Hepatobiliary surgery is a key treatment for many liver and bile duct issues. Liver health is very important. Surgery is often needed for cancers, tumors, and severe diseases.
Conditions needing hepatobiliary surgery include liver and bile duct cancers, benign tumors, and complex gallbladder diseases. Experts like Professor Alberto Sanchez-Fueyo and Medical Expert. They aim to make treatments better.
Getting care from specialized centers is very important. These centers have the best results. They use a team approach and the latest methods.
Key Takeaways
- Liver and bile duct cancers require surgical intervention.
- Benign hepatic tumors can be treated with hepatobiliary surgery.
- Complex gallbladder diseases often necessitate surgical care.
- High-volume centers achieve better outcomes due to advanced protocols.
- Novel immunomodulatory therapies are being developed to improve treatment.
The Hepatobiliary System: Structure and Function
It’s key to know how the hepatobiliary system works to treat diseases. This system includes the liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts. It’s vital for digestion, breaking down food, and getting rid of toxins.
Anatomy of the Liver and Biliary Tract
The liver is huge and sits in the upper right of your belly. It has lobes and connects to the biliary tract. This includes the intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts, the gallbladder, and the common bile duct.
The biliary tract’s main job is to move bile from the liver to the small intestine. This helps with fat digestion.
Physiological Functions
The liver does many important things, like cleaning toxins and making proteins. It also helps break down nutrients and drugs. The bile ducts and gallbladder work together to store and release bile. This helps break down fats.
Signs of Hepatobiliary Dysfunction
When the hepatobiliary system isn’t working right, you might see jaundice, belly pain, or changes in stool or urine color. These signs can mean there’s a problem with the liver or biliary tract. This could be an obstruction, infection, or even cancer. You’ll need to get checked out.
Common Hepatobiliary Conditions Requiring Surgical Intervention
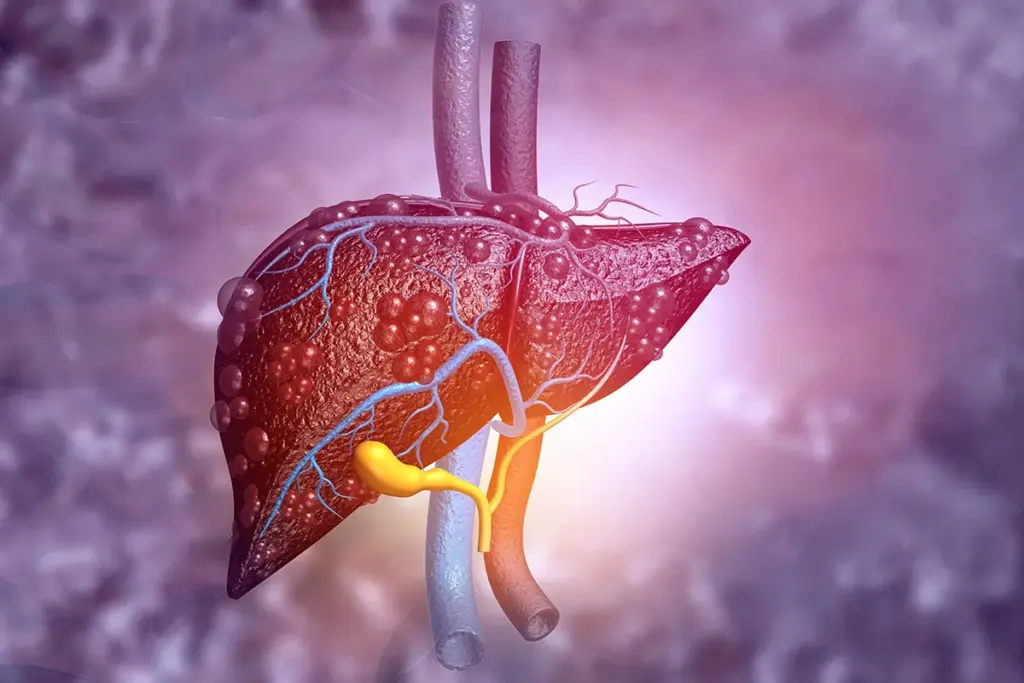
Many conditions of the liver and biliary tract need surgery. These include cancers and non-cancerous growths. Such disorders can greatly affect how well a patient does.
