lumbar | Stomach | Pillow under the abdomen |
By carefully positioning the patient and getting consent, we make sure the injection is safe and effective.
Step-by-Step Facet Joint Injection Procedure
To make facet joint injections work well, we follow a detailed plan. This includes cleaning the area, using X-rays for guidance, placing the needle carefully, and giving the right medicine.
Sterilization and Draping Techniques
The first thing we do is make sure everything is clean. We sterilize the skin and drap the area to keep it safe. We wear gloves, gowns, and use clean tools to avoid infections.
We clean the skin with an antiseptic and cover it with sterile drapes. This careful start is key for a safe and effective procedure.
Fluoroscopic Guidance and Anatomical Landmarks
Fluoroscopic guidance helps us find the right spot in the spine. This imaging lets us see where the needle is going in real time. It makes sure we’re safe and accurate.
We match the X-ray images with the patient’s body to find the right spot. This is very important for getting the medicine where it needs to go.
Needle Insertion and Advancement Technique
We put the needle in slowly, watching on the X-ray screen. We use different views to make sure it’s in the right place. We check its path often to keep it on track.
When the needle is in the right spot, we might use a little contrast to check. Then we give the medicine.
Medication Administration Protocol
We use a mix of local anesthetic and corticosteroid for the injection. It goes into or around the facet joint, depending on the method.
We watch for any signs of trouble or pain during the shot. If needed, we adjust our approach to keep the patient comfortable and the treatment effective.
Anatomical Considerations for Different Spinal Regions
The spine’s anatomy changes with each region, making facet joint injections unique. Knowing the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine’s anatomy is key for success and safety.
Cervical Facet Joint Injection Technique
Cervical facet joints are smaller and more delicate. They need a precise technique. The procedure includes:
- Using a smaller gauge needle to minimize trauma
- Employing fluoroscopic guidance to navigate the complex cervical anatomy
- Targeting the facet joint with a mixture of local anesthetic and corticosteroid
Thoracic Facet Joint Injection Technique
The thoracic spine is tricky due to the rib cage. Important points are:
- Understanding the articulation between the ribs and the thoracic vertebrae
- Using a posterior approach to access the facet joints
- Carefully navigating around the rib cage to avoid complications
Thoracic facet joint injections are less common but need the same care as cervical or lumbar.
Lumbar Facet Joint Injection Technique
Lumbar facet joint injections are common for lower back pain. The method includes:
- Patient positioning to optimize access to the lumbar facet joints
- Fluoroscopic guidance to accurately target the joint
- Injection of therapeutic agents into the joint space
Lumbar facet joint injections help diagnose and treat facet joint syndrome, a common cause of chronic low back pain.
In conclusion, knowing the anatomy of each spinal region is vital for facet joint injections. Tailoring the technique to the specific anatomy of the cervical, thoracic, or lumbar spine helps healthcare providers achieve better results for their patients.
Intra-articular vs. Periarticular Facet Joint Injection Approaches
Facet joint injections can be given in two ways: intra-articular or periarticular. Each method has its own uses and challenges. Knowing these differences is key for managing pain well.
Intra-articular Technique and Challenges
Intra-articular facet injections put the medicine right into the joint. This method needs very precise needle placement. It often uses fluoroscopy or CT scans for accuracy.
The challenges of intra-articular injections include:
- It can be hard to reach some facet joints because of their location or degeneration.
- Advanced imaging is needed to make sure the needle is in the right spot.
- There’s a higher risk of problems if the needle isn’t placed correctly.
Even with these challenges, intra-articular injections can be very effective. They offer targeted pain relief for those with facet joint syndrome.
Periarticular Technique for Difficult Access Cases
Periarticular facet injections put the medicine around the joint, not inside it. This method is used when getting into the joint is hard or not possible. It’s good for:
- When the joint is very damaged, making it hard to inject.
- If the joint’s shape or scar tissue makes direct access tough.
- When you want the medicine to spread out more around the painful area.
Periarticular injections might not be as precise as intra-articular ones. But they can also give a lot of pain relief. They’re a good option when things get tough.
In conclusion, both intra-articular and periarticular facet joint injections have their roles in treating facet joint pain. The right choice depends on the patient’s body, the situation, and the doctor’s skills. Understanding the benefits and challenges of each helps doctors tailor treatments for each patient’s needs.
Post-Procedure Care and Patient Monitoring
We make sure patients are safe by watching them closely after facet joint injections. This watchful eye is key to spotting any quick reactions or possible problems.
Immediate Post-Procedure Observations
Right after the procedure, patients stay in a recovery area for a bit. Our medical team checks for any bad signs, like more pain, swelling, or trouble moving. They also keep an eye on the patient’s vital signs to make sure they’re okay.
Key observations include:
- Pain levels at the injection site
- Any signs of infection or allergic reaction
- Neurological status, including numbness or weakness
Discharge Instructions and Activity Restrictions
Before leaving, patients get clear instructions on what to do next. They learn about what activities to avoid, how to take their meds, and what to watch for. They’re told how to handle any side effects and when to get help.
| Activity | Recommended Action |
| Driving | Avoid driving for at least 24 hours post-procedure |
| Physical Activity | Limit strenuous activities for 2-3 days |
| Medication | Follow the prescribed medication regimen |
Follow-up Recommendations
Follow-up care is a big part of the treatment. Patients usually have a follow-up visit to check how the injection is working. This is also a chance to talk about any ongoing issues or problems.
