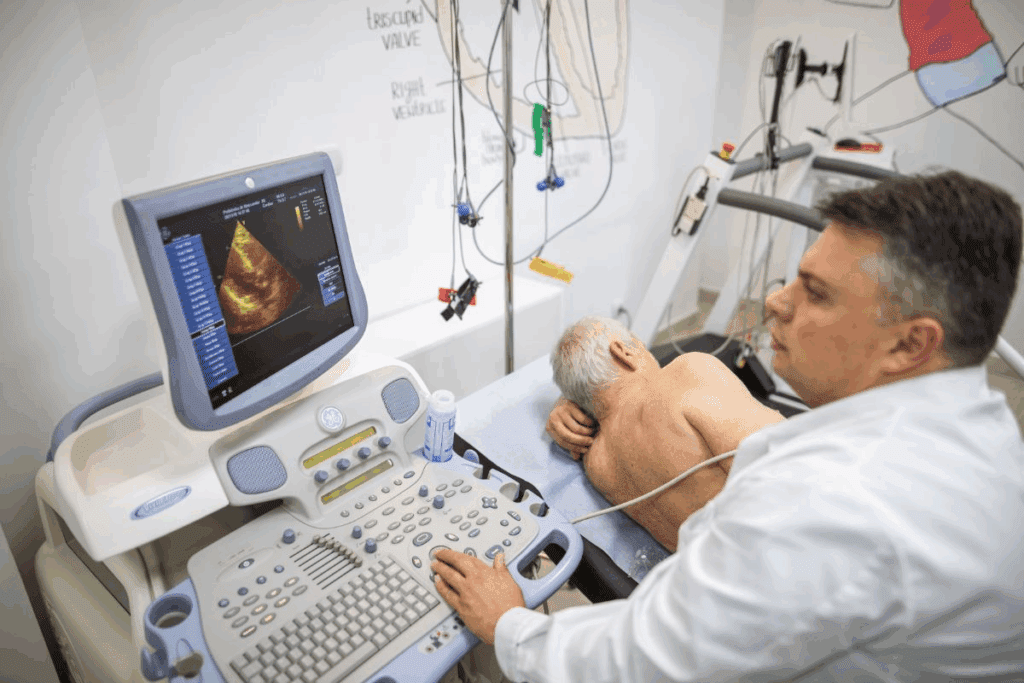
Feeling an irregular heartbeat can be scary. It’s important to know about supportive therapies for heart arrhythmia. At Liv Hospital, we use global knowledge and focus on our patients to offer top care for heart rhythm issues.
Diagnosing heart problems like atrial fibrillation (AFib) starts with tests. These include blood tests, electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), Holter monitor, event recorder, and echocardiogram. Knowing about these tests is key to managing the condition well.
We will look at seven main therapies to help with symptoms of heart arrhythmia. These aim to improve life quality and lower the chance of serious problems. The therapies include managing medicines, catheter ablation, and changing lifestyle habits, among others.
Discover 7 heart arrhythmia supportive therapy for symptom relief.
Cardiac arrhythmia is when the heart beats irregularly. It affects millions and can change daily life. We’ll look at what it is, its types, symptoms, and when it’s dangerous.
Cardiac arrhythmia is any irregular heartbeat. It happens when the heart’s electrical signals go wrong. This can make the heart beat too fast, too slow, or irregularly.
There are many types, including:
Symptoms of heart arrhythmia vary. Common ones are:
These happen because the heart isn’t pumping blood well. This can reduce oxygen to the body. Some people with arrhythmia don’t show symptoms, while others have severe ones.
Not all arrhythmias are harmless. Some can be deadly. Arrhythmias that make the heart beat too fast or slow can lead to fainting, heart failure, or sudden death. Seek medical help if you have:
Arrhythmias like AF and VA can cause anxiety, depression, and poor quality of life. Knowing the causes and symptoms is key to managing and treating them.