Statistical Overview of Surgical Indications
In the U.S., the top reasons for liver and biliary surgery are clear. These include liver cancers that spread, primary liver tumors, cancers of the biliary tract, and non-cancerous liver growths. Studies show that patients do better at hospitals that do a lot of these surgeries.
Mortality rates fall from 7.6% at small hospitals to 3.9% at big ones. This shows why getting care at a specialized place is key.
Epidemiology in the United States
In the U.S., liver and biliary diseases are a big problem for healthcare. Liver cancers that spread from other cancers are a top reason for surgery.
Epidemiological studies show that liver and bile duct cancers are getting more common. This means more people need surgery.
This highlights the need for better surgery techniques and the role of big hospitals in helping patients.
Primary Liver Malignancies
Primary liver malignancies, like hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, need accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. These cancers start in the liver and are hard to treat because of the liver’s important role. They are complex and pose big challenges in surgery.
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common liver cancer. It often happens in people with chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. Risk factors include hepatitis B and C, alcohol abuse, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
To diagnose HCC, doctors use CT and MRI scans and check serum alpha-fetoprotein levels. Treatments include surgery, liver transplant, and locoregional therapies. Research aims to find better treatments by studying the tumor environment and developing biomarkers.
Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma starts in the bile ducts inside the liver. It’s a very aggressive and often deadly cancer. Risk factors include primary sclerosing cholangitis, liver fluke infestation, and certain biliary anomalies.
Diagnosing this cancer is hard and often needs imaging, ERCP, and biopsy. Treatment mainly involves surgery, aiming for complete removal. But, because it’s often diagnosed late, surgery is not always possible. New treatments like targeted molecular therapies and immunotherapy offer hope for better outcomes.
Secondary Liver Metastases
Secondary liver metastases are a big challenge in medicine. They often need a team effort to treat. The liver is a common place for cancer to spread from other parts of the body. This affects how long a patient might live and their quality of life.
Doctors look at many things when treating secondary liver metastases. They check the patient’s health, how much of the liver is affected, and if cancer is in other places too. New treatments like surgery, chemotherapy, and others have helped some patients live longer.
Colorectal Liver Metastases
Colorectal liver metastases are the most common type. Surgical resection can lead to long-term survival or even a cure for some. Doctors decide if surgery is right based on several factors.
Studies show that a multidisciplinary team approach is key for colorectal liver metastases. This team includes surgeons, medical oncologists, radiologists, and more. Working together helps find the best treatment for each patient.
Non-Colorectal Metastases
Non-colorectal liver metastases are less common but just as challenging. Treatment depends on the original cancer, how much of the liver is affected, and the patient’s health. Systemic therapy is often the main treatment, but locoregional therapies like ablation and embolization might also be used.
There’s ongoing research to find the best ways to treat non-colorectal liver metastases. The goal is to improve patient outcomes by combining local and systemic treatments.
Benign Hepatic Tumors and Cysts
The liver can have different benign tumors and cysts. Some might need surgery. These can be without symptoms or have vague signs, making it hard to diagnose and treat.
Hepatic Adenoma
Hepatic adenoma is a rare, benign liver tumor linked to hormonal contraceptives. It can burst, causing severe bleeding. To manage it, stop hormonal contraceptives and remove large adenomas surgically.
Focal Nodular Hyperplasia
Focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) is a benign growth. It’s thought to be a non-cancerous, regenerative response to an unusual blood vessel. Usually, FNH doesn’t need treatment unless it’s causing symptoms or there’s doubt about its nature.
Hemangioma
Hemangioma is the most common benign liver tumor. It’s often found by chance and doesn’t usually cause symptoms. But, big hemangiomas can press on other organs or cause blood clots. Treatment is usually not needed unless there are complications.
