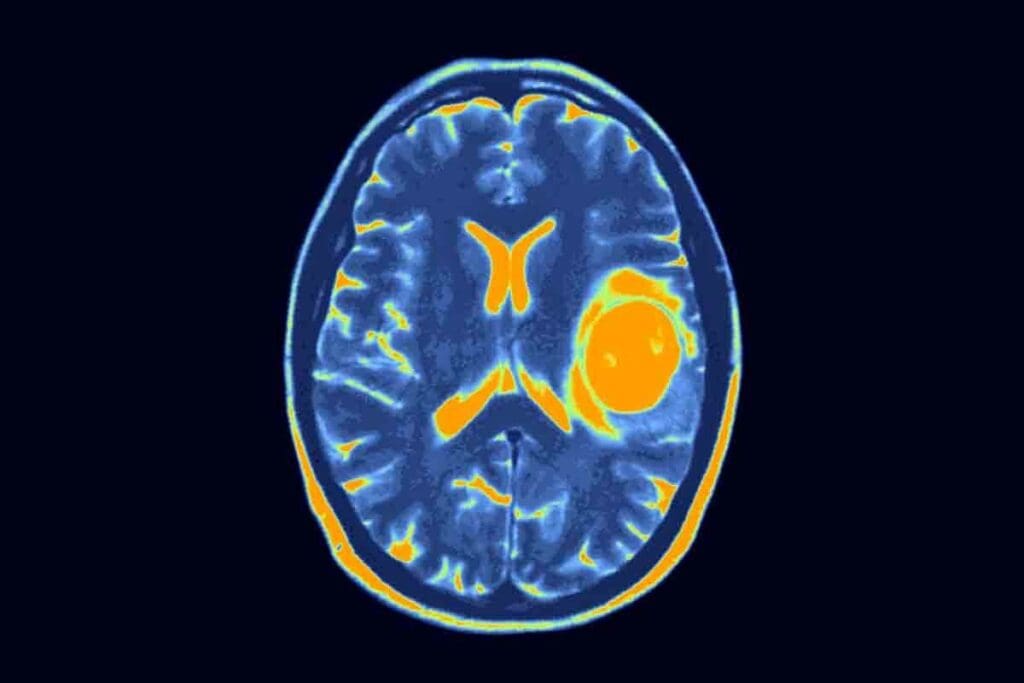
Glioblastoma is a rare but aggressive brain tumor that affects children. It’s also known as pediatric glioblastoma or pediatric GBM. This serious condition needs immediate medical care.
Pediatric brain and CNS tumors are rare. They happen in about 5.6 per 100,000 kids in the U.S. and 7.3 per 100,000 teens. Knowing the causes, symptoms, and treatments is key to the best care. A study onNCBI shows that some factors like radiation and genetic syndromes raise the risk of these tumors.
At Liv Hospital, we focus on top-notch healthcare with care and skill. Our team works hard to support families with pediatric GBM.
Key Takeaways
- Pediatric GBM is a rare but aggressive brain tumor.
- Incidence rates of pediatric brain and CNS tumors are approximately 5.6 per 100,000 in childhood.
- Certain genetic syndromes increase the risk of developing high-grade gliomas.
- Prompt medical attention is key for the best care.
- Institutions like Liv Hospital offer full support for families with pediatric GBM.
What Makes Glioblastoma in Children Different from Adult Cases
Glioblastoma in kids is quite different from what adults face. It’s a rare and aggressive brain cancer. It brings its own set of challenges in finding and treating it.
Definition and Classification of Pediatric Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM)
Pediatric GBM is a high-grade glioma. It’s classified by its look and molecular makeup. The World Health Organization (WHO) calls it a grade IV tumor because it’s so aggressive.
But, kids’ GBM often has different molecular profiles than adults’. This can change how it’s classified and treated.
Recent studies show the importance of molecular diagnostics in kids’ GBM. They look for specific genetic mutations and changes. These can affect how the tumor behaves and responds to treatment.