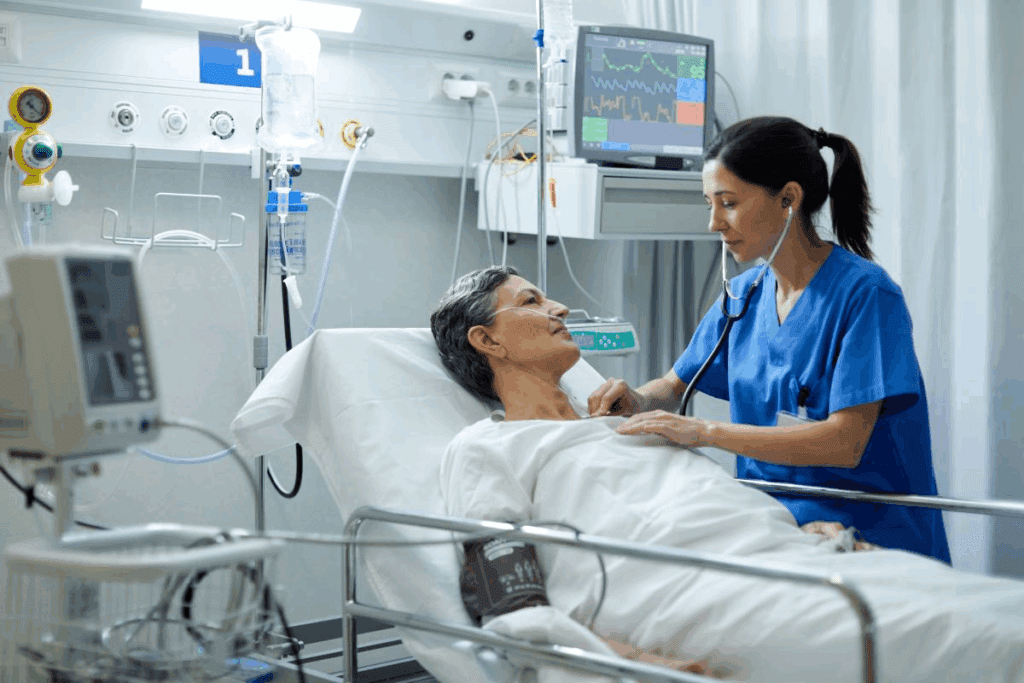

Managing heart arrhythmia involves supportive therapy to ease symptoms and improve life quality. This therapy includes various treatments for irregular heartbeats. Understanding these treatments helps patients make informed care choices.
The main goals of arrhythmia treatment are to control the heartbeat, prevent blood clots, and enhance life quality. Doctors aim to reset the heartbeat, control the heart rate, and prevent blood clots. These goals are key to managing arrhythmia and lowering complication risks.
Resetting and controlling the heartbeat is vital for a normal rhythm. Preventing blood clots is critical to avoid stroke. Healthcare providers tailor treatments to meet each patient’s needs.
Personalized treatment is essential for heart arrhythmia management. Each patient’s condition and treatment response can differ greatly. Healthcare providers consider the arrhythmia type, severity, overall health, and lifestyle when planning treatments. This approach ensures patients receive care that meets their unique needs.
Success in arrhythmia treatment is measured by symptom relief, life quality improvements, and complication prevention. Regular check-ups allow for treatment plan adjustments. Doctors say effective treatment requires understanding the causes and symptoms.
Success in arrhythmia treatment goes beyond symptom relief. It aims to improve overall heart health and well-being. A holistic approach to care leads to better outcomes and improved life quality for patients.
Medication management is key in treating arrhythmia. It helps ease symptoms and prevents serious problems. We use different medicines to manage irregular heartbeats, each playing a unique role in helping patients.
Antiarrhythmic medications are vital in managing arrhythmia. They help control the heart’s rhythm, either by slowing it down or speeding it up. They are essential in keeping the heart rhythm normal and reducing symptoms of irregular heartbeat. We prescribe these medicines to patients with recurring arrhythmias to control their condition.
Beta blockers are also important in managing arrhythmia. They block the hormone epinephrine’s effects, slowing the heart rate and reducing its workload. This can greatly reduce symptoms like palpitations and shortness of breath. Beta blockers are used to treat symptoms of atrial fibrillation and other arrhythmias.