Simple and Complex Cysts
Simple hepatic cysts are common, fluid-filled, and usually don’t cause problems. Complex cysts have parts that look like tumors, which can worry doctors. Treatment options include draining the cyst, using a special solution to close it, or surgery for cysts that cause symptoms or are complex.
|
Condition |
Characteristics |
Management |
|---|---|---|
|
Hepatic Adenoma |
Rare, associated with hormonal contraceptives |
Discontinue hormonal contraceptives, surgical resection |
|
Focal Nodular Hyperplasia |
Non-neoplastic, regenerative lesion |
Conservative unless symptomatic |
|
Hemangioma |
Most common benign liver tumor, usually asymptomatic |
Conservative unless complications arise |
|
Simple and Complex Cysts |
Fluid-filled lesions, simple or complex |
Aspiration, sclerotherapy, or surgical intervention |
Biliary Tract Malignancies
Biliary tract malignancies include gallbladder and extrahepatic bile duct cancers. These cancers are hard to treat because they are often found late. This makes treatment more difficult.
The biliary tract is key for making, storing, and moving bile. Cancers can start in the gallbladder or extrahepatic bile ducts. Knowing how the biliary tract works is important for finding and treating these cancers.
Gallbladder Cancer
Gallbladder cancer is rare but very aggressive. It’s linked to gallstones and inflammation. It’s hard to find early because it often doesn’t show symptoms.
When symptoms do appear, like jaundice and pain, it’s usually in the later stages. Treatment includes surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation. For early stages, surgery is the main treatment. For more advanced cases, a mix of treatments is used.
Extrahepatic Bile Duct Cancer
Extrahepatic bile duct cancer, or cholangiocarcinoma, starts in the bile ducts outside the liver. It’s classified by where it is in the biliary tree. Doctors use imaging and biopsies to diagnose it.
Treatment depends on where the cancer is and how far it has spread. Surgery is the main treatment for cancers that can be removed. For cancers that can’t be removed, palliative care helps manage symptoms and improve life quality.
Research on biliary tract malignancies is ongoing. Scientists are looking for new ways to treat and diagnose these cancers. Early detection and team care are key to better outcomes for these patients.
Complex Gallbladder Diseases
Managing complex gallbladder diseases is a detailed process. It involves understanding the different types of gallbladder problems. These conditions need a thorough diagnosis and treatment plan.
Complicated Cholelithiasis
Complicated cholelithiasis is when gallstones cause more serious issues. This can include gallstone pancreatitis or choledocholithiasis. Such cases often need a more serious treatment, like surgery.
Gallbladder Polyps
Gallbladder polyps are growths on the gallbladder’s lining. Most are harmless, but some may need to be removed. This is true if they’re big or if symptoms appear.
Acute and Chronic Cholecystitis
Acute cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder, usually from gallstones. Chronic cholecystitis is ongoing inflammation that can harm the gallbladder’s function. Both may need surgery, depending on symptoms and complications.
|
Condition |
Common Symptoms |
Treatment Approach |
|---|---|---|
|
Complicated Cholelithiasis |
Severe abdominal pain, jaundice |
Surgical intervention |
|
Gallbladder Polyps |
Often asymptomatic, occasional biliary colic |
Monitoring or surgical removal |
|
Acute Cholecystitis |
Severe right upper quadrant pain, fever |
Antibiotics, possible surgery |
|
Chronic Cholecystitis |
Recurrent episodes of biliary colic |
Surgical removal of the gallbladder |
Studies show that quick diagnosis and treatment are key. They help avoid more problems and improve health outcomes.
Bile Duct Injuries and Strictures
Iatrogenic bile duct injuries and benign biliary strictures are big worries in liver and bile duct surgery. They can happen because of many medical procedures, like laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
Iatrogenic Bile Duct Injuries
Iatrogenic bile duct injuries are a big risk in liver and bile duct surgeries. Studies show these injuries happen more often in laparoscopic surgeries than in open ones.
Diagnosis and Treatment: Finding these injuries early is key. Treatment usually involves both endoscopic and surgical methods.
|
Type of Injury |
Frequency |
Management Strategy |
|---|---|---|
|
Bile Duct Laceration |
Common |
Endoscopic Stenting |
|
Bile Duct Stricture |
Less Common |
Surgical Reconstruction |
Benign Biliary Strictures
Benign biliary strictures can come from iatrogenic injuries, chronic pancreatitis, or other inflammatory conditions.
