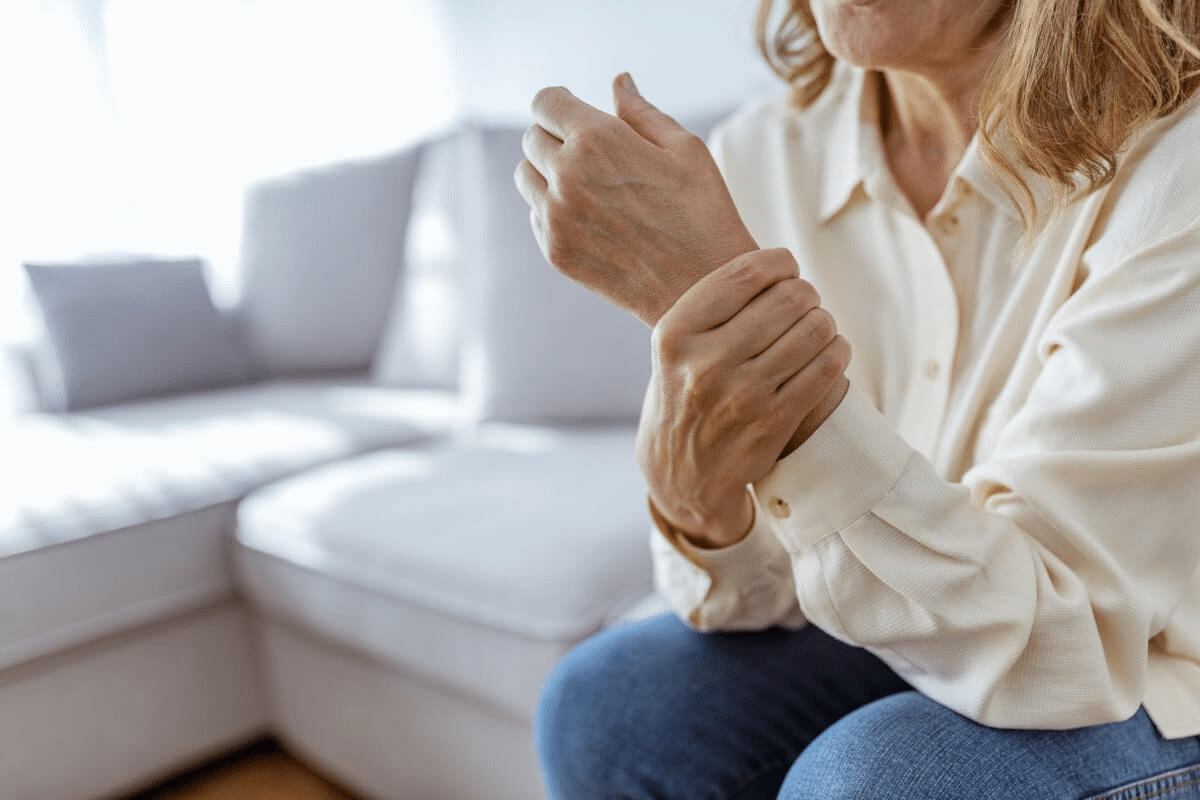
Explaining common causes of soreness in hands and wrist, including arthritis, carpal tunnel syndrome, and overuse injuries.
Do you often feel pain in your hands and wrists? It can really get in the way of your daily life. Millions of people worldwide deal with this issue. It’s caused by many things, from simple strain to serious conditions.
It’s important to know why your hands hurt. This knowledge helps find the right treatment. The reasons range from sudden injuries to ongoing problems like repetitive stress, arthritis, and carpal tunnel syndrome. Liv Hospital has experts from around the world to help with these issues.
Key Takeaways
- Hand and wrist pain can result from various causes, including injuries and long-term conditions.
- Repetitive stress, arthritis, and carpal tunnel syndrome are common underlying causes.
- Understanding the cause is key to effective treatment and relief.
- Liv Hospital offers access to internationally-trained specialists.
