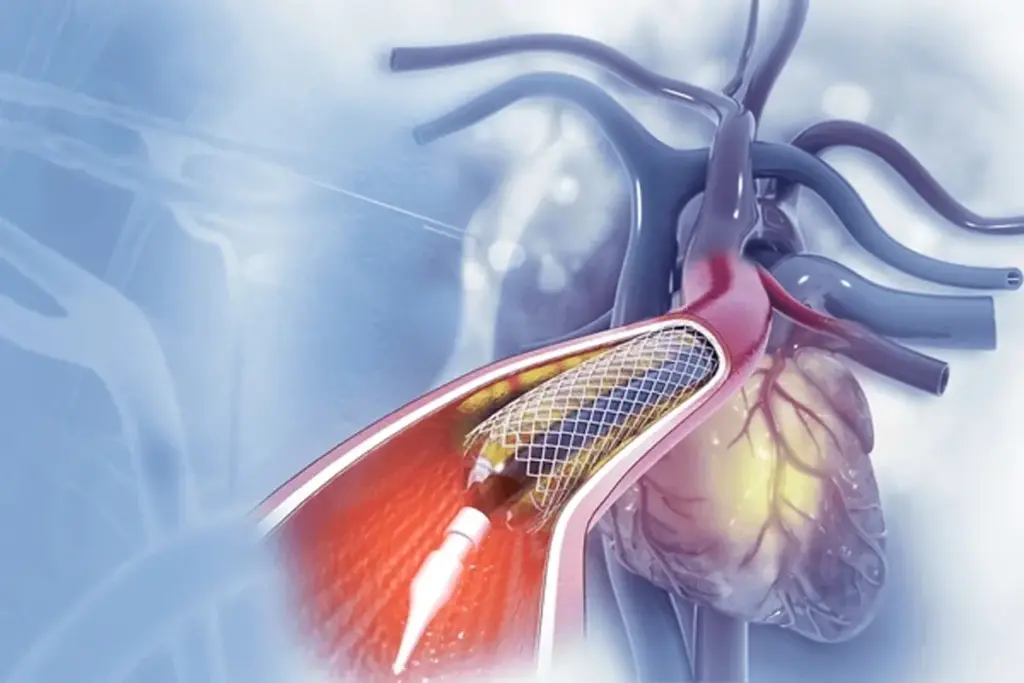
Coronary heart disease affects millions worldwide. Many get heart stent placement surgery each year. In the U.S., hundreds of thousands get stents every year. Answering is getting a heart stent a big deal (low risk, high benefit) and addressing the query, is a heart stent serious.
A stent is a tiny tube that keeps arteries open. It improves blood flow to the heart. This surgery is key for treating coronary heart disease. It’s important for patients and their families to understand its role.
Key Takeaways
- The significance of heart stent placement lies in its ability to restore blood flow.
- Stent surgery is a common treatment for coronary heart disease.
- Understanding the procedure’s seriousness can help patients prepare.
- The stent helps keep arteries open, reducing the risk of further complications.
- Patients should discuss their individual risks and benefits with their doctor.
