Last Updated on November 26, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
Uterine fibroids are benign tumors that affect many women. They can cause symptoms similar to cancer. Accurate imaging is key for diagnosing and treating them well.
At Liv Hospital, we use the latest technology and focus on our patients. We offer the most accurate uterine fibroids imaging. Our team uses MRI, ultrasound, and CT scans, each with its own benefits and drawbacks.
MRI is the top choice for uterine fibroids imaging. It’s very accurate in showing the size, number, and location of fibroids. In fact, MRI can spot up to 80 to 91 percent of confirmed fibroids.
Key Takeaways
- MRI is highly accurate for detecting uterine fibroids, identifying up to 80 to 91 percent of confirmed cases.
- Uterine fibroids are benign smooth muscle cell tumors that can cause significant symptoms.
- Accurate imaging is critical for effective diagnosis and treatment.
- MRI provides detailed assessment of the number, size, and location of fibroids.
- Liv Hospital uses advanced technology and patient-focused care for accurate uterine fibroids imaging.
Understanding Uterine Fibroids and Their Clinical Significance
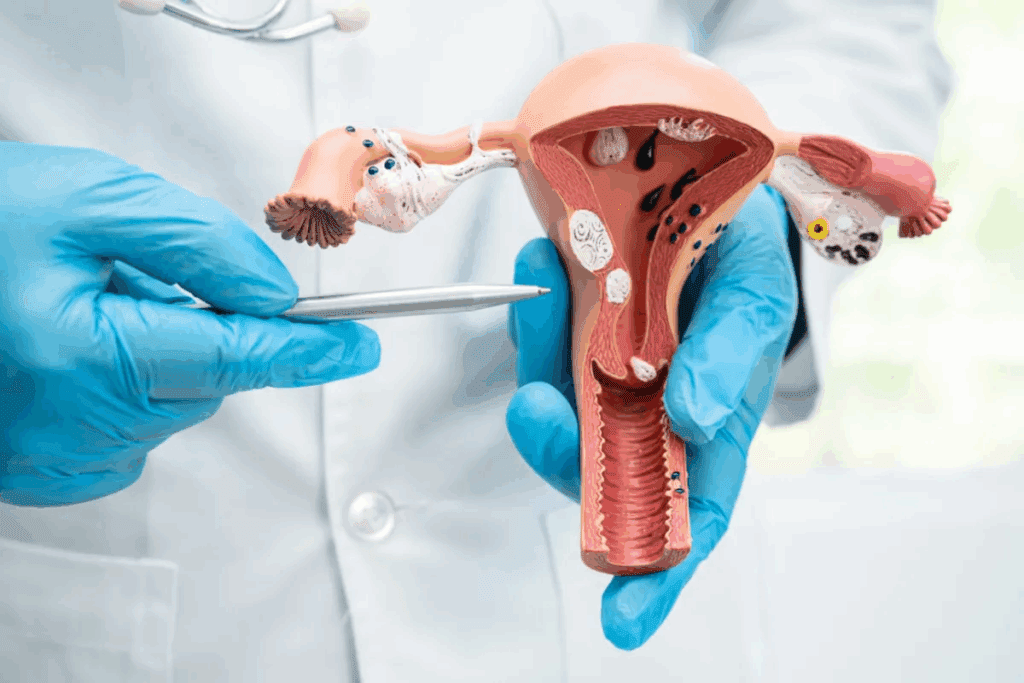
Uterine fibroids, also known as uterine leiomyomas, are common among women. They can greatly affect their quality of life. These growths come from the uterus’s smooth muscle layer and are a common gynecological problem.
Definition and Prevalence of Uterine Leiomyomas
Uterine leiomyomas are benign neoplasms found in or around the uterus. They are made of smooth muscle cells and fibrous tissue. Up to 80% of women have them by age 50, but many don’t show symptoms.
The exact reason for uterine fibroids is not known. But, genetics, hormones, and environment play a role in their growth.