Incidence Rates and Epidemiology
Glioblastoma is much rarer in kids than in adults. It makes up a small part of all childhood brain tumors. The exact rates vary by age and location, but it’s rare in kids.
Research has found some risk factors for pediatric GBM. These include genetic predisposition and environmental exposures. But, more research is needed to understand it better.
Biological and Clinical Differences Between Pediatric and Adult GBM
Pediatric GBM has different genetic mutations than adult GBM. Adult GBM often has IDH mutations, but kids’ GBM usually doesn’t. Instead, kids’ GBM might have H3K27M mutations in diffuse midline gliomas.
Kids with GBM also show different symptoms and treatment responses. Understanding these differences is key to creating age-specific treatments.
Managing pediatric GBM needs a team effort. It involves neurosurgeons, oncologists, radiologists, and more. By understanding the unique aspects of pediatric GBM, we can improve treatment outcomes and quality of life for these young patients.
Genetic and Environmental Causes of Pediatric Glioblastoma
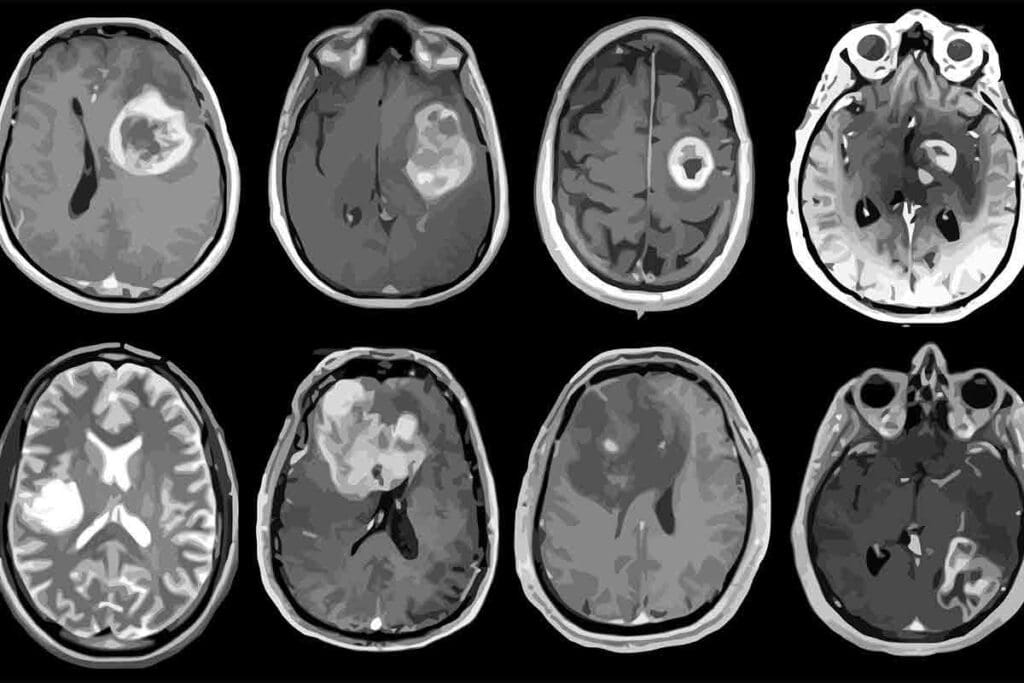
Recent studies have uncovered genetic mutations and environmental risks linked to pediatric glioblastoma. Knowing these causes is key to finding better treatments and improving patient care.
Known Genetic Mutations in Childhood GBM
Research has pinpointed several genetic mutations linked to childhood glioblastoma. The TP53 gene, which controls cell division, is often mutated in pediatric GBM. Other important mutations include changes in the EGFR and PTEN genes, which affect cell growth and signaling.
These genetic changes can cause cells to grow uncontrollably, leading to tumors. Knowing the specific mutations in a child’s glioblastoma helps doctors choose the right treatments, like glioblastoma multiforme chemotherapy.