Understanding Heart Stents and Their Purpose
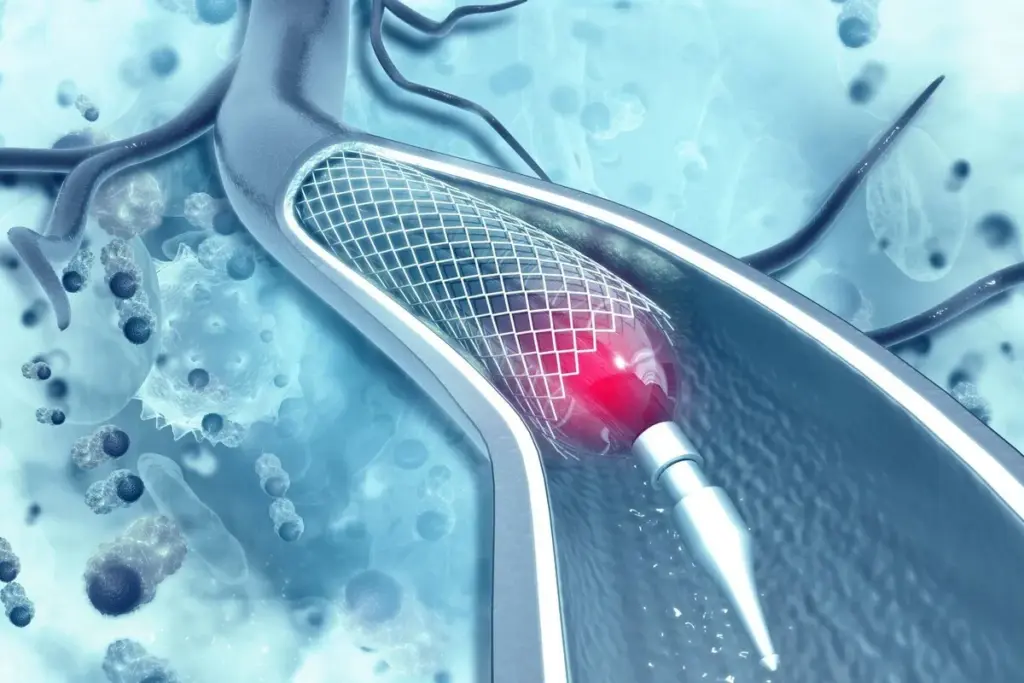
Heart stents are key for those with coronary artery disease. They are small, mesh-like devices that keep arteries open. This improves blood flow to the heart.
What is a Heart Stent?
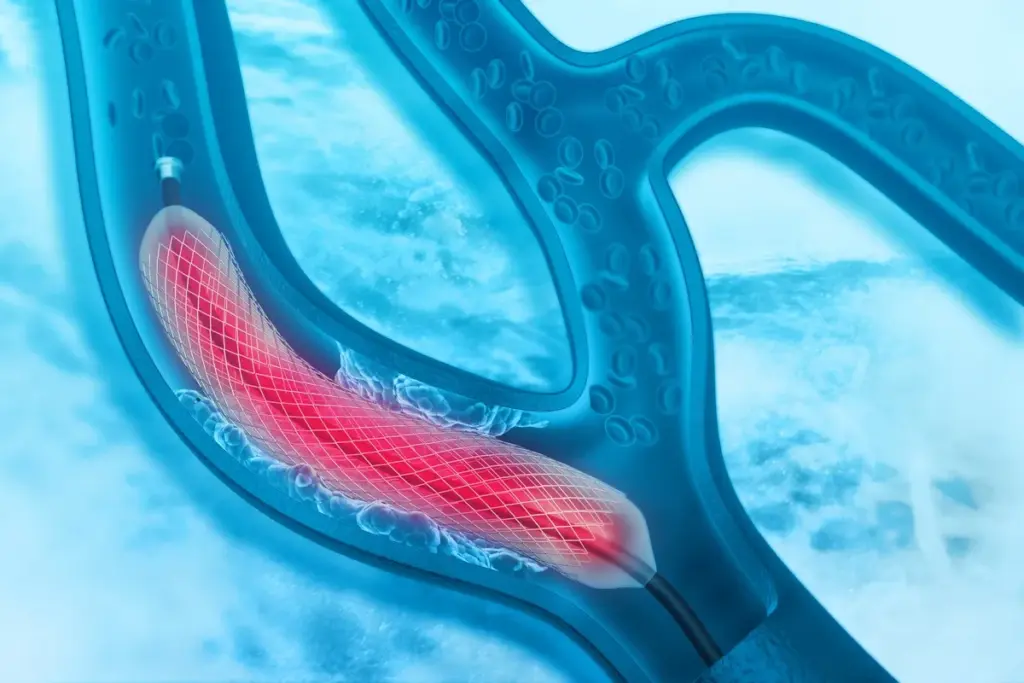
A heart stent is a tiny, expandable tube. It’s made of metal or fabric and goes into a narrowed or blocked artery. Most are made of wire mesh and stay in forever. Some are made of bioabsorbable material.
Types of Heart Stents Available
There are many types of heart stents, each with its own benefits.
Bare Metal Stents
Bare metal stents are made of stainless steel or other metals. They might cause less allergic reactions but could lead to restenosis more often.
Drug-Eluting Stents
Drug-eluting stents have a special coating. This coating helps prevent new tissue growth, lowering restenosis risk.
Bioabsorbable Stents
Bioabsorbable stents dissolve over time. They aim to reduce long-term complications.
