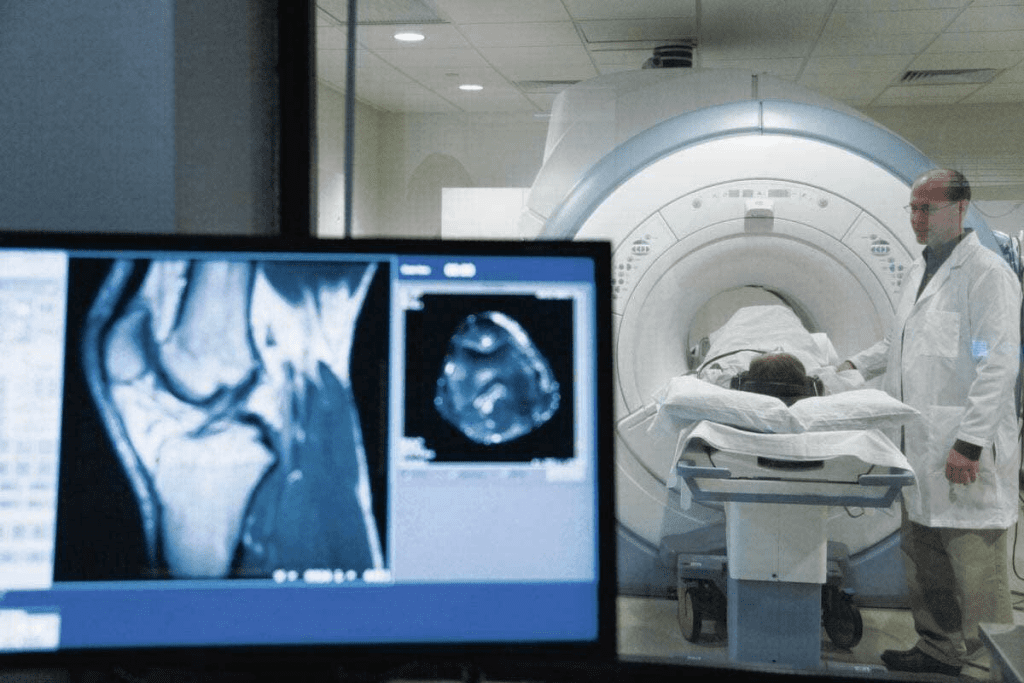
Advanced imaging methods are key in medical diagnostics and research. Techniques like functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) help us see brain activity and metabolic changes.
fMRI measures brain activity by looking at blood flow changes. On the other hand, PET scans use radioactive tracers to show cellular activity. Knowing the differences and similarities between these methods is vital for accurate diagnosis and research.
At places like Liv Hospital, picking between FMRI and PET scans is important for patient care. We will look at the main differences, similarities, and benefits of each method. This will help us make better choices.
Key Takeaways
- FMRI measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow.
- PET scans visualize cellular activity using radioactive tracers.
- Understanding the differences between FMRI and PET scans is key for accurate diagnosis.
- Each method has its own clinical benefits and uses.
- Choosing between FMRI and PET scans is important for patient care.
Understanding Medical Imaging Technologies
Medical imaging technologies have changed how we diagnose diseases. They let doctors see the body in great detail. This has made patient care better and opened new ways to research and treat diseases.
The Evolution of Neuroimaging
Neuroimaging has grown a lot over time. Tools like functional magnetic resonance imaging (FMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) are key for brain health. We’ll look at how these tools have changed and their role in medicine today.
The growth of neuroimaging has been amazing. It has changed how we see the brain and its work. For example, comparing MRI and PET scans shows what each can do best.
The Role of Advanced Imaging in Modern Medicine
Advanced imaging is key in today’s medicine. It helps doctors make accurate diagnoses and treatment plans. These tools are used in many areas, from oncology to neurology, and keep getting better.
| Imaging Modality | Primary Use | Key Benefits |
| FMRI | Brain activity mapping | High spatial resolution, non-invasive |
| PET | Cancer detection, neurological disorders | High sensitivity, functional information |
It’s important for doctors to know the differences between imaging tools. As we learn more about medical imaging technologies, we see each tool’s special strengths and uses.
What is FMRI?
FMRI is a non-invasive imaging technique. It measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow. This method has changed neuroscience, allowing for detailed brain function mapping.
Basic Principles of Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
FMRI works by linking brain activity to blood flow and oxygen changes. When a brain area is active, it needs more oxygen. So, the body sends more blood to that area.
FMRI machines use strong magnetic fields and radio waves to detect these changes. It relies on the magnetic differences between oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor hemoglobin.
How FMRI Measures Brain Activity
FMRI indirectly measures brain activity by tracking blood oxygenation changes. This is through the BOLD (Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent) contrast mechanism.
