For those with complex aortic aneurysms, fenestrated aneurysm repair (FEVAR) is changing the game. At Liv Hospital, we lead in this field. We blend our expertise with a patient-centered approach to offer top-notch treatments.
FEVAR is a cutting-edge, minimally invasive method for treating complex aortic aneurysms. It’s perfect for those near vital branches. We use custom endograft devices with fenestrations to keep blood flowing to important organs. This makes it a safer choice than traditional open surgeries.
Recent studies highlight FEVAR’s benefits. They show it makes more patients eligible for treatment. It also has high success rates and lowers risks during surgery. Our team is committed to delivering world-class care. We offer full support and guidance to international patients.
Key Takeaways
- FEVAR is a minimally invasive treatment for complex aortic aneurysms.
- Customized endograft devices maintain blood flow to vital organs.
- FEVAR offers a safer alternative to traditional open surgeries.
- High technical success rates and lower perioperative risks are associated with FEVAR.
- Liv Hospital provides full international patient support and guidance.
Understanding Aortic Aneurysms and Treatment Challenges
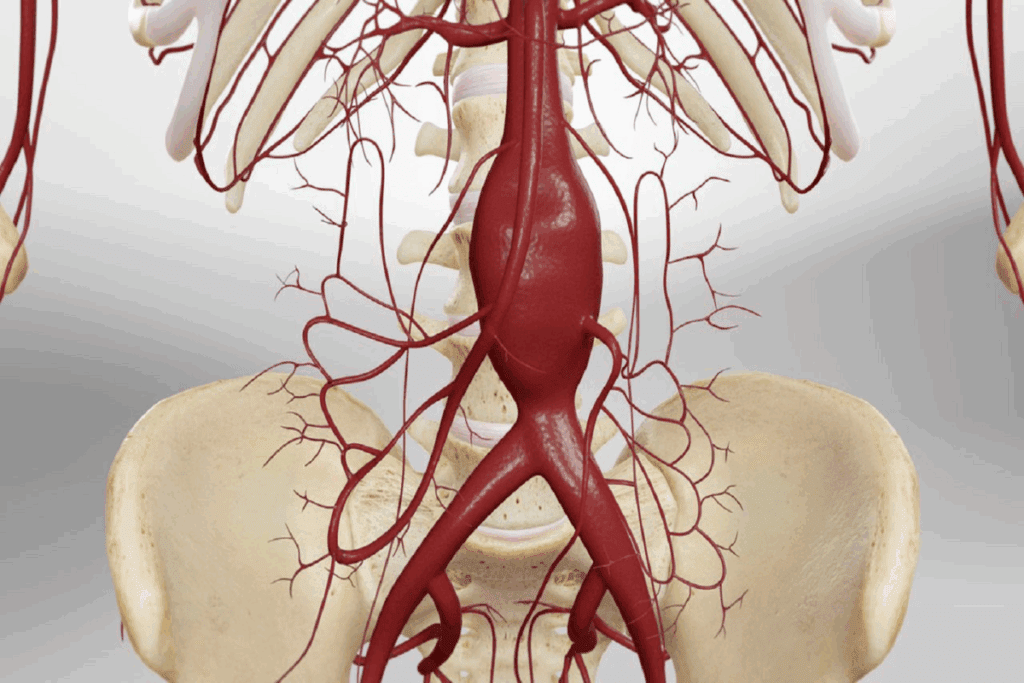
It’s important to understand aortic aneurysms to choose the right treatment. Aortic aneurysms happen when the aorta gets too big. They can occur anywhere along the aorta.
Types and Locations of Aortic Aneurysms
Aortic aneurysms are divided into two types: abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA) and thoracic aortic aneurysms (TAA). Where and how big the aneurysm is affects treatment choices.
AAA is more common and happens below the kidneys. TAA can be in the aortic root, the top part of the aorta, or the arch. The location and how close it is to important blood vessels are key in picking a treatment.