Clinical Symptoms and Indications for Imaging
Many women with uterine fibroids don’t show symptoms. But, some may feel:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Prolonged menstrual periods
- Pelvic pressure or pain
- Frequent urination
- Constipation
If symptoms appear, imaging is key for diagnosis and treatment. The right imaging can greatly help manage uterine fibroids.
Imaging is needed to see the size, number, and location of fibroids. It also checks their effect on nearby areas. This info is essential for choosing the best treatment.
The Role of Medical Imaging in Fibroid Diagnosis

Medical imaging is key for finding and treating uterine fibroids. It helps us see the size, number, and where fibroids are. This info is important for picking the right treatment.
Importance of Accurate Imaging for Treatment Planning
Getting the right images is vital for planning treatment. It helps doctors know how bad the fibroids are. This info helps choose between surgery, medicine, or less invasive options.
Key factors assessed through imaging include:
- Fibroid size and number
- Location within the uterus
- Proximity to other pelvic structures
- Presence of any other uterine abnormalities
| Imaging Modality | Advantages | Limitations |
| Ultrasound | Widely available, cost-effective | Limited detail for complex cases |
| MRI | High detail, soft tissue contrast | Higher cost, less availability |
| CT Scan | Quick, useful for large fibroids | Radiation exposure, less detail for soft tissues |
Evolution of Imaging Techniques for Uterine Pathology
Imaging for uterine problems has gotten much better. Ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans have all improved. These changes help us see fibroids more clearly.
Thanks to these advances, we can now diagnose and treat fibroids better. As technology keeps getting better, we’ll see even more improvements in finding and treating fibroids.
Ultrasound: The First-Line Imaging Modality
Ultrasound is often the first choice for diagnosing uterine fibroids. It’s widely available and doesn’t hurt. This makes it a great starting point for doctors.
Transabdominal vs. Transvaginal Ultrasound Techniques
There are two main ways to use ultrasound for fibroids: transabdominal and transvaginal. Transabdominal ultrasound gives a bigger view of the area. Transvaginal ultrasound shows more detail of the uterus and fibroids. We usually use both for a full picture.
- Transabdominal ultrasound is good for big fibroids or a big uterus.
- Transvaginal ultrasound is better for small fibroids and how close they are to the uterine cavity.
Advantages and Limitations of Fibroid Ultrasound
Ultrasound is great for looking at fibroids because it’s safe and doesn’t use harmful radiation. It also lets doctors see things in real-time. But, it has some downsides.
Ultrasound’s main benefits are:
- It’s easy to find and not very expensive.
- It can show movement during the scan.
- It doesn’t use harmful radiation.
But, there are also some drawbacks:
- The quality of the images depends on the person doing the scan.
- It can be hard to see fibroids in very big uteruses.
- It’s not always clear what’s happening inside the fibroids.
Characteristic Myoma Ultrasound Images
Fibroids usually look like dark spots in the ultrasound. They might have:
- A darker look than the rest of the uterus.
- A shadow behind them.
- Fluid or calcium inside if they’re breaking down.
Knowing how ultrasound works for fibroids helps doctors use it better. This way, they can decide when to use other tests too.
CT Scanning for Uterine Fibroids
While MRI is the top choice for seeing uterine fibroids, CT scans have their own uses. We use CT scans when looking at fibroids with other problems in the belly or pelvis. Or when an MRI can’t be done because of certain reasons.
When Uterine Leiomyoma CT Is Utilized
CT scans are used in emergencies or when fibroids might be causing sudden pain. They help check if fibroids are pressing on other parts of the pelvis. Or if there’s a chance they could turn cancerous.
Key scenarios for CT scanning include:
- Acute pelvic pain potentially related to fibroid torsion or degeneration
- Suspected malignancy or complex adnexal masses
- Assessment of fibroid size and location in relation to surrounding structures
- Patients with contraindications to MRI, such as certain metal implants
Limitations of Uterine Fibroids CT Scan
CT scans have big downsides when it comes to looking at uterine fibroids. The main problem is they don’t show soft tissues as well as MRI does. This makes them not so good for looking at fibroids closely.