Anticoagulants are critical for patients at risk of stroke due to arrhythmia. These medicines prevent blood clots that can cause stroke. By thinning the blood, anticoagulants greatly lower the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. We closely watch patients on anticoagulant therapy to ensure their safety and treatment effectiveness.
In summary, medication management is a complex but essential approach in controlling arrhythmia. It helps alleviate symptoms and prevents serious issues like stroke. By customizing medication plans for each patient, we can greatly enhance their quality of life.
Catheter ablation is a top choice for treating arrhythmic heartbeats that don’t respond to meds. It’s a minimally invasive method. Catheters send energy to the heart, creating scar tissue that stops the abnormal signals.
This method’s success comes from pinpointing the arrhythmia’s source. Advanced tech helps our electrophysiologists find and mark the heart areas causing the rhythm issues. Then, the catheter goes there to apply the needed energy.
Precision is key in this process. We aim to get rid of the arrhythmia source without harming the heart’s normal functions. Sophisticated systems guide us, giving real-time data during the procedure.
There are two main methods in catheter ablation: radiofrequency and cryoablation. Radiofrequency ablation uses heat to create lesions, stopping the bad signals. Cryoablation uses cold to do the same. The choice depends on the patient’s condition and the arrhythmia type.
“The choice between radiofrequency and cryoablation depends on various factors, including the location and type of arrhythmia, as well as the patient’s overall health condition.”
Recovery from catheter ablation is usually quick, with most back to normal in a few days. The procedure’s success varies by arrhythmia type and patient condition. Yet, many see big improvements in symptoms and life quality.
Like any procedure, there are risks and complications. But, these are low when done by skilled electrophysiologists in a top-notch facility.
We keep a close eye on our patients after the procedure. This ensures a smooth recovery and checks if the treatment worked. Follow-up care is key to see if more treatments are needed.
Implantable cardiac devices have changed how we treat heart arrhythmias. They offer many options for managing heart conditions. These devices help control heart rhythms, lessen symptoms, and lower the risk of serious problems.
Pacemakers are small devices that help manage slow heart rates. They send electrical impulses to the heart to keep it beating normally. They’re great for people with slow heart rates that cause symptoms.
Getting a pacemaker is a minor surgery done under local anesthesia. The device goes in the chest. Leads, thin wires, guide it to the heart through a vein.
ICDs are advanced devices that catch and fix dangerous heart rhythms. They’re for people at high risk of sudden cardiac death.
ICDs can do different things to fix the heart rhythm. They can pace, convert, or defibrillate the heart. They’re very good at preventing sudden death and saving lives.
CRT devices are special pacemakers. They make the left and right ventricles beat together better. This improves the heart’s pumping power. They’re for heart failure patients with certain arrhythmias.
CRT makes symptoms better, improves life quality, and boosts exercise ability. It also cuts down on hospital stays and death risk.
| Device Type | Primary Use | Key Benefits |
| Pacemakers | Bradycardia management | Regulates heart rate, improves symptoms |
| ICDs | Prevention of sudden cardiac death | Detects and corrects life-threatening arrhythmias |
| CRT | Heart failure treatment | Improves heart pumping efficiency, reduces hospitalization risk |
Restoring a normal heart rhythm is key for arrhythmia patients. Cardioversion is a main treatment. It aims to switch an abnormal rhythm back to normal. We’ll look at electrical and pharmacological cardioversion, their success, and safety.
Electrical cardioversion uses shocks to fix the heart rhythm. It’s for emergencies or when drugs don’t work. A controlled electric shock is given to the chest to reset the rhythm.
Pharmacological cardioversion uses drugs to fix the rhythm. It’s best for stable patients with ongoing arrhythmias. Different drugs work in different ways and have side effects.