The BOLD signal comes from the magnetic field changes due to oxygen-rich blood. When a brain area is active, more oxygenated blood flows, changing the magnetic field. FMRI can detect this.
The BOLD Signal Explained
The BOLD signal is key to FMRI. It shows the magnetic difference between oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood. By measuring these differences, FMRI can tell which brain areas are active.
To show how FMRI data is presented, here’s a table on the BOLD signal:
| Aspect | Description |
| BOLD Signal Basis | Difference in magnetic properties between oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin |
| Detection Method | FMRI machines using powerful magnetic fields and radio waves |
| Significance | Allows for the mapping of brain activity with high spatial resolution |
Understanding the BOLD signal is key to making sense of FMRI data. It helps us see how the brain works and what happens in neurological conditions.
What is PET Scanning?
PET scanning helps us understand how cells in the body work and change. It’s a key tool in medicine, helping doctors find and treat diseases better.
Fundamentals of Positron Emission Tomography
PET scanning uses positron emissions from special tracers in the body. These tracers go to areas where cells are very active, like tumors or inflamed spots.
The steps are:
- A small amount of radioactive tracer is given to the patient.
- The tracer goes to active areas and emits positrons.
- When positrons meet electrons, they create gamma rays that the PET scanner catches.
- The scanner turns these signals into detailed images of the body’s activity.
Radioactive Tracers and Their Function
Radioactive tracers are key in PET scanning. The most used one is Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG), a special glucose molecule. It’s great for finding tumors and checking how well treatments work because cancer cells use more glucose.
| Tracer | Application | Clinical Use |
| Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) | Cancer detection, tumor staging | Oncology |
| Rubidium-82 | Myocardial perfusion imaging | Cardiology |
| Oxygen-15 | Brain function, blood flow studies | Neurology |
The Detection Process in PET
PET scanning uses advanced tech to catch gamma rays from positron-electron collisions. The scanner has detectors around the patient, capturing these rays to show how the body’s cells are working.
While PET scanning is very useful, it has some downsides. It involves radiation and can sometimes give false results. Yet, its insights into the body’s metabolic processes are invaluable in today’s medicine.
FMRI vs PET Scans: 7 Key Differences
When we compare FMRI and PET scans, we find key differences. These differences help decide which scan is best. It’s important for doctors and patients to know these differences.
Difference #1: Physical Principles and Technology
FMRI uses the magnetic properties of hemoglobin to measure brain activity. PET scans, on the other hand, use radioactive tracers to detect metabolic changes.
FMRI Technology: It uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to show brain activity.
PET Scan Technology: It involves injecting radioactive tracers that build up in active areas.
Difference #2: Radiation Exposure
FMRI doesn’t use radiation, making it safer for repeated scans. PET scans, though, do involve some radiation from the tracers.
Difference #3: Spatial and Temporal Resolution
FMRI gives high spatial resolution, showing brain structures clearly. PET scans also offer valuable insights but focus more on metabolic activity.
| Imaging Technique | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution |
| FMRI | High | Moderate |
| PET Scan | Moderate | Low |
Difference #4: Cost and Accessibility
FMRI and PET scans differ in cost and availability. FMRI machines are more common in hospitals. They are used for many purposes.
PET scans are more expensive and less common. They require special equipment and radioactive tracers.
Knowing these differences helps doctors choose the right scan for their patients.
Similarities Between FMRI and PET Scans
FMRI and PET scans share many similarities in neuroimaging. They both offer insights into how our brains work.
Both methods measure blood flow to understand brain activity. This is key in neuroscience research and diagnosing diseases.
Measuring Blood Flow as Proxy for Neural Activity
FMRI and PET scans use blood flow to show brain activity. FMRI looks at the BOLD signal, while PET scans use radioactive tracers.
This method helps researchers see which parts of the brain are active. It’s useful for studying brain function and diseases.
Applications in Neuroscience Research
These imaging techniques are vital in neuroscience. They help us understand the brain in health and disease.
- Studying the neural basis of cognition and behavior
- Investigating neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease
- Understanding the effects of neuroplasticity and recovery after brain injury
FMRI and PET scans help researchers. They work together to improve our knowledge of the brain. This leads to new treatments for brain diseases.
Complementary Roles in Clinical Diagnosis
In clinics, FMRI and PET scans have different roles. FMRI is used for brain mapping before surgery. PET scans help diagnose and stage cancer, and check heart function.
Together, they give a full view of brain function and problems. This helps doctors diagnose and treat many conditions.
Knowing how FMRI and PET scans are similar helps us use them better. This improves research and treatment in clinics.
FMRI Advantages and Limitations
FMRI is a non-invasive imaging method with many benefits and challenges. It is a valuable tool in neuroscience and clinical diagnostics.