Notable limitations include:
- Inability to accurately differentiate between various types of fibroid degeneration
- Limited sensitivity for detecting small or multiple fibroids
- Exposure to ionizing radiation, which is a consideration for younger patients
Typical Appearance of Uterine Fibroid on CT
On CT scans, uterine fibroids show up as clear masses in the uterus. They can look the same or different in density, depending on if they have calcifications, degeneration, or necrosis.
Characteristic features on CT include:
- Iso- or hypodense masses relative to the myometrium
- Possible presence of calcifications, which are often coarse and peripheral
- Variable enhancement patterns following contrast administration
Knowing when to use CT scans for uterine fibroids is key. It helps pick the best imaging method for each patient’s needs.
Fibroid MRI: The Gold Standard in Leiomyoma Imaging
MRI is the top choice for seeing uterine leiomyomas. It gives us clear pictures of fibroids’ size, number, and type. This helps us plan better treatments and improve patient care.
MRI Protocols for Fibroid Imaging
We use special MRI plans to see uterine anatomy and problems well. These plans include T1 and T2 images and contrast-enhanced shots. They help us spot and understand fibroids for better treatment.
Research shows MRI is the best for finding uterine fibroids. It can spot up to 80 to 91 percent of them (PMC4516148). This makes MRI very useful, mainly for complex or many fibroids cases.
Superior Tissue Characterization with MRI
MRI is great at telling different fibroid types apart. It can see submucosal, intramural, and subserosal fibroids. It also spots degenerating or calcified ones. This detail is key for making treatment plans and predicting results.
Detection Rates and Accuracy of MRI Fibroids Imaging
MRI is very good at finding and understanding fibroids. It beats ultrasound and CT in this area. Thanks to MRI, we can give patients accurate diagnoses and effective treatments, boosting their life quality.
In short, MRI is the top choice for fibroid imaging. It’s accurate, finds most fibroids, and shows their details well. As we keep improving in gynecological imaging, MRI’s role in managing fibroids will stay important.
Comparative Analysis: MRI vs. Ultrasound for Fibroids
MRI and ultrasound are both used to diagnose uterine fibroids. Each has its own strengths and weaknesses. Knowing these differences helps doctors choose the best imaging method for each patient.
Detection Sensitivity and Specificity Comparison
MRI is better at finding uterine fibroids, thanks to its detailed images. It’s great for spotting small or submucosal fibroids. Ultrasound is useful but can be affected by the skill of the operator and the patient’s body type.
Despite its limitations, ultrasound is often the first choice. It’s more affordable and easier to get than MRI.
| Imaging Modality | Detection Sensitivity | Detection Specificity |
| MRI | High | High |
| Ultrasound | Moderate | Moderate |
Size and Number Assessment Differences
MRI is better at measuring fibroid size and count. Its high-resolution images are key for planning surgery. Ultrasound can also measure these, but it might not be as accurate for big or multiple fibroids.
Using transvaginal ultrasound can help improve ultrasound’s accuracy. It’s a good option for getting more precise measurements.
Cost and Accessibility Considerations
MRI gives better images but is pricier and less common than ultrasound. Ultrasound is cheaper and quicker to get. It’s often the first choice for initial checks.
Choosing between MRI and ultrasound depends on the patient’s needs and the clinical situation. It’s about finding the right balance between accurate diagnosis and cost and availability.
Comparative Analysis: MRI vs. CT for Uterine Leiomyomas
When diagnosing uterine leiomyomas, doctors often choose between MRI and CT scans. Each has its own benefits. It’s key to know how they differ in soft tissue detail, radiation, and use in clinics.
Soft Tissue Contrast Differences
MRI stands out for its clear soft tissue images, unlike CT scans. This makes MRI great for seeing uterine leiomyomas. MRI doesn’t use harmful radiation, which is a big plus for patients needing many scans or who are sensitive to radiation.