Environmental Risk Factors Under Investigation
Genetic factors are a big part of pediatric glioblastoma, but environmental risks are also being looked into. Exposure to ionizing radiation is a known risk, as it can damage DNA and cause tumors.
Other environmental risks, like certain chemicals and pesticides, are also being studied. But more research is needed to understand their role in pediatric glioblastoma.
Current Research on Causative Mechanisms
Research is ongoing to understand how genetic and environmental factors combine to cause pediatric glioblastoma. Advances in genetic sequencing and molecular analysis are uncovering new targets for therapy. They are also revealing the disease’s underlying mechanisms.
As we learn more about pediatric glioblastoma, we’re getting closer to better treatments. This will help improve outcomes for children with this serious disease.
Recognizing the Warning Signs and Symptoms of Glioblastoma in Children
It’s important to know the symptoms of glioblastoma in kids for early treatment. Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a serious brain cancer. It shows differently in kids than in adults. So, parents and caregivers need to watch for warning signs.
Common Neurological Symptoms
Children with glioblastoma may have various neurological symptoms. These include:
- Headaches: Often one of the earliest symptoms, headaches can be severe and frequent.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms can occur due to increased intracranial pressure.
- Seizures: Seizures are a common presenting symptom, specially if the tumor is located in a region that affects motor control or sensory processing.
- Weakness or Numbness: Depending on the tumor’s location, children may experience weakness or numbness in parts of their body.
Symptoms Based on Tumor Location in the Brain
The location of the glioblastoma in the brain affects symptoms. For example:
- Tumors in the frontal lobe can cause changes in personality, mood, or motor function.
- Tumors in the temporal lobe may lead to difficulties with speech, memory, or seizures.
- Tumors affecting the brainstem can result in problems with breathing, swallowing, or controlling facial expressions.
Behavioral and Cognitive Changes
Glioblastoma can also cause behavioral and cognitive changes. These include:
- Memory Problems: Difficulty remembering recent events or learning new information.
- Concentration Issues: Trouble focusing or maintaining attention.
- Mood Swings: Increased irritability, anxiety, or depression.
When Parents Should Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Parents should seek immediate medical attention if their child has:
- Sudden severe headache
- Seizure activity
- Weakness or numbness in limbs
- Changes in vision, speech, or cognitive function
Early recognition and prompt medical evaluation are key. They help diagnose glioblastoma and start the right treatment.
The Diagnostic Journey: From First Symptoms to Confirmation
When a child shows signs of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), we start a journey to find out what’s happening. This journey is key to understanding the tumor and finding the right treatment.
Initial Medical Assessment Process
The first step is a detailed medical check-up. We collect the child’s medical history and examine their symptoms and how long they’ve had them. A thorough neurological exam checks their motor skills, reflexes, and thinking abilities.
This initial check helps doctors spot any brain problems and guides further tests.