Anatomical Complexities Near Vital Branch Vessels
Aneurysms near important blood vessels are tricky because they can cut off blood to vital organs. The fenestrated endovascular aortic repair (FEVAR) method is helpful here. It keeps blood flowing through these vessels.
Dealing with aneurysms near vital branches needs advanced imaging and careful planning. This is to make sure the treatment works well.
Limitations of Traditional Surgical Approaches
Old-school surgery for aortic aneurysms is very invasive. It comes with big risks like serious illness or death. This has led to the creation of new methods like FEVAR.
FEVAR can cause spinal cord ischemia (SCI) in 4.3% to 40% of cases. This depends on how much of the aorta is covered and other factors. Knowing these risks helps doctors choose the best patients for the treatment.
Fenestrated Aneurysm Repair: A Detailed Look

Fenestrated endovascular aneurysm repair (FEVAR) is a complex method for treating aortic aneurysms not fit for standard EVAR. This advanced procedure has grown with new endovascular techniques and device technology. It offers hope to those with complex aortic aneurysms.
Definition of “Fenestrated” in Medical Context
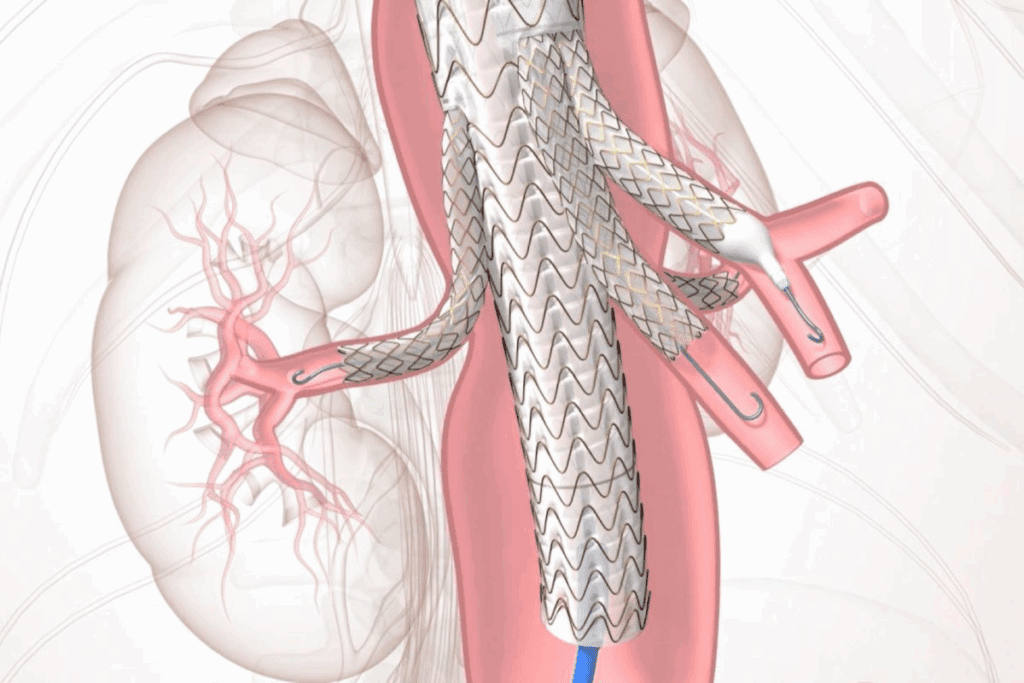
In medicine, “fenestrated” means having special openings in a device, like an endograft. These openings match the patient’s blood vessels, keeping blood flow to important areas. This design lets the endograft cover the aneurysm while keeping vital organs supplied.
We make custom fenestrated endografts for each patient. This ensures a perfect fit and the best results. We use detailed images and planning to design the fenestrations just right.