CT scans, though fast and common, don’t show soft tissues as well. This makes it harder to tell different uterine masses apart. Yet, CT scans are useful for big or complex fibroids.
Radiation Exposure Considerations
CT scans use X-rays, which means they expose patients to radiation. This is a big worry, mainly for young people or those needing many follow-ups. MRI, using magnetic fields and radio waves, doesn’t expose patients to radiation. This makes MRI safer for long-term scans.
Clinical Scenarios Favoring Each Modality
Even with MRI’s benefits, CT scans have their place. In emergencies, CT’s speed is key. Also, for those who can’t have MRI due to certain implants, CT is a good option.
In summary, picking MRI or CT for uterine leiomyomas depends on several things. These include the need for detailed images, radiation concerns, and specific medical situations. Knowing each modality’s strengths helps doctors choose the best for their patients.
Special Considerations in Fibroid Imaging
When we image uterine fibroids, we must think about several important factors. This ensures we can diagnose them correctly and plan the best treatment. We need to know how different imaging methods work and what makes fibroids unique.
Differentiating Fibroids from Other Uterine Masses on Imaging
One big challenge is telling fibroids apart from other growths in the uterus. Getting the diagnosis right is key to avoid mistakes and treat patients properly. We use tools like ultrasound and MRI to look at these masses closely. For example, ultrasound shows fibroids as clear, dark spots, while MRI makes them look darker on certain images.
“Being able to tell fibroids from other growths is vital for good care,” say radiology experts. Looking closely at how they appear on images helps us make this important distinction.
Imaging Degenerating and Calcified Fibroids
Degenerating and calcified fibroids are harder to image. Degenerating fibroids can look different on scans because of the type of degeneration. Calcified fibroids, with their calcium deposits, show up well on CT scans.
- Cystic degeneration looks like a dark spot in the fibroid on ultrasound.
- Hyaline degeneration shows up as a dark area on MRI.
- Calcifications are bright on CT scans.
Challenges in Imaging Submucosal and Pedunculated Fibroids
Submucosal and pedunculated fibroids are tricky to image. Submucosal fibroids stick into the uterine cavity, making them hard to spot on ultrasound. Pedunculated fibroids, with their stalks, can look like ovarian tumors.
We use MRI for its detailed view of soft tissues to correctly identify these fibroids. MRI helps us see the stalk of a pedunculated fibroid and its connection to the uterus, helping us diagnose them.
By understanding these special imaging needs, we can improve our ability to diagnose fibroids accurately. This leads to better care for our patients.
Clinical Applications of Advanced Imaging for Fibroids
Advanced imaging has many uses in managing fibroids. It improves how we diagnose and plan treatments. MRI is key in diagnosing and treating uterine fibroids.
Pre-surgical Planning with MRI
MRI is vital for planning surgeries for fibroids. It gives clear images of fibroid size, number, and location. This info is key for surgeons to decide the best surgery.
- MRI helps pinpoint fibroid locations, lowering surgery risks.
- It shows how fibroids relate to the uterus and blood vessels.
- MRI spots issues like adhesions that might affect surgery plans.
Monitoring Treatment Response
Advanced imaging, like MRI, tracks how well fibroid treatments work. It checks for changes in fibroid size and blood flow after treatment.
Monitoring treatment response is key to knowing if a treatment is working. MRI helps see who’s getting better and who might need different or more treatments.
- MRI tracks how much fibroids shrink and symptoms improve after treatment.
- It spots any treatment side effects, like changes in the uterus or ovaries.
- MRI guides in adjusting treatment plans for the best results.
Emerging Imaging Techniques
New imaging methods are coming up in fibroid care. Emerging imaging techniques like contrast-enhanced ultrasound and diffusion-weighted MRI are being looked into. They might make fibroid imaging better.
- Contrast-enhanced ultrasound shows fibroid blood flow in real-time.
- Diffusion-weighted MRI can tell fibroids apart from other uterine growths.
- New methods could lead to more accurate diagnoses and better treatment plans.