Both methods have their own success and safety levels. The choice depends on the patient’s condition and arrhythmia type. It’s important to talk about risks and benefits with a doctor.
| Aspect | Electrical Cardioversion | Pharmacological Cardioversion |
| Method | Uses electrical shocks | Uses antiarrhythmic medications |
| Application | Often used in emergency situations | Preferred for stable patients with persistent arrhythmias |
| Effectiveness | High immediate success rate | Variable success rate depending on the medication and patient condition |
| Safety Considerations | Requires sedation or anesthesia; risk of skin burns | Potential side effects from medications; risk of proarrhythmia |
Knowing about cardioversion methods helps patients and doctors make better choices. It’s vital to think about the patient’s health, history, and needs when deciding between electrical and drug treatments.
Changing your lifestyle is key to managing heart arrhythmia symptoms. Making smart choices about what you eat, how you exercise, and how you handle stress can greatly improve your heart health. This can also make your life better overall.
Eating right is a big part of managing arrhythmia. Eating foods high in omega-3s, like salmon and walnuts, is good. Also, eat more fruits, veggies, and whole grains. But, cut down on sodium, caffeine, and alcohol as they can make arrhythmia worse.
Nutritional Tips:
Staying active is good for your heart, but pick exercises that are safe for arrhythmia patients. Walking, swimming, and cycling are usually okay. But, avoid very intense workouts that might trigger arrhythmia.
| Exercise Type | Benefits | Precautions |
| Brisk Walking | Improves cardiovascular health | Avoid overexertion |
| Swimming | Low-impact, full-body workout | Watch for cold water triggers |
| Cycling | Enhances cardiovascular fitness | Start with moderate intensity |
Handling stress and getting good sleep are key to managing arrhythmia. Try meditation, deep breathing, and yoga to reduce stress. Also, having a regular sleep schedule and a calming bedtime routine can help you sleep better.
Stress Reduction Techniques:
By making these lifestyle changes, people with heart arrhythmia can better manage their symptoms. It’s important to work with your healthcare team to create a plan that fits your needs and goals.
Studies show that mind-body therapies like yoga and meditation help people with arrhythmia. These methods focus on the mind and body connection. They aim to lower stress and anxiety, which can make arrhythmia symptoms worse.
Yoga and meditation are good for both body and mind. For those with arrhythmia, they can lessen stress and improve heart health. Regular practice can lead to better symptom management and improved quality of life.
A study in the Journal of the American Heart Association found yoga reduces anxiety and depression in atrial fibrillation patients. Another study showed meditation lowers stress and improves heart rate variability.
Breathing techniques are useful for managing arrhythmia symptoms. Diaphragmatic breathing, for example, calms the nervous system and reduces arrhythmia episodes. By focusing on controlled breathing, individuals can potentially reduce the severity of symptoms.
The “4-7-8” breathing technique, or “Relaxation Breath,” is effective. It involves breathing in for 4 counts, holding for 7 counts, and exhaling for 8 counts. This slows the heart rate and promotes relaxation.
Biofeedback and relaxation training are also helpful for arrhythmia management. Biofeedback uses equipment to monitor heart rate and blood pressure. It helps individuals control these functions through training and practice.
| Mind-Body Therapy | Benefits for Arrhythmia Patients |
| Yoga | Reduces stress and anxiety, improves heart rate variability |
| Meditation | Decreases stress, enhances overall well-being |
| Breathing Techniques | Calms the nervous system, reduces symptom severity |
| Biofeedback | Helps gain control over physiological processes |
By adding mind-body approaches to their treatment, people with arrhythmia can manage symptoms better. They can also enjoy a better quality of life. Always talk to a healthcare provider before starting any new therapy or practice.
We look into how nutritional supplements help treat arrhythmia. Supplements are key in managing heart arrhythmia symptoms and boosting health. By knowing the value of electrolyte balance and the benefits of certain supplements, patients can team up with their doctors to create a full treatment plan.
Keeping magnesium, potassium, and calcium in balance is vital for a healthy heart rhythm. These electrolytes control the heart’s electrical activity. Imbalances can cause arrhythmia symptoms, so it’s important to get enough through diet and supplements.
Magnesium helps control heart rhythm and is often used to ease arrhythmia symptoms. Potassium is also key for a stable heart rhythm. Calcium is important for heart health, but it must be balanced with other electrolytes to avoid problems.