- Proper diagnosis is critical for addressing hand and wrist soreness.
Understanding the Prevalence of Hand and Wrist Pain
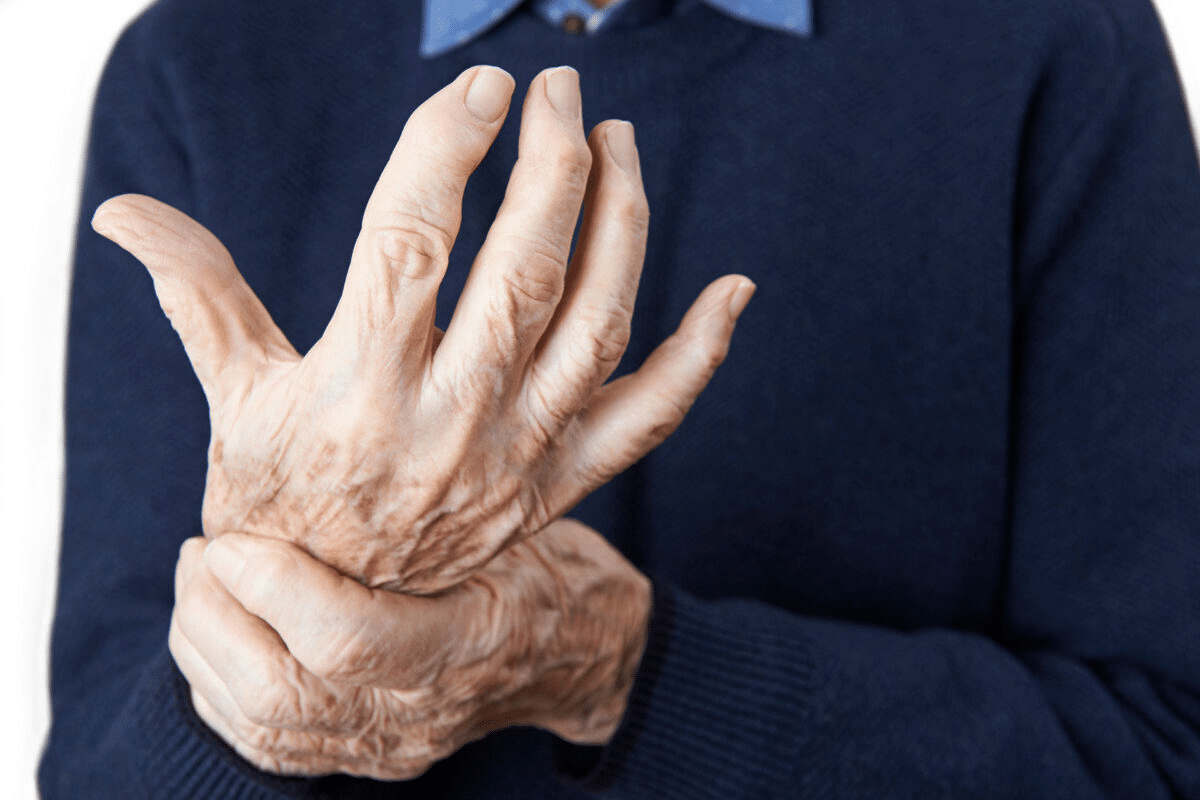

Hand and wrist pain is a big problem that affects many people. It can really hurt your quality of life and how much you can work.
Recent studies show that hand and wrist pain is a big reason for visits to the emergency room. About 21.44% of these visits are because of these pains. This shows how common hand and wrist pain is.
Statistical Overview of Hand and Wrist Complaints
Many people go to orthopedic clinics and emergency rooms because of hand and wrist pain. We need to understand why this happens and who is at risk.
- Sports and repetitive work can lead to wrist injuries and disorders.
- Hand and wrist pain happens to people of all ages, but some groups are more affected.
A study found that people who do manual labor and athletes are more likely to get hand and wrist injuries. This shows how important it is to prevent these problems and take care of ourselves.