Radiological Reporting of Uterine Fibroids
Diagnosing and treating uterine fibroids gets better with detailed radiology reports. These reports are key to managing fibroids well. They give important info to both radiologists and gynecologists.
Essential Elements in Fibroid Radiology Reports
A good radiology report for uterine fibroids should have several important parts. These include:
- Size and Location: Detailed measurements and where fibroids are in the uterus.
- Number: How many fibroids are found.
- Type: What kind of fibroids they are, like submucosal or intramural.
- Characteristics: What the fibroids look like, like if they’re degenerating or calcified.
A study in the Journal of Radiology says, “Detailed reporting of fibroid characteristics helps in planning treatment and managing patients.”
“The radiologist plays a key role in diagnosing and managing uterine fibroids by giving detailed and accurate imaging reports.”
FIGO Classification System in Imaging Reports
The FIGO (International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics) system is used more in radiology reports. It helps standardize how fibroids are described. It groups fibroids by where they are in the uterus.
| FIGO Type | Description |
| 0 | Pedunculated intracavitary |
| 1 | |
| 2 | ≥ 50% intramural |
Communication Between Radiologists and Gynecologists
Good communication between radiologists and gynecologists is vital for patient care. Radiologists should give clear, detailed reports. Gynecologists should share important clinical info to help understand imaging findings.
By working together and using systems like the FIGO classification, healthcare teams can give patients the best care for their needs.
Conclusion: Optimizing Imaging Selection for Uterine Fibroids
We’ve looked at how different imaging methods help diagnose and manage uterine fibroids. These include ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI. MRI is the top choice for fibroid imaging because it can show tissue details very well.
Choosing the right imaging is key for good treatment plans and patient care. Ultrasound is often the first choice for checking on fibroids. CT scans are used when their special features are needed.
When we need to know more about fibroids, MRI is the best option. It can show the size, number, and where fibroids are. This makes MRI very useful for planning surgeries and checking how treatments are working.
Knowing what each imaging method can do helps doctors choose the best one for each patient. This approach improves how well patients do with fibroid imaging.
FAQ
What is the most accurate imaging modality for diagnosing uterine fibroids?
MRI is now the top choice for seeing uterine fibroids. It’s very good at showing the size, number, and where fibroids are.
What are the advantages of using ultrasound for fibroid imaging?
Ultrasound is often first used for fibroids because it’s easy to get and not too expensive. It’s a good starting point.
What are the limitations of CT scanning in imaging uterine fibroids?
CT scans aren’t as good for fibroids because they don’t show soft tissues as well as MRI. This makes them less accurate for finding and figuring out fibroids.
How does MRI compare to ultrasound in detecting uterine fibroids?
MRI is better at finding and knowing about fibroids, even small or many. It’s more precise for planning treatments.
What are the benefits of using MRI for pre-surgical planning?
MRI gives clear details on fibroid size, number, and location. This is key for planning surgery and making treatment choices.
How are submucosal and pedunculated fibroids challenging to image?
Submucosal and pedunculated fibroids are hard to see because of where they are and how they look. They need careful checking and might need more tests.
What is the FIGO classification system used for in fibroid imaging?
The FIGO system helps standardize fibroid reports. It’s a way for doctors and radiologists to talk and make treatment plans.
Why is communication between radiologists and gynecologists important in fibroid imaging?
Good talk between doctors and radiologists is key for right diagnosis and care. It helps mix imaging info into treatment plans.
What are the emerging imaging techniques for fibroid diagnosis and treatment?
New MRI methods are being worked on to better diagnose and treat fibroids. They could help patients more.
How can imaging selection be optimized for uterine fibroids?
Choosing the right imaging for fibroids means thinking about the patient and the imaging options. It helps make the best treatment plans.
Reference
- Zeinali, A. M. H., Abbasi, K., & Shirzad, M. (2018). Fenestrated endovascular aortic aneurysm repair (FEVAR) for complex thoracoabdominal and abdominal aortic aneurysms: First Iranian series report with mid-term follow-up. PMCID: PMC6246430.