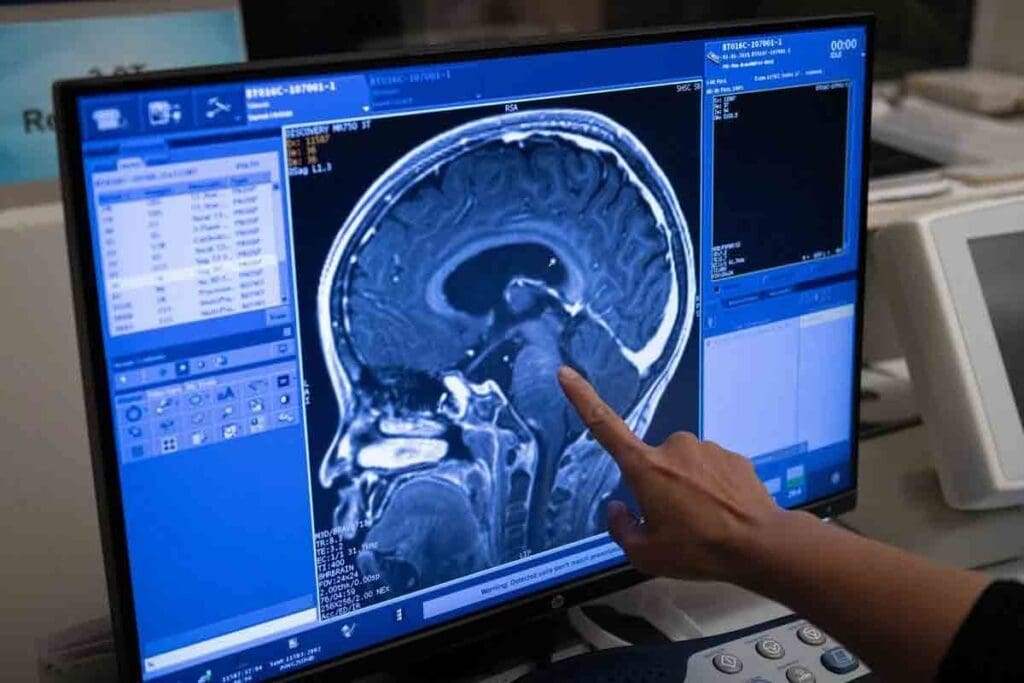
Advanced Imaging Techniques
Advanced imaging is vital for diagnosing glioblastoma multiforme. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the main tool used. MRI gives clear brain images, showing the tumor’s size and its effect on the brain.
At times, Computed Tomography (CT) scans or Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans are also used to get more details.
Biopsy and Pathological Analysis
A biopsy is key to confirming the diagnosis. A neurosurgeon takes a tumor sample. The sample is then studied by a pathologist to confirm the tumor type and grade.
This step is vital for knowing if it’s glioblastoma multiforme and how aggressive it is.
Molecular Testing and Genetic Profiling
Molecular testing and genetic profiling are also important. These tests find specific genetic changes in the tumor, like IDH1 or IDH2 mutations. Knowing the tumor’s genetics helps predict how it might behave and how it might react to certain treatments.
By combining all these steps, we can accurately diagnose glioblastoma multiforme in children. This allows us to create a treatment plan that fits their unique needs.
Standard Treatment Protocols for Pediatric Glioblastoma Multiforme
Treating pediatric glioblastoma requires a strong treatment plan. It involves many medical areas. A team of experts is needed to manage it.
Surgical Approaches and Limitations
Surgery is often the first step in treating pediatric GBM. The goal is to remove as much of the tumor as possible safely. Maximal safe resection is the main strategy, but GBM’s spread limits how much can be removed.
We use advanced surgery methods. These include intraoperative MRI and neuro-navigation. They help remove more tumors while keeping brain function intact.
Radiation Therapy Considerations in Developing Brains
Radiation therapy is key in treating pediatric GBM. But, it’s hard to use in kids because their brains are more sensitive. We plan radiation carefully to avoid lasting brain damage.
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and proton therapy help target the tumor precisely. This reduces harm to healthy brain areas.
Chemotherapy Regimens for Children
Chemotherapy is a big part of treating pediatric GBM. We use different drugs, sometimes together. The choice depends on the tumor and the child’s health.
Multidisciplinary Care Team Approach
Children with GBM need a team of specialists. This includes neurosurgeons, radiation oncologists, and more. They work together to create a treatment plan that fits the child’s needs.
| Treatment Modality | Key Considerations | Benefits |
| Surgery | Maximal safe resection, intraoperative MRI | Reduces tumor burden, improves symptoms |
| Radiation Therapy | IMRT, proton therapy, dose planning | Controls tumor growth, precise delivery |
| Chemotherapy | Molecular profiling, combination regimens | Targets tumor cells, improves survival |
Breakthrough Treatments and Clinical Trials
The field of pediatric glioblastoma treatment is changing fast. New therapies are being developed. These could lead to better results for kids with glioblastoma multiforme.
Targeted Molecular Therapies
Targeted molecular therapies are a big step forward. They target specific genetic changes in tumors. This could lead to treatments that work better and have fewer side effects.