Demographics Most Affected by Hand Pain
Hand pain affects many people, but some groups are more likely to get it. This is because of different reasons.
- People between 30 and 60 are more likely to get hand pain because of wear and tear.
- Athletes and those who do manual labor are at higher risk because of repetitive strain and possible injuries.
Knowing who is most at risk helps us develop better ways to prevent and treat hand and wrist pain. Healthcare providers can then give more focused care and advice.
Prevention and early treatment are very important for managing hand and wrist pain. By knowing who is most at risk, we can take steps to avoid it.
The Complex Anatomy of the Hand and Wrist
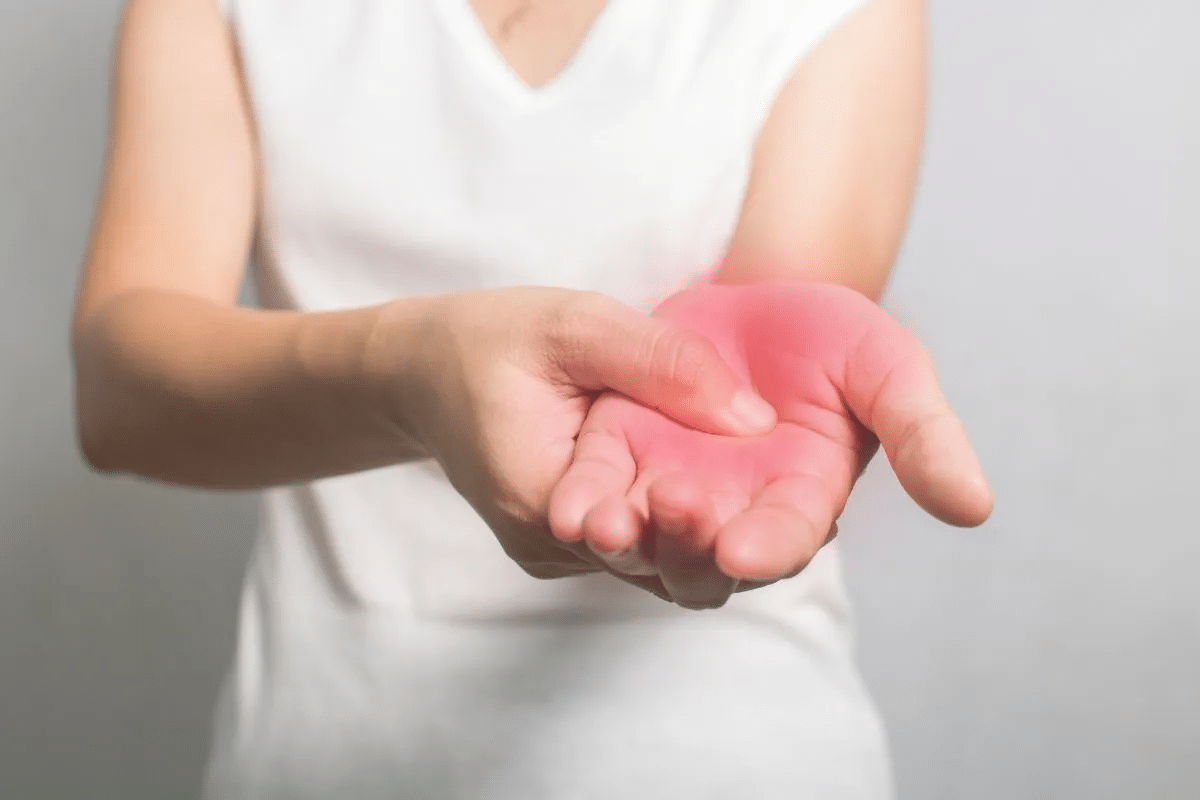

The hand and wrist are amazing parts of our body. They have bones, ligaments, tendons, and nerves that can get hurt and cause pain. Knowing how these parts work is key to understanding why we might feel pain in our hands and wrists.
