When a cold hits, ear pain often follows. Many wonder how to ease this uncomfortable symptom.
At Liv Hospital, we focus on cold-related ear pain. We use proven, patient-focused care to help you feel better and recover.
Studies reveal that about two-thirds of colds in healthy kids and adults cause negative middle ear pressure. This affects people all over the world.
5 quick tips to relieve a head cold and earache by reducing nasal congestion and promoting Eustachian tube drainage.
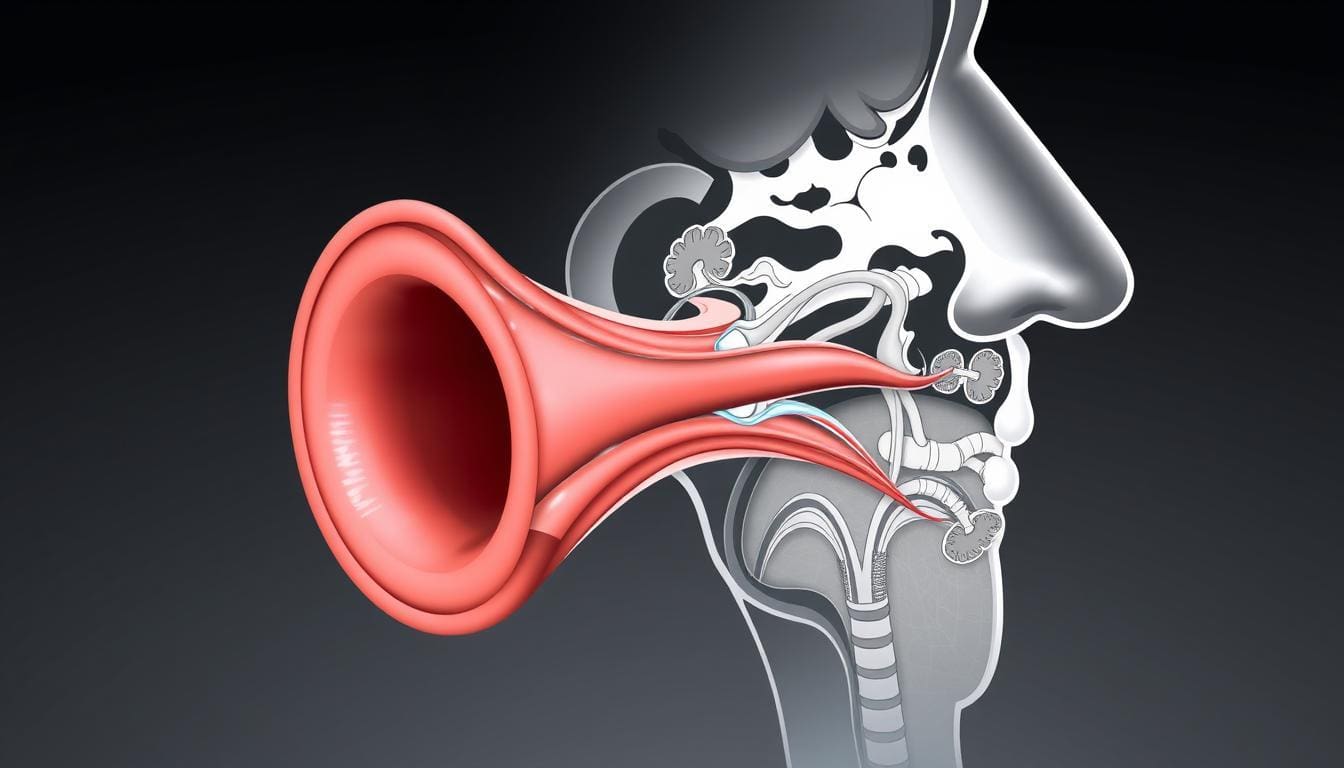
Ear pain during a cold is not just a coincidence. It’s caused by how the cold virus affects our ear, mainly the Eustachian tube. When we catch a cold, the virus infects our nose and throat, causing symptoms like congestion and cough. This can lead to ear discomfort or pain because of the connection between our nasal passages, throat, and ears.
Cold viruses can make the Eustachian tube inflamed or blocked. This blockage stops the middle ear from being ventilated properly. As a result, fluid or pressure builds up, causing ear pain. The Eustachian tube’s dysfunction is a key factor in why we experience earaches during a cold.
The Eustachian tube is vital for equalizing air pressure in our ears with the environment. When it’s blocked or inflamed due to a cold, we can experience ear pain, hearing difficulties, or a feeling of fullness. Proper functioning of the Eustachian tube is essential for maintaining ear health, specially during a cold.
Symptoms | Causes | Effects |
Ear pain or discomfort | Eustachian tube blockage or inflammation | Pressure buildup or fluid accumulation in the middle ear |
Hearing difficulties | Fluid buildup or pressure imbalance | Temporary hearing loss or muffled hearing |
Feeling of fullness in the ear | Eustachian tube dysfunction | Discomfort or pain due to pressure imbalance |
“The Eustachian tube is a critical structure that connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx, playing a vital role in pressure regulation and ventilation of the middle ear.”
