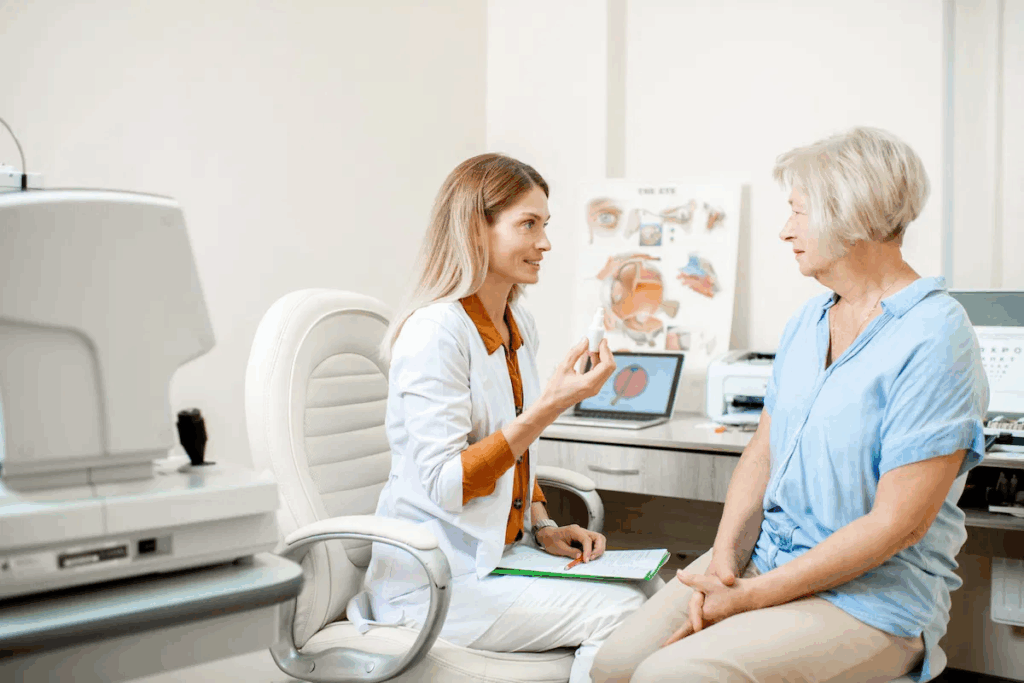
Drusen are small, yellowish spots on the retina, often seen with age. They are made of lipids, proteins, and cellular debris between the retinal pigment epithelium and Bruch’s membrane. While drusen might seem harmless, they are a big sign of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). AMD can cause vision loss if not treated. Learn aboutfatty deposits in the retina (drusen). This essential guide explains what they are and how they affect your vision.
Knowing about drusen is key to catching AMD early. At Liv Hospital, we stress the need for regular eye checks. These help keep an eye on your macula and vision. Spotting drusen and other risk factors early helps us protect your sight and address any worries.
Key Takeaways
- Drusen are small yellowish formations on the retina associated with aging.
- They are composed of lipids, proteins, and cellular debris.
- Drusen can be an indicator of age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
- Regular eye exams are key for checking macula health.
- Early spotting of drusen and AMD can save your vision.
Understanding Drusen as Fatty Deposits in the Retina
Drusen are fatty deposits that build up under the retina, affecting vision. They are a key sign of many retinal diseases. Knowing about drusen helps us understand retinal health better.
Composition and Biological Structure
Drusen are made of lipids, proteins, and waste from photoreceptor cells. Their formation is complex. It involves the buildup of waste, which can grow over time and harm the retina.
The structure of drusen varies. They contain lipids like cholesterol and phospholipids, proteins, and other parts of cells. Knowing what drusen are made of is key to finding new treatments and tests.
Component | Description | Significance |
Lipids | Includes cholesterol and phospholipids | Major constituent of drusen |
Proteins | Various proteins involved in disease processes | Indicative of disease mechanisms |
Cellular Debris | Waste material from photoreceptor cells | Accumulation leads to drusen growth |
Visual Appearance and Detection
Drusen look like small, yellow spots on the retina. They can be seen with an ophthalmoscope during a detailed eye exam. Tools like optical coherence tomography (OCT) give clear images of drusen, helping doctors understand them better.
Drusen can look different. Some are hard and clear, while others are soft and blend together. Spotting and understanding drusen is vital for diagnosing and tracking retinal diseases.
Types of Drusen and Their Clinical Significance
Knowing about the different types of drusen is key to spotting the risk of macular degeneration. It helps in planning the right treatment. Drusen are mainly hard and soft, each with its own traits and eye health effects.