By keeping a close eye on patients after facet joint injections and giving them clear instructions, we make sure they get the best care. This helps them through their whole treatment.
Managing Possible Complications of Facet Joint Injections
Facet joint injections are generally safe but can have risks and complications. These can range from mild to severe. It’s important to know and manage these risks.
Common Complications and Their Incidence
Common issues include pain or discomfort at the injection site, vasovagal reactions, and a temporary increase in pain. Table 1 shows the common complications and how often they happen, based on studies.
| Complication | Incidence Rate |
| Temporary pain or discomfort | 2-5% |
| Vasovagal reactions | 1-3% |
| Transient increase in pain | 5-10% |
Serious Adverse Events and Warning Signs
Though rare, serious problems like infection, nerve damage, and spinal cord injury can happen. It’s key for doctors to watch for signs like severe pain, fever, or neurological issues. This helps them act quickly.
Prevention and Management Strategies
To prevent issues, start with the right patient, use careful technique, and follow clean procedures. Afterward, keep an eye on patients, have plans for bad reactions, and tell them what to watch for.
Knowing about facet joint injection risks and how to handle them can make care safer and better for patients.
Evaluating Efficacy and Expected Outcomes
Facet joint injections are used to manage pain. They have both diagnostic and therapeutic benefits. It’s important for patients and doctors to know how well they work.
Diagnostic Value Assessment
Facet joint injections help find the source of pain. A local anesthetic is injected into the joint. This helps doctors see if the joint is causing the pain.
Key factors in diagnostic value assessment include:
- The accuracy of the injection technique
- The patient’s pain response to the anesthetic
- The duration of pain relief
Therapeutic Benefits and Duration
Facet joint injections also help treat pain. They reduce inflammation and relieve pain. A mix of local anesthetic and corticosteroid is often used.
The therapeutic benefits can vary among patients, but generally include:
- Significant pain reduction
- Improved functional ability
- Enhanced quality of life
The benefits can last from weeks to months. It depends on the case and treatment.
When to Consider Repeat Injections or Alternative Treatments
Deciding on repeat injections or other treatments depends on the first result. If the first injection helps a lot, more injections might be needed if pain comes back.
Factors influencing the decision for repeat injections or alternative treatments include:
- The duration of pain relief from the initial injection
- The patient’s overall response to the treatment
- The presence of any side effects or complications
If injections don’t work well, other treatments might be tried. These could be other procedures, physical therapy, or medication.
Conclusion
Facet joint injections are a key treatment for spine pain. They help patients with different spinal issues. This guide covered the steps from choosing patients to aftercare.
It’s vital to use the right technique and pick the right patients for facet joint injections. Knowing the spine’s anatomy and possible risks helps doctors improve results.
Deciding on facet joint injections should be thorough. They can greatly help patients feel better and live better lives.
Healthcare professionals can make a big difference by following this guide. They can better care for patients and manage spine pain more effectively.
FAQ
What is a facet joint injection?
A facet joint injection is a small procedure to find and treat pain in the spine’s facet joints.
What are facet injections used for?
They help find and treat pain from facet joint syndrome or similar conditions.
How is a facet joint injection performed?
A doctor injects a local anesthetic and sometimes a corticosteroid into the facet joint. They use X-ray guidance.
What is the difference between intra-articular and periarticular facet joint injections?
Intra-articular injections go directly into the joint. Periarticular injections go around it. The choice depends on the situation and doctor’s preference.
Are facet joint injections painful?
The procedure is done under local anesthesia. Patients might feel some discomfort, but it’s usually mild and short-lived.
How long does a facet joint injection procedure take?
The actual procedure takes 15-30 minutes. But, you’ll spend more time at the facility for preparation and recovery.
What are the possible complications of facet joint injections?
Risks include infection, bleeding, nerve damage, and allergic reactions. But, serious problems are rare.
How long does it take to recover from a facet joint injection?
Most people can go back to normal activities right after. Some might need to avoid hard activities for a bit.
How long do the effects of a facet joint injection last?
Pain relief time varies. Some feel better for months, while others might not last as long.
Can facet joint injections be repeated?
Yes, if they help a lot, injections can be done again. But, not too often to avoid steroid side effects.
Are facet joint injections covered by insurance?
Insurance coverage varies. Always check with your provider to see if they cover facet joint injections.
What are the alternatives to facet joint injections?
Options include other procedures, physical therapy, medication, and sometimes surgery.
References
- Manchikanti, L., Kaye, A. D., Soin, A., Albers, S. L., Beall, D., Latchaw, R., Sanapati, M., Shah, S., Alev, N., Diwan, S., Gharibo, C., Harned, M., Knezevic, N. N., Kosanovic, R., Pampati, V., Sanapati, J., Simopoulos, T., Singh, V., Slipman, C. W., … Hirsch, J. A. (2020). Comprehensive evidence-based guidelines for facet joint interventions in the management of chronic spinal pain. Pain Physician, *23*(4S), S1–S127. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32942795/

