Studies show that some genetic changes in glioblastoma can be treated with specific drugs. This could slow down or stop tumor growth.
Researchers are also looking at combining these therapies with other treatments. This could make treatments even more effective. Early results from clinical trials are promising.
Immunotherapy Approaches for Pediatric Patients
Immunotherapy is another area of research that’s showing promise. It uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. This includes treatments like checkpoint inhibitors and CAR-T cell therapy.
These treatments aim to make the body better at finding and attacking cancer cells. This could lead to treatments that are more effective and less harsh.
Clinical trials are underway to test these treatments in kids with glioblastoma. For example, CAR-T cell therapy has shown promise in treating pediatric brain tumors. As research continues, immunotherapy is expected to play a bigger role in treating glioblastoma in kids.
Promising Clinical Trials in the United States
In the United States, many clinical trials are looking into new treatments for pediatric glioblastoma. These trials are key to finding better treatments. They involve new combinations of therapies and even new approaches like oncolytic virus therapy.
One study at Emory University is exploring new ways to treat pediatric brain tumors, including glioblastoma. You can learn more about their research on their website. Such studies are important for improving treatment options for kids with glioblastoma.
Novel Drug Delivery Systems
Researchers are also working on better ways to deliver drugs for pediatric glioblastoma. New methods, like convection-enhanced delivery and nanoparticles, aim to make treatments more effective and reduce side effects. These methods help ensure drugs reach the tumor site better.
For example, scientists are looking at using nanoparticles to deliver chemotherapy directly to glioblastoma cells. This could reduce harm to healthy tissues. Such innovations could greatly improve treatment options for kids with glioblastoma.
| Treatment Approach | Description | Potential Benefits |
| Targeted Molecular Therapies | Focus on specific genetic mutations or pathways | More effective with fewer side effects |
| Immunotherapy | Harnesses the immune system to fight cancer | Potentially less toxic and more effective |
| Novel Drug Delivery Systems | Improves delivery of therapeutic agents | Enhances treatment efficacy and reduces side effects |
Understanding Prognosis and Quality of Life Considerations
When a child is diagnosed with glioblastoma, it’s hard to grasp their prognosis. The outlook for kids with glioblastoma multiforme changes a lot. It depends on where the tumor is, how much of it can be removed, and certain genetic traits.
Current Survival Statistics
Thanks to new treatments, survival rates for kids with glioblastoma are getting better. But, glioblastoma is a tough cancer to beat. Studies show that kids’ survival chances are improving, but they’re not as good as other childhood cancers.
| Time Frame | Survival Rate |
| 1 Year | 60% |
| 2 Years | 30% |
| 5 Years | 15% |
Prognostic Factors That Influence Outcomes
Several factors are key in predicting how well a child will do with glioblastoma. These include:
- Tumor Location: Tumors in easier-to-reach parts of the brain might have a better chance of being removed fully.
- Extent of Resection: How much of the tumor can be taken out greatly affects the prognosis.
- Molecular Characteristics: Certain genetic changes can affect how well the tumor responds to treatment.
Managing Treatment Side Effects
It’s important to manage glioblastoma treatment side effects to keep kids’ quality of life good. Side effects can include brain problems, changes in thinking, and emotional issues. A team of doctors and therapists is key in helping kids deal with these effects.
Neurological and Cognitive Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is vital for kids to get better from glioblastoma’s brain and thinking. This includes physical, occupational, and cognitive therapy. Each program is made to fit the child’s needs.
By understanding the prognosis and focusing on quality of life, families and doctors can give the best care to kids with glioblastoma.
Resources and Support for Families Facing Pediatric GBM
The journey through pediatric GBM is filled with challenges. Having the right resources and support can make a big difference for families. Diagnosing and treating glioblastoma multiforme in children needs a team effort. This includes medical treatment, emotional support, and financial help.