Management Strategies: Treatment can be endoscopic dilation or surgical bypass. It depends on the stricture’s severity and where it is.
Hepatobiliary Trauma
Trauma to the hepatobiliary system can come from blunt and penetrating injuries. This makes managing these injuries very complex. The liver, bile ducts, and gallbladder can all be affected, leading to serious health issues.
Blunt and Penetrating Liver Injuries
The liver is very sensitive to both blunt and penetrating trauma. Blunt injuries often happen in car accidents or falls. Penetrating injuries usually come from gunshot or stab wounds.
The severity of liver injuries can vary a lot. This means treatment can range from just watching the injury to needing surgery.
Bile Duct and Gallbladder Trauma
Injuries to the bile ducts and gallbladder are less common but just as tough. Bile duct injuries can happen from medical mistakes or outside trauma. Gallbladder trauma often goes hand in hand with liver injuries.
It’s very important to diagnose and treat these injuries quickly. This helps avoid problems like bile leaks or strictures.
Hepatobiliary Complications of Pancreatitis
There’s a complex link between pancreatitis and liver and bile duct problems. Chronic pancreatitis can cause many issues in the liver and bile ducts. This is because the pancreas and bile system are closely connected.
Biliary Pancreatitis
Biliary pancreatitis happens when a gallstone blocks the pancreatic duct. This blockage causes pancreatitis. It’s a big reason for acute pancreatitis and can harm the liver and bile ducts. It’s important to catch and treat it early to avoid more problems.
Pancreatic Pseudocysts with Biliary Involvement
Pseudocysts can form after pancreatitis and might affect the bile system. These fluid pockets can block or press on the bile ducts. This can lead to jaundice and other liver and bile duct issues. Imaging tests like CT or MRI help find and check these pseudocysts.
Biliary Strictures Secondary to Chronic Pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis can cause strictures in the bile ducts. These strictures are due to scarring and inflammation. They can lead to serious problems like blocked bile flow and infections. Treatment might include endoscopic or surgical methods to open up the blockage.
|
Complication |
Clinical Features |
Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|
|
Biliary Pancreatitis |
Abdominal pain, elevated pancreatic enzymes |
Supportive care, ERCP |
|
Pancreatic Pseudocysts |
Abdominal mass, obstructive jaundice |
Drainage (endoscopic or surgical) |
|
Biliary Strictures |
Obstructive jaundice, cholangitis |
Endoscopic stenting, surgery |
Studies show that treating liver and bile duct problems linked to pancreatitis needs a team effort. Knowing how pancreatitis affects the liver and bile ducts helps doctors give better care to patients with these tough conditions.
Liver Transplantation for End-Stage Hepatobiliary Disease
For those with advanced liver disease, liver transplantation can be a lifesaver. This surgery replaces a sick liver with a healthy one from a donor. It’s considered for those with end-stage liver disease when other treatments fail.
Cirrhosis and Chronic Liver Failure
Cirrhosis, or scarring of the liver, often leads to liver transplant. It causes serious problems like high blood pressure in the liver and brain damage. Liver transplantation can greatly improve survival and quality of life for these patients.
Acute Liver Failure
Acute liver failure is when the liver fails quickly. It can be caused by viruses, drugs, or toxins. Quick action and listing for transplant are key to survival.
Metabolic Liver Diseases
Metabolic disorders like primary biliary cholangitis can also lead to liver failure. Liver transplant is a good treatment for these conditions. It helps fix liver problems and metabolic issues.
Selection Criteria and Contraindications
Choosing who gets a liver transplant involves a detailed check-up. This includes looking at medical history, current health, and how well they might recover. Contraindications include active substance abuse, severe heart or lung disease, and certain infections. A team of experts decides if a patient is a good candidate.
The main things considered for transplant are:
- How sick the liver is
- How well they can recover
- If they don’t have any big health issues
- If they can follow treatment and have support
Liver transplant is a lifesaving option for severe liver disease. Places like UT Health North Campus Tyler provide full care. Knowing who can get a transplant helps doctors improve patient results.