— Medical Reference
Understanding the link between a head cold and earache shows how important it is to address Eustachian tube dysfunction. By knowing the causes and symptoms, we can take steps to ease ear pain and prevent further issues.

Cold viruses can cause ear pain, which is a sign we should pay attention to. When we catch a cold, the viruses can affect our ears in different ways. This can lead to discomfort and pain.
Ear pain from a cold can show up in various ways. Some common symptoms include:
It’s important to tell the difference between an ear infection and cold-related earache. Both can be uncomfortable, but they need different treatments. An ear infection, like otitis media, causes inflammation and fluid buildup in the middle ear. Cold-related earache is usually due to the Eustachian tube not working right because of the cold virus.
Key differences include:
The time ear pain lasts during a cold can vary. Usually, if the pain is from the cold, it should get better as the cold symptoms fade. But, if the pain doesn’t get better or gets worse, it might mean an ear infection.
To alleviate ear pain from a cold, managing the cold symptoms well and using the right pain relief is key. We’ll talk more about this later.
In summary, knowing the symptoms of cold-related ear pain and when to see a doctor is important. By recognizing the signs and telling the difference between cold-related earache and ear infections, we can take the right steps to ease the pain and avoid complications.
Earaches from a cold can be really tough. But, there are quick ways to feel better. When you have cold and sore ears, finding relief is key. Here are some tips to help with ear discomfort cold symptoms.
Using over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers is a simple way to ease ear pain. Medicines like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can lessen pain and swelling. Doctors say, “Pain relief is just a dose away,” for earaches. Always follow the dosage to stay safe and effective.
Putting a warm compress on your ear can really help. The warmth cuts down pain and makes ear discomfort cold feel better. Soak a cloth in warm water, wring it out, and put it on your ear for a few minutes. Do this as often as you need to ease the pain.
Nasal decongestants and sprays can also help with ear pain from a cold. They clear your nose, which opens the Eustachian tubes. These tubes connect your middle ear to your nose. When they’re blocked, you feel ear pain. Using a nasal decongestant can clear this blockage and lessen ear discomfort.
“Using nasal decongestants can be a game-changer when it comes to managing cold-related ear pain.”
Medical Expert
How you sleep can affect ear pain. Sleeping with your head higher can ease pressure in the Eustachian tubes. This simple change can make a big difference, helping with cold and sore ears.
By using these tips, you can find quick relief from earaches from a cold. Don’t forget to drink water and rest well to help your body heal.
Topical numbing drops are a quick fix for earache pain from colds. These drops, like those with lidocaine, numb the ear canal area right away.
Lidocaine-based drops numb the ear nerves, cutting down on pain. Lidocaine is a local anesthetic that stops nerve signals, giving temporary pain relief. It numbs the eardrum and nearby areas, easing earache pain from colds.
Doctors say lidocaine is safe when used correctly. It’s a good choice for quick earache relief.
To use these drops right, follow the proper steps. Start by washing your hands. Then, tilt your head to the side so the affected ear is up.
By doing these steps, you can use topical numbing drops to ease earache pain from colds. But, if your pain doesn’t go away or gets worse, see a doctor for help.
Looking into natural remedies can be a soft way to ease ear pain from a cold. It’s key to talk to a doctor before trying them, though. This is true for kids or if your cold is really bad or you have an ear infection.
Many herbal solutions have been used to help with ear pain from colds. Here are a few:
Essential oils can also help with ear pain, but use them carefully:
Remember, while these natural remedies might help, they shouldn’t replace doctor’s care. If your ear pain gets worse or doesn’t go away, see a doctor for the right treatment.
Children are more likely to get earaches when they have a cold. This is because their immune systems are not fully developed. Also, their Eustachian tubes are different. So, we need to find ways to help them feel better without risking their safety.
Managing earache pain in kids depends on their age. For the youngest, acetaminophen is often the best choice. It’s safe and helps with pain and fever. But, always check the dosage based on the child’s age and weight.
For older kids, ibuprofen might be an option. But, always talk to a pediatrician before giving any medicine.
“The American Academy of Pediatrics advises that children under 6 months should not be given ibuprofen,” highlighting the need for age-specific guidance.
There are ways to comfort a child with an earache. Warm compresses on the ear can help. So can gentle massage around the ear and jaw. Making sure they drink plenty of water and rest is also important.
Putting the child’s head up while they sleep can help too. This can reduce congestion and ear pressure.
Some earaches need medical help. If your child has severe pain, a high fever, or discharge, call your pediatrician. Also, if they show signs of hearing loss or have a persistent earache, get professional advice.
Watching for these signs and getting medical help when needed is key. It helps prevent serious problems and ensures your child gets the right care.
To avoid earaches during cold season, we need to practice good hygiene and make lifestyle changes. Understanding how colds and earaches are linked helps us protect our ears.