Bones, Joints, and Ligaments
The wrist has eight small bones called carpal bones and two long bones in the forearm. These bones and joints let us move our wrist in many ways. Ligaments, strong tissues, keep these bones together, making the wrist stable.
Tendons, Muscles, and Nerves
Tendons link muscles to bones and help us move our hands and wrists. The way tendons and muscles work together lets us do things like grip and perform fine tasks. Nerves, like the median, ulnar, and radial nerves, send signals from our hands to our brain, helping us feel and move.
Why This Complex Structure Is Prone to Pain
The detailed design of the hand and wrist lets us do amazing things. But it also makes these areas more likely to hurt. Things like overuse, injuries, and health problems can affect the bones, joints, and other parts, causing pain.
Key factors contributing to pain include:
- Overuse or repetitive strain injuries
- Trauma or acute injuries
- Degenerative conditions such as arthritis
- Inflammatory conditions like tendonitis
Knowing what causes pain is important for treating hand and wrist pain well.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Leading Cause of Soreness in Hands and Wrist
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is caused by the median nerve getting compressed. This leads to hand pain and discomfort. The median nerve runs from the forearm to the hand through a narrow space in the wrist.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome often causes a pins and needles feeling in the thumb and fingers. This feeling is more common at night. Symptoms also include numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand.
Doctors diagnose it through physical exams, medical history, and sometimes tests like nerve conduction studies.
Common Symptoms:
- Numbness or tingling in the thumb, index, middle finger, and part of the ring finger
- Pain or burning sensation in the wrist or hand
- Weakness or clumsiness in the hand
- Difficulty distinguishing hot and cold temperatures
Risk Factors and Causes
Several factors can lead to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. These include repetitive motion, wrist anatomy, health factors, and lifestyle.
|
Risk Factor |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Repetitive Motion |
Activities that involve repetitive hand or wrist motions, such as typing or assembly line work. |
|
Wrist Anatomy |
A smaller carpal tunnel or other anatomical differences that may compress the median nerve. |
|
Health Factors |
Conditions like diabetes, hypothyroidism, and rheumatoid arthritis that can affect the nerves. |
|
Lifestyle |
Activities or conditions that cause vibration, such as using vibrating tools. |
Treatment Options
Treatment for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome varies based on severity. It may include:
- Wrist splinting to keep the wrist straight
- Corticosteroid injections to reduce swelling
- Physical therapy to improve wrist and hand mobility
- Surgery in severe cases to release the compressed median nerve
Early treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent further damage.
Tendonitis and Tenosynovitis: When Overuse Leads to Pain
Tendonitis and tenosynovitis often come from too much use or repetitive actions. They cause pain in the hands. These issues happen when the tendons and their sheaths get inflamed, leading to pain and less function.
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a type of injury from too much strain. It affects the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist. It makes the wrist and thumb hurt, mainly when you make a fist or turn your wrist.
Symptoms of De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis include:
- Pain or tenderness on the thumb side of the wrist
- Difficulty moving the thumb and wrist
- A sensation of catching or snapping when moving the thumb
Trigger Finger
Trigger finger, or stenosing tenosynovitis, is linked to tendonitis. It happens when the tendon and its sheath in the finger get inflamed. This causes pain, stiffness, and a feeling of locking or catching when bending your fingers.
Treatment for trigger finger often involves:
- Resting the affected finger
- Avoiding activities that aggravate the condition
- Splinting to limit movement
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for tendonitis and tenosynovitis usually includes rest, physical therapy, and sometimes medicine to reduce swelling. In serious cases, corticosteroid shots or surgery might be needed.
|
Condition |
Common Symptoms |
Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|
|
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis |
Pain on thumb side of wrist, difficulty grasping |
Rest, splinting, corticosteroid injections |
|
Trigger Finger |
Pain, stiffness, locking sensation in fingers |
Rest, splinting, NSAIDs, corticosteroid injections |
|
Tendonitis |
Pain, swelling, reduced mobility |
Rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE), physical therapy |
Knowing the causes and signs of tendonitis and tenosynovitis is key to managing and preventing them. By using the right treatments, people can ease pain and get their hands and wrists working better.