Omega-3 fatty acids are studied for their heart health benefits, including rhythm support. Research shows omega-3 supplements may cut down arrhythmia episodes in some, but results differ.
Talking to a healthcare provider about omega-3 supplements is vital. They can interact with other meds or cause issues in some people.
Always talk to a healthcare provider before starting supplements. They can figure out the best plan for you and make sure supplements won’t clash with other treatments.
Doctors can also check electrolyte levels and adjust supplements as needed. This teamwork ensures supplements work well and safely.
Managing arrhythmia means using many therapies that fit each patient’s needs. We know every patient is different. So, we use medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and devices to help.
We make a personalized treatment plan for each patient. We consider their arrhythmia type, health, and what they prefer. This plan might include medicines, ablation, devices, or cardioversion.
Our goal is to manage symptoms, avoid problems, and improve life quality. We work with our patients to create a plan that meets their needs.
Regular checks are key to see if the plan is working. We use ECGs, Holter monitors, and patient reports to track progress. This helps us find ways to improve.
By keeping a close eye and making changes, we can get better results. And we can lower the risk of complications.
Patients with severe arrhythmias need an emergency action plan. This plan tells them what to do in an arrhythmia episode. It includes when to get medical help and how to use emergency medicines.
| Component | Description | Action |
| Emergency Contact | List of emergency contacts, including healthcare providers and family members | Call or notify contacts as needed |
| Medication | List of emergency medications, including dosage and administration instructions | Administer medication according to plan |
| Symptom Recognition | Identification of symptoms that require immediate medical attention | Seek medical help if symptoms occur |
With a detailed emergency plan, arrhythmia patients feel safer. They’re better prepared to handle their condition.
Managing heart arrhythmia well needs a full plan. This includes medical help, changing your lifestyle, and using devices. Knowing about different therapies helps people control their condition better. This improves their symptoms, life quality, and health.
We looked at many therapies like medicines, catheter ablation, and devices. We also talked about lifestyle changes, mind-body methods, and supplements. A plan made just for you can help manage arrhythmia well.
Controlling heart arrhythmia means working with your doctor closely. This way, you can change your treatment as needed. A complete plan can lessen symptoms, stop problems, and make you feel better overall.
Managing arrhythmia is a long journey. But with the right care and support, you can live a full and healthy life. We urge those with heart arrhythmia to be active in their care. Work with your healthcare team to create a plan that fits your needs.
Cardiac arrhythmia is when your heartbeat is not regular. It happens due to abnormal electrical signals in the heart.
Symptoms include palpitations, shortness of breath, dizziness, and feeling tired. Some people might not notice any symptoms.
There are many types, like atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia. Also, there’s supraventricular tachycardia and bradycardia.
Doctors use tests like electrocardiogram (ECG) to find arrhythmia. They also use Holter monitoring or event monitoring.
Treatment aims to ease symptoms and improve life quality. It also aims to lower risks of stroke or heart failure.
These medicines help control arrhythmia symptoms. They also prevent complications and improve life quality.
It’s a procedure that uses heat or cold to destroy bad heart pathways. This stops arrhythmia.
Devices like pacemakers and ICDs manage arrhythmia symptoms. They improve life quality and lower risks.
Eating right, exercising, and managing stress can help. These changes improve symptoms and overall health.
Yoga, meditation, and biofeedback can reduce stress. They help improve symptoms and well-being.
Supplements like magnesium and omega-3 fatty acids might help. But, always talk to a doctor first.
It’s key for a tailored treatment plan. It helps monitor progress and adjust as needed for better health.
It’s a plan for what to do in an arrhythmia emergency. It outlines steps to take.
Yes, it can be if not treated or managed well. It raises the risk of stroke or heart failure.
You need a mix of treatments like medicines and lifestyle changes. Other options include catheter ablation or devices.
Treatment varies based on the arrhythmia type and severity. It includes medicines, procedures, and lifestyle changes.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2025). 7 Key Supportive Therapies for Heart Arrhythmia and. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10600027/
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!
WhatsApp us