The Evolution of Endovascular Techniques
Endovascular methods have greatly improved over time. This is thanks to new device technology and techniques. Fenestrated endografts are a key part of this progress, treating complex aortic aneurysms that were once untreatable.
Endografts have gotten better, lasting longer and being more flexible. These improvements mean more people can get endovascular repair, even those with tough anatomies.
When FEVAR Becomes Necessary
FEVAR is needed for aortic aneurysms near critical blood vessels. It’s chosen based on detailed images of the aneurysm and its blood vessels.
We recommend FEVAR for aneurysms near the renal or visceral arteries. This is because FEVAR can precisely treat these cases. It keeps blood flowing to vital organs, making it a safer option than traditional surgery.
The Technical Aspects of Fenestrated Endografts
Fenestrated endografts have special designs that are key for endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. They are made to fit each patient’s body perfectly. This ensures the aneurysm is effectively blocked.
Custom-Designed Fenestrations and Scallops
Fenestrated endografts have special parts for vital branch vessels. This is vital for keeping blood flow to important organs. The design is made with precise imaging and measurements to fit the patient’s arteries.
“The precision needed in making fenestrated endografts is unmatched,” say experts. “Each one shows the progress in endovascular tech.”
Materials and Engineering Considerations
The materials in fenestrated endografts are picked for their strength and safety. New materials have led to better endograft repair systems. The design focuses on the graft’s flexibility, strength, and durability.
- High-quality fabric to minimize porosity and promote graft incorporation
- Stent material that provides adequate radial force while maintaining flexibility
- Sealing mechanisms to prevent endoleaks
Stent Graft Customization Process
The process of making fenestrated endografts is a team effort. It starts with detailed images to see the patient’s body. This info helps create a custom design for the patient’s needs.
“The ability to customize fenestrated endografts has greatly improved endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. It’s a big step forward in treating complex aortic issues.”
In summary, the tech behind fenestrated endografts is essential for endovascular treatment today. With custom designs, advanced materials, and careful engineering, these devices offer hope for those with complex aortic aneurysms.
Standard EVAR vs. FEVAR: Critical Differences
FEVAR and Standard EVAR are two ways to treat aortic aneurysms. They differ in how they are used and their complexity. Knowing these differences helps choose the best treatment for patients.
Anatomical Suitability Comparison
Whether a patient is right for Standard EVAR or FEVAR depends on their anatomy. Standard EVAR works well for simple aortic aneurysms. FEVAR is for more complex cases, like those with short necks or involved branch vessels.
Key anatomical considerations include the aortic neck’s length and shape, branch vessels, and the aneurysm’s overall shape. FEVAR’s custom fenestrations can include these vessels, making it a good option for complex cases.
Procedural Complexity and Duration
FEVAR is more complex and takes longer than Standard EVAR. It needs detailed planning and a custom-made endograft. The procedure involves more steps, like cannulating branch vessels, which requires skill and experience.
The increased complexity of FEVAR means longer procedures and more radiation for everyone involved. But, FEVAR’s benefits in treating complex aneurysms often make it worth it.
Cost and Resource Considerations
FEVAR is more expensive and resource-intensive than Standard EVAR. The custom endografts and specialized equipment add to the costs. But, FEVAR is a valuable option for complex cases that can’t be treated with Standard EVAR or open surgery.
Even with higher costs, FEVAR can be cost-effective in the long run. It avoids more invasive procedures, saving money and improving outcomes.
Learning Curve for Surgeons
Surgeons face a steep learning curve with FEVAR. It’s complex and requires precise skills. They need specialized training to master FEVAR, including customizing endografts and cannulating vessels.
Training and experience are key to mastering FEVAR. As surgeons get more experience, they become better at handling its challenges. This improves patient results.
The FEVAR Procedure: Detailed Surgical Approach
FEVAR is a complex procedure that needs careful planning and skilled hands. We’ll walk you through the main steps of this endovascular aortic repair procedure.