Arthritis in the Hands and Wrists
Arthritis is a common cause of hand and wrist pain. It can make simple tasks hard to do. This condition affects many people’s daily lives.
Osteoarthritis: Wear and Tear Pain
Osteoarthritis is a disease that wears down the cartilage in joints. This leads to pain and stiffness in the hands and wrists. It’s more common in older adults and can get worse with injuries.
Osteoarthritis in the wrist is relatively uncommon. It usually happens to people who have had wrist injuries. It can cause a lot of pain and limit movement, making daily tasks hard.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: When Your Immune System Attacks
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease. It makes the body attack the lining of joints, causing inflammation, pain, and damage. RA often affects the wrists and hands, leading to stiffness and pain.
The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis can vary. They often include swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected joints. Getting a diagnosis early and starting treatment is key to managing the condition and preventing damage.
Other Forms of Inflammatory Arthritis
There are other types of inflammatory arthritis that can affect the hands and wrists. These include psoriatic arthritis, linked to psoriasis, and gout, known for sudden, severe pain and swelling.
Knowing the specific type of arthritis is important for finding the right treatment. Each type has its own characteristics and needs different approaches.
Location-Specific Hand Pain and Their Causes
Hand pain in different spots can tell us a lot about what’s causing it. Pain can show up in many places on the hand, each with its own reasons. Knowing these can help figure out and fix hand pain.
Bottom of Hand Pain (Palm and Heel of Hand)
Pain in the palm or heel of the hand can come from several things. Carpal tunnel syndrome is a big one, caused by the median nerve getting squished. Other reasons include palmar fasciitis and flexor tendonitis. Doing the same thing over and over, like gripping, can make these problems worse.
|
Cause |
Description |
Common Activities |
|---|---|---|
|
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome |
Compression of the median nerve |
Typing, assembly line work |
|
Palmar Fasciitis |
Inflammation of the palmar fascia |
Gripping, manual labor |
|
Flexor Tendonitis |
Inflammation of the flexor tendons |
Wrist flexion, gripping |
Side of Hand Soreness (Ulnar and Radial Sides)
Pain on the sides of the hand can be from different things. De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a common problem on the radial side, caused by tendon inflammation. On the ulnar side, ulnar nerve entrapment can cause pain.
Left Hand vs. Right Hand Pain: Is There a Difference?
Left hand and right hand pain can be different, depending on which hand you use more and what you do with it. Right-handed people might get more injuries in their right hand. Left-handed people might have more issues with their left hand. But, both hands can get hurt by things like arthritis.
Ganglion Cysts and Other Soft Tissue Causes
Ganglion cysts are usually not cancerous but can be very painful. They often appear on the wrist or hand and can grow in size. Knowing what causes them, their symptoms, and how to treat them is key to managing pain.
Identifying Ganglion Cysts
Ganglion cysts look like lumps or masses on the hand or wrist. They are filled with a jelly-like fluid and can hurt, pressing on nerves. The exact reason for ganglion cysts is not known, but they are linked to wear and tear, joint or tendon irritation, and sometimes trauma.
A healthcare provider will usually check for ganglion cysts by touch. They might also use X-rays or an MRI to confirm the diagnosis and check for other conditions.
Treatment Options for Soft Tissue Conditions
Treatment for ganglion cysts and other soft tissue causes of hand pain depends on how severe the symptoms are and how they affect daily life. Here are some options:
- Monitoring: For small, painless cysts, waiting and watching might be the best approach.
- Immobilization: Wearing a wrist splint can help reduce pain and might make the cyst smaller.
- Aspiration: Draining the cyst with a needle.