How Stents Work to Improve Blood Flow
Stents expand to open up blocked arteries. This lets blood flow better to the heart. It helps lessen symptoms like chest pain and shortness of breath. It also lowers the risk of heart attacks.
|
Stent Type |
Material |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Bare Metal Stents |
Stainless Steel |
Less likely to cause allergic reactions |
|
Drug-Eluting Stents |
Metal with medication coating |
Reduces risk of restenosis |
|
Bioabsorbable Stents |
Bioabsorbable material |
Reduces risk of long-term complications |
The Heart Stent Procedure Explained
A heart stent procedure is a minimally invasive treatment for coronary artery disease. It involves placing a small, mesh-like device (stent) in the coronary arteries. This helps improve blood flow to the heart.
Preparation for Stent Placement
Before a stent placement, patients go through tests to check their heart health and artery condition. They may stop certain medications, fast, and arrange for a ride home. Sedation is given to help them relax during the procedure.
Step-by-Step Process of Stent Insertion
The stent insertion process has several key steps:
Cardiac Catheterization
A cardiac catheterization is done to access the coronary arteries. A small incision is made in a blood vessel in the groin or arm. Then, a catheter is threaded through to the heart.
Angioplasty and Stent Deployment
With the catheter in place, angioplasty is done to widen the blocked artery. A balloon on the catheter is inflated to compress the plaque. Then, a stent is deployed to keep the artery open. The stent stays in the artery permanently, improving blood flow and reducing symptoms.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
After the procedure, patients are monitored for a few hours. They may get medication to prevent blood clots on the stent. Most patients can go home the same day or the next day. It’s important to follow the doctor’s instructions on medication, follow-up appointments, and lifestyle changes.
Is a Heart Stent Serious? Evaluating the Procedure’s Significance
Heart stent procedures are common but raise questions about their severity. They affect heart health in many ways. It’s important to understand the procedure’s seriousness, its comparison to other surgeries, and its psychological impact on patients.
Classification as a Minimally Invasive Procedure
Stent placement is seen as a minimally invasive procedure. It doesn’t require open-heart surgery. Instead, a catheter is used to place the stent in the blocked artery. This method shortens recovery time and lowers the risk of complications compared to more invasive surgeries.
This minimally invasive approach makes stent placement appealing for some patients. Yet, it’s important to remember that it’s a serious medical intervention. It requires careful thought and preparation.
Comparing Stent Placement to Major Heart Surgeries
Comparing stent placement to major surgeries like CABG is helpful. CABG involves open-heart surgery to bypass blocked arteries. In contrast, stent placement is less invasive and has a shorter recovery time.
|
Procedure |
Invasiveness |
Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|
|
Stent Placement |
Minimally Invasive |
Short (few days to a week) |
|
CABG |
Invasive |
Long (several weeks to months) |
Psychological Impact of Receiving a Stent
Getting a stent can deeply affect a patient’s mental state. The diagnosis and procedure can lead to anxiety and fear about the heart’s condition. Healthcare providers must offer support and counseling to help patients deal with these feelings.
It’s key to understand the stent impact on heart health to manage patient expectations and improve outcomes. Recognizing the psychological effects helps healthcare providers support their patients better during this challenging time.
Potential Risks and Complications of Stent Placement
It’s important for patients to know the risks of stent placement. This helps them make better choices about their health. Stent placement saves lives, but knowing the possible problems is key.
Short-Term Complications
Short-term issues can happen right after or soon after the procedure. These include:
Bleeding and Bruising
Bleeding at the site where the catheter was inserted is common. Bruising can also happen.
Allergic Reactions
Some people might have an allergic reaction to the dye used during the procedure.
Arrhythmias
Irregular heartbeats or arrhythmias can happen during or after the stent is placed.
Long-Term Risks
Long-term risks can appear months or years after the procedure.
Restenosis
Restenosis, or the arteries narrowing again, is a big long-term risk.
Stent Thrombosis
Stent thrombosis, a blood clot in the stent, is rare but serious.
Infection
Infection at the stent site is rare but a possible long-term risk.