Pre-Operative Planning and Measurements
Good planning is key for FEVAR’s success. We use CT angiography to see the aneurysm and its relation to important blood vessels. This helps us make a graft that fits the patient’s body perfectly.
- High-resolution imaging to visualize the aortic anatomy
- Precise measurements to guide graft customization
- 3D reconstruction to plan the optimal graft placement
Intraoperative Techniques and Challenges
During the FEVAR, we use advanced methods to place the graft right and connect the blood vessels. Good imaging and skilled navigation help us face the procedure’s challenges.
Intraoperative challenges may include:
- Navigating complex aortic anatomy
- Achieving precise graft placement
- Successful cannulation of branch vessels
Branch Vessel Cannulation Strategies
Cannulating branch vessels is a key part of FEVAR. We use special guidewires and catheters to do this. The method we choose depends on the blood vessel’s location and shape.
Completion Angiography and Technical Success Verification
After we’ve placed the graft and connected the blood vessels, we do a final check. We use angiography to see if everything is working right. We check the graft’s position, the blood vessel connections, and if there are any leaks.
With careful planning and skilled surgery, we can make FEVAR a safe and effective choice for treating complex aortic aneurysms.
Patient Selection and Clinical Indications for FEVAR
Doctors must carefully choose patients for FEVAR. They look at the patient’s body and health history. This helps decide if the patient is right for the procedure.
Anatomical Requirements and Exclusion Criteria
FEVAR helps those with complex aortic aneurysms. It’s best for aneurysms near important blood vessels. The doctor needs to know the aneurysm’s size and where it is.
Patients with aneurysms near the kidneys or intestines might be good candidates. But, some features can make a patient not fit for FEVAR. For example, very twisted aortas or narrow blood vessels in the legs can be risky.
Risk Stratification for Candidate Selection
Doctors must figure out the patient’s risk for FEVAR. They look at the patient’s overall health and any other diseases. This includes heart and kidney function and other vascular diseases.
“Choosing the right patient for FEVAR is key,” says a top vascular surgeon. “We look at each patient’s unique situation to get the best results and avoid problems.”
Alternative Options for Non-Candidates
Patients not fit for FEVAR have other options. These include EVAR, open surgery, or other endovascular methods. The best choice depends on the patient’s body, the aneurysm, and their health.
In summary, picking the right patient for FEVAR is complex. It involves looking at the body, health history, and risk. This careful approach helps find the best candidates for FEVAR and leads to good results.
Clinical Outcomes and Evidence-Based Results
Fenestrated endovascular aneurysm repair (FEVAR) is a top choice for treating complex aortic aneurysms. It offers great results. We’ll look at the evidence, focusing on success rates, durability, and how it affects patients’ lives.
Short-term Technical Success Rates
FEVAR is very successful in the short term. Technical success means the endograft is placed right, the target vessels are open, and there are no leaks. The key to these results is careful planning and execution.
Mid and Long-term Durability Data
Long-term success is key for FEVAR. Studies show it works well over time, with few complications. Regular checks are vital to keep the repair working and catch any problems early.
Comparative Studies: FEVAR vs. Open Repair vs. Standard EVAR
Studies help us see how FEVAR stacks up against open repair and standard EVAR. FEVAR is safer and less risky than open repair, which is great for complex cases. It’s also better than standard EVAR for treating more complex anatomies, even if it’s a bit more complex itself.
Quality of Life Improvements
FEVAR’s impact on patients’ lives is huge. It’s less invasive than open repair, leading to quicker recovery times and fewer complications. This means better quality of life for patients.
Recovery Process and Post-FEVAR Management
Recovery after FEVAR is a detailed process. It includes post-operative care, watching for complications, and managing them. Our goal is to make sure the endovascular aortic repair procedure works well in the long run.
Immediate Post-Operative Care
Right after FEVAR, it’s key to watch the patient closely. We check if the aortic repair is working right. This is done in the first few days after the procedure.