- Surgery: Removing the cyst surgically, often considered if other treatments don’t work or if the cyst is big and painful.
|
Treatment Option |
Description |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Monitoring |
Observing the cyst without immediate intervention |
Avoids unnecessary procedures |
|
Immobilization |
Using a splint to reduce wrist movement |
Reduces pain and cyst size |
|
Aspiration |
Draining the cyst’s fluid |
Quick relief from pain and swelling |
|
Surgery |
Surgical removal of the cyst |
Permanent solution for recurring cysts |
Seeing a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and to find the best treatment plan is very important.
Traumatic Injuries Leading to Hand and Wrist Pain
Falls or sports injuries often cause hand and wrist pain. Falling forward onto your hand can lead to sprains, strains, and fractures. Knowing about these injuries helps in managing and recovering from them.
Fractures and Sprains
Fractures and sprains are common in the hand and wrist. A fracture happens when bones break. A sprain is when ligaments stretch or tear. Both can result from falls or direct blows.
Symptoms include pain, swelling, and limited movement. Severe cases might show visible deformities. If you think you have a fracture or severe sprain, see a doctor quickly to avoid long-term problems.
Dislocations
A dislocation is when bones in a joint move out of place. In the hand and wrist, this can cause pain, swelling, and trouble moving. Getting medical help right away is key to correct alignment and avoiding further issues.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovering from hand and wrist injuries involves several steps. First, use the rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) method to reduce pain and swelling. For serious injuries, physical therapy is needed to build strength and mobility.
Rehab programs are made for each injury. They include exercises to improve flexibility and strengthen muscles. Sometimes, occupational therapy is suggested to help with daily tasks.
Always follow your healthcare provider’s advice for the best recovery. This helps avoid future problems.
Occupational and Repetitive Strain Injuries
Many jobs require doing the same thing over and over, which can hurt hands and wrists. Workers in different fields face the risk of getting hurt on the job.
High-Risk Professions
Some jobs are more likely to cause hand and wrist injuries because of the repetitive tasks. For example, people working in factories, assembly lines, and jobs that involve heavy lifting or repetitive actions are at a higher risk.
Examples of high-risk professions include:
- Assembly line workers
- Manufacturing workers
- Construction workers
- Office workers who perform repetitive tasks on computers
As Medical Expert, an occupational health specialist, says, “Repetitive strain injuries are a big worry in the workplace. It’s important to take steps to prevent them.”
Ergonomic Considerations
Good workplace ergonomics are key to avoiding repetitive strain injuries. It’s important to make sure the workspace supports good posture and doesn’t strain hands and wrists too much.
“Ergonomic changes can greatly lower the risk of musculoskeletal disorders,” a study in the Journal of Occupational Rehabilitation found.
Some things to consider for better ergonomics include:
- Adjusting the height of workstations
- Using ergonomic keyboards and mice
- Providing regular breaks
- Promoting proper lifting techniques
Prevention Strategies in the Workplace
There are steps employers can take to lower the risk of work-related injuries. By making the workplace safer, employers can protect their workers’ health.
Prevention strategies include:
- Conducting regular ergonomic assessments
- Providing training on proper work techniques
- Encouraging regular breaks and stretching exercises
- Monitoring worker health and addressing concerns promptly
By understanding the risks and taking action, employers can help keep their workers safe and healthy. This reduces the chance of injuries happening on the job.
Self-Care Strategies for Hand and Wrist Pain Relief
Self-care is key in managing hand and wrist pain. Simple strategies in your daily life can help ease pain and boost hand function.
Rest and Activity Modification
Resting your hands and wrists is essential. Stay away from activities that make pain worse. Modify tasks to lessen strain.
For example, if typing hurts your wrist, adjust your workspace or take breaks to stretch.
Wearing a wrist brace or cast can offer support and reduce pain by limiting movement. Taking pain relievers as directed can also help manage discomfort.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Heat and cold therapies can help with hand and wrist pain. Cold therapy, like an ice pack, can reduce swelling and numb pain. Heat therapy, like a warm bath or heating pad, relaxes muscles and boosts blood flow.
Switching between heat and cold can be helpful. Start with cold to cut down inflammation, then use heat to relax muscles.