Mortality Rates and Serious Complications
Mortality rates for stent placement are low. But, serious complications can happen.
|
Complication |
Description |
Frequency |
|---|---|---|
|
Bleeding and Bruising |
Bleeding at the catheter site |
Common |
|
Restenosis |
Re-narrowing of the arteries |
Moderate |
|
Stent Thrombosis |
Blood clot within the stent |
Rare |
Recovery After Heart Stent Placement
The recovery after a heart stent is key to good health. A smooth recovery is key to the success of the stent placement procedure.
Hospital Stay Duration
Patients usually stay in the hospital overnight after the procedure. This lets doctors watch for any immediate problems.
Activity Restrictions Following Stent Placement
After leaving the hospital, patients should avoid hard work. This means no heavy lifting, bending, or intense exercise. Following these rules is important for a safe recovery.
Medication Regimen Post-Stent
Following the medication plan is a big part of recovery. This includes:
Antiplatelet Therapy
Antiplatelet drugs stop blood clots from forming on the stent. Dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) is often used, with two types of drugs.
Other Essential Medications
Patients may also take drugs for high blood pressure, cholesterol, or diabetes. It’s important to take all medications as your doctor says.
Returning to Normal Life
Most people can get back to normal in a few days to a week. But, always listen to your healthcare team’s advice.
“With proper care and adherence to the recommended lifestyle changes, patients can significantly improve their heart health post-stent placement,” notes the American Heart Association.
Understanding the recovery process and following guidelines can help patients get better faster. It also lowers the chance of complications.
Long-Term Implications of Having a Heart Stent
After getting a heart stent, patients often wonder about the long-term effects. A stent can greatly improve daily life by reducing chest pain and shortness of breath. This allows people to do their usual activities again.
Impact on Daily Life
Having a heart stent can make life better. Stents are very good at opening blocked arteries. This improves blood flow and reduces symptoms like angina, making physical activities easier.
Stent Longevity and Possible Restenosis
Stents are made to last a long time, but they can narrow again. A study in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology says the chance of this happening depends on the stent type. Regular check-ups are key to keeping an eye on the stent and heart health.
Follow-Up Care and Monitoring
It’s important to see a healthcare provider regularly. They will check how the stent is doing and your heart health. This might include stress tests or angiograms to make sure everything is okay.
Long-Term Survival Rates and Outcomes
Studies show that heart stent patients live longer than those without stents. The
“The use of stents has revolutionized the treatment of coronary artery disease, significantly improving patient outcomes.”
Survival rates over time depend on lifestyle changes, sticking to medication, and ongoing medical care.
In summary, while a heart stent has long-term effects, proper care and monitoring can greatly improve life and survival rates.
When is a Heart Stent Necessary?
To know if a heart stent is needed, doctors look at symptoms and test results. A heart stent is a tiny, mesh tube. It helps open up narrow or blocked arteries, improving blood flow to the heart.
Symptoms and Conditions Requiring Stent Placement
Heart stents are often needed for specific heart issues. These include:
- Stable Angina: Chest pain or discomfort when the heart muscle doesn’t get enough oxygen-rich blood. It usually happens during physical exertion or stress.
- Unstable Angina: A more serious form of angina that can happen at rest. It’s a sign of a serious condition that may lead to a heart attack.
- Heart Attack: When blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked for too long. This damages or kills part of the heart muscle.
Emergency vs. Elective Stent Procedures
Stent placement can be urgent or planned. Emergency stent placement is needed during a heart attack to quickly restore blood flow. Elective stent placement is planned for patients with stable or unstable angina.
Diagnostic Tests That Determine Stent Necessity
Several tests help decide if a stent is needed. These include:
Angiography
A procedure that uses dye and X-rays to see the coronary arteries and find blockages.
Stress Tests
Tests that watch the heart’s activity during exercise. They look for signs of ischemia or poor blood flow.
Cardiac CT Scans
A non-invasive test that uses X-rays to make detailed pictures of the heart. It helps find blockages or other problems.
These tests are key in figuring out if a heart stent is needed and how urgent it is.
Alternatives to Heart Stent Placement
Heart stents are a common fix for coronary artery disease. But, there are other treatments that might be better for you. These depend on your health, medical history, and what you prefer.
Medication-Based Treatments
For some, medicine can be a good choice instead of stents. Drugs like beta-blockers, nitrates, and antiplatelet drugs can help. It’s key to talk to your doctor about the right medicine for you.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
CABG surgery is a bigger deal than stents. It uses grafts to bypass blocked arteries. It might be an option for complex cases or when stents don’t work. Talk to a cardiologist to see if CABG is right for you.