Characteristics of Hard Drusen
Hard drusen are small, yellow nodules under 63 microns. They are seen as normal age-associated findings in older people. They are clear and easy to spot during eye exams.
Characteristics of Soft Drusen
Soft drusen are bigger, over 125 microns, and look like dome-shaped bumps. They are linked to a higher risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). They are larger and less clear than hard drusen.
Drusen can harm the retina, which is key for clear vision. Their size and shape tell us about the retina’s health and AMD risk.
Type of Drusen | Size | Appearance | Clinical Significance |
Hard Drusen | Less than 63 microns | Small, punctate, well-defined | Normal age-associated finding |
Soft Drusen | Exceeds 125 microns | Dome-shaped, less distinct edges | Increased risk of AMD |
Distinguishing between hard and soft drusen is vital for AMD risk assessment. Understanding their traits helps doctors manage patients better. This can lower the chance of AMD getting worse.
The Macula and Its Vulnerability to Drusen
It’s important to know how drusen affect the macula. The macula is key for clear vision. We’ll see how drusen impact this important eye part.
Anatomy of the Macula
The macula is at the retina’s center, the back of the eye. It helps us see details and colors. It has many photoreceptor cells for sharp vision. Good macula health is key for reading, driving, and face recognition.
The macula’s complex design makes it prone to drusen buildup. Drusen are fatty deposits under the retina. They can signal early AMD.
How Drusen Disrupt Macular Function
Drusen can block oxygen and nutrients to retina cells. This causes inflammation and stress. It can damage photoreceptor cells, leading to vision distortion and advanced AMD.
Drusen can also harm the retinal pigment epithelium. This further damages the macula. We’ll look at how drusen lead to severe AMD next.
While drusen are a sign of AMD, not everyone with them will get severe AMD. Yet, it’s vital to watch and manage drusen to keep the macula healthy.
Epidemiology and Risk Assessment
Studies have shown us a lot about drusen, a sign of macular health. Knowing about these factors helps us catch age-related macular degeneration (AMD) early.
Prevalence Statistics
Hard drusen is common in adults from 43 to 86 years old, found in 93.6% of them. This shows how common drusen is in older adults.
Let’s look at the numbers by age:
Age Group | Prevalence of Hard Drusen |
43-54 years | 80.2% |
55-64 years | 90.1% |
65-74 years | 93.6% |
75-86 years | 95.4% |
Critical Risk Factors
Several things can increase your chance of getting drusen. These include smoking, obesity, high cholesterol, and family history. These factors help drusen grow and can lead to AMD.
Here’s a closer look at these risk factors:
- Smoking: It can double your risk of AMD.
- Obesity: It raises the risk because of metabolic changes.
- High Cholesterol: It helps drusen form.
- Family History: Your genes play a big role.
Knowing about drusen’s prevalence and risk factors helps us understand AMD better. This knowledge lets us take steps to prevent it.
Progression from Drusen to Macular Degeneration
It’s key to know how drusen turn into macular degeneration to treat it early. Drusen, mainly soft ones, raise the risk of getting advanced age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Conversion Rates to Advanced Disease
Research shows soft drusen are more likely to lead to AMD than hard drusen. The risk depends on drusen size, number, and other eye changes.
- Soft Drusen: Big and many soft drusen increase AMD risk.
- Hard Drusen: Hard drusen are less risky but need watchful eye care.
We’ll dive deeper into conversion rates and risk factors. This will help spot who’s at higher risk of AMD.
Pathophysiological Mechanisms
The shift from drusen to AMD involves complex cell and molecule interactions. It’s mainly about how the retina gets less oxygen and nutrients.
Key Mechanisms:
- Build-up of waste under the retina.
- Inflammation and oxidative stress.
- Damage to the retina’s structure.
Grasping these mechanisms is vital for finding ways to slow or stop AMD.
We’re committed to ongoing research on drusen and AMD. Our goal is to better patient care through early detection and treatment.
Clinical Symptoms and Visual Changes
Drusen in the retina can cause noticeable visual problems. These issues can affect daily life. Spotting these signs early is key to getting help.
Early Manifestations
Drusen may first show up as mild vision issues. These can be easy to miss. Some early signs include:
- Hazy or blurry vision
- Difficulty adapting to changes in lighting
- Blind spots or missing areas of vision
- Need for brighter light when reading or performing daily tasks
Drusen can mess with the retina’s function, mainly in the macular area. It’s important for people to watch for these signs and get checked by a doctor.