Benefits of FMRI Technology
One key advantage of FMRI is its high spatial resolution. This allows for detailed brain activity mapping. It’s very useful in neuroscience research and planning before surgery. Also, FMRI is non-invasive, which makes it safer for patients than other imaging methods.
FMRI can measure changes in brain blood flow and oxygen levels. These changes show neural activity. This info is key to understanding how the brain reacts to different things.
- High spatial resolution for detailed brain mapping
- Non-invasive, reducing the risk to patients
- Ability to measure changes in blood flow and oxygenation
FMRI Disadvantages and Challenges
FMRI also has some limitations. One big challenge is its sensitivity to motion artifacts. These can cause wrong results if not handled right. Also, FMRI isn’t good for all patients, like those with metal implants or pacemakers.
| Advantages | Limitations |
| High spatial resolution | Sensitivity to motion artifacts |
| Non-invasive | Not suitable for patients with certain metal implants |
| Measures changes in blood flow and oxygenation | Limited temporal resolution compared to some other techniques |
In summary, FMRI has many advantages like being non-invasive and having high spatial resolution. But, it also has limitations to consider. Knowing these fmri pros and cons is key for using it well in research and clinical settings.
PET Scan Advantages and Limitations
PET scans are a key tool in modern medicine. They help us understand the body’s metabolic processes. This is vital for diagnosing and managing many conditions.
Benefits of PET Technology
PET scans have many benefits. They can show cellular activity and metabolic changes. This is very useful in fields like oncology, neurology, and cardiology.
They can spot diseases early, even before symptoms show. This early detection can greatly improve treatment results.
- High sensitivity for detecting metabolic changes
- Ability to assess the extent of disease spread
- Guiding treatment decisions with precise metabolic information
PET Scan Disadvantages
PET scans also have some downsides. One major concern is radiation exposure. They use radioactive tracers, which can expose patients to radiation.
Another issue is their high cost. This can limit their use in some healthcare settings.
Also, PET scans don’t offer the same detailed images as MRI or CT scans. So, they’re often used with these scans for a full view.
Clinical Applications of FMRI
FMRI is used in many ways in clinical practice. It helps plan surgeries and assess neurological disorders. Its detailed brain function mapping is key in neurology and psychiatry.
Presurgical Brain Mapping
FMRI is vital for planning brain surgeries. It shows where brain areas control important functions like speech and movement. This helps surgeons avoid harming these areas during surgery.
Benefits of FMRI in Presurgical Planning:
- Enhanced precision in identifying critical brain areas
- Reduced risk of postoperative neurological deficits
- Improved surgical outcomes through better planning
Neurological Disorder Assessment
FMRI helps diagnose and track neurological disorders. It looks at how brain activity changes in conditions like stroke and Alzheimer’s. This helps doctors understand and manage these diseases better.
| Neurological Disorder | FMRI Application |
| Stroke | Assessing brain activity changes post-stroke |
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Monitoring disease progression through brain activity changes |
| Multiple Sclerosis | Evaluating the impact on brain function and connectivity |
Psychiatric Condition Evaluation
In psychiatry, FMRI explores the brain’s role in mental health issues. It looks at brain activity in depression, schizophrenia, and anxiety. This helps find new treatments.
FMRI’s role in psychiatry is evolving, with ongoing research aimed at developing biomarkers for psychiatric disorders.
Clinical Applications of PET Scans
PET scans have many uses in medicine, from finding cancer to studying the brain and heart. We’ll look at how PET scans help in these areas. They are key in modern healthcare.
Oncology and Cancer Detection
PET scans are very important in fighting cancer. They help see how far cancer has spread and if treatments are working. They also spot cancer coming back.
PET scans give detailed info on tumors. This helps doctors plan treatments that fit each patient’s needs.
Neurological Disease Diagnosis
PET scans help diagnose brain diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. They show how the brain works and changes. This info helps doctors catch problems early and keep track of them.
PET scans give a full picture of brain health. They work with other scans to show the brain’s condition.
Cardiac Function Assessment
In cardiology, PET scans check how well the heart works. They look at blood flow and heart health. This info is key for treating heart disease.
PET scans show their value in cardiology. They give important details for heart care.
Understanding MRI vs FMRI Differences
MRI and FMRI are two imaging techniques used in medicine and research. MRI focuses on the body’s structure, while FMRI looks at brain function. Both are non-invasive and help doctors and scientists understand the body.
Structural vs Functional Imaging
MRI shows detailed images of the body’s parts. It’s great for seeing organs, bones, and tissues. This makes MRI useful for diagnosing many health issues.
FMRI, on the other hand, measures brain activity. It detects changes in blood flow to see how the brain works. FMRI is key in neuroscience and for planning brain surgeries.