Reducing colds and flu is key to avoiding earaches. Vaccinations are a powerful tool. They help lower the chance of getting ear infections.
Frequent handwashing with soap and water is vital. It stops viruses from spreading. Also, staying away from people who are sick helps prevent catching a cold.
Proactive Measure | Benefit |
Vaccinations | Reduces risk of flu and pneumococcal disease |
Frequent Handwashing | Prevents spread of cold and flu viruses |
Avoiding Sick Contacts | Reduces risk of catching a cold |
Changing our lifestyle can also help. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle boosts our immune system. Eating well, with lots of fruits, veggies, and whole grains, is important.
It’s also key to avoid smoking and secondhand smoke. Smoke can harm the Eustachian tubes and raise ear infection risk. Stress management, like meditation or deep breathing, also strengthens our immune system.
By taking these steps, we can lower earache risk during cold season. It’s about caring for our health and being aware of how our actions affect our ears.
Ear pain during a cold can be more than just uncomfortable. It might be a sign of a bigger issue that needs a doctor’s check-up. While many cold-related earaches get better on their own, knowing when to see a doctor is key to avoid bigger problems.
Certain symptoms mean your ear pain might be more serious than a simple cold. If you notice any of these, it’s time to visit a doctor:
The American Academy of Otolaryngology says ear pain can be a sign of a bigger issue. It needs medical attention.
“It’s important to watch your symptoms and get medical help if you have severe or ongoing ear pain.”
— American Academy of Otolaryngology
If you need to see a doctor, they might suggest different treatments. These depend on the cause and how bad your ear pain is. Some possible treatments include:
Treatment | Description |
Antibiotics | Given if the ear pain is from a bacterial infection |
Ear Drops | Helps to ease pain and reduce swelling |
Tympanocentesis | A procedure to drain fluid from the middle ear |
It’s also key to follow up with your doctor if your symptoms don’t get better or get worse. Early action can stop bigger problems and help you heal faster.
In summary, while ear pain from a cold is common, knowing the signs of complications and when to see a doctor is vital. This helps manage the issue effectively and prevents long-term problems.
Managing recurring cold-related ear pain needs a full plan. We must tackle the symptoms and the root causes. Building resistance to colds and fixing any ear problems are key steps.
It’s important to fight off frequent colds to manage ear pain. Good hygiene, like washing hands often, is a must. Getting flu and pneumococcal vaccines and controlling allergies also help. These steps can lessen colds and their ear pain.
Key Strategies for Building Resilience:
Ear pain from colds can also stem from ear structure problems. Eustachian tube issues are common. It’s essential to tackle these problems for lasting relief.
Structural Issue | Description | Potential Treatment |
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction | Dysfunction of the tube connecting the middle ear to the back of the nose and throat | Nasal decongestants, balloon dilation |
Anatomical Abnormalities | Variations in ear anatomy that may predispose to ear pain | Surgical correction in severe cases |
Knowing why ear pain happens and using these strategies can help a lot. It’s also wise to talk to a doctor for the best treatment plan.
Ear pain from a cold can be really uncomfortable. But, most of the time, it’s not serious and will get better by itself. Knowing how cold viruses can cause ear pain helps you take steps to feel better.
This article has given you tips to ease ear pain from colds. You can try over-the-counter pain relievers and nasal decongestants. Or, you can use natural remedies. If your ear pain doesn’t go away, see a doctor to check for any serious issues.
By being proactive about ear pain from colds, you can lessen your discomfort. This helps keep your ears healthy. We urge you to take care of your ear health and find relief from cold-related earaches.
Ear pain with a cold often comes from Eustachian tube issues. This leads to fluid buildup and pressure in the ear. The cold virus can block the Eustachian tubes, making it hard to balance air pressure in the ears.
Ear infections cause more severe symptoms like fever, discharge, or hearing loss. Cold-related earache usually comes with congestion and a runny nose, along with ear pain.
Try over-the-counter pain relievers and warm compresses. Use nasal decongestants and sleep right to ease ear pain. Topical numbing drops, like lidocaine, can also help.
Yes, herbal solutions and essential oils might help with ear pain. But, always check with a healthcare professional before trying new remedies, even for kids.
Use pain management and comforting methods suitable for kids. If symptoms don’t get better, contact your pediatrician for advice.
To avoid earaches, get vaccinated against flu and pneumococcal disease. Practice good hygiene and avoid sick people. These steps can help protect your ears.
See a doctor for persistent or severe ear pain, fever, discharge, or hearing loss. Your doctor might prescribe antibiotics or further tests.
Stay healthy with a balanced diet, exercise, and enough sleep. Fixing issues like nasal septum deviation can also help prevent ear problems.
Yes, colds can make ears sore due to Eustachian tube issues and congestion. Using nasal decongestants and sleeping right can help.
Ear pain from a cold usually goes away in a few days to a week. But, if it doesn’t get better, see a doctor for help.
MedlinePlus. (n.d.). Tonsillectomy – adult. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002930.htm
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!
WhatsApp us