Exercises and Stretches for Hand Health
Gentle exercises and stretches can make your hands and wrists more flexible and strong. Wrist extensions, tilting your wrist up, and flexions, tilting it down, are good.
Other exercises include spreading your fingers apart and then bringing them together. Also, rotate your wrists in both directions. Do these exercises gently and without pain.
Doing these exercises regularly keeps your hands healthy and prevents future pain.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Hand Pain
Knowing when to get medical help for hand pain is key. It helps treat the issue and avoid lasting damage. Hand pain can come from many sources, like small injuries or serious conditions like arthritis or carpal tunnel syndrome.
Warning Signs That Require Immediate Care
Some symptoms mean you should see a doctor right away. These include:
- Severe pain that doesn’t get better with rest or medicine.
- Swelling or bruising around the hand or wrist.
- Numbness or tingling that lasts a long time.
- Deformity or trouble moving the hand or fingers.
- Loss of function or weakness in the hand.
Diagnostic Approaches Your Doctor May Use
When you see a doctor, they will use different methods to find out what’s wrong. These might include:
- Physical examination to check how well you can move, how strong you are, and where it hurts.
- Imaging tests like X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to see bones, joints, and soft tissues.
- Nerve conduction studies to check nerve function, which is important for conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome.
These tools help find the cause of hand pain. They guide the right treatment.
Treatment Options from Medical Professionals
Treatment for hand pain depends on what’s causing it. Common options are:
- Medications like pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Physical therapy to make movement and strength better.
- Corticosteroid injections to lessen swelling.
- Surgery when other treatments don’t work or the problem needs surgery.
Your doctor will suggest the best treatment for your situation.
Conclusion: Living with and Managing Hand and Wrist Pain
Managing hand and wrist pain needs a mix of self-care, medical help, and lifestyle changes. Knowing what causes pain and using the right strategies can help. This way, people can feel better and live better lives.
Handling hand and wrist pain means tackling the root causes. This might mean changing how you do things, doing exercises, or seeing a doctor. With the right mix of treatments and lifestyle tweaks, lasting relief is possible.
In short, hand and wrist pain can really affect your day-to-day. But, by taking action and using a whole approach, you can lessen pain and get back to normal. By focusing on self-care, medical care, and making your environment better, you can keep your hands and wrists healthy for a long time.
FAQ
Why do my hands ache all the time?
Hand pain can come from many sources. This includes injuries from repetitive tasks, arthritis, or other health issues. It’s important to see a doctor to find out why and how to feel better.
What are the causes of sore hands?
Sore hands can happen for many reasons. This includes too much use, injury, or conditions like tendonitis or arthritis. Knowing the cause helps in finding the right way to treat it.
Why does the bottom of my hand hurt?
Pain in the palm or heel of your hand can be from carpal tunnel syndrome, wrist strain, or arthritis. Finding out what’s causing the pain is key to treating it.
Why does my right hand hurt?
Right-hand pain can stem from many things. This includes injuries from overuse or health issues. If you use your right hand a lot, you might be more likely to get hurt.
What does it mean when your hands ache?
Aching hands can signal several problems. This includes arthritis, tendonitis, or injuries from repetitive actions. Paying attention to how long and how bad the pain is helps figure out what’s wrong.
How can I relieve hand and wrist pain?
To ease hand and wrist pain, try resting, using heat or cold, and doing exercises. Sometimes, you might need to see a doctor to find and treat the cause.
When should I seek medical attention for hand pain?
If your hand pain is severe, you have numbness or tingling, or trouble moving your hands or wrists, see a doctor. Also, if you’ve had injuries, get checked out by a healthcare professional.
Can occupational factors contribute to hand pain?
Yes, jobs that involve repetitive tasks, poor work setup, or heavy lifting can hurt your hands. Taking breaks and keeping good posture can help prevent this.
Are there exercises that can help alleviate hand pain?
Yes, certain exercises can help with hand pain. They improve flexibility, strength, and movement. A doctor or occupational therapist can help you find the right exercises for you.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6857228/