Advanced Diagnostic Modalities in Hepatobiliary Conditions
Advanced diagnostic techniques are key for accurately diagnosing and managing hepatobiliary disorders. These methods help healthcare professionals see the hepatobiliary system in detail. This makes it easier to make precise diagnoses and treatment plans.
Cross-sectional Imaging
Cross-sectional imaging, like CT scans and MRI, is vital for diagnosing hepatobiliary conditions. These imaging methods give detailed views of the liver and biliary tract. They help spot issues like tumors, cysts, and bile duct blockages.
- CT Scans: Useful for detecting liver lesions and assessing their characteristics.
- MRI: Offers superior soft tissue contrast, aiding in the diagnosis of complex hepatobiliary conditions.
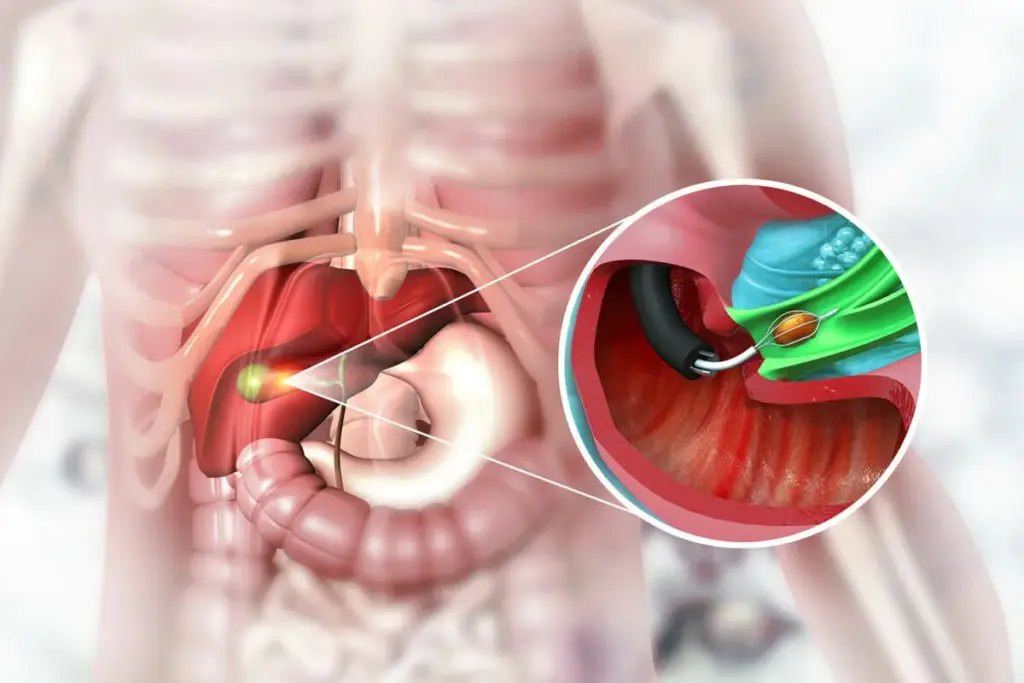
Endoscopic Procedures
Endoscopic procedures, such as ERCP and EUS, are key for diagnosing and treating biliary disorders. These methods allow for direct visualization of the biliary tract. They also enable the performance of therapeutic interventions.
- ERCP: Enables the diagnosis and treatment of bile duct obstruction and other biliary pathologies.
- EUS: Provides detailed imaging of the biliary tract and surrounding structures, facilitating the diagnosis of various hepatobiliary conditions.
Laboratory and Pathological Assessment
Laboratory tests and pathological assessments are essential in diagnosing hepatobiliary diseases. These include liver function tests, tumor markers, and histopathological examination of liver biopsies.
- Liver Function Tests: Help in assessing liver damage and dysfunction.
- Tumor Markers: Aid in diagnosing and monitoring hepatobiliary malignancies.
- Histopathological Examination: Provides definitive diagnosis through the examination of tissue samples.