Lifestyle Modifications for Heart Health
Changing your lifestyle can also help. Eating well, exercising, quitting smoking, and managing stress are all important.
“Lifestyle changes can significantly impact the progression of heart disease and reduce the need for more invasive procedures.” explains a top cardiologist.
|
Lifestyle Change |
Benefit |
|---|---|
|
Adopting a heart-healthy diet |
Reduces cholesterol and blood pressure |
|
Regular physical activity |
Improves cardiovascular health and overall well-being |
|
Quitting smoking |
Significantly reduces cardiovascular risk |
Making an Informed Decision: Questions to Ask Your Doctor
Talking to your doctor about alternatives is important. Ask about risks, monitoring, and lifestyle changes. This helps you make a well-informed choice.
Conclusion: Putting Heart Stent Procedures in Perspective
Heart stent procedures are a big deal in medicine. They can really help patients. It’s important to know the good and bad sides of stent placement.
We’ve looked at heart stent procedures in this article. We talked about what they do, how they’re done, and the risks. We also talked about how they can change a patient’s life.
Stent placement can greatly help patients. But, there are risks and complications to think about. Knowing these helps patients make better choices for their health.
Heart stent procedures are key for many people’s heart health. By understanding the risks and benefits, patients and doctors can work together. This helps get the best results for everyone.
FAQ
What is the significance of heart stent placement?
Heart stent placement is key for better blood flow to the heart. It lowers the risk of heart attack and eases symptoms of coronary artery disease.
How serious is stent surgery?
Stent surgery is a minimally invasive procedure. But, it’s a serious medical step that needs careful thought and preparation.
Is stent placement life-threatening?
Stent placement is usually safe. But, there are risks like bleeding, infection, and stent thrombosis. These can be serious in rare cases.
What is the heart stent procedure?
The heart stent procedure involves putting a small, mesh-like device into a narrowed or blocked artery. It helps improve blood flow to the heart.
What is the importance of stents for heart health?
Stents are vital for heart health. They restore blood flow, lower heart attack risk, and ease symptoms of coronary artery disease.
What are the risks of stent placement?
Risks of stent placement include bleeding, infection, stent thrombosis, and restenosis. These are among the possible complications.
How does stent surgery compare to major heart surgeries?
Stent surgery is less invasive and risky than major heart surgeries like CABG. It’s considered a safer option.
What is the recovery process like after stent placement?
Recovery after stent placement involves a short hospital stay and activity limits. Patients also need to follow a medication regimen to prevent complications.
What are the possible complications of stent placement?
Complications of stent placement include bleeding, infection, stent thrombosis, restenosis, and kidney damage. These are among the possible risks.
How does stent placement impact heart attack risk?
Stent placement greatly reduces heart attack risk. It improves blood flow and eases symptoms of coronary artery disease.
What is the impact of stent placement on long-term heart health?
Stent placement positively impacts long-term heart health. It reduces heart attack risk, eases symptoms, and improves cardiovascular well-being.
How complex is the stent procedure?
The stent procedure is relatively straightforward and minimally invasive. But, it requires careful preparation and execution.
What is the urgency of stent placement?
The urgency of stent placement varies by patient condition. Some cases require emergency stent placement to prevent heart attack or serious complications.
What is the survival rate after stent placement?
Survival rates after stent placement are generally high. Most patients see significant improvements in cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
How does stent placement compare to bypass surgery?
Stent placement and bypass surgery are both effective for coronary artery disease. They differ in invasiveness, risks, and benefits. The choice depends on individual patient needs.
What are the benefits and risks of stent placement?
Benefits of stent placement include improved blood flow, reduced heart attack risk, and symptom relief. Risks include bleeding, infection, stent thrombosis, and restenosis.
When is stent placement necessary for blocked arteries?
Stent placement is needed for blocked or narrowed arteries causing symptoms or putting the patient at risk of heart attack or serious complications.
What are the outcomes for patients after stent placement?
Outcomes after stent placement vary by individual. But, most patients see significant improvements in cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22073449/


