Patients usually stay in the hospital for a short time to get better. Our team keeps an eye on their health, manages pain, and looks for any problems.
Long-term Surveillance Protocols
Keeping an eye on patients long-term is very important. Regular check-ups help catch and handle any issues early. This includes things like endoleaks or graft migration.
We use CT scans to check the graft and how the aneurysm is doing. We also look at the patient’s overall health and change the check-up plan if needed.
Managing Possible Complications
Even with FEVAR’s success, problems can happen. We work hard to find and fix these issues quickly. This helps keep the patient’s quality of life good.
Problems like endoleaks, graft kinking, or migration can occur. Our team knows how to handle these with different treatments. Sometimes, this means more endovascular procedures or even open surgery.
Patient Experience and Rehabilitation
Helping patients feel better and get back to normal is key. We offer lots of support to help them regain strength and do their usual activities.
We create a special plan for each patient’s recovery. This might include physical therapy, changes in lifestyle, and ongoing check-ups. Our goal is to make sure patients are well and healthy in the long run.
Conclusion: Advancements and Future Directions in Fenestrated Endovascular Repair
Fenestrated endovascular aortic repair has changed how we treat complex aortic aneurysms. It offers a less invasive option compared to open surgery. This method has brought new hope to many patients.
The term “fenestrated” means the graft has special holes for the patient’s visceral arteries. This precise placement helps keep blood flowing to important organs. As research grows, so does the success of this treatment, opening it up to more patients.
Looking ahead, the future of FEVAR looks bright. New technologies and techniques are on the horizon. We expect better results and wider use of this therapy. Our goal is to provide top-notch care and support to patients from around the world.
By exploring new frontiers in fenestrated endovascular repair, we’re making a big impact on vascular surgery. This progress is improving lives globally.
FAQ
What is Fenestrated Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (FEVAR)?
FEVAR is a new way to treat aortic aneurysms. It uses a special endograft with holes to keep blood flowing to important organs.
How does FEVAR differ from standard EVAR?
FEVAR is for complex aneurysms near vital vessels. It keeps blood flowing to these areas, unlike standard EVAR.
What is the definition of “fenestrated” in the medical context?
“Fenestrated” means a device has special holes. These holes help keep blood flowing to vital organs or vessels.
What are the benefits of FEVAR over open surgery?
FEVAR is less invasive than open surgery. It means less recovery time, fewer complications, and less harm to the patient.
How is the FEVAR procedure performed?
The procedure starts with planning and ends with precise techniques. It requires great skill and care.
What are the criteria for patient selection for FEVAR?
Patients are chosen based on their aneurysm’s complexity. They must have a suitable aneurysm for FEVAR.
What are the possible complications of FEVAR?
FEVAR can have complications like endoleak and graft migration. But, these can be managed with proper care and follow-up.
What is the recovery process like after FEVAR?
Recovery involves immediate care and long-term monitoring. Patients usually get back to normal in a few weeks.
How does FEVAR impact quality of life?
FEVAR improves life for those with complex aneurysms. It keeps blood flowing and reduces rupture risk, helping patients live normally again.
What are the future directions in FEVAR?
FEVAR is growing, with new tech and techniques. The goal is to help more patients with better devices.
What is the difference between fenestrated and non-fenestrated endografts?
Fenestrated endografts have holes for blood flow to vital areas. Non-fenestrated ones do not.
How is endovascular aortic repair (EVAR) defined?
EVAR is a minimally invasive method for treating aortic aneurysms. It uses an endograft to block the aneurysm from blood flow.
What is the role of fenestration in endovascular aortic repair?
Fenestration is key in FEVAR. It ensures blood keeps flowing to vital organs or vessels.
Reference
- Yoon, W. J., et al. (2019). Fenestrated endovascular aneurysm repair versus snorkel EVAR for complex aneurysms: A review. PMC.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6774433




