Interventional radiology procedures, such as percutaneous drainage and embolization, are available for treating various hepatobiliary conditions. These procedures expand the diagnostic and therapeutic options against these diseases.
The Impact of Specialized Hepatobiliary Care
Specialized hepatobiliary care has a huge impact on patient results. As hepatobiliary surgery grows, so does the need for specialized care. This care is key to better patient outcomes.
Studies show that high-volume centers do better than low-volume ones. They have lower death rates. This volume-outcome relationship is very important in hepatobiliary surgery.
Volume-Outcome Relationship in Surgery
Hospitals and surgeons with more experience in hepatobiliary surgery get better results. They handle complex cases better because of their experience and skill.
|
Hospital Volume |
Mortality Rate |
Complication Rate |
|---|---|---|
|
High |
2% |
10% |
|
Low |
5% |
20% |
Multidisciplinary Team Approach
A multidisciplinary team approach is key for complex hepatobiliary conditions. It brings together surgeons, radiologists, oncologists, and more. This team works together for better care.
This teamwork leads to better diagnosis, treatment plans, and patient results. It’s all about working together for the best outcome.
The Liv Hospital Model of Excellence
The Liv Hospital model is a top example of specialized care. It combines a team approach with the latest technology and facilities. Liv Hospital is a leading place for hepatobiliary surgery.
In summary, specialized care, including a team approach and high-volume centers, is vital. It helps improve patient results in hepatobiliary surgery.
Conclusion: Advances and Future Directions in Hepatobiliary Surgery
The field of hepatobiliary surgery is changing fast. This is thanks to new surgical methods, better diagnostic tools, and more treatment choices. Researchers are working hard to make treatments better and find new ways to fight liver and biliary diseases.
New discoveries in liver and biliary surgery have made treating complex diseases easier. Thanks to less invasive surgeries and better imaging, patients are recovering faster and feeling better sooner. This means a better life for those needing hepatobiliary surgery.
New technologies like robotics and artificial intelligence will make surgeries even more precise. Specialized centers will be key in moving the field forward. They will help make hepatobiliary surgery even better.
Scientists are learning more about liver and biliary diseases every day. This knowledge will lead to new treatments and ways to diagnose these conditions. As a result, patients will have even better outcomes in hepatobiliary surgery.
FAQ
What is hepatobiliary surgery?
Hepatobiliary surgery deals with the liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts. It includes operations to diagnose and treat various conditions affecting these organs.
What are the common conditions that require hepatobiliary surgery?
Liver cancer, gallstones, and bile duct injuries are common reasons for surgery. Also, complex gallbladder diseases and liver tumors may need surgical treatment.
What is the hepatobiliary system, and how does it function?
The hepatobiliary system includes the liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts. It’s key for digestion, metabolism, and detoxification. The liver makes bile, stored in the gallbladder, aiding in fat digestion and vitamin absorption.
What are the signs of hepatobiliary dysfunction?
Signs include jaundice, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and changes in stool or urine color. These symptoms suggest bile duct obstruction, liver disease, or gallbladder issues.
What is the importance of specialized care in hepatobiliary surgery?
Specialized care is vital due to the complexity of these surgeries. High-volume centers with experienced teams offer better outcomes and care.
What are primary liver malignancies, and how are they treated?
Primary liver malignancies include hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Treatment depends on the cancer stage and type, and may include surgery, liver transplant, chemotherapy, or targeted therapy.
What is liver transplantation, and who is eligible for it?
Liver transplantation replaces a diseased liver with a healthy one from a donor. Eligibility depends on liver disease, overall health, and absence of contraindications.
What are the advanced diagnostic modalities used in hepatobiliary conditions?
Advanced diagnostics include CT, MRI, ERCP, and lab/pathological assessments. These tools help diagnose and manage various conditions.
What is the volume-outcome relationship in hepatobiliary surgery?
The volume-outcome relationship shows that more procedures lead to better outcomes. High-volume centers have better results due to more experience.
What is the multidisciplinary team approach in hepatobiliary care?
This approach involves surgeons, medical oncologists, radiologists, and pathologists working together. It provides complete care for patients with hepatobiliary conditions.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11374351/[1