Structural imaging, like MRI, shows the body’s anatomy at a moment. Functional imaging, like FMRI, reveals how the body works, like the brain’s activity.
When to Use MRI Instead of FMRI
Choosing between MRI and FMRI depends on the task. MRI is best for detailed body images. For example, it’s great for seeing brain and spinal cord lesions in multiple sclerosis.
FMRI is better for studying brain function. It helps in planning neurosurgery by showing important brain areas. This guides surgeons during operations.
Knowing the differences between MRI and FMRI helps doctors make better choices. This ensures patients get the right diagnosis and treatment.
Hybrid Imaging: Combined PET-MRI Technology
Hybrid PET-MRI imaging is a big step forward in medical diagnostics. It combines PET scans’ functional info with MRI’s detailed images. This gives a deeper look into how our bodies work.
Medical imaging is changing fast with hybrid technologies. By mixing PET and MRI, doctors can get better at diagnosing and researching. This makes healthcare better for everyone.
Advantages of Multimodal Imaging
Hybrid PET-MRI imaging has many benefits. It lets doctors get both functional and anatomical info at the same time. This makes diagnosis and treatment planning more accurate.
It also means fewer scans for patients, making them more comfortable. And it saves money on tests.
This tech is great for spotting and treating diseases, like cancer and brain disorders. It gives doctors a clearer picture of what’s going on inside the body.
Current Applications and Future Potentials
Hybrid PET-MRI is used in many areas, like cancer, brain, and heart studies. Studies show it’s good for catching diseases early and tracking how treatments work like in neuroscience research.
Application Area
| Benefits of Hybrid PET-MRI | |
| Oncology | Accurate tumor staging and treatment response assessment |
| Neurology | Enhanced understanding of brain disorders through combined functional and structural imaging |
| Cardiology | Comprehensive assessment of cardiac function and anatomy |
The future of hybrid PET-MRI looks bright. More research will make it even better. We’ll see more accurate tests and better treatments.
Conclusion: Choosing Between FMRI and PET Scans
Choosing between FMRI and PET scans requires knowing their differences and uses. We’ve looked at how each works, their benefits, and limits. This helps us see their roles in medical imaging.
The right choice depends on the research or clinical need. FMRI is great for brain studies because it’s detailed and safe. PET scans are better for cancer work because they show how cells are working.
It’s key to know how PET scans and MRI differ, and to compare FMRI and PET scans. Both look at brain function but in different ways. They help each other in research and diagnosis. Picking between them means thinking about what you need to know and what each can offer.
Understanding FMRI and PET scans helps professionals and researchers make better choices. This leads to more accurate diagnoses and better treatments.
FAQ
What is the main difference between FMRI and PET scans?
FMRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to measure brain activity. PET scans, on the other hand, use radioactive tracers to detect metabolic processes.
How do FMRI and PET scans compare in terms of radiation exposure?
FMRI doesn’t use radiation. PET scans, though, do expose patients to small amounts of radiation.
What are the advantages of FMRI over PET scans?
FMRI has higher spatial resolution and is non-invasive. It also doesn’t use radiation. Plus, it’s more affordable and widely available.
What are the clinical applications of FMRI?
FMRI helps in neurology and psychiatry. It’s used for brain mapping before surgery and for diagnosing neurological and psychiatric conditions.
How are PET scans used in clinical practice?
PET scans are key in oncology for cancer detection. They’re also used in neurology and cardiology for diagnosing diseases.
Can FMRI and PET scans be used together?
Yes, combining PET-MRI technology offers the best of both worlds. It provides detailed information for diagnosis and research.
What is the difference between MRI and FMRI?
MRI focuses on structural imaging. FMRI, on the other hand, measures brain activity by detecting blood flow changes.
Are there any disadvantages to using FMRI?
FMRI faces challenges like susceptibility to artifacts and limited temporal resolution. It can also cause claustrophobia or motion issues in patients.
What are the limitations of PET scans?
PET scans expose patients to radiation and have lower spatial resolution than FMRI. They also require radioactive tracers, posing logistical challenges.
How do I choose between FMRI and PET scans for my research or diagnosis?
The choice depends on your specific needs. FMRI is best for brain mapping and high-resolution studies. PET scans are ideal for metabolic studies and certain clinical uses like oncology.
What is the future of hybrid PET-MRI imaging?
Hybrid PET-MRI technology is set to grow. It will offer better diagnostic and research capabilities by combining the strengths of both modalities.
References
- Chen, K., & Chen, X. (2011). Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of Cancer Biology: Current Status and Future Prospects. Seminars in Oncology. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3060704/



