Specialized Treatment Centers in the United States
Families facing pediatric GBM can find care at specialized centers across the United States. These centers, linked to major children’s hospitals, have teams ready to help. They include neurosurgeons, oncologists, and more. Some top centers are:
- Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia
- Boston Children’s Hospital
- Texas Children’s Hospital
- Children’s Hospital Los Angeles
- NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital
These centers offer the latest treatments and may be part of clinical trials. This gives families access to new therapies.
Financial Assistance Programs
Treating pediatric GBM can be very expensive. Luckily, there are programs to help with medical costs, travel, and more. Some include:
- The Children’s Cancer and Blood Foundation
- CureSearch for Children’s Cancer
- The Pediatric Brain Tumor Foundation
- National Brain Tumor Society
These groups offer financial aid and help with navigating the healthcare system.
Psychological Support Services
The emotional impact of a GBM diagnosis is huge for the whole family. Psychological support is key to managing stress and uncertainty. Many centers offer:
- Counseling for patients and families
- Support groups for parents and siblings
- Mental health experts for pediatric oncology
Groups like the Pediatric Brain Tumor Foundation also offer specific support for families with brain tumors.
Patient Advocacy Organizations and Support Groups
Patient advocacy groups are vital for families. They provide education, advocacy, and community support. These groups offer:
- Info on the latest research and treatments
- Advocacy for better policies for pediatric cancer
- Online and in-person support groups
These organizations help families find the resources they need. They ensure no family faces GBM alone.
Conclusion: The Future of Pediatric Glioblastoma Research and Care
Pediatric glioblastoma multiforme is a complex condition. Ongoing research and new treatments are key to better outcomes for kids.
Research is now focused on finding more effective treatments. This includes molecular targeted treatments and immunotherapy. These methods have shown promise in clinical trials for gsb glioblastoma.
We are committed to top-notch healthcare for all patients, including those from abroad. By understanding more about pediatric glioblastoma and finding new treatments, we aim to improve life and survival rates for these children.
As research keeps moving forward, we’re dedicated to giving kids with glioblastoma the best care. We ensure they get the latest and most effective treatments and support.
FAQ
What is pediatric glioblastoma multiforme (GBM)?
Pediatric glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a rare and aggressive brain cancer in kids. It starts from the brain’s glial cells.
How common is glioblastoma in children?
Glioblastoma is rare in kids, making up a small part of brain tumors in children. But it’s very aggressive and serious.
What are the symptoms of glioblastoma in children?
Symptoms vary based on the tumor’s location and size. Kids might have headaches, seizures, nausea, vomiting, and changes in behavior or thinking.
How is pediatric glioblastoma diagnosed?
Doctors use imaging tests like MRI or CT scans, biopsy, and molecular testing. These help confirm cancer and identify genetic mutations.
What are the treatment options for pediatric glioblastoma?
Treatment includes surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. The plan depends on the tumor, its size, and the child’s health.
Are there any new or experimental treatments for pediatric glioblastoma?
Yes, new treatments are being explored. These include targeted therapies, immunotherapy, and new drug delivery systems. Clinical trials are ongoing to test these.
What is the prognosis for children with glioblastoma?
The outlook varies based on the tumor’s genetics, treatment success, and the child’s health. While survival rates have improved, glioblastoma is a tough disease.
What resources are available to support families affected by pediatric glioblastoma?
Families can find help through specialized centers, financial aid, psychological support, and advocacy groups.
What is the role of genetic mutations in pediatric glioblastoma?
Genetic mutations are key in developing and growing pediatric glioblastoma. Certain mutations, like in BRAF or H3K27M genes, affect treatment and prognosis.
Can environmental factors contribute to the development of pediatric glioblastoma?
Research suggests environmental factors might play a part in some cases. But more study is needed to understand these risks.
References
- Singla, A. K., et al. (2021). Clinical behaviour and outcome in pediatric glioblastoma. Journal of Pediatric Neuro-Oncology, 8(1), Article 22. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8024182/




