Advanced Symptoms
As drusen grow, symptoms get worse. Advanced symptoms may include:
- Significant vision loss or distortion
- Difficulty recognizing faces or objects
- Central blind spots that interfere with daily activities like reading or driving
- Colors appearing less vivid or distorted
Advanced cases can really hurt your quality of life. So, it’s important to keep an eye on the disease and manage it well.
It’s important to know the signs of drusen to catch it early. This way, patients and doctors can work together to manage the condition.
Diagnostic Approaches and Monitoring
Diagnosing drusen involves using both clinical exams and advanced imaging. These methods help doctors spot drusen and track how they change over time.
Clinical Examination Techniques
Ophthalmoscopy is key in finding drusen. It lets doctors see the retina and spot drusen. They can then judge the risk of drusen turning into serious eye problems.
Fundus photography also plays a big role. It takes detailed pictures of the retina. These photos help doctors see how drusen change over time.
Advanced Imaging and Assessment
New imaging methods have changed how we diagnose and watch drusen. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) gives clear images of the retina. It helps doctors understand drusen better and spot early signs of trouble.
Fundus autofluorescence is another tool that shows how active the retina is. It helps doctors see drusen more clearly. Together, these methods help manage drusen better.
It’s important to keep checking on drusen regularly. This way, doctors can catch any changes early and stop vision loss.
Management Strategies and Treatment Options
Managing drusen requires a mix of preventive steps and medical treatments. It’s key to stop drusen from turning into age-related macular degeneration (AMD). This helps keep your vision sharp.
Preventive Measures
Lifestyle changes are important for managing drusen. Eating foods full of fruits, veggies, and omega-3s is good. Quitting smoking is also key, as it lowers AMD risk.
Regular eye checks are vital. They help spot drusen early and track any changes.
Supplements can help too. Antioxidants and zinc might slow AMD growth. The AREDS formula is often suggested for those at risk.
Medical and Surgical Interventions
For advanced drusen or high AMD risk, medical treatments are needed. Anti-VEGF injections are a common choice. They stop new blood vessels from growing in the retina.
Laser therapy might be used in some cases. But it’s not common and only for specific situations.
Eye doctors play a big role in finding the right treatment. New imaging tools like OCT help manage drusen better.
Conclusion: Living with Drusen and Protecting Your Vision
Drusen are fatty deposits that can harm your vision. They can lead to macular degeneration. To protect your eyes, you need to act early.
Regular eye exams are key. They help track drusen and catch any changes fast. This is important for your eye health.
Managing drusen means making healthy choices. Eating well, with foods full of omega-3 and antioxidants, helps. Quitting smoking and managing health issues also helps keep your eyes safe.
It’s important to work with your doctor to manage drusen. By staying informed and proactive, you can lower the risk of losing your vision. With the right care, you can keep your eyes healthy and your life full of quality.
FAQ
What are drusen in the eye?
Drusen are small, yellowish spots that form under the retina, in the macula. This area is key for central vision. They are made of lipids and proteins and linked to aging and AMD.
What is the difference between hard and soft drusen?
Hard drusen are small and normal with age. Soft drusen are larger and riskier, often leading to AMD.
How do drusen affect the macula?
Drusen can harm the macula by building up under the retina. This can cause blurred and distorted vision.
What are the risk factors for developing drusen?
Drusen risk factors include aging, family history, smoking, and genetics.
Can drusen be prevented?
While you can’t prevent drusen entirely, a healthy lifestyle helps. This includes a balanced diet, exercise, and not smoking.
How are drusen diagnosed?
Drusen are found through a detailed eye exam. This includes a dilated fundus exam, OCT, and fundus photography.
What is the treatment for drusen?
There’s no specific treatment for drusen. But managing AMD risk factors and regular check-ups can slow disease progression.
Can drusen cause blindness?
Drusen themselves don’t cause blindness. But they can lead to AMD, which can cause vision loss if untreated.
How often should I have my eyes checked if I have drusen?
Regular eye exams are key for monitoring drusen and AMD. The exam frequency depends on your risk factors and drusen severity.
Are there any medical interventions for drusen?
No specific treatments exist for drusen yet. But research is exploring options like anti-VEGF therapy and other therapies.
What lifestyle changes can help manage drusen?
Eating a healthy diet, quitting smoking, exercising, and protecting your eyes from UV light can help manage drusen and AMD risk.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559